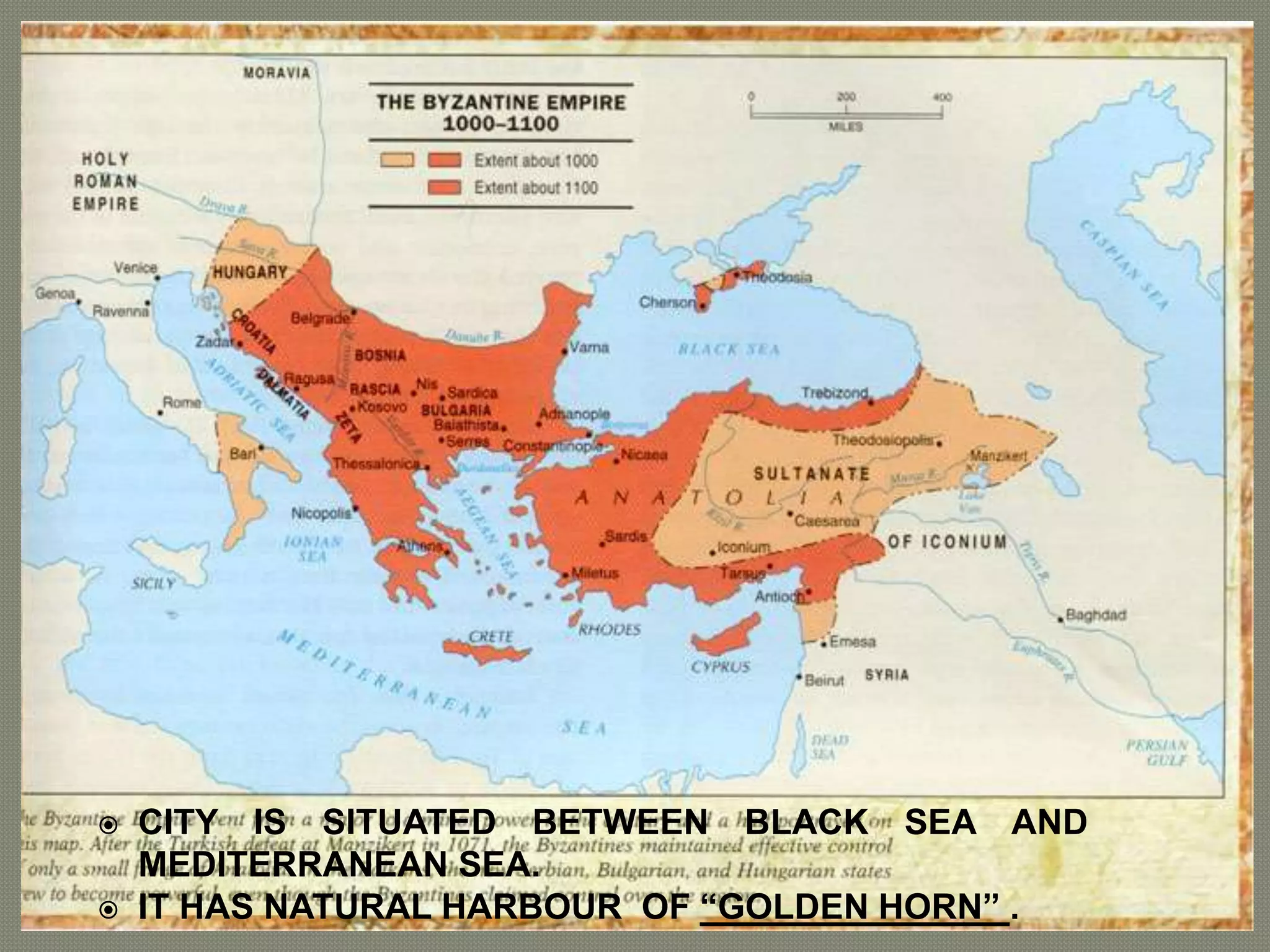
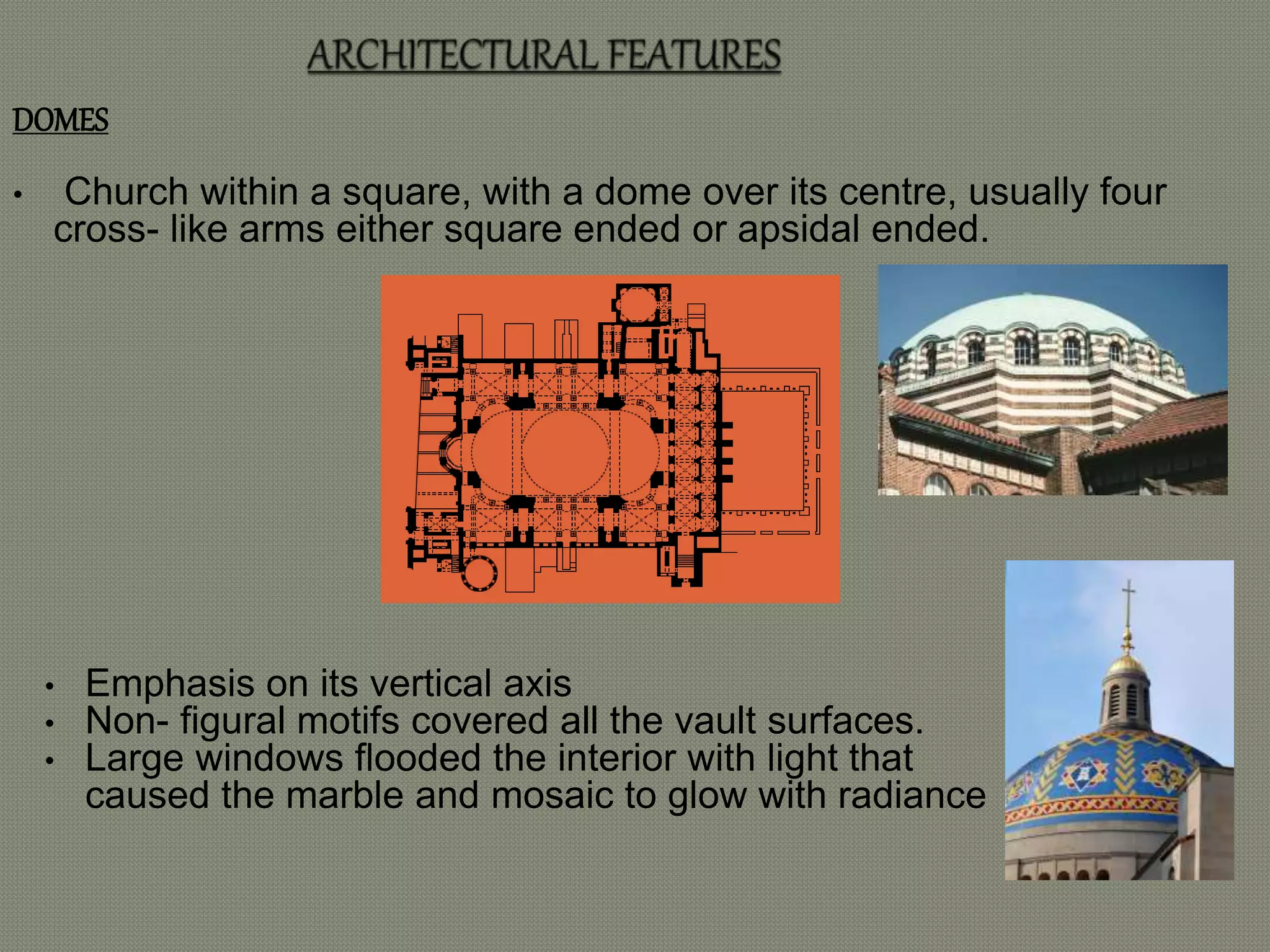
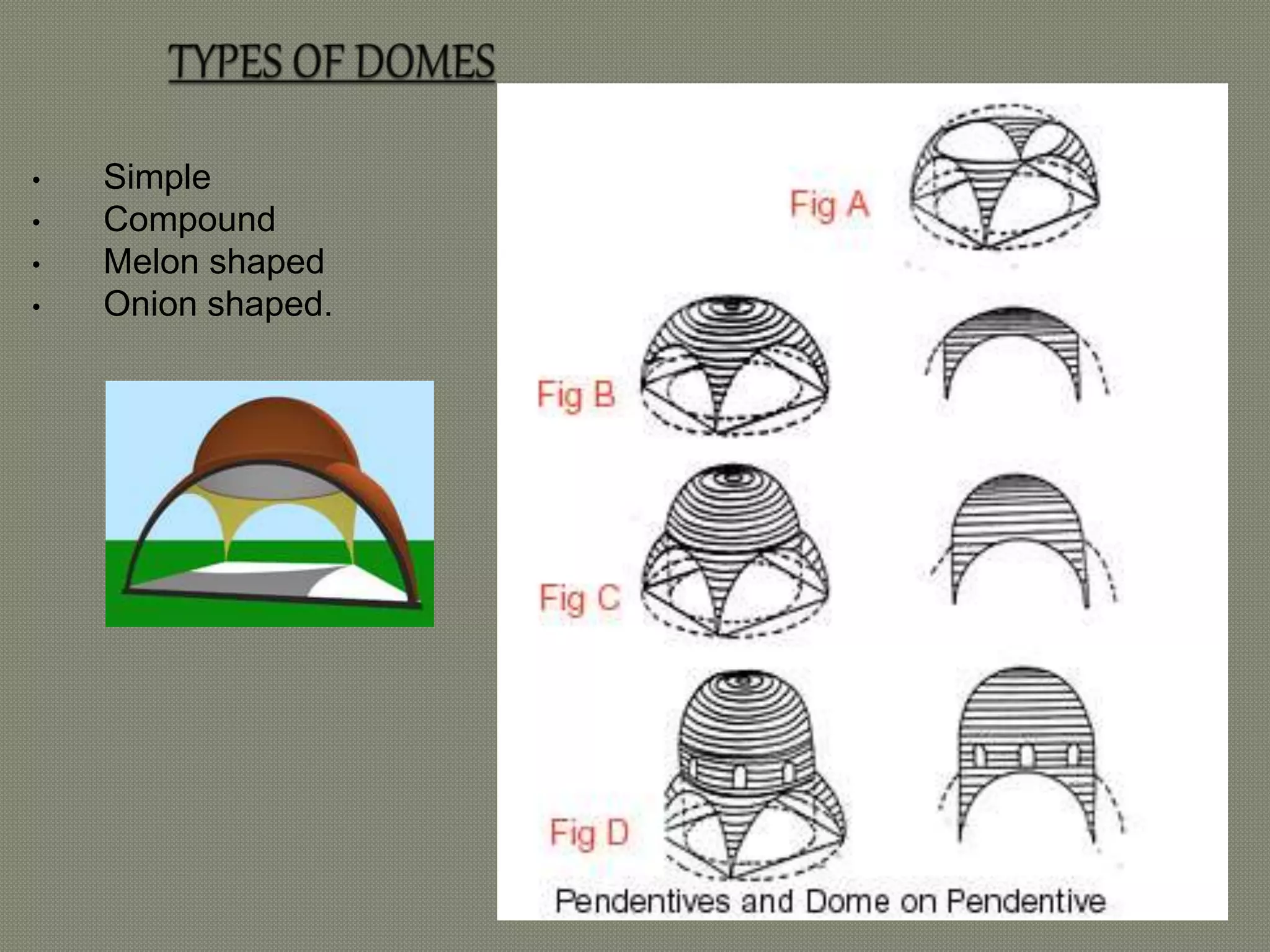
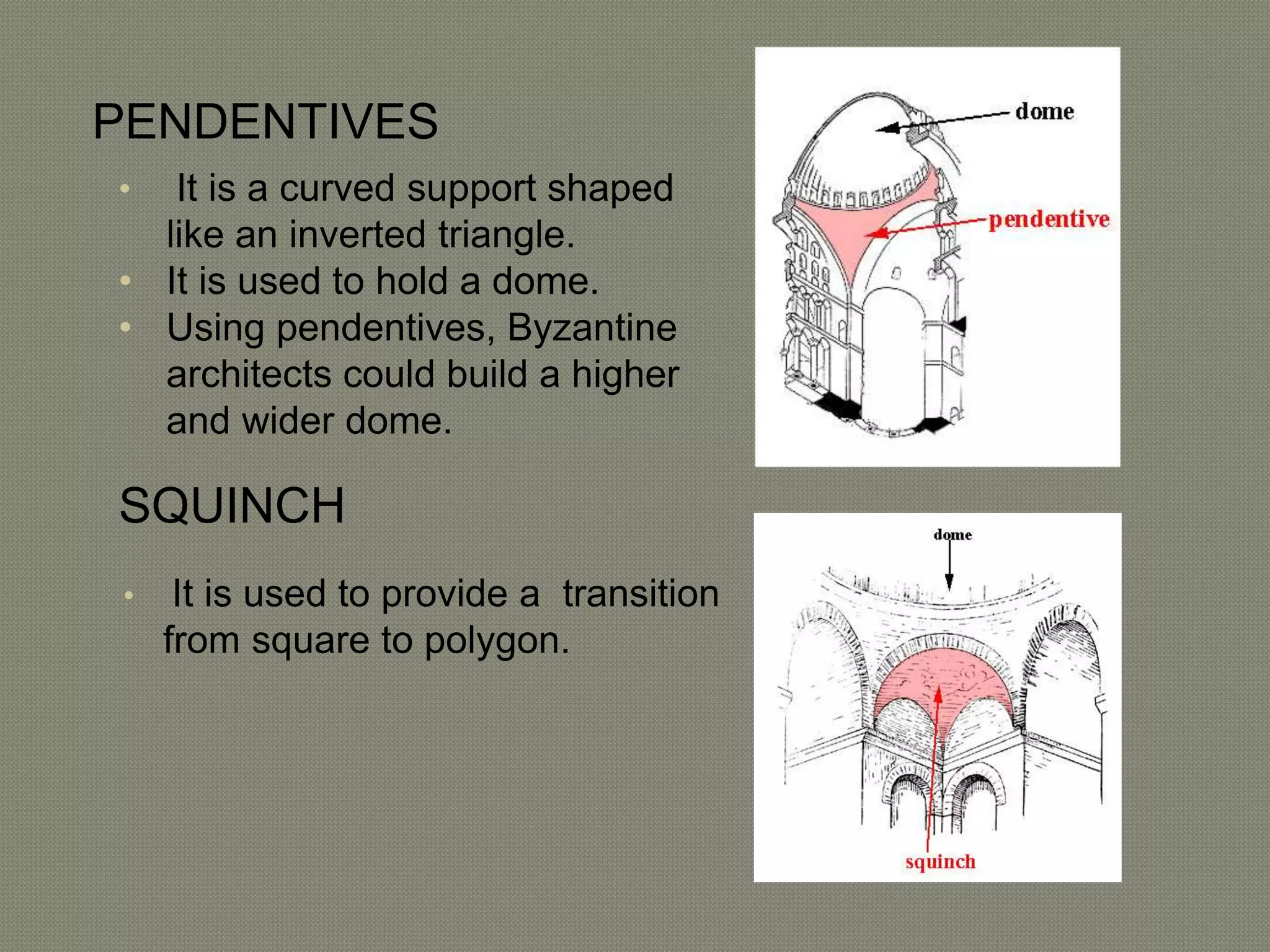
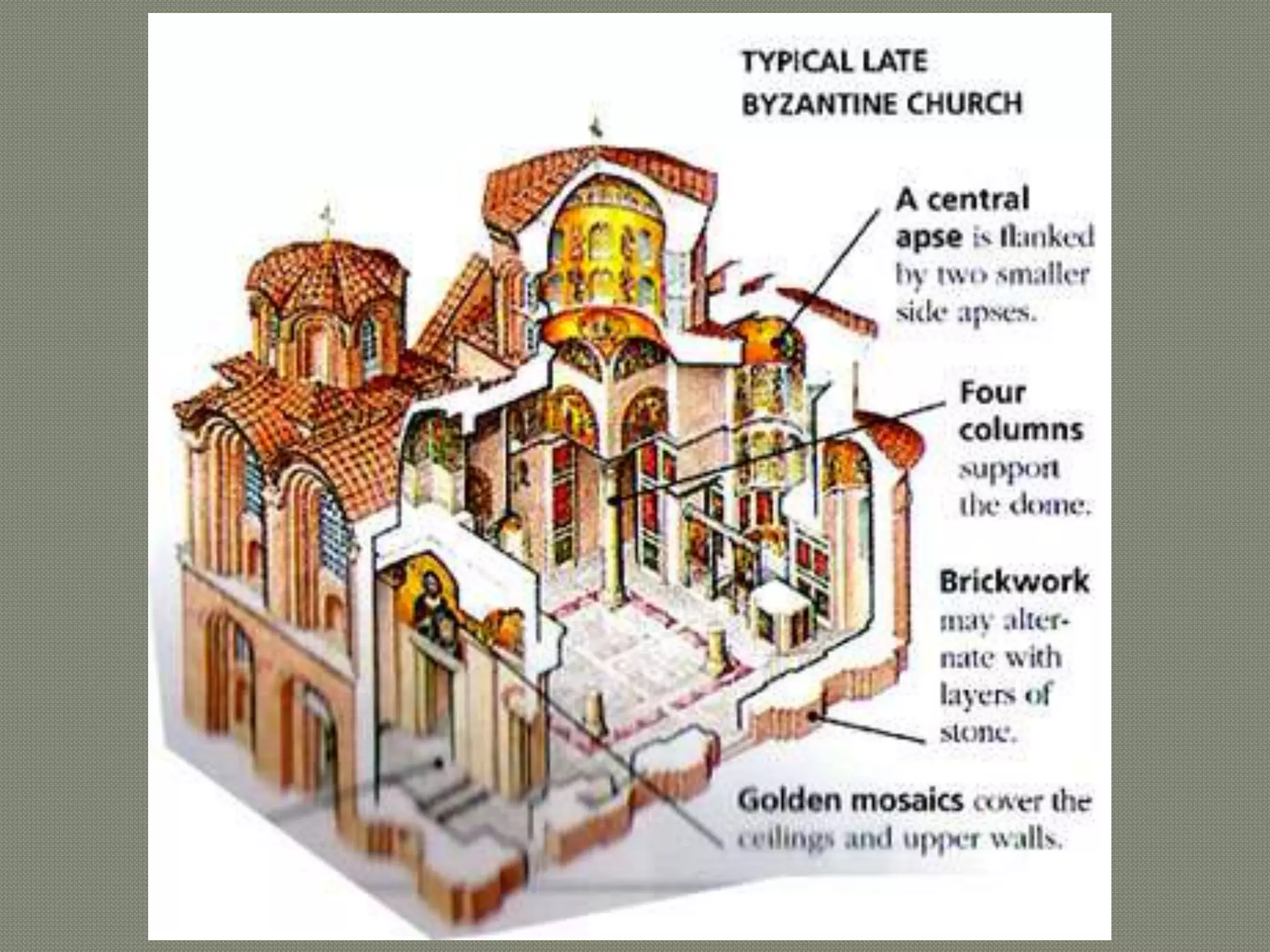
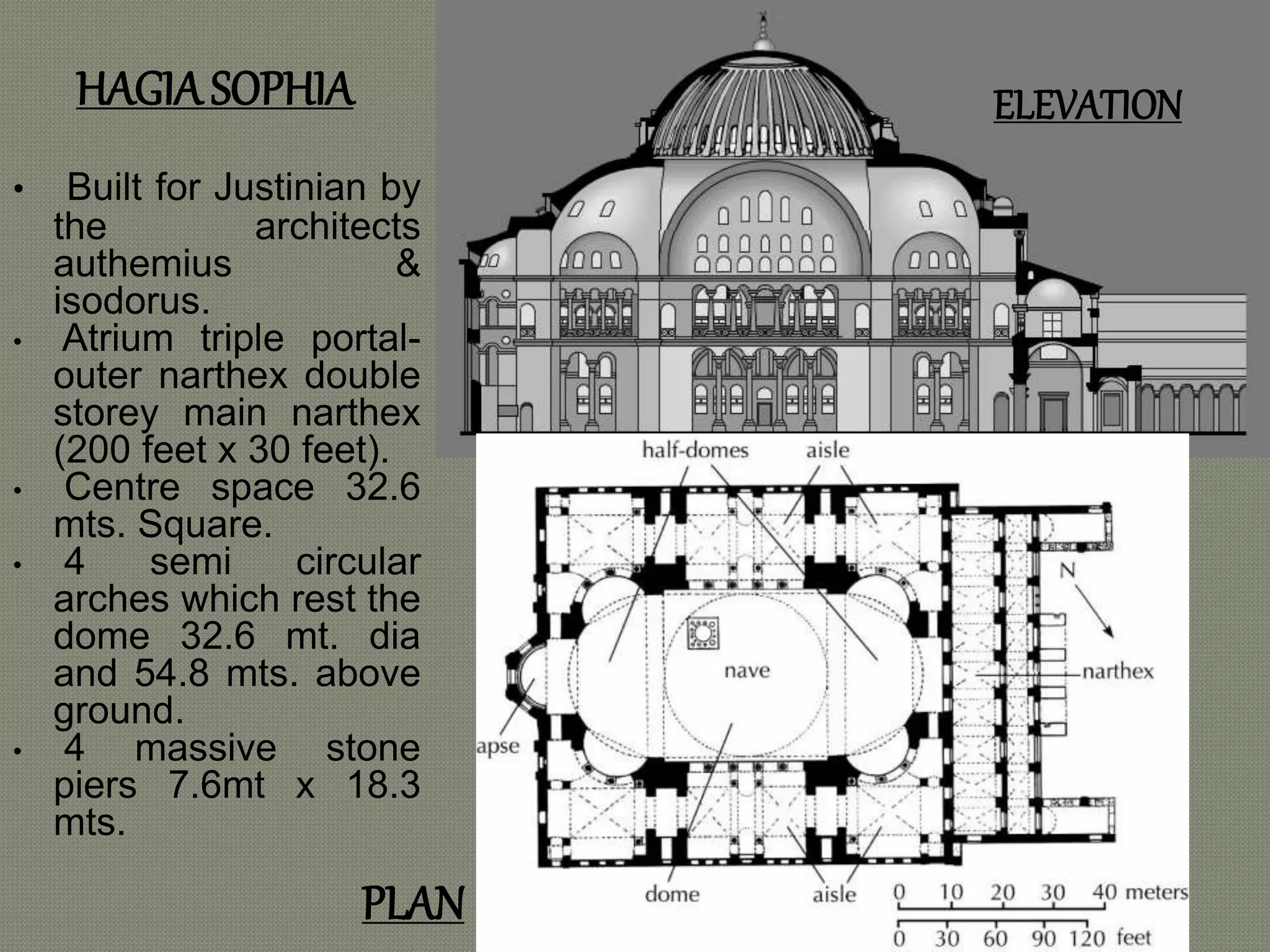
The early Greek settlers of Byzantium were led by Byzas, who gave his name to the city. Byzantium was strategically located between the Black Sea and Mediterranean with a natural harbor of the Golden Horn. The Byzantine style of architecture used lime concrete, bricks, marble, mosaics, and domes supported by pendentives. Two important early examples are the 6th century Church of Sergius and Bacchus in Istanbul, with its 15.8 meter diameter dome on pendentives, and Hagia Sophia in Istanbul, known for its massive central dome supported by semi-domes and exedrae.