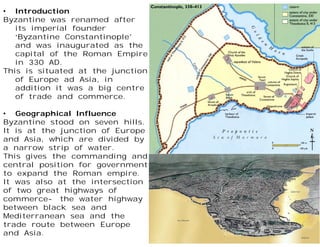
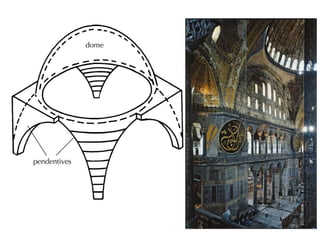
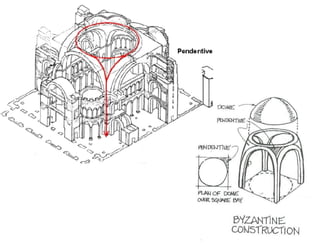
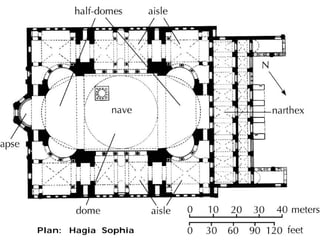
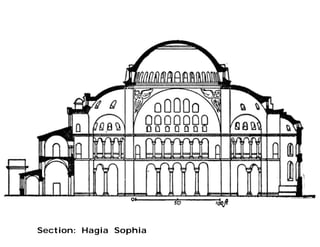
Byzantine architecture was influenced by its location between Europe and Asia at the junction of important trade routes. Buildings used local materials like brick and stone with marble imported from quarries. The hot climate led to small, high windows and domes with arcaded courtyards. Byzantine architecture fused oriental and Roman styles, using massive decoration and introducing dome construction. Churches often had a central dome surrounded by smaller domes with a smooth external profile and internal/external correspondence. Famous examples include Hagia Sophia, built in 532-537 AD with a large central dome carried by pendentives, and St. Mark's Basilica in Venice symbolizing the city's history.