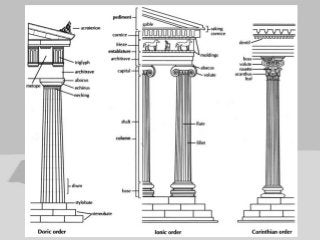
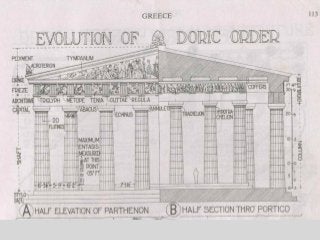
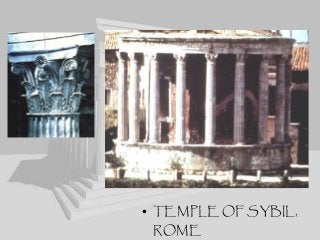
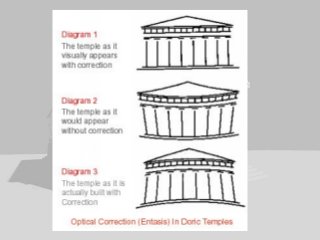
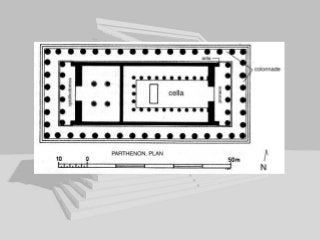
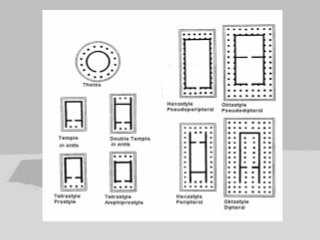
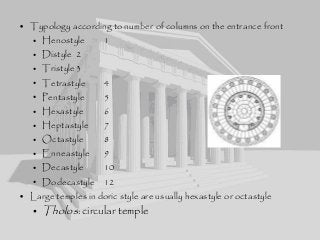
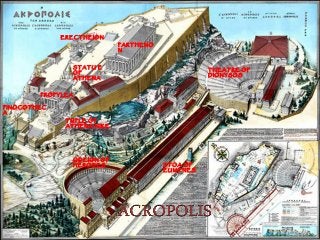
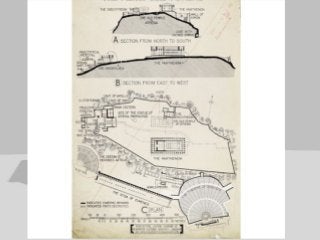
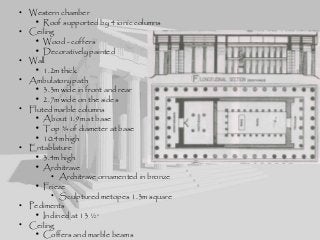
Greek architecture developed over several periods and was influenced by geographical, climatic, and religious factors. The Greeks established three classical architectural orders - Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian - which are distinguished by their columns and entablatures. Temples were the most important buildings, constructed using local marble and limestone with precise joints. Through techniques like entasis, the Greeks aimed to create perfectly proportioned structures that appeared balanced to the human eye.