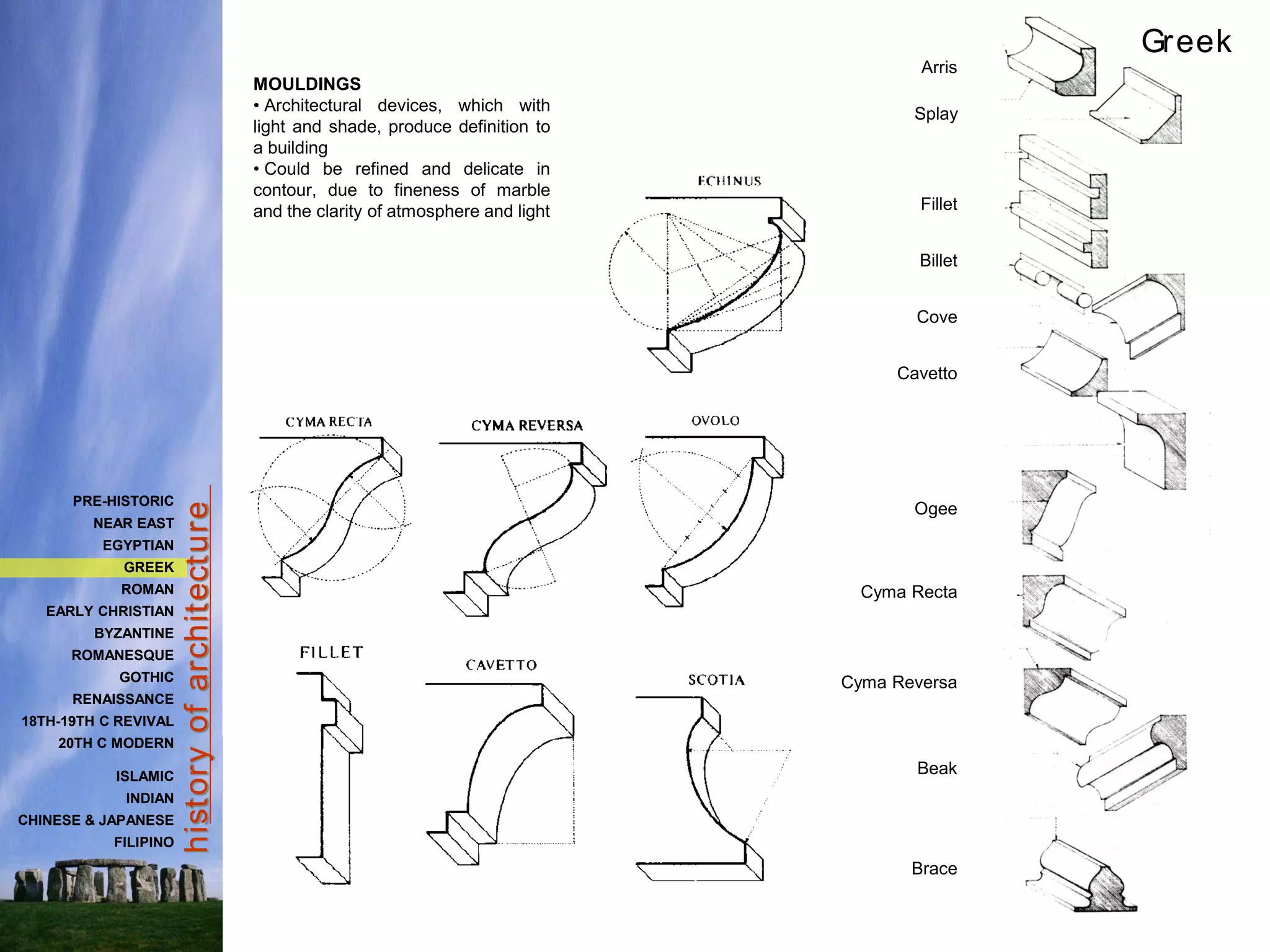
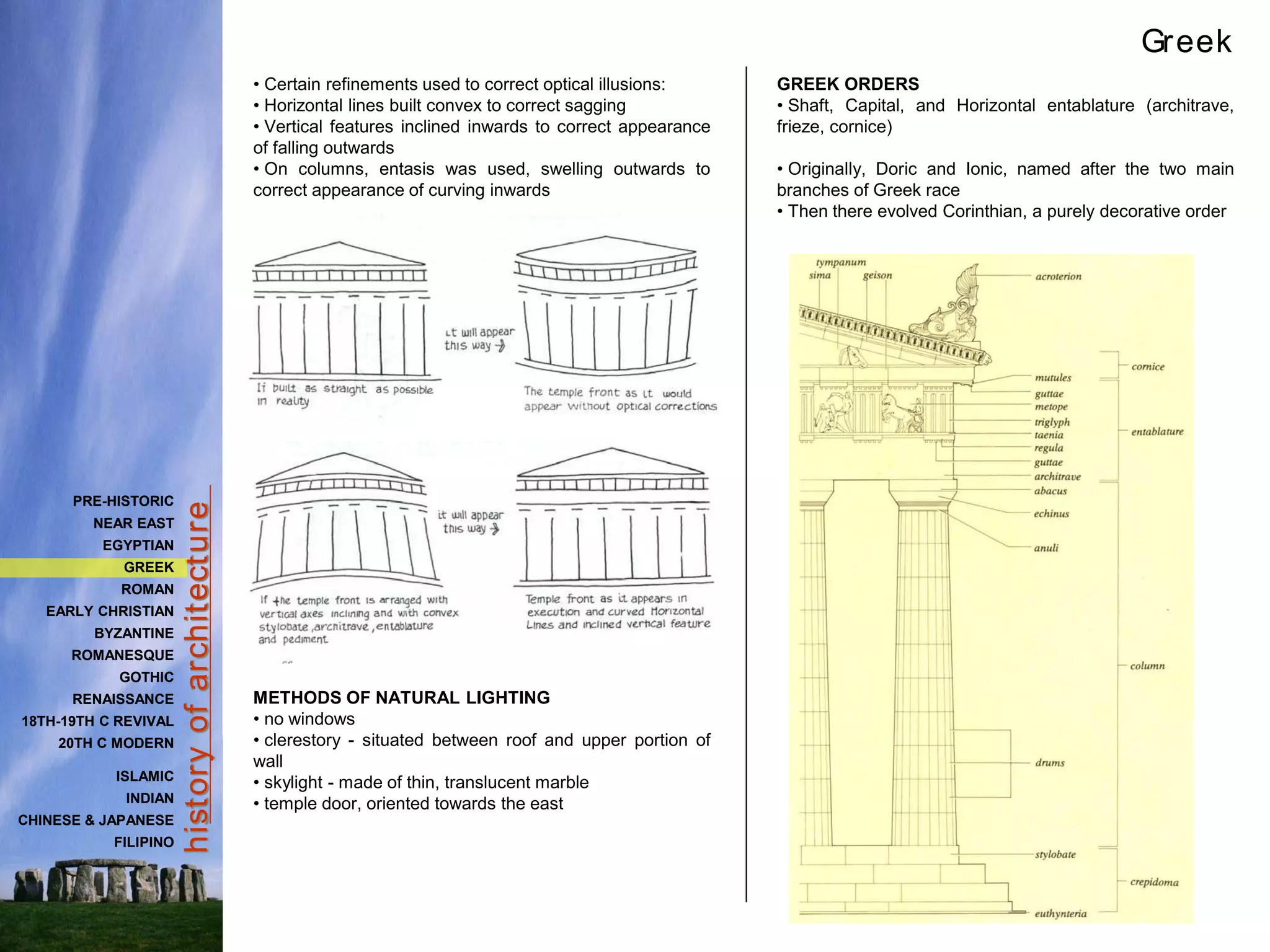
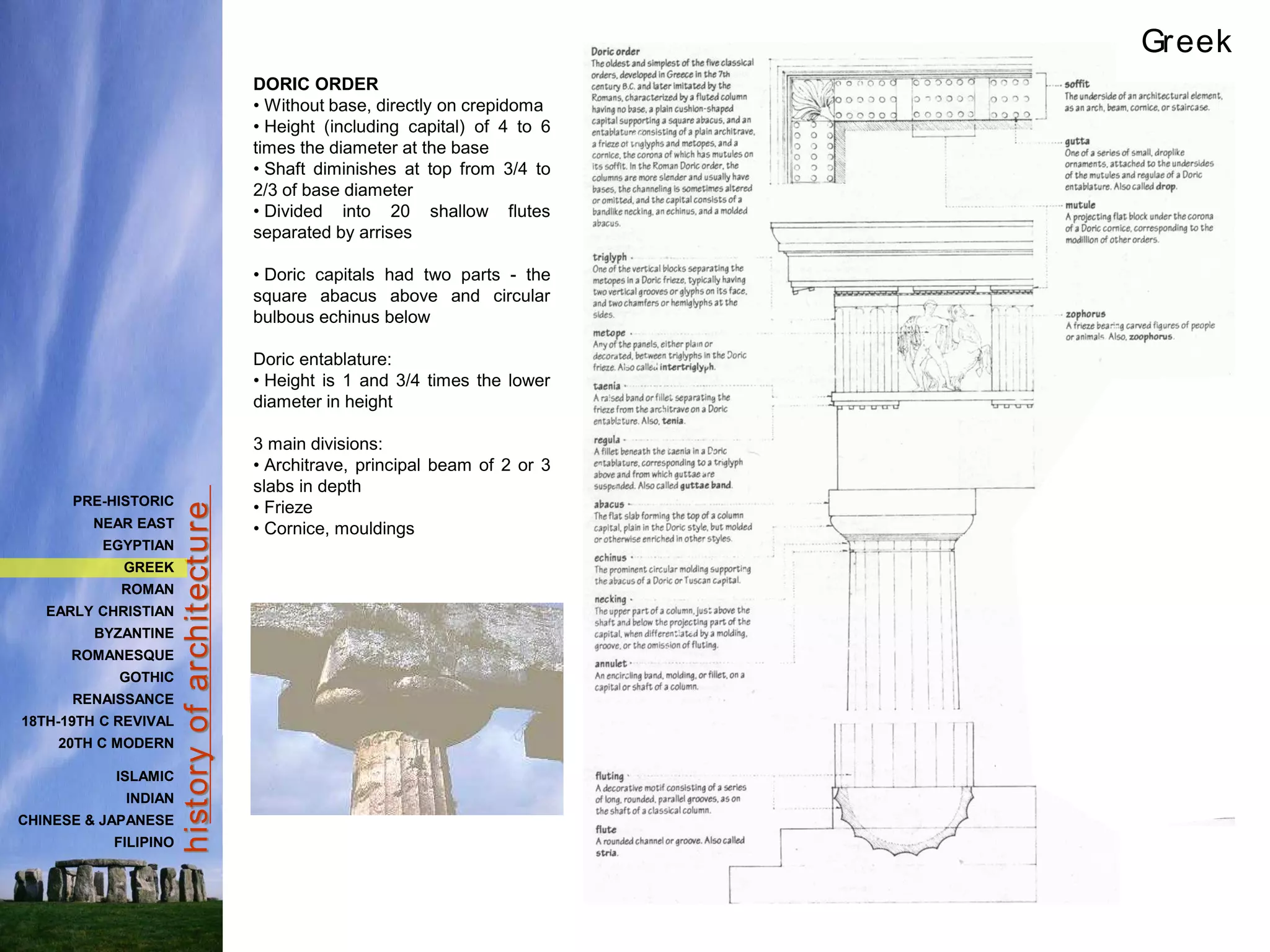
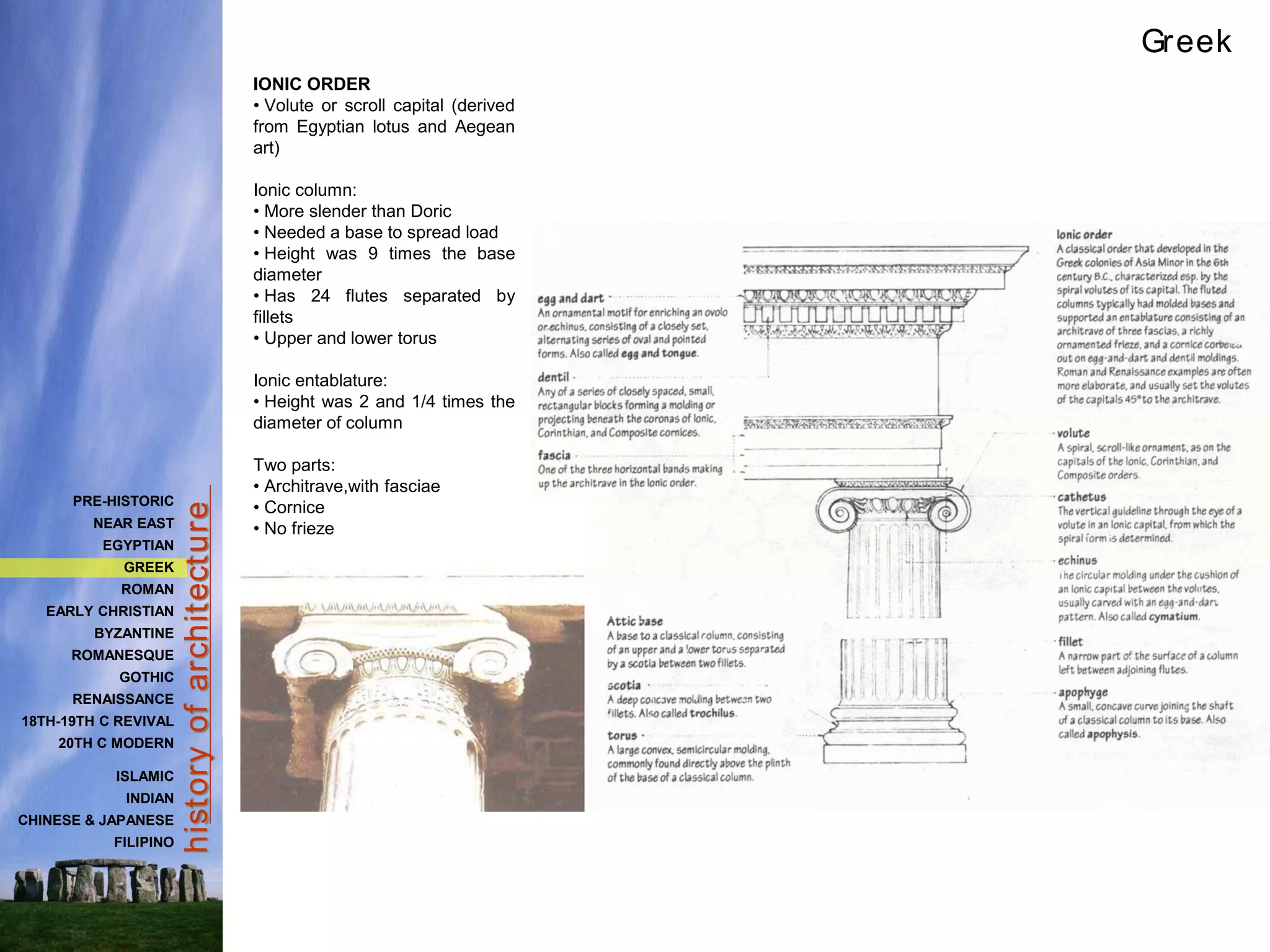
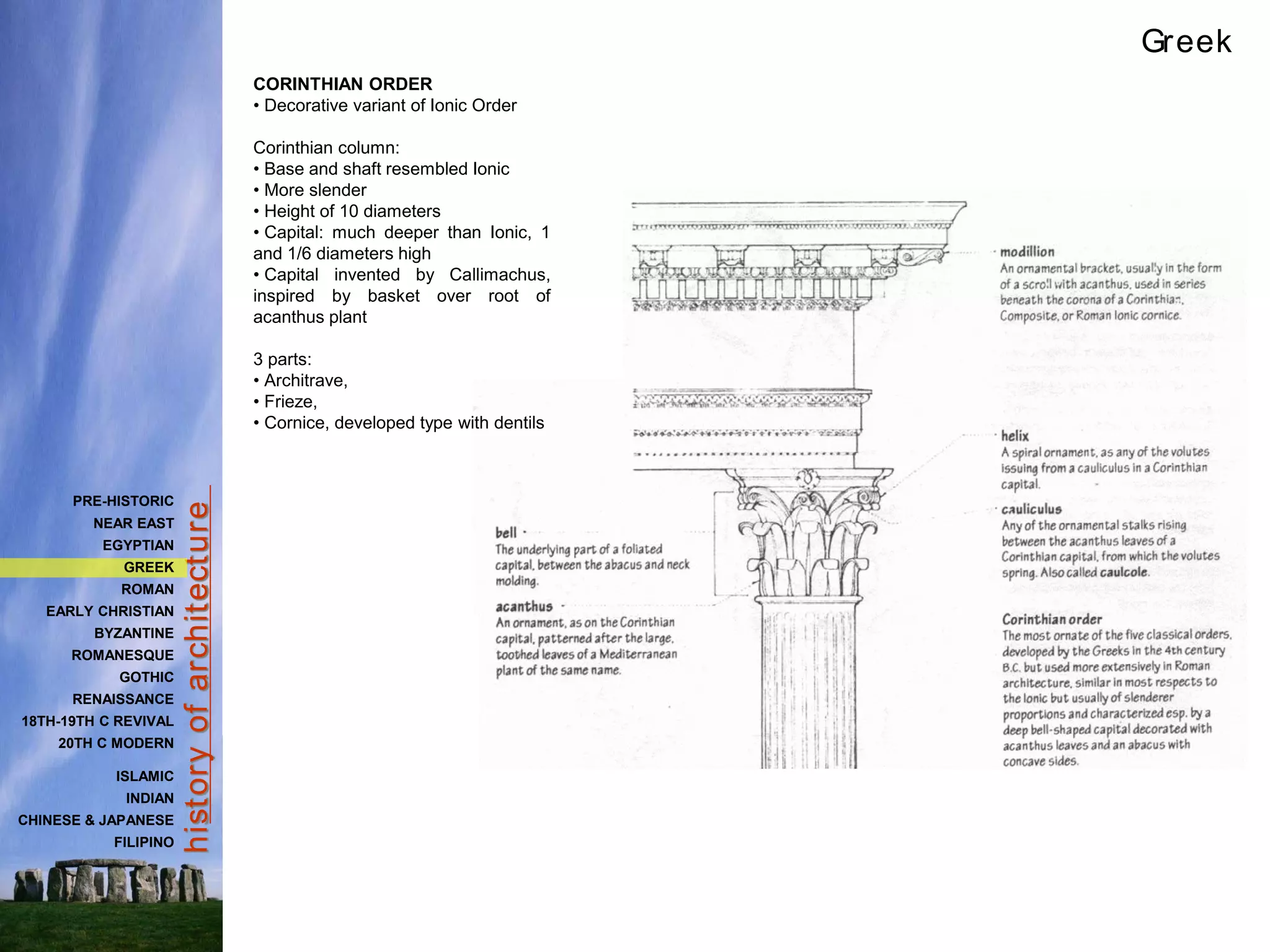
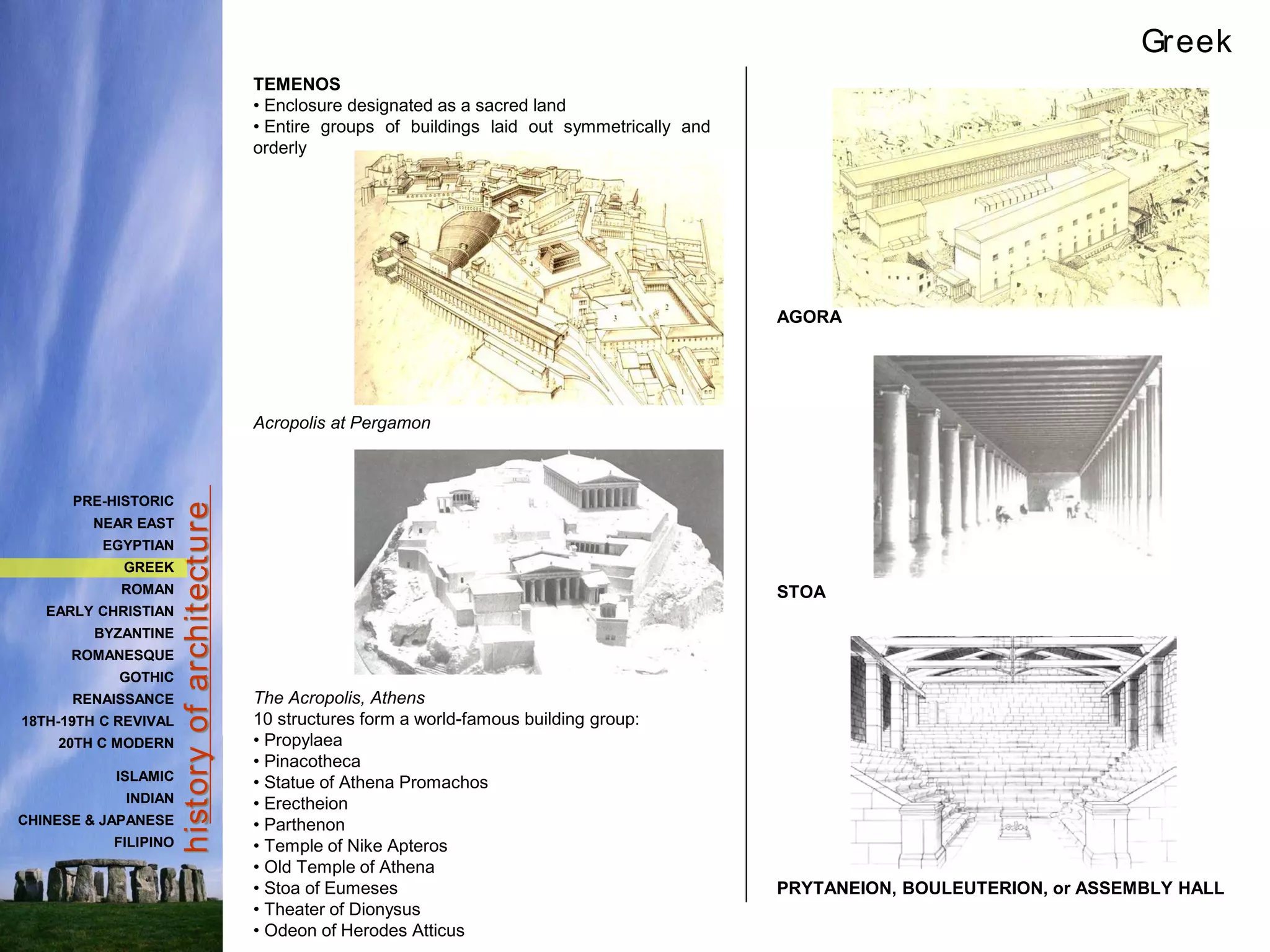
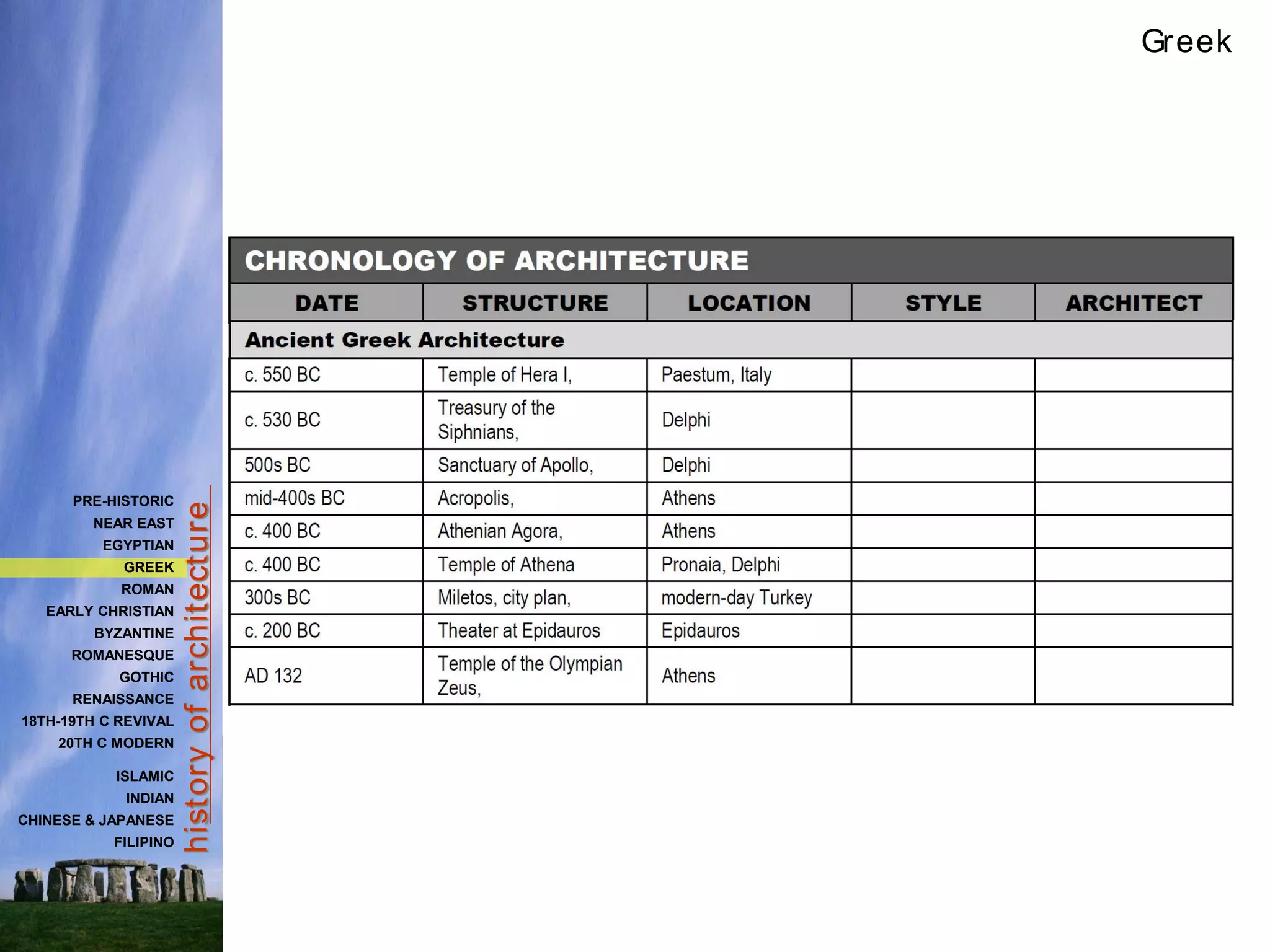
The document provides a history of Greek architecture from ancient to Hellenistic periods. It describes the influences of Minoan and Mycenaean civilizations and the development of city-states and democracy. Greek architecture is known for its use of columns, trabeated construction, and three classical orders of Doric, Ionic and Corinthian. Important building types included temples, houses, palaces, and theaters. Major works included the Parthenon, Temple of Artemis, and Theater of Epidauros. Greek architecture emphasized symmetry, proportion and precision through careful use of entasis and refinements.