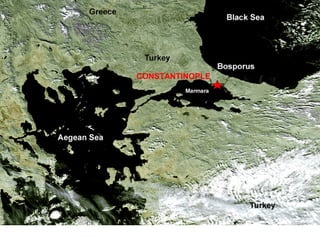
The Byzantine Empire grew to become a powerful and influential empire with its capital of Constantinople, which was well protected and situated on a natural harbor. Constantinople became a thriving cultural and economic center as a crossroads of trade between Europe, Asia, and Africa. Under Emperor Justinian in the 6th century, the Byzantine Empire reached its greatest extent as he recodified Roman law and had the general Belisarius expand the empire's territories, though this also led to a schism between the Eastern Orthodox and Roman Catholic churches. Byzantine culture preserved Greek and Roman learning and influenced neighboring Slavic peoples. The empire eventually declined as it faced numerous invasions, falling to the Ottoman Turks in 1453