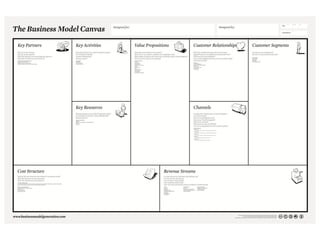
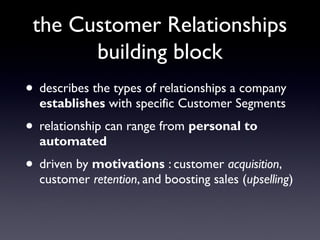
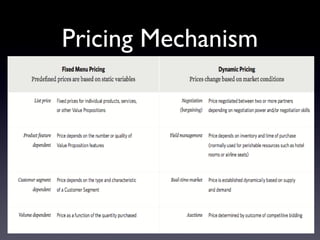
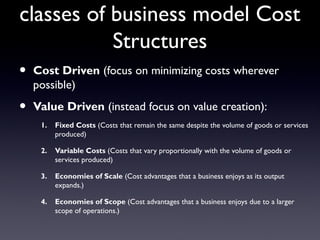
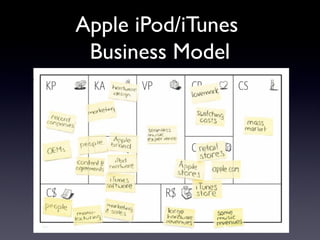
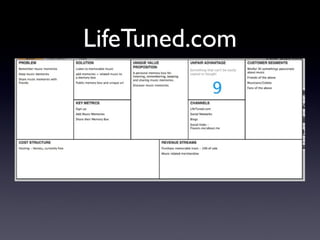
The document provides an overview of the Business Model Canvas, which is a tool used to describe, design, challenge, and invent new business models. It outlines the 9 building blocks of a business model: 1) Customer Segments, 2) Value Proposition, 3) Channels, 4) Customer Relationships, 5) Revenue Streams, 6) Key Resources, 7) Key Activities, 8) Key Partnerships, and 9) Cost Structure. Each building block is defined and examples are provided of how companies can analyze and understand each component of their business model.