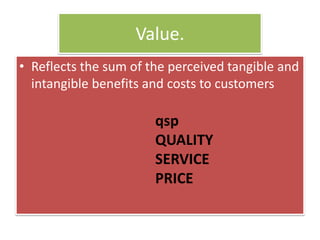
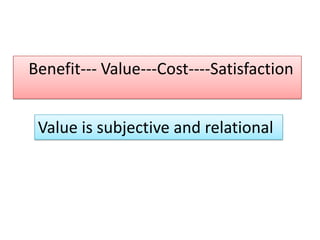
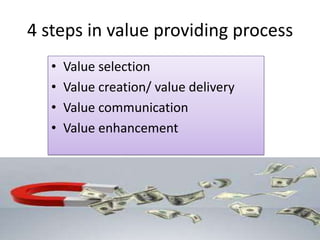
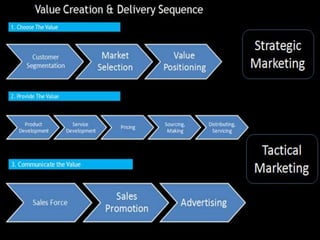
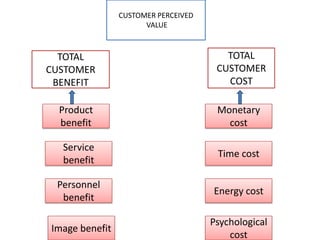
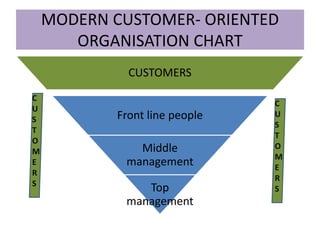
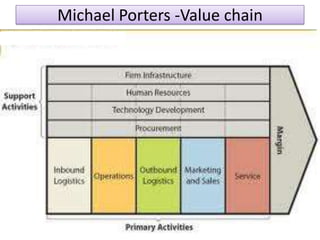
The document discusses the concept of creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers at a profit (CCDVTMP). It outlines four steps in the value providing process: value selection, value creation/delivery, value communication, and value enhancement. The goal is to provide benefits that exceed costs for customers in order to increase their satisfaction and build competitive advantage.