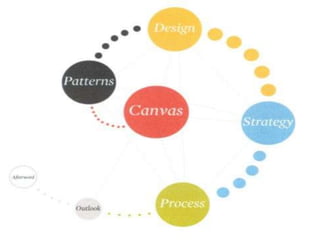
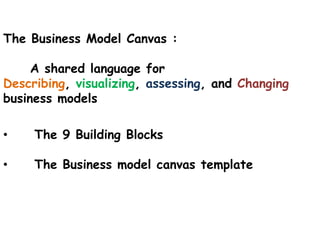
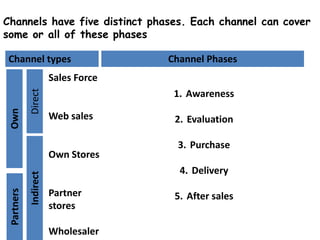
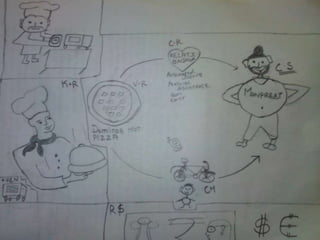
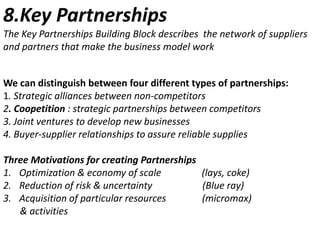
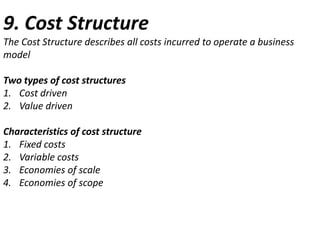
The document presents the Business Model Canvas, a framework designed to help entrepreneurs describe, visualize, and innovate business models using nine essential building blocks: customer segments, value propositions, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, key partnerships, and cost structure. Each block highlights critical elements such as types of customers and relationships, revenue generation, required resources, key activities needed for success, and the partnership network essential for operations. This tool is aimed at fostering creativity and strategic thinking for businesses looking to create value and improve their models.