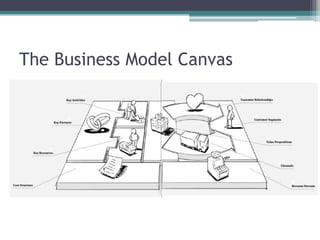
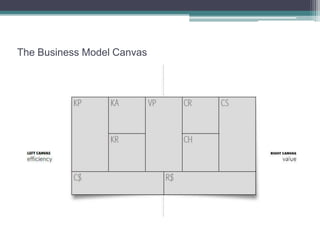
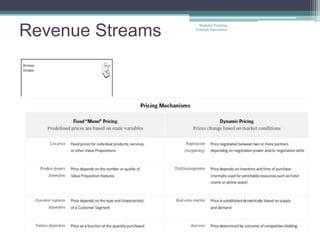
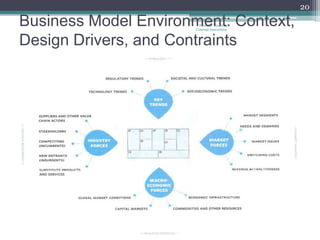
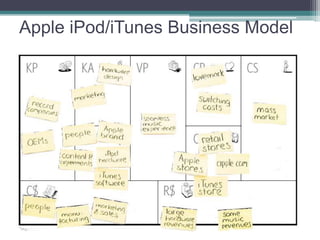
The document outlines the 'Business Model Canvas,' detailing components such as customer segments, value propositions, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, key partners, and cost structure. It emphasizes the importance of understanding customer needs and optimizing the business model for competitive advantage, using Apple's iPod/iTunes model as an example of effective integration. Additionally, it includes a practical exercise for participants to create business models tailored to specific customer segments.