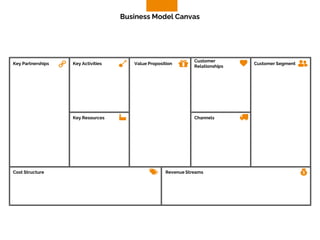
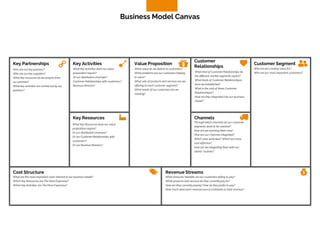
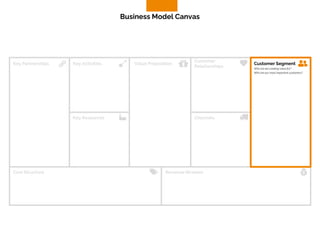
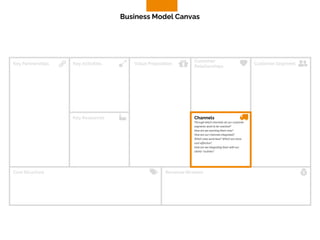
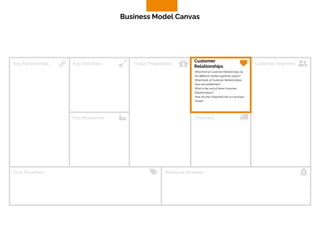
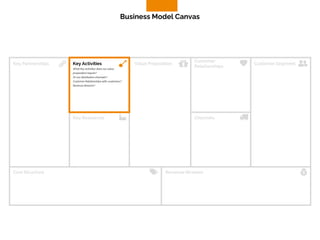
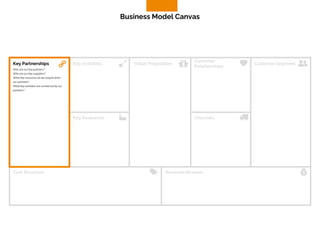
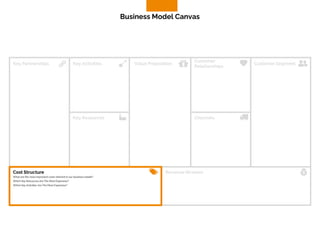
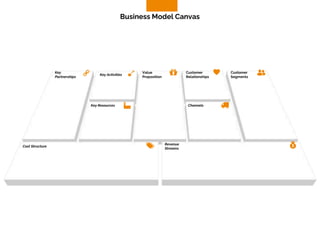
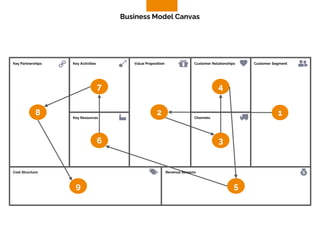
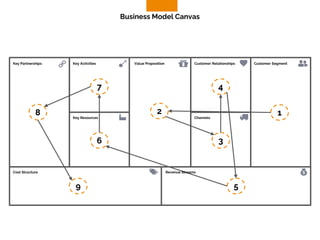
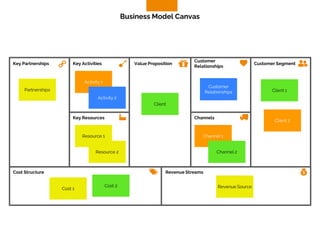
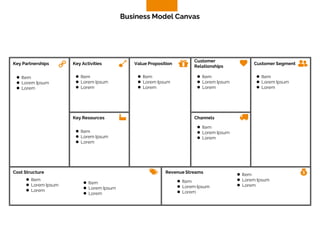
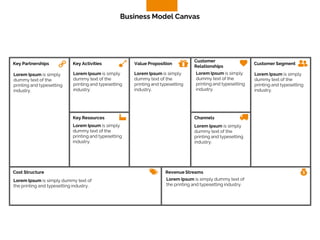
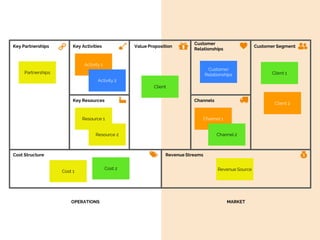
The document discusses the components of a business model canvas which includes key partnerships, activities, value propositions, customer relationships, segments, key resources, channels, cost structure, and revenue streams. It emphasizes the importance of understanding customer needs and factors affecting customer retention, as well as identifying effective channels and resources to deliver value. The detailed exploration of each element serves as a guideline for creating and analyzing business models strategically.