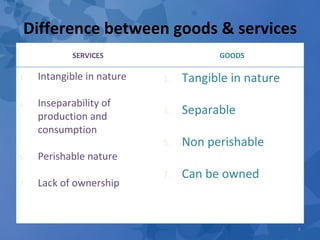
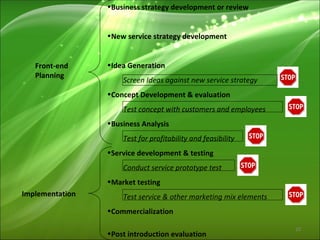
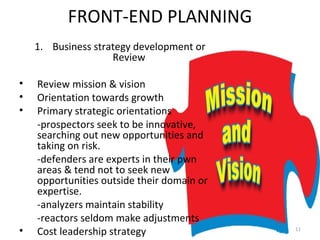
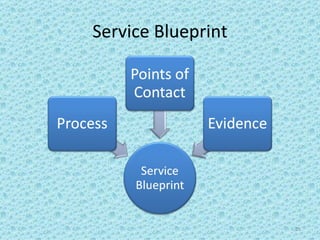
The document discusses the process of new service development. It begins by defining what a service is and the differences between goods and services. It then outlines the types of new services and describes the new service development process. This includes front-end planning, idea generation, concept development and evaluation, business analysis, implementation through testing, commercialization, and post-introduction evaluation. The key steps involve reviewing business strategy, developing a new service strategy, generating and screening ideas, developing service concepts, evaluating concepts with customers and employees, analyzing business factors, testing the service, launching it commercially, and ongoing evaluation.