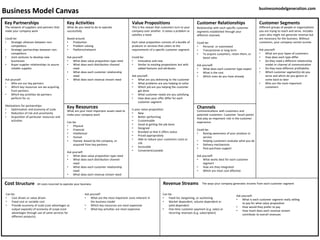
This document provides an overview of the key elements of a business model canvas, including value propositions, customer segments, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, key partnerships, and cost structure. For each element, it poses questions to help define that aspect of the business model. The business model canvas is a tool used to align all aspects of a business around delivering value to customers.