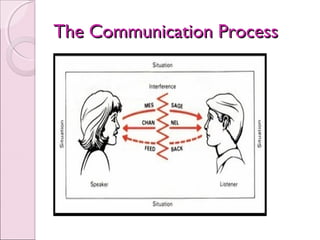
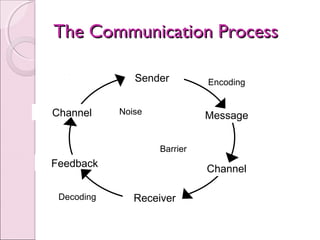
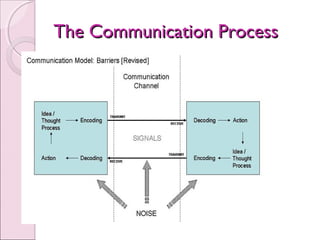
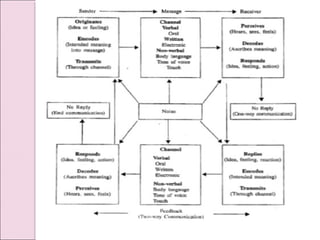
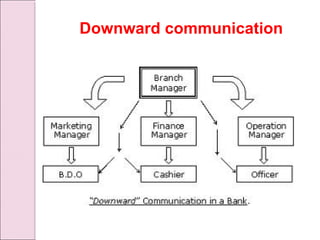
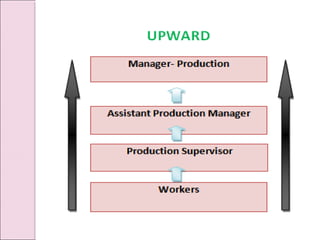
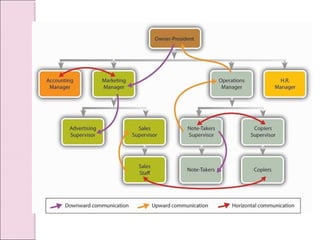
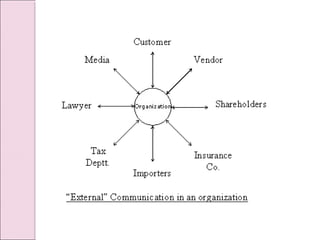
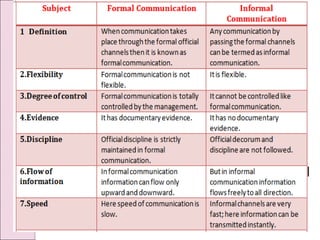
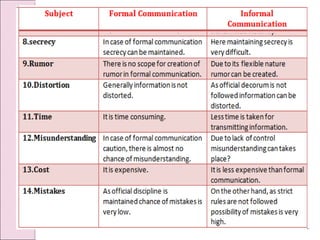
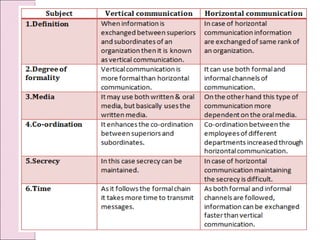
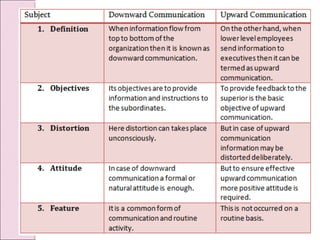
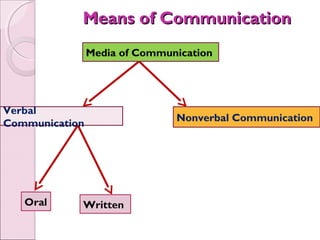
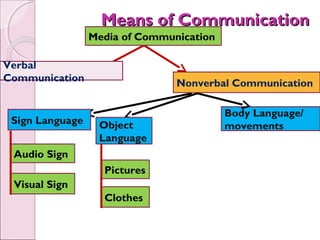
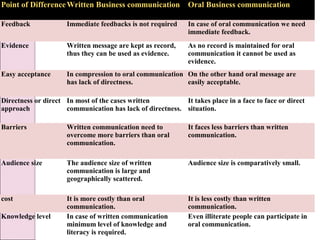
Business communication involves transmitting messages between a sender and receiver through symbolic interaction. It is a process that involves encoding and decoding meanings through words, behaviors, and other symbols. Effective communication requires understanding between the parties involved. There are various types of communication in businesses, including downward, upward, horizontal, and diagonal flows of information that utilize both verbal and nonverbal channels like written documents, speeches, body language, and more. Feedback is also essential for communication to be a two-way process that allows for message confirmation, problem solving, understanding, and improvements over time.