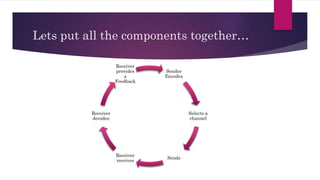
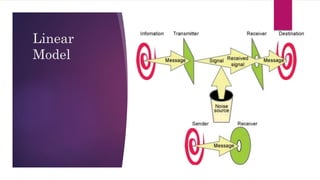
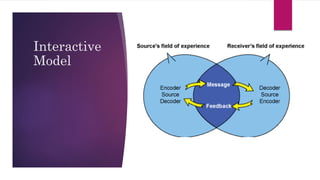
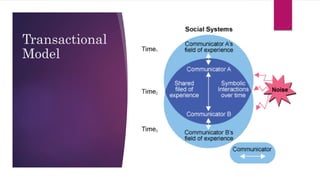
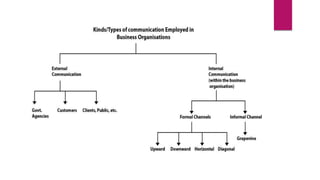
The document outlines the communication process, defining it as the exchange of information between individuals and detailing its components such as sender, receiver, context, and feedback. It discusses organizational communication as essential for coordinating activities to achieve goals, highlighting types including formal, informal, downward, upward, horizontal, and diagonal communication. Additionally, it mentions models of communication and the advantages of effective organizational communication.