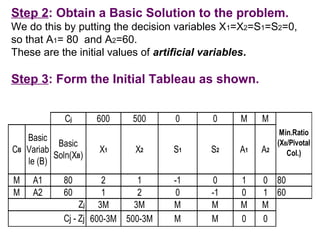
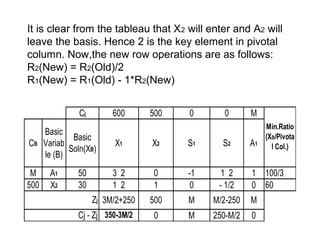
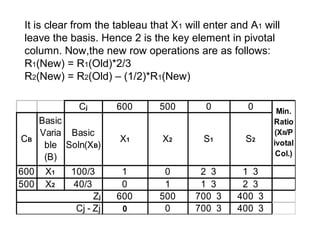
The Big-M method is used to handle artificial variables in linear programming problems. It assigns very large coefficients to the artificial variables in the objective function, making them undesirable to include in optimal solutions. This removes the artificial variables from the basis. As an example, the document presents a linear programming problem to minimize an objective function subject to constraints, and shows the steps of converting it to an equivalent problem using artificial variables and applying the Big-M method to arrive at an optimal solution without artificial variables.