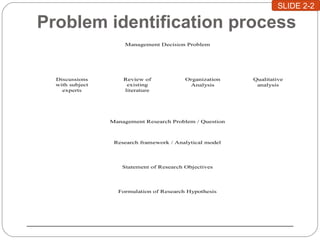
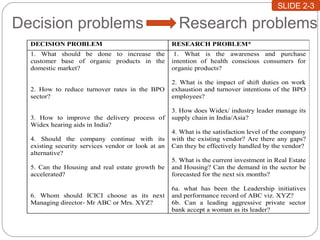
This document discusses the formulation of a research problem and development of research hypotheses. It defines a research problem as a gap in existing knowledge that hinders effective decision making. The process of identifying a research problem involves discussing the issue with experts, reviewing literature, analyzing the organization, and qualitative analysis. This leads to identifying a specific management research problem to address. Research objectives and hypotheses are then formulated. Hypotheses make assumptions about expected relationships between variables and should be stated in a simple, measurable, and testable way.