This document discusses the key aspects of communication including:
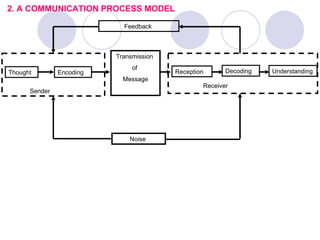
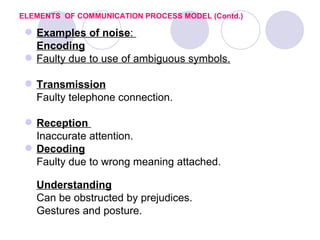
1) It defines communication as the exchange of information between two or more people and outlines the basic communication process model.
2) It describes the main characteristics of communication as a two-way process, continuous process, and one that needs proper understanding.
3) The main purposes of communication are conveying the right message, coordinating efforts, developing good relations, and making policies effective.
4) Principles for effective communication include clarity, consistency, attention, timeliness, and obtaining feedback.