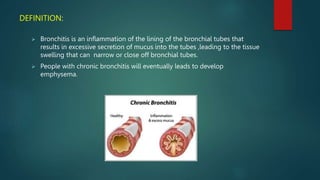
This document provides an overview of chronic bronchitis, including its definition, causes, pathophysiology, clinical features, investigations, treatment, and prevention. Chronic bronchitis is defined as inflammation of the bronchial tubes resulting from excessive mucus secretion that can narrow the airways. The main cause is cigarette smoking. Symptoms include wheezing, breathlessness, cough, and excess mucus production for at least 3 months per year. Treatment involves bronchodilators, glucocorticoids, and physiotherapy to improve lung function and reduce exacerbations. Prevention focuses on quitting smoking, breathing moist air, exercise, and avoiding irritants.