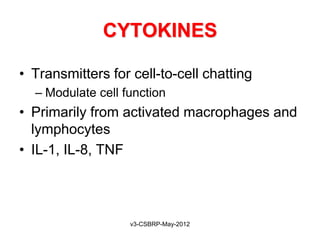
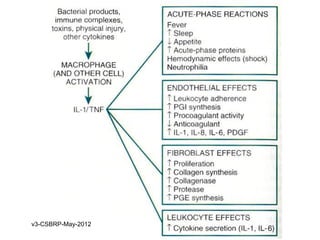
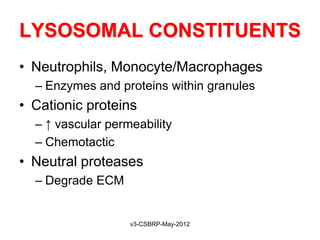
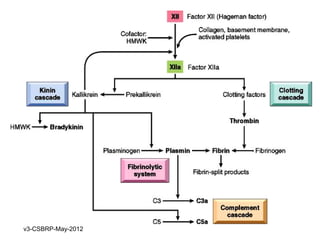
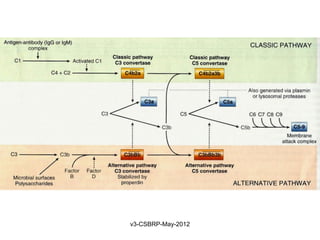
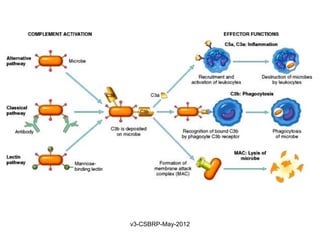
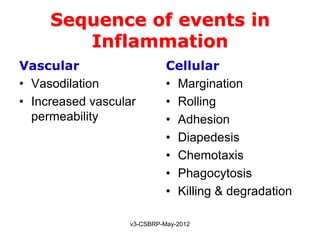
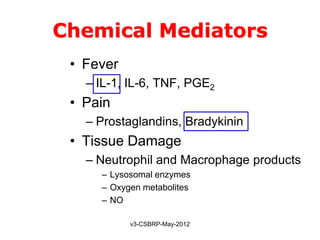
This document summarizes the key events and mediators involved in the inflammatory response. It describes the vascular and cellular events of inflammation and the cardinal signs reflected clinically. It then details the major chemical mediators - from cells and plasma - that contribute to inflammation through actions like vasodilation, increased permeability, chemotaxis, fever, and tissue damage. These include histamine, bradykinin, prostaglandins, leukotrienes, cytokines, and complement proteins. The document explains the general properties and roles of these mediators in amplifying and maintaining the inflammatory response.





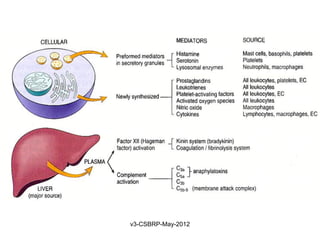
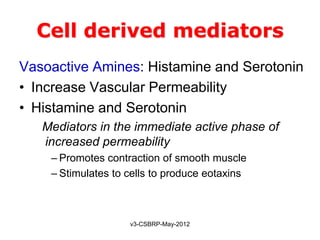
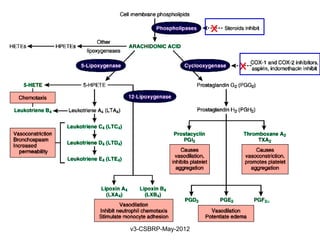
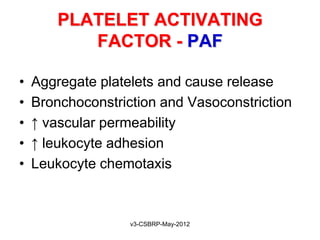
![Chemical Mediators
General properties:
• They are generated from:
Cells
Plasma proteins
• Mediators are produced in response to various stimuli
• One mediator can stimulate the release of other
[Guarantees amplification and maintenance of inflammatory response]
• Mediators vary in their range of cellular targets
• Majority are short-lived [Short t ½ and are harmful]
v3-CSBRP-May-2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inflammation-5-120815190014-phpapp01/85/Inflammation-5-8-320.jpg)