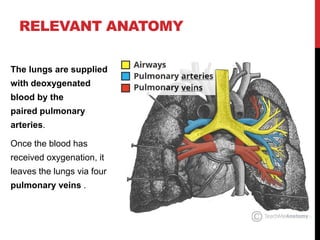
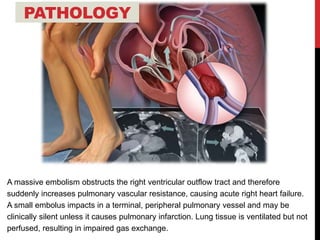
1) Pulmonary embolism refers to obstruction of a pulmonary artery, most commonly by a thrombus originating from the legs or pelvis.
2) Risk factors include conditions contributing to Virchow's triad of venous stasis, hypercoagulability, and endothelial injury.
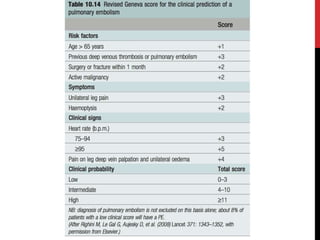
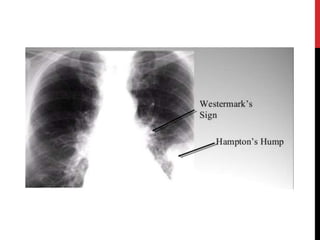
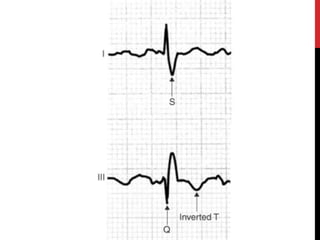
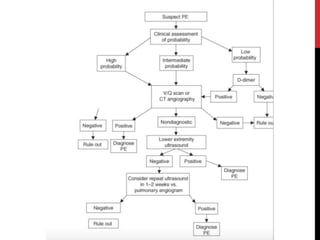
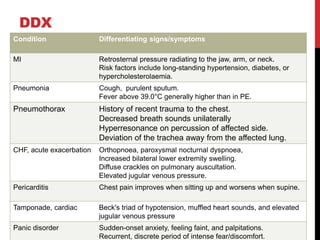
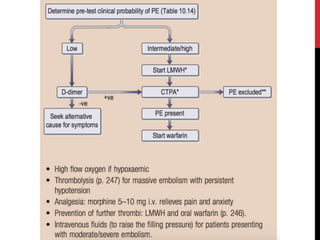
3) Presentation includes dyspnea, chest pain, cough, hemoptysis, and leg swelling or pain. Investigations include D-dimer, chest imaging, ventilation-perfusion scan, and pulmonary angiogram. Management focuses on oxygenation, fluid resuscitation, and anticoagulation.