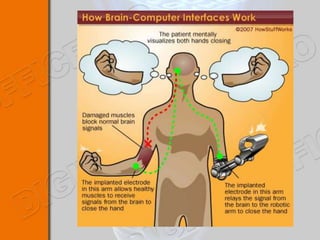
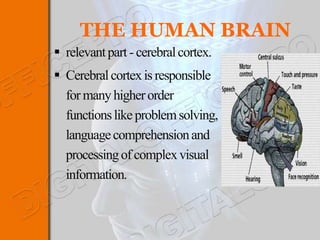
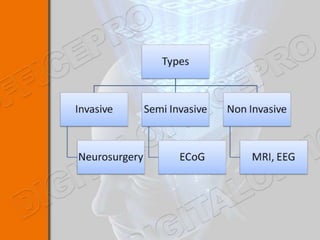
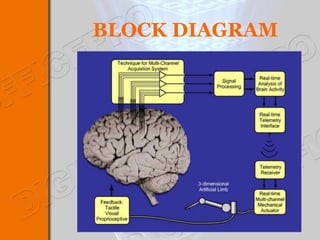
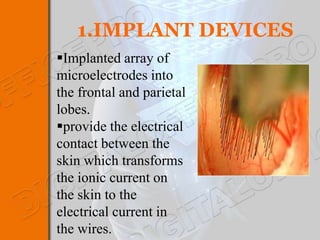
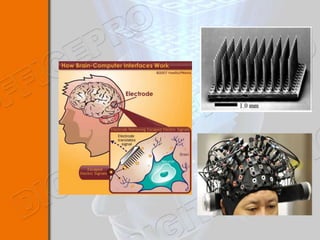
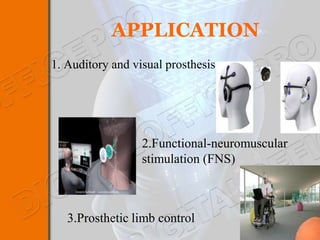
This document discusses brain-machine interfaces (BMI). A BMI establishes a communication link between the brain and external devices. Signals from the brain are detected via implants and transformed to control signals. There are invasive, partially invasive and non-invasive BMI approaches. A typical BMI system includes implant devices to detect brain signals, signal processing to analyze the signals, an external device to be controlled, and feedback. Potential applications include assisting people with disabilities and developing prosthetics. However, BMIs also face challenges regarding signal detection and processing.