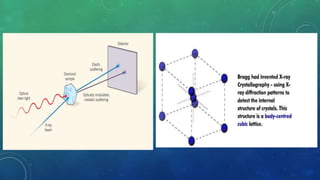
1. The document discusses X-ray diffraction, which occurs when X-rays interact with the atomic planes of a crystal, causing interference patterns.
2. It introduces Bragg's law, which relates the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation to the diffraction pattern produced by a crystalline lattice, and is used to determine crystal structures.
3. Some applications of Bragg's law and X-ray diffraction are identifying unknown crystal structures, computed tomography, and the Braggs' discoveries about crystal structures like sodium chloride and diamond.