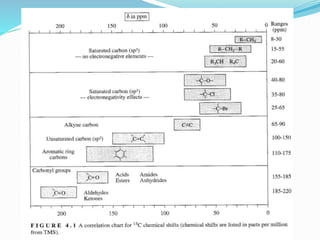
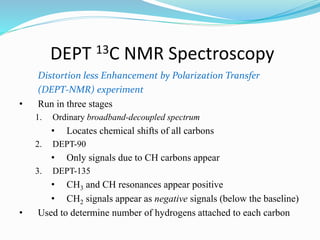
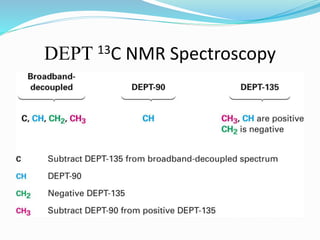
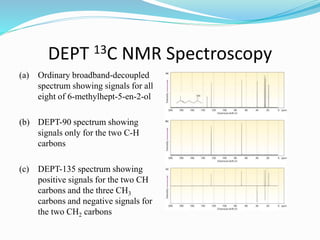
C13 NMR spectroscopy provides information about carbon atoms in molecules. It works based on the absorption of radio waves by carbon-13 nuclei in a magnetic field. There are a few key points:
1) C13 NMR is difficult to analyze due to the low natural abundance of C13 and its weaker magnetic resonance compared to protons.
2) Different types of carbon atoms (CH, CH2, CH3) can be distinguished based on their chemical shifts and coupling patterns. Proton decoupling is used to simplify spectra.
3) DEPT experiments analyze carbon types by enhancing signals from different hybridized carbons (CH, CH2, CH3) in different ways. This allows determining the number and type