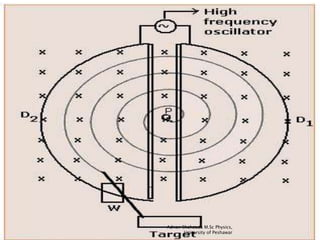
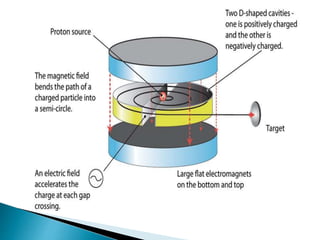
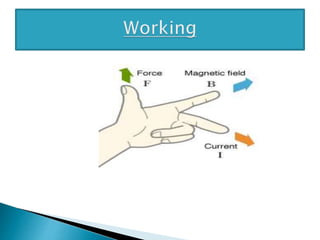
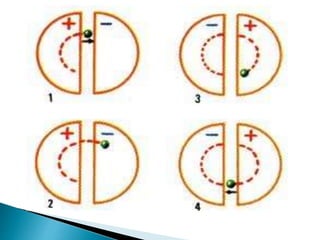
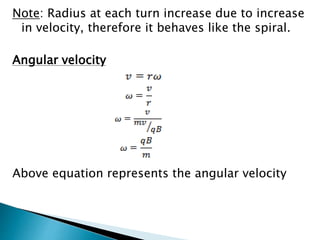
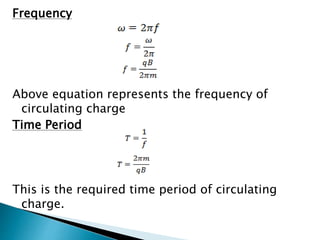
A particle accelerator is a device that increases the kinetic energy of electrically charged particles through the use of electric and magnetic fields. The cyclotron, invented in 1931, is an early type of particle accelerator that uses a high frequency oscillator to accelerate positively charged particles in a spiral path between two "D-shaped" electrodes placed in a strong magnetic field. As the particles accelerate, they travel in larger circular paths until they exit and can be used for nuclear reaction experiments or medical treatments like cancer therapy.