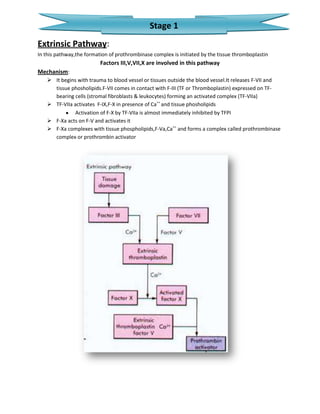
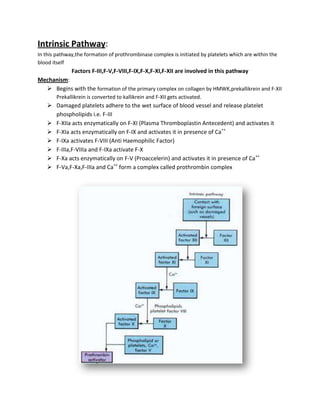
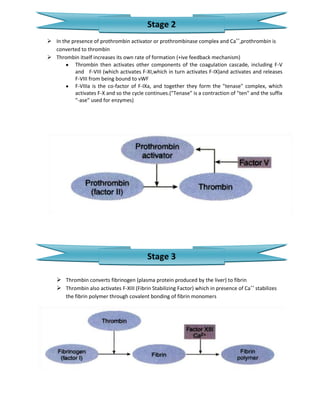
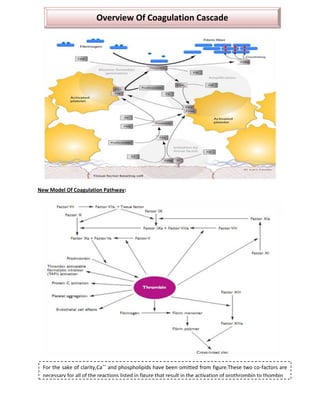
The document summarizes the blood clotting (coagulation) mechanism. It occurs when blood is shed from damaged blood vessels or tissues. There are two pathways - the extrinsic pathway which is initiated by tissue factor, and the intrinsic pathway initiated by platelets. Both pathways involve a cascade of coagulation factors and ultimately lead to the formation of a prothrombinase complex. This converts prothrombin to thrombin via the common pathway. Thrombin then converts fibrinogen to fibrin to form a mesh and stabilize the platelet plug, sealing the break in the blood vessel.