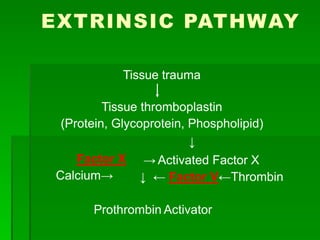
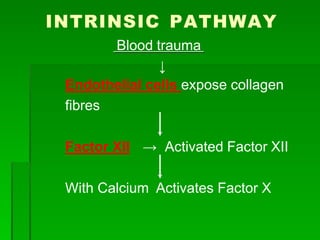
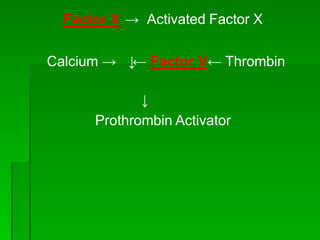
Blood clotting is a process called coagulation where blood loses fluidity and forms a mesh of fibrin fibrils entangling blood cells. There are 12 coagulation factors involved in a sequential process to convert fibrinogen into fibrin. First, the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways form prothrombin activator which converts prothrombin to thrombin. Thrombin then converts fibrinogen to fibrin to form the clot. Anticoagulants like heparin and warfarin prevent clotting by interfering with parts of this coagulation cascade.