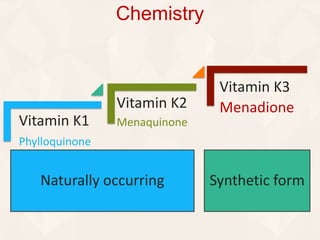
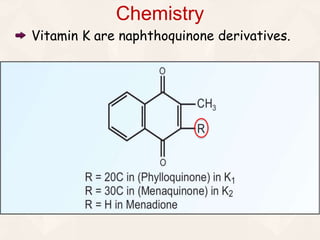
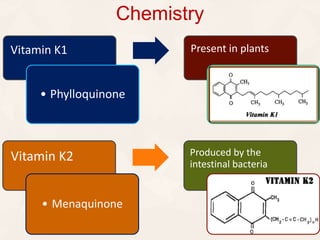
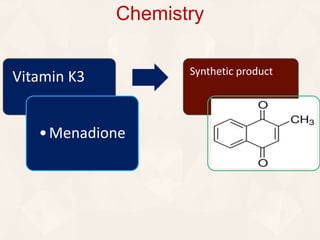
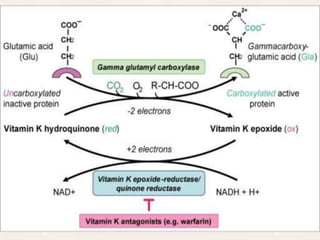
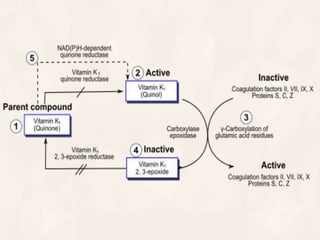
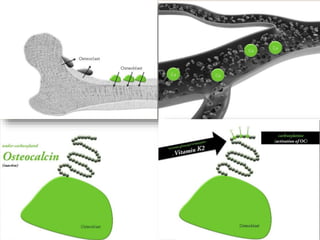
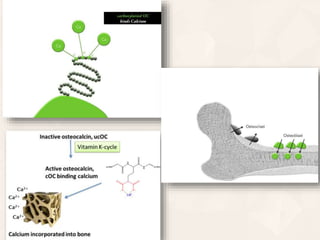
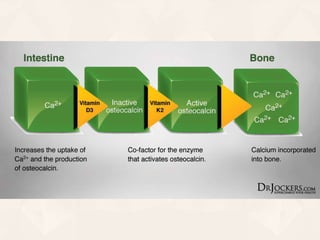
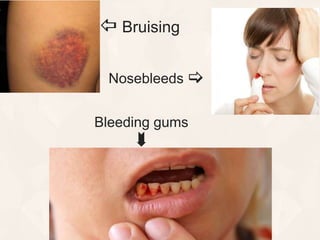
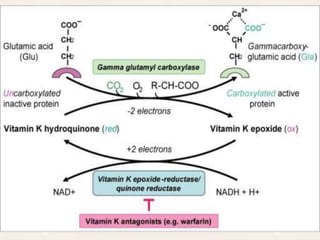
Vitamin K exists in three forms - vitamin K1, K2, and K3. It functions as a coenzyme in the liver to enable the carboxylation of blood clotting factors and proteins involved in bone mineralization. A daily recommended intake of 70-140 μg is needed to support blood coagulation and bone health, with deficiency leading to increased bleeding risks.