This document discusses vitamin A, including its classification, sources, absorption, transport, storage, functions, deficiency, toxicity, and recommended daily intake. Some key points:
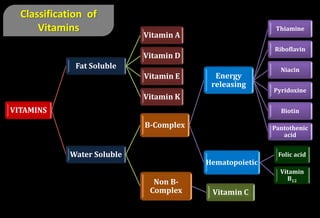
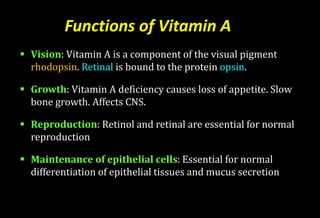
- Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is essential for vision, growth, reproduction, and epithelial cell maintenance. It cannot be made by the body and must come from diet.
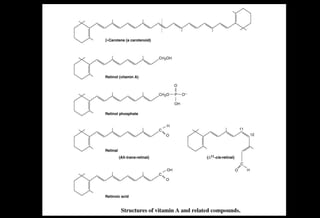
- Major sources include liver, dairy, eggs, carrots and other orange vegetables. Beta-carotene from plants is a provitamin A that the body can convert to vitamin A.
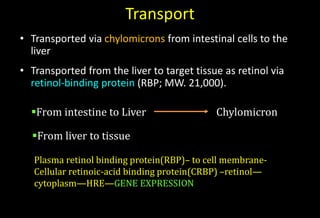
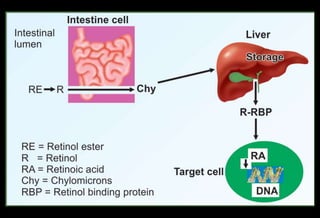
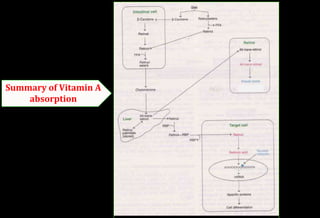
- It is absorbed in intestinal cells and transported to the liver bound to retinol binding protein in the bloodstream. The liver stores significant amounts.
-











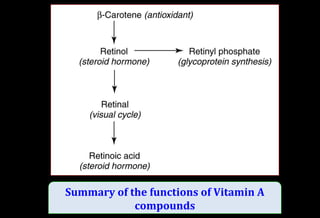


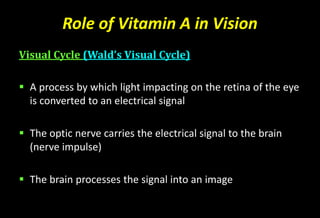
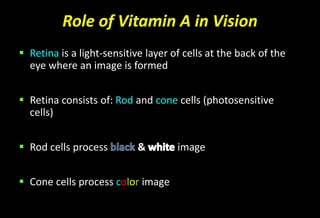
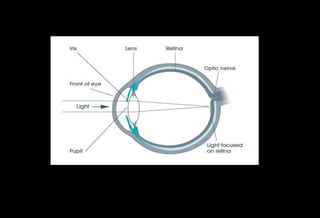
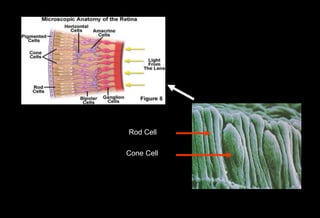
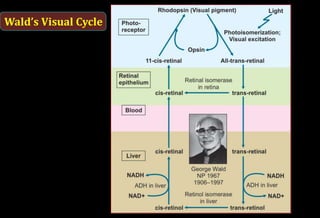
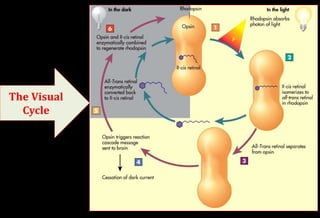
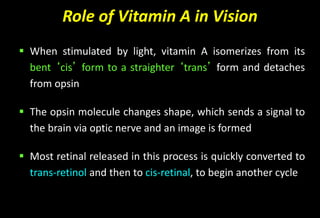
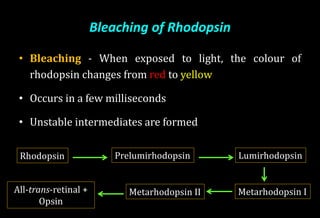
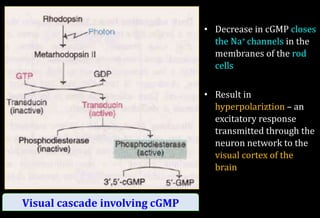
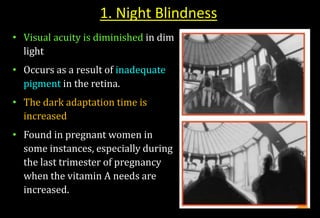
![Role of Vitamin A in Vision
Normal vision depends on the retina and on adequate
vitamin A
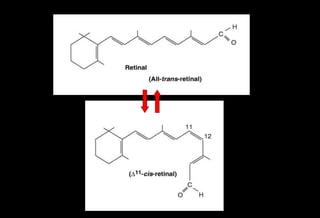
In the retina, vitamin A in the form of retinal binds to a
protein called opsin to make rhodopsin [11-cis – retinal-
opsin] in rod cells
Rhodopsin is a light-sensitive pigments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vitamina-151219041057/85/Vitamin-A-26-320.jpg)