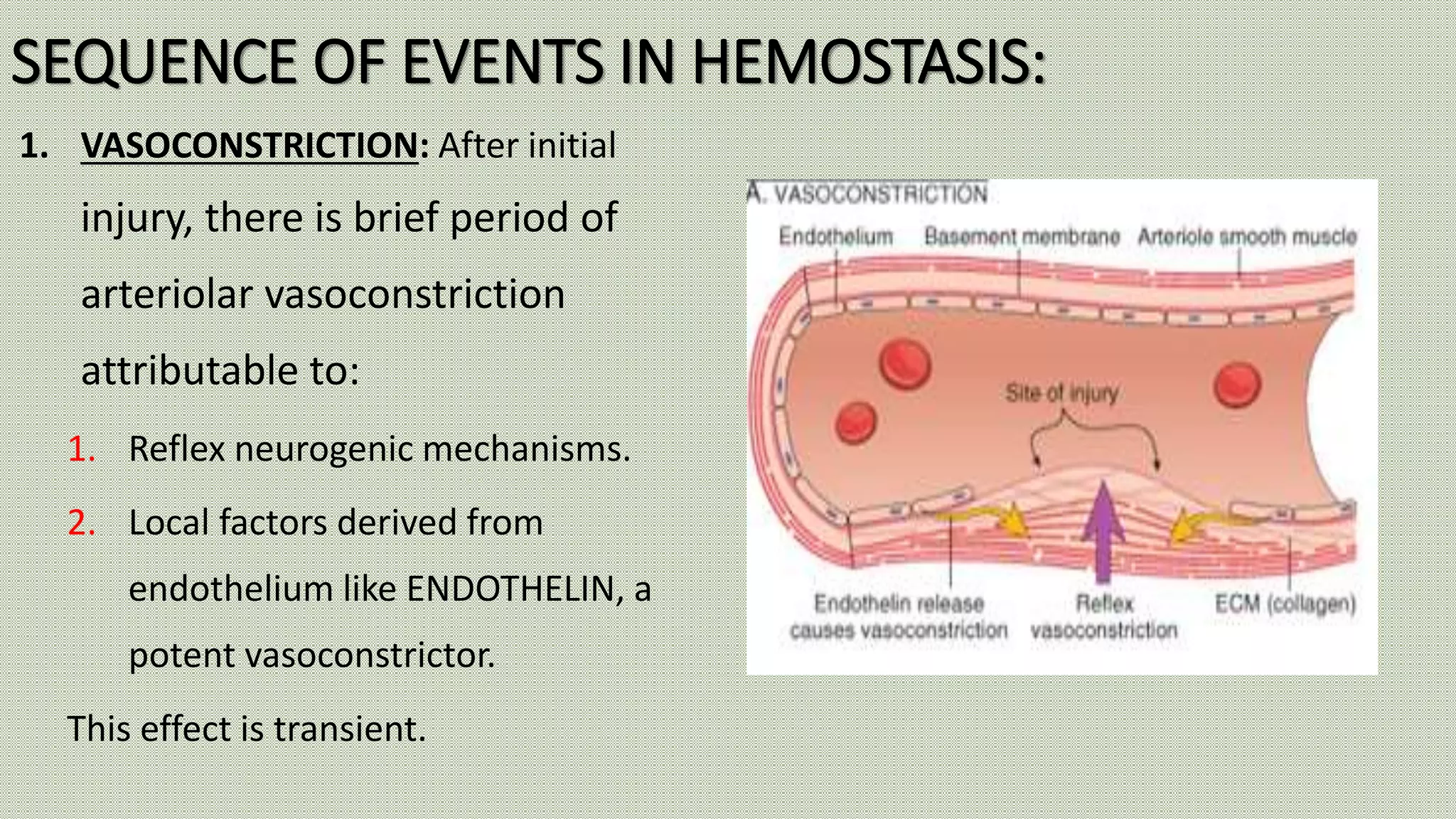
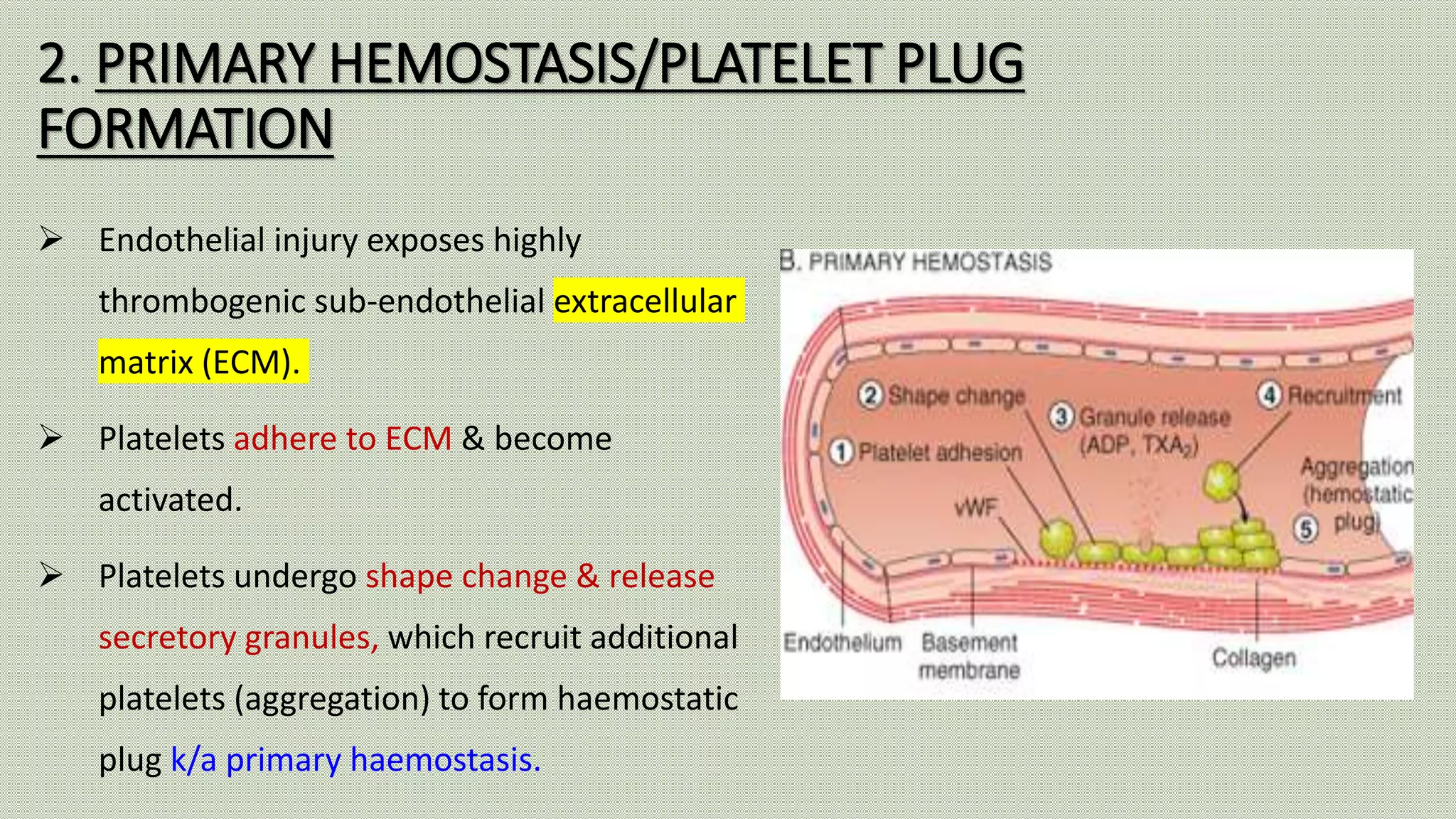
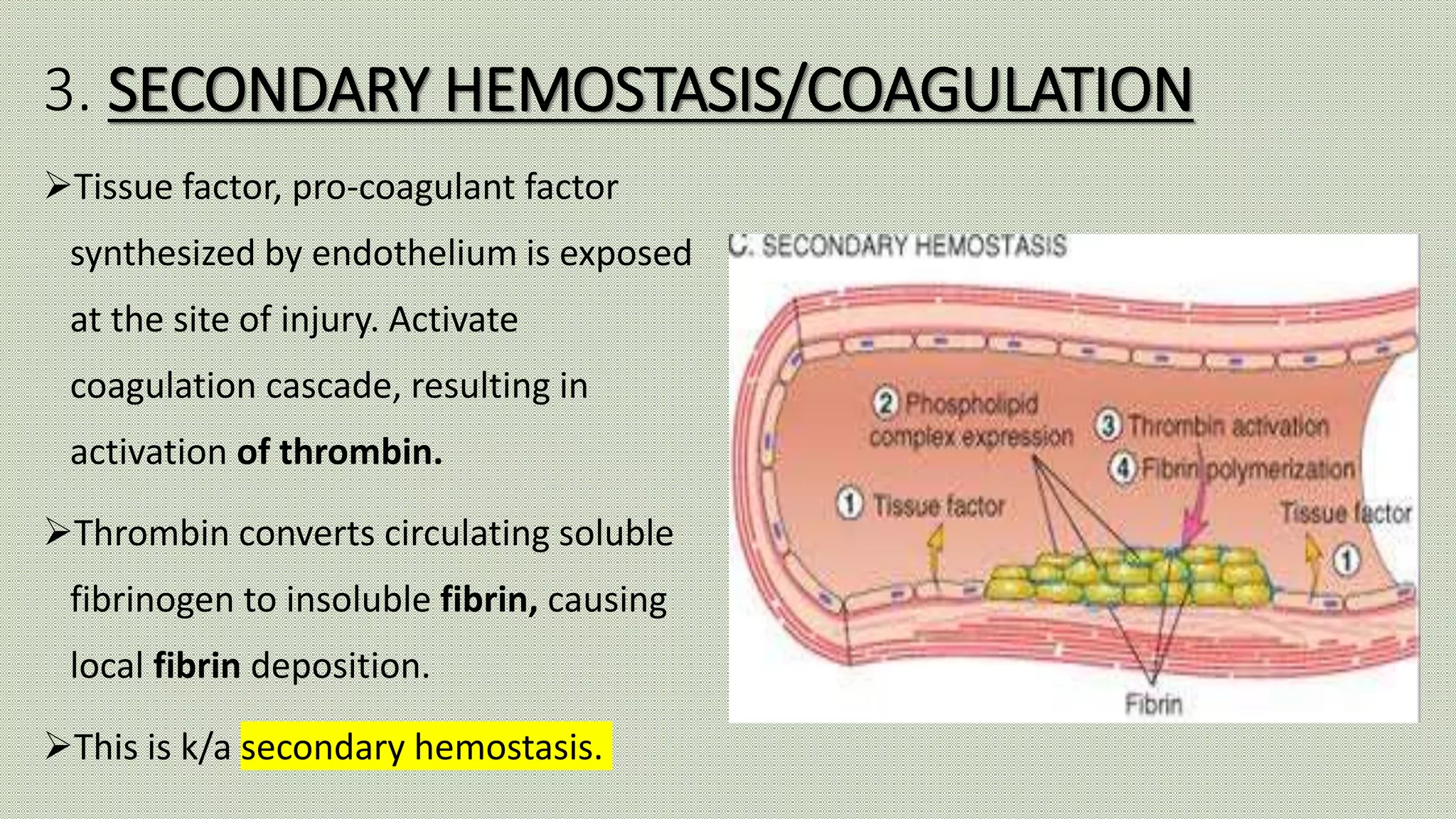
Normal haemostasis involves platelet plug formation, coagulation cascade, and fibrin clot formation to stop bleeding at the site of vascular injury. It is regulated by the endothelium, platelets, and coagulation factors. The coagulation cascade can be initiated through the intrinsic or extrinsic pathway, both leading to thrombin generation and fibrin clot formation. Counter-regulatory mechanisms like fibrinolysis and natural anticoagulants limit clot formation to the site of injury. Laboratory tests monitor components of the coagulation cascade like platelet count and function, prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, and fibrinogen levels.