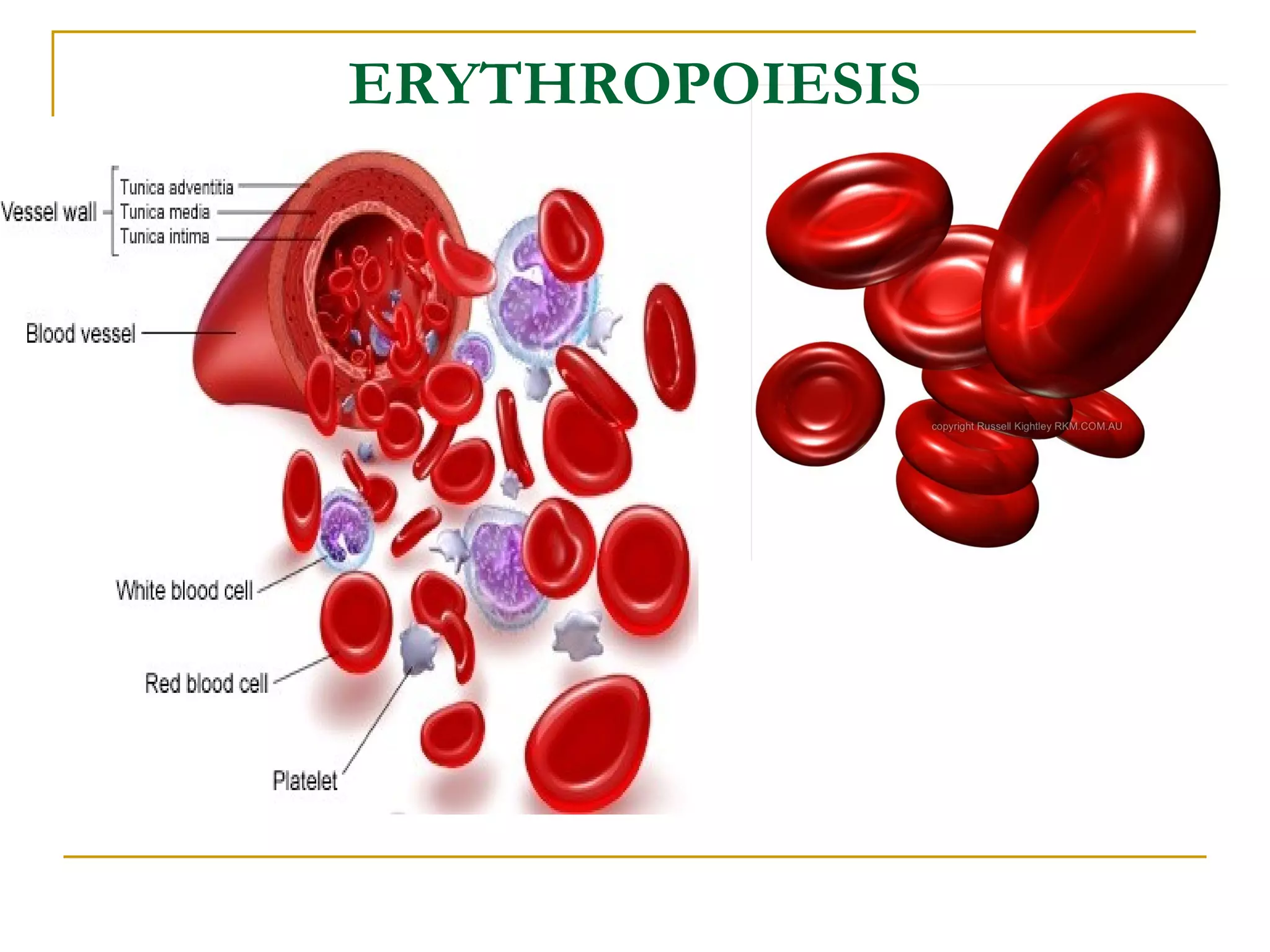
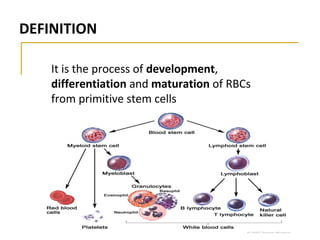
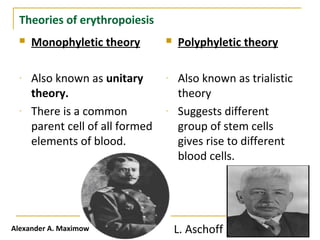
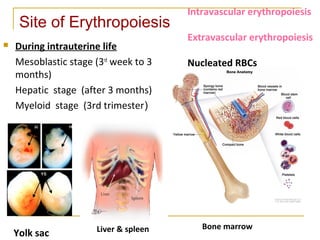
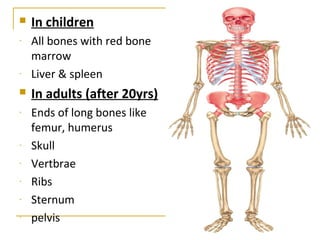
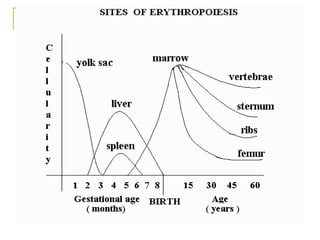
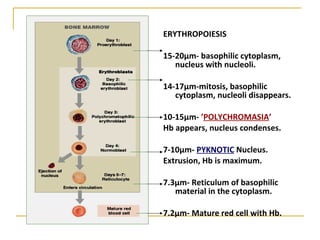
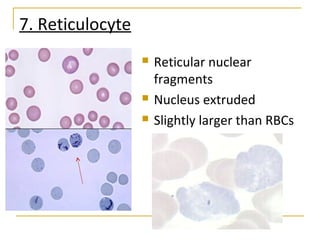
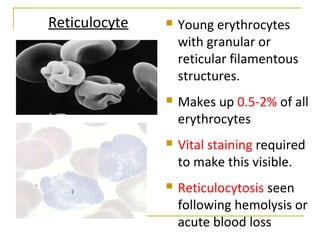
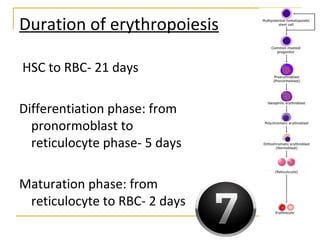
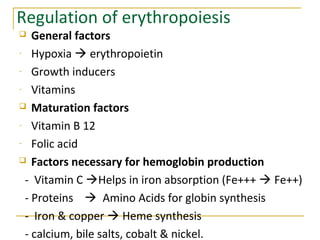
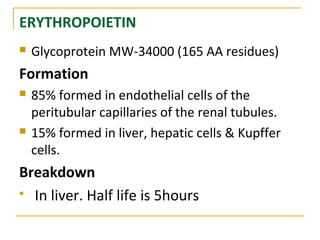
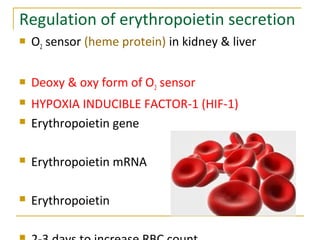
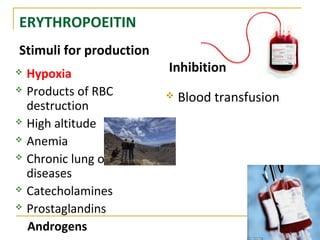
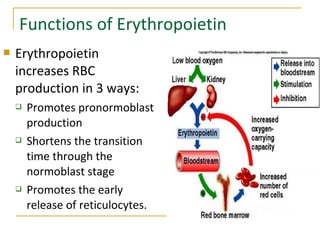
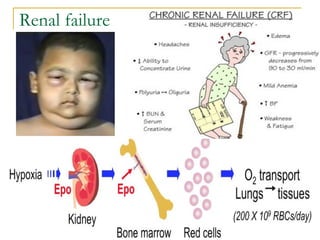
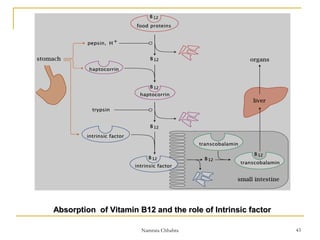
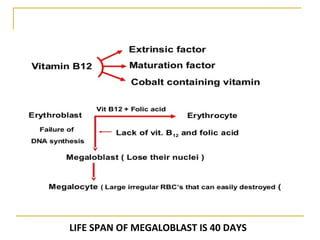
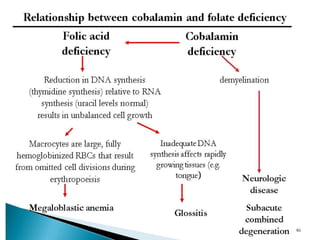
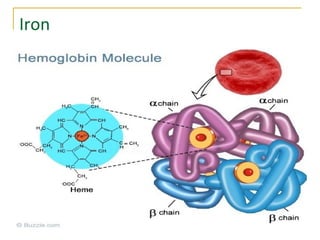
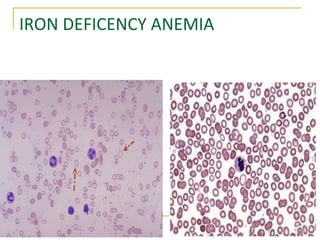
Erythropoiesis is the process where red blood cells are produced. It occurs in multiple stages starting with stem cells in the bone marrow that differentiate into erythroid progenitor cells and progress through normoblast stages as the cells take up hemoglobin and lose their nuclei to become reticulocytes and then mature red blood cells. Key regulators of erythropoiesis include erythropoietin, iron, vitamin B12 and folic acid which promote red blood cell production and maturation. Hypoxia is the main stimulant for increased erythropoietin secretion from the kidneys which then acts to accelerate the production of red blood cells from progenitor cells in the bone marrow.