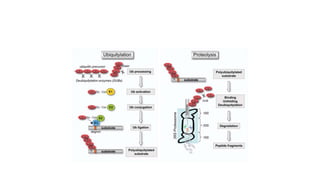
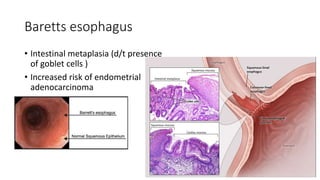
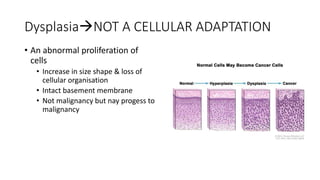
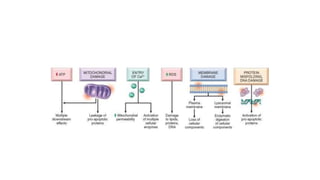
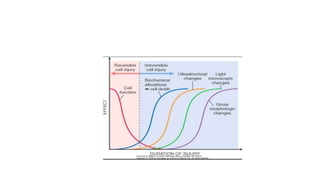
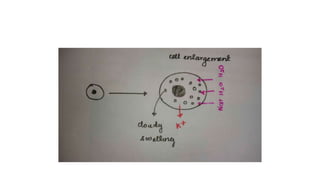
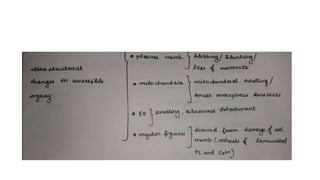
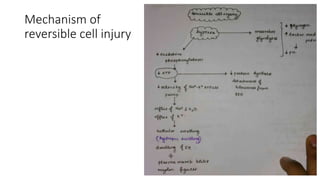
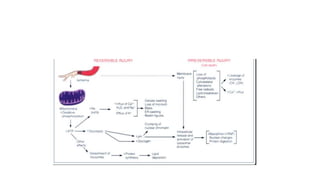
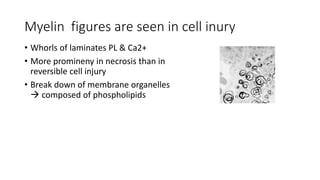
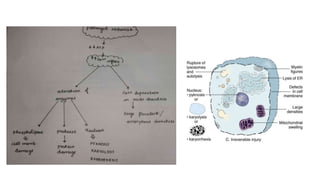
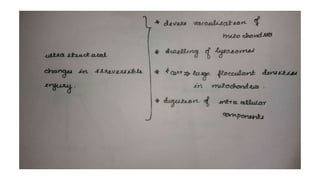
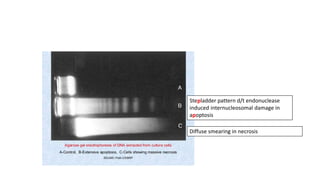
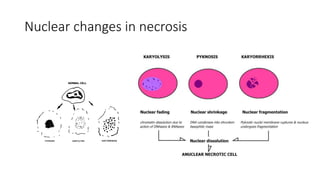
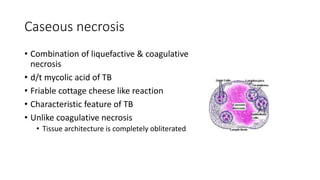
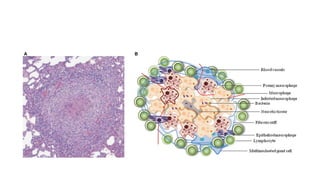
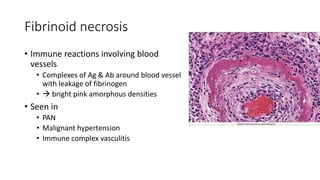
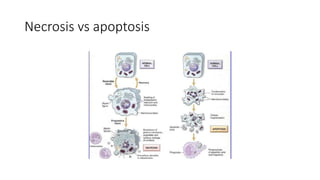
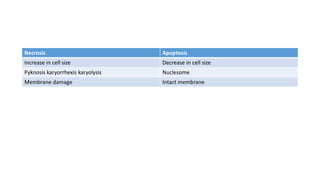
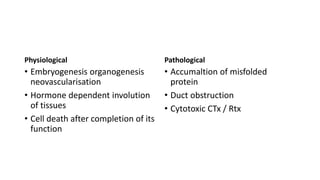
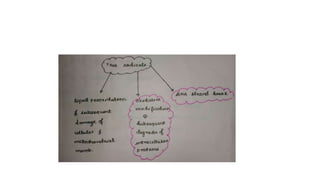
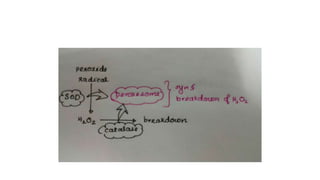
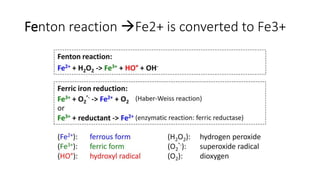
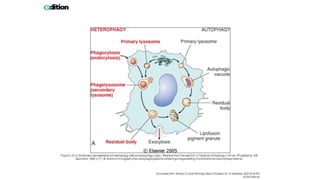
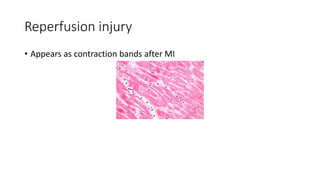
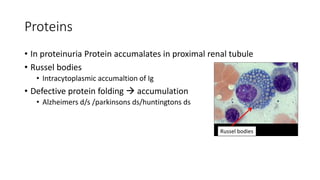
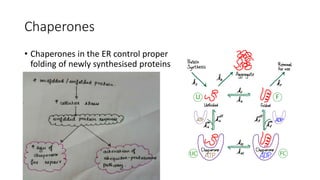
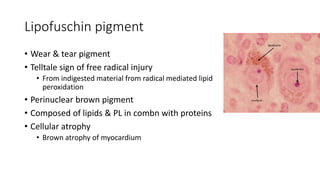
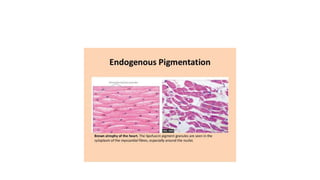
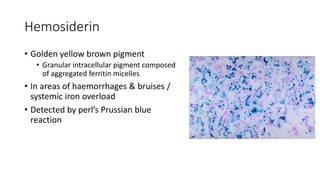
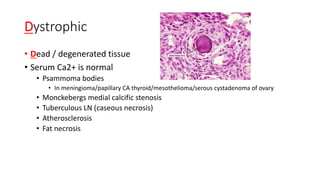
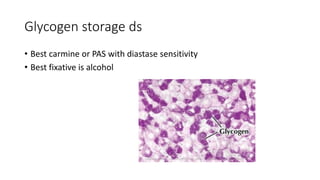
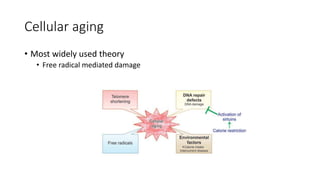
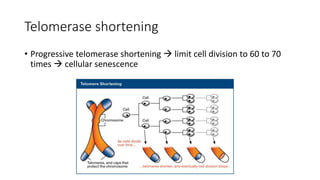
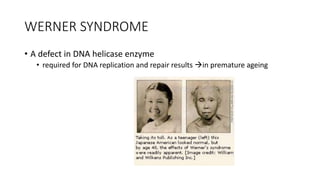
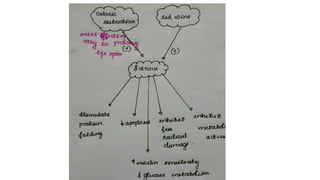
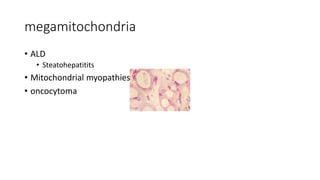
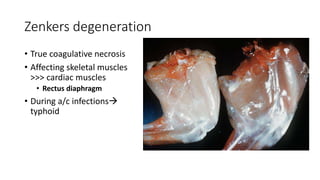
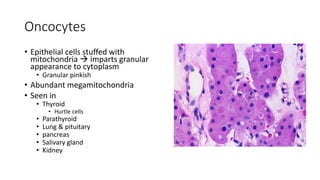
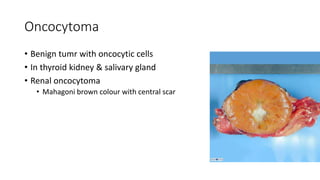
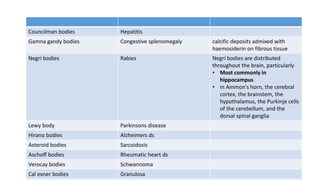
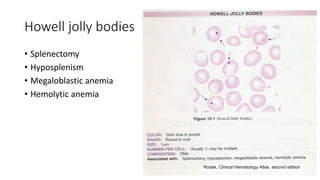
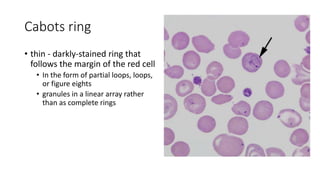
The document discusses various topics related to pathology including causes of cell injury, hypoxia, cellular adaptive responses, mechanisms of cell injury, features of reversible and irreversible injury, necrosis, apoptosis, calcification, pigmentation, and cellular aging. The key points are:
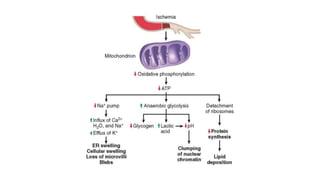
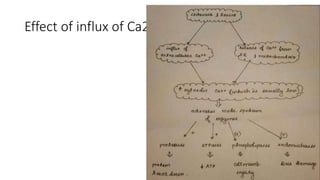
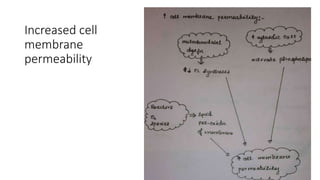
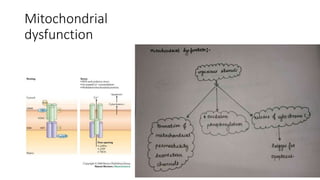
1. Hypoxia is the most common cause of cell injury, usually due to ischemia. Neurons are the most susceptible tissue to hypoxic damage.
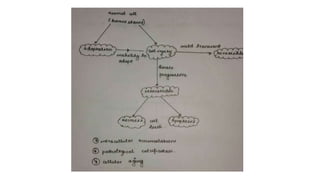
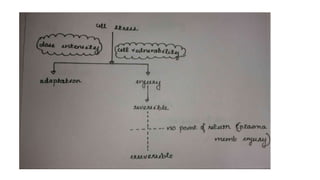
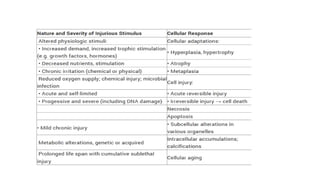
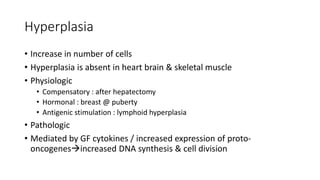
2. Cellular adaptive responses to injury include atrophy, hypertrophy, hyperplasia, metaplasia, dysplasia.
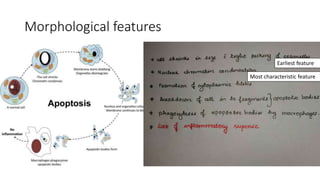
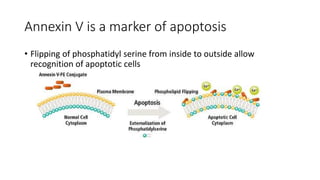
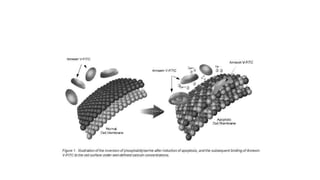
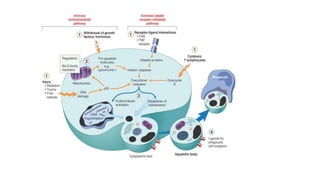
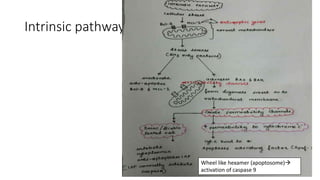
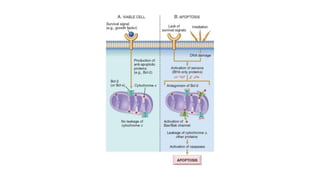
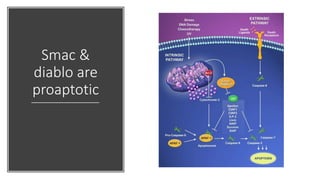
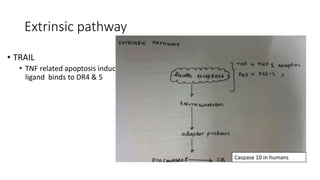
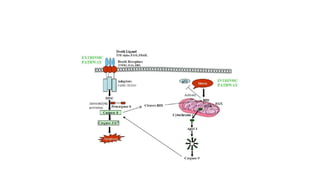
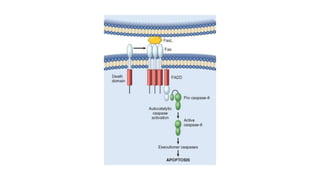
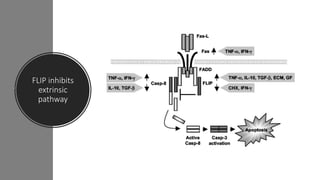
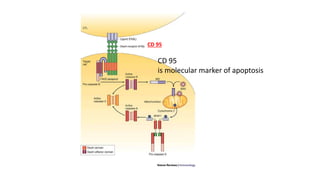
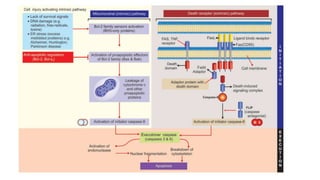
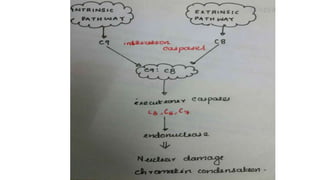
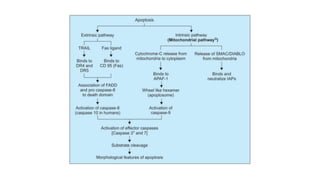
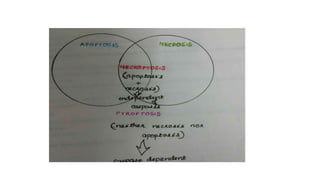
3. Apoptosis is an active and programmed form of cell death, while necrosis is unprogrammed cell death due to severe injury