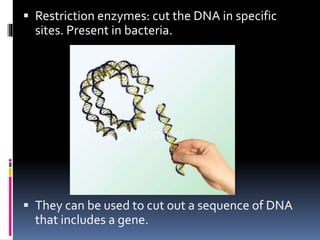
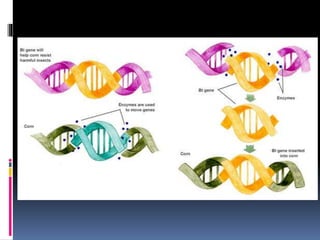
This document discusses biotechnology and genetic engineering. It provides examples of how biotechnology is used in forensics, agriculture, and genetic engineering. Genetic engineering involves transferring genes between organisms, such as placing human genes in bacteria. The document also discusses applications of genetic engineering like creating pest-resistant and herbicide-resistant crops through biotechnology techniques.