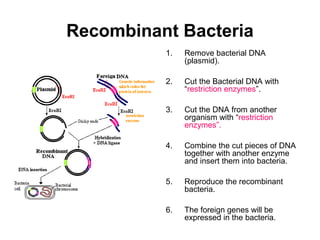
This document discusses genetic engineering techniques such as selective breeding, recombinant DNA, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), gel electrophoresis, and transgenic organisms. Recombinant DNA allows combining DNA from different organisms and was first used in the 1970s with bacteria. Genetically modified plants and animals are created through insertion of foreign DNA and have applications such as producing human proteins and increasing disease resistance. PCR and gel electrophoresis are techniques used to analyze and identify DNA.