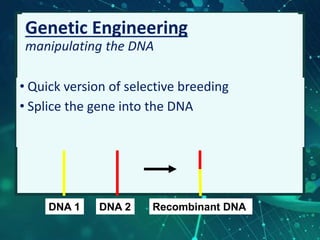
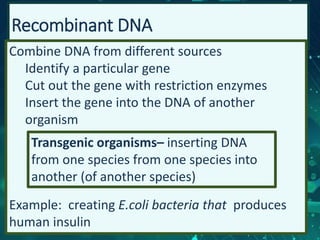
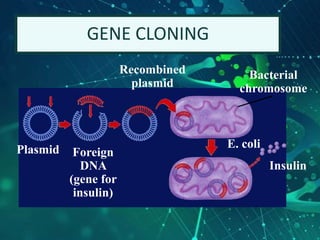
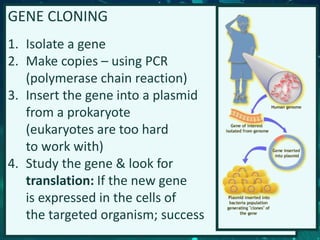
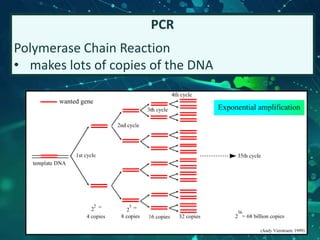
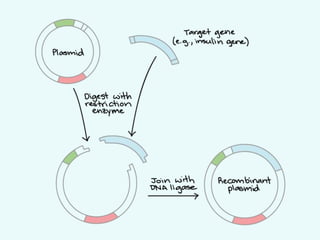
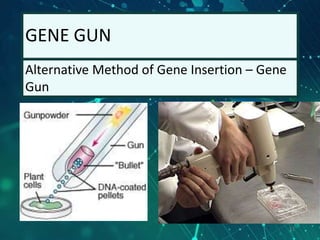
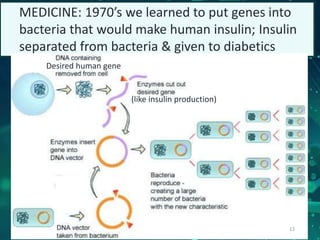
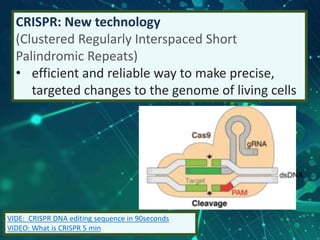
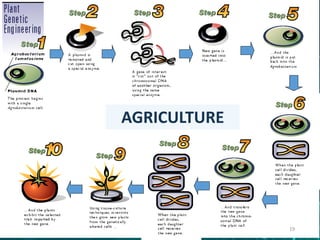
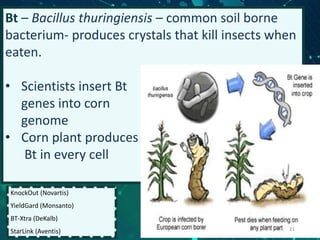
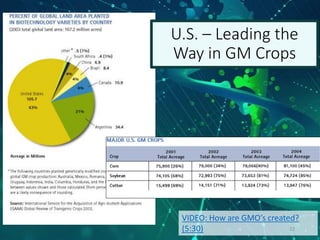
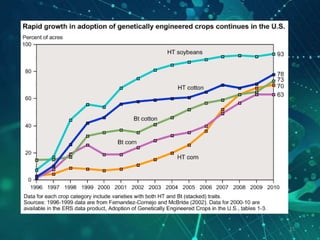
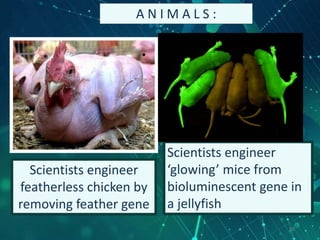
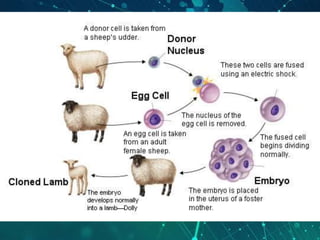
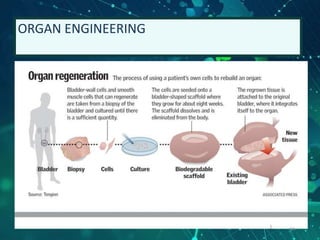
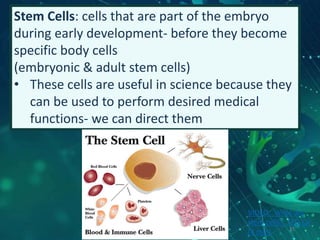
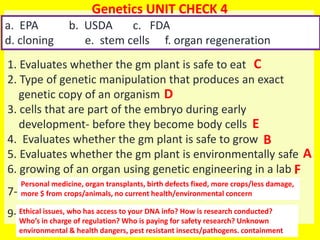
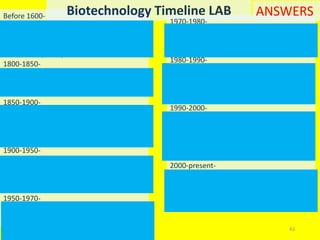
This document provides an overview of genetic engineering and biotechnology concepts through a series of slides. It discusses how DNA from different organisms can be spliced together, and how genetic engineering involves manipulating genes. Examples are given of inserting select genes into organisms to improve traits or have them mass produce certain proteins. The document also summarizes gene cloning techniques like PCR and discusses applications of genetic engineering in medicine, agriculture, and animal science. Ethical considerations around topics like patenting life forms and conducting safety research are also briefly outlined.