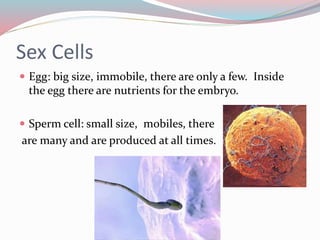
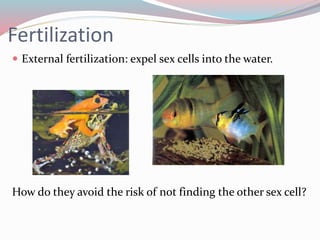
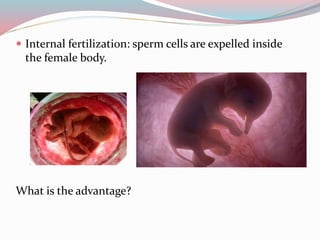
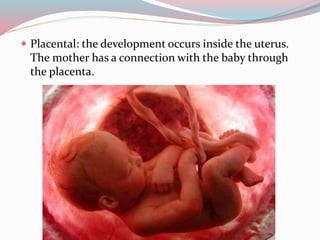
The document discusses different types of sex cells and fertilization methods in species. It describes eggs as large, immobile and few in number, providing nutrients, while sperm are small, mobile and produced continuously in large numbers. External fertilization involves releasing sex cells into water, while internal increases chances of fertilization. The document also covers parenting strategies like monogamy, polygyny, polyandry and differences in offspring development methods between viviparous placental, marsupial, oviparous, ovoviviparous and ovuliparous species.