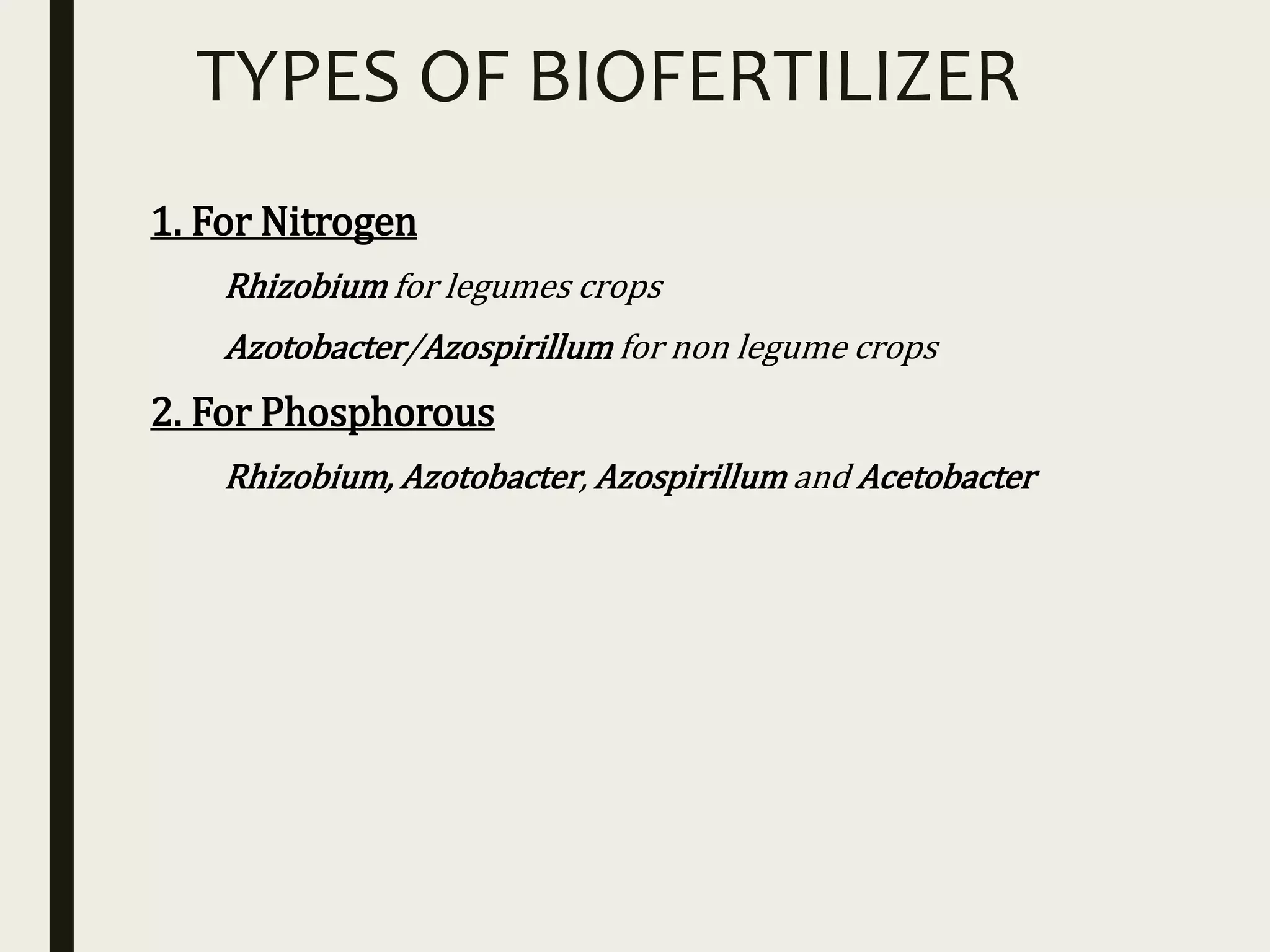
This document discusses biofertilizers and biopesticides as alternatives to chemical fertilizers and pesticides. It notes that while chemical fertilizers boosted agriculture in the 20th century, they also caused environmental problems. Biofertilizers using beneficial microorganisms can increase yields without harm. They fix nitrogen or solubilize phosphorus. Types include Rhizobium for legumes and Azotobacter for non-legumes. Biocompost is an organic fertilizer made from sugar industry waste. Biopesticides are biochemical pesticides from natural sources like bacteria, fungi and plants. They control pests non-toxically through mechanisms like insect sex pheromones or plant extracts in traps. They are usually less