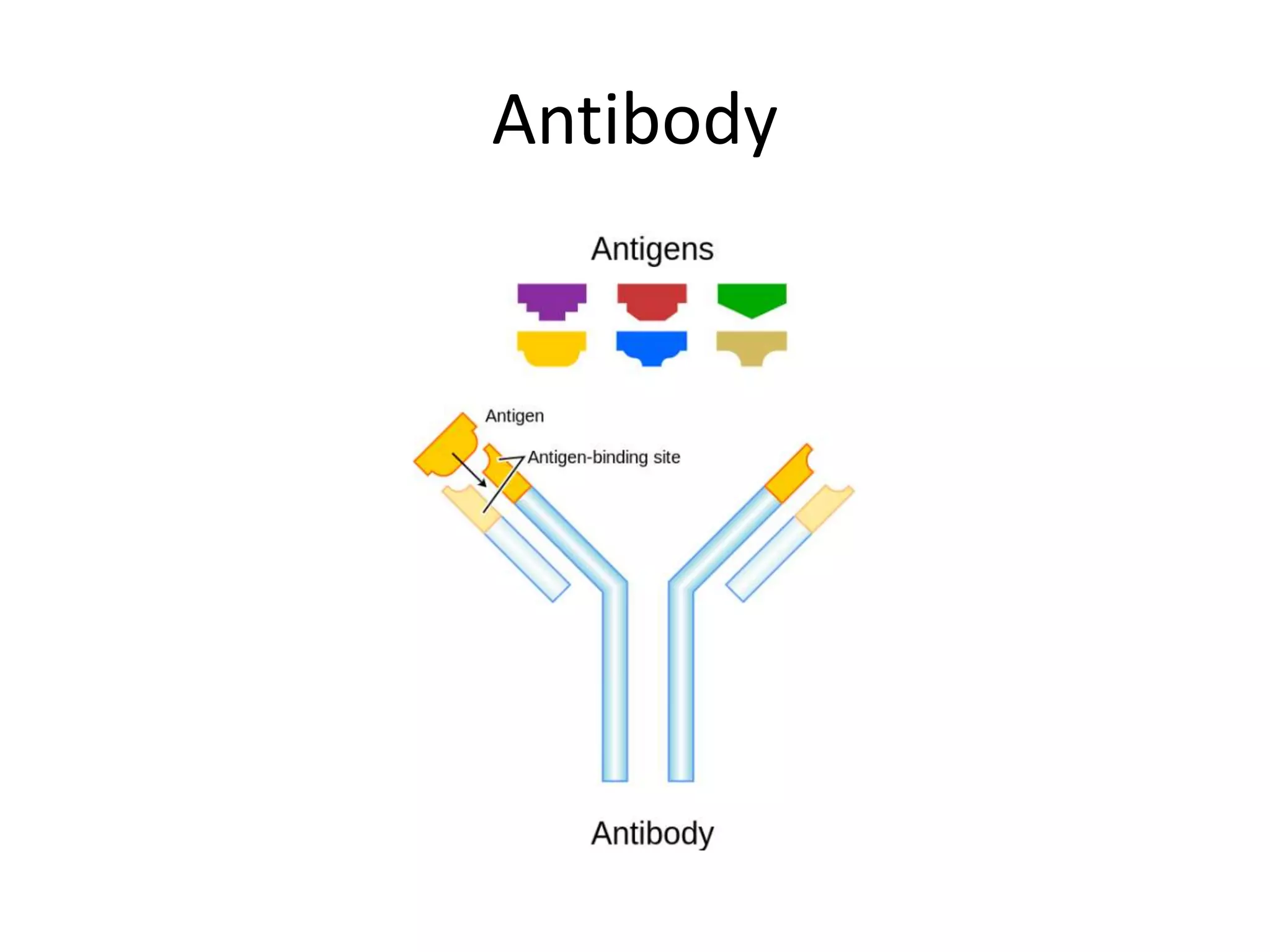
The document discusses antigen-antibody interactions, including that an antigen induces an immune response and antibodies are produced by B cells to neutralize pathogens. It describes the specific chemical interaction between antibodies and antigens, with non-covalent interactions like hydrogen bonds and van der Waals forces forming the basis of this binding. Finally, it lists several immunological tests that utilize this interaction, such as radioimmunoassay, ELISA, Western blot, and immunofluorescence.