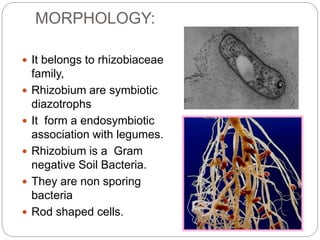
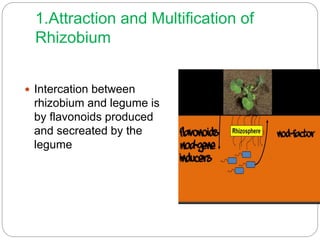
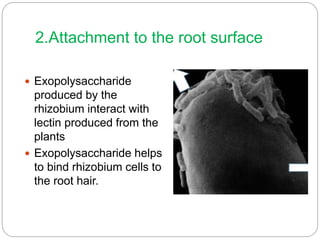
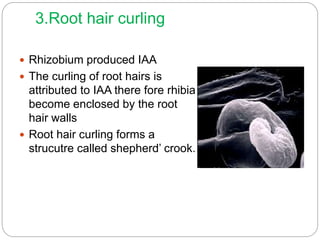
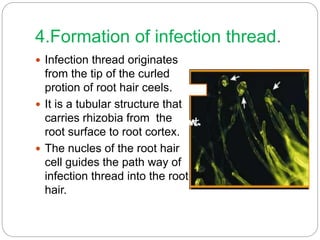
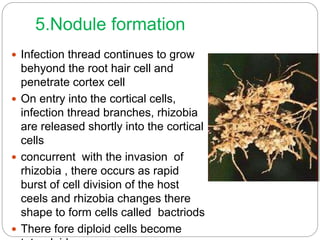
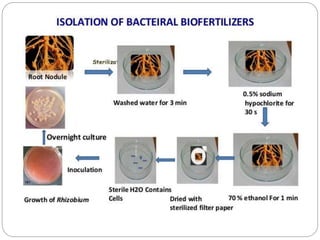
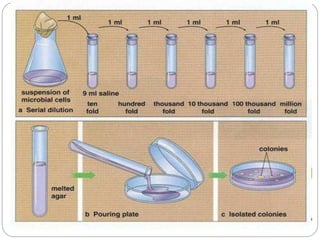
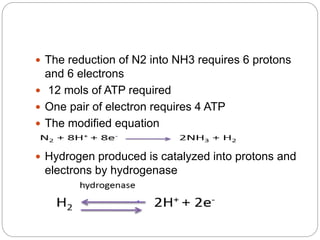
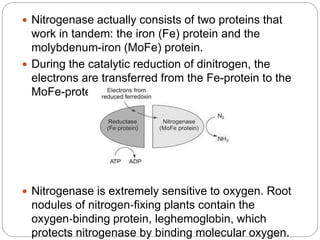
This document discusses Rhizobium, a soil bacteria that forms a symbiotic relationship with legumes to fix atmospheric nitrogen. It begins with an introduction to Rhizobium's morphology, characteristics, and classification. It then covers the cross inoculation groups of Rhizobium, the process of nodule formation in legumes, and methods for isolating Rhizobium from nodules. Finally, it details the mechanism of nitrogen fixation, including the role of the nitrogenase enzyme and electron transfer process within the root nodule.