1. The seminar discusses developing transgenic plants resistant to insects through the transfer of resistance genes from microorganisms, higher plants, and animals into crop plants.
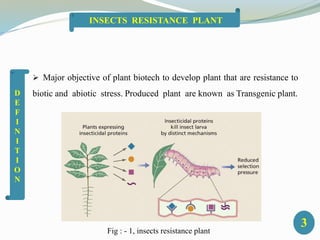
2. Major objectives of plant biotechnology are to develop plants resistant to biotic and abiotic stresses. Resistance to insects has been achieved by introducing genes encoding Bt toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis and other insecticidal proteins.
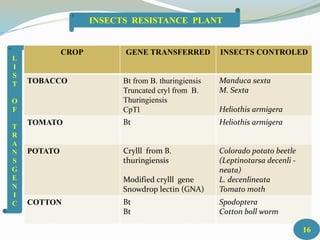
3. Useful genes have been isolated from microbes like B. thuringiensis, higher plants like beans and tobacco, and animals like mammals. These genes have been successfully used to engineer insect-resistant crops like cotton, potato, tomato, and tobacco.