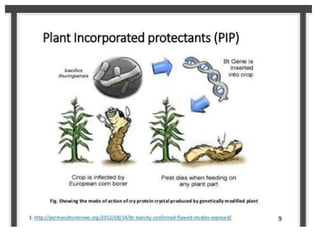
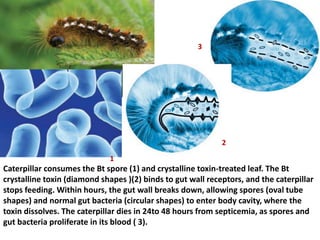
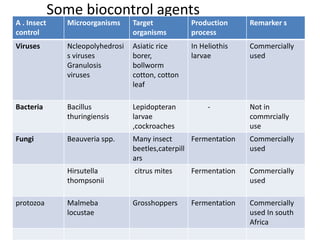
The document discusses biopesticides as a natural alternative to chemical pesticides. It defines biopesticides as products made from minerals, bacteria, plants or animals that can control pests. Biopesticides are classified into microbial, plant, and biochemical pesticides. Microbial pesticides include bacteria like Bacillus thuringiensis, viruses, and fungi. Plant pesticides involve introducing pesticide genes into plants. Biochemical pesticides use pheromones or plant extracts. Biopesticides have advantages like specificity, low amounts needed, and low risk of pest resistance, but their effects can be slower than chemical pesticides.