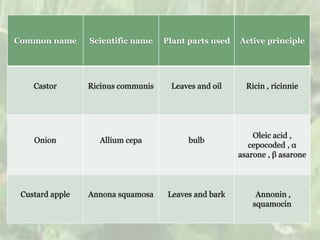
Plant extracts and bacteria like Bacillus thuringiensis were among the earliest biopesticides. While biopesticides saw limited use with the rise of chemical pesticides, there are now over 245 registered biopesticide ingredients. Biopesticides are generally less toxic than chemical pesticides and often affect only the target pest. They can be effective in small amounts but require knowledgeable application as part of integrated pest management. Common biopesticides are derived from bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa, yeasts, and plants.