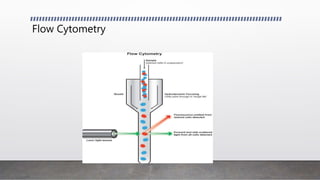
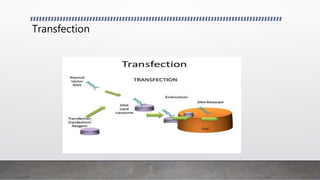
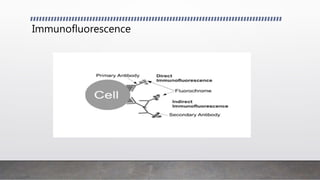
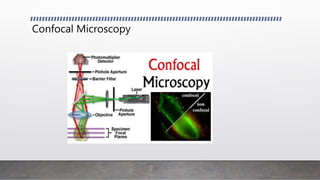
This document discusses advanced animal cell culture techniques. It introduces cell culture and explains that animal cells can be removed and grown outside their original environment. It then describes several specific techniques: Western blotting detects proteins in cell mixtures; flow cytometry measures and characterizes labeled cells using fluorescence; transfection introduces nucleic acids into cells; immunofluorescence uses fluorescent antibodies to detect proteins in cells and tissues; and confocal microscopy uses a pinhole to increase resolution and contrast of microscope images.