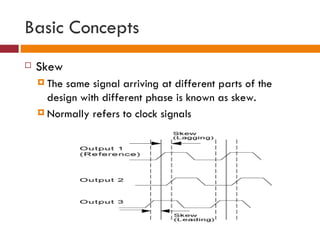
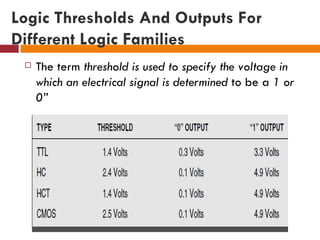
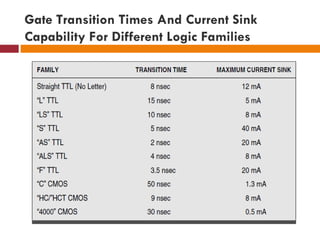
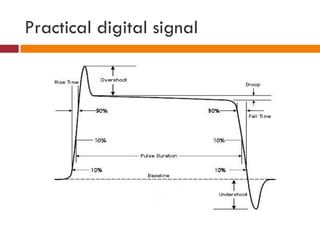
This document discusses logic families, which are groups of logic gates that have compatible logic levels and power supply characteristics. It then lists several common logic families such as RTL, DTL, ECL, TTL, PMOS, NMOS, CMOS, and BiCMOS. The document goes on to define basic concepts related to logic gates such as fan-in, fan-out, gate delay, wire delay, skew, logic levels, current levels, noise margin, rise/fall time, propagation delay, and power dissipation. It provides information on logic thresholds and outputs as well as gate transition times and current sink capabilities for different logic families.