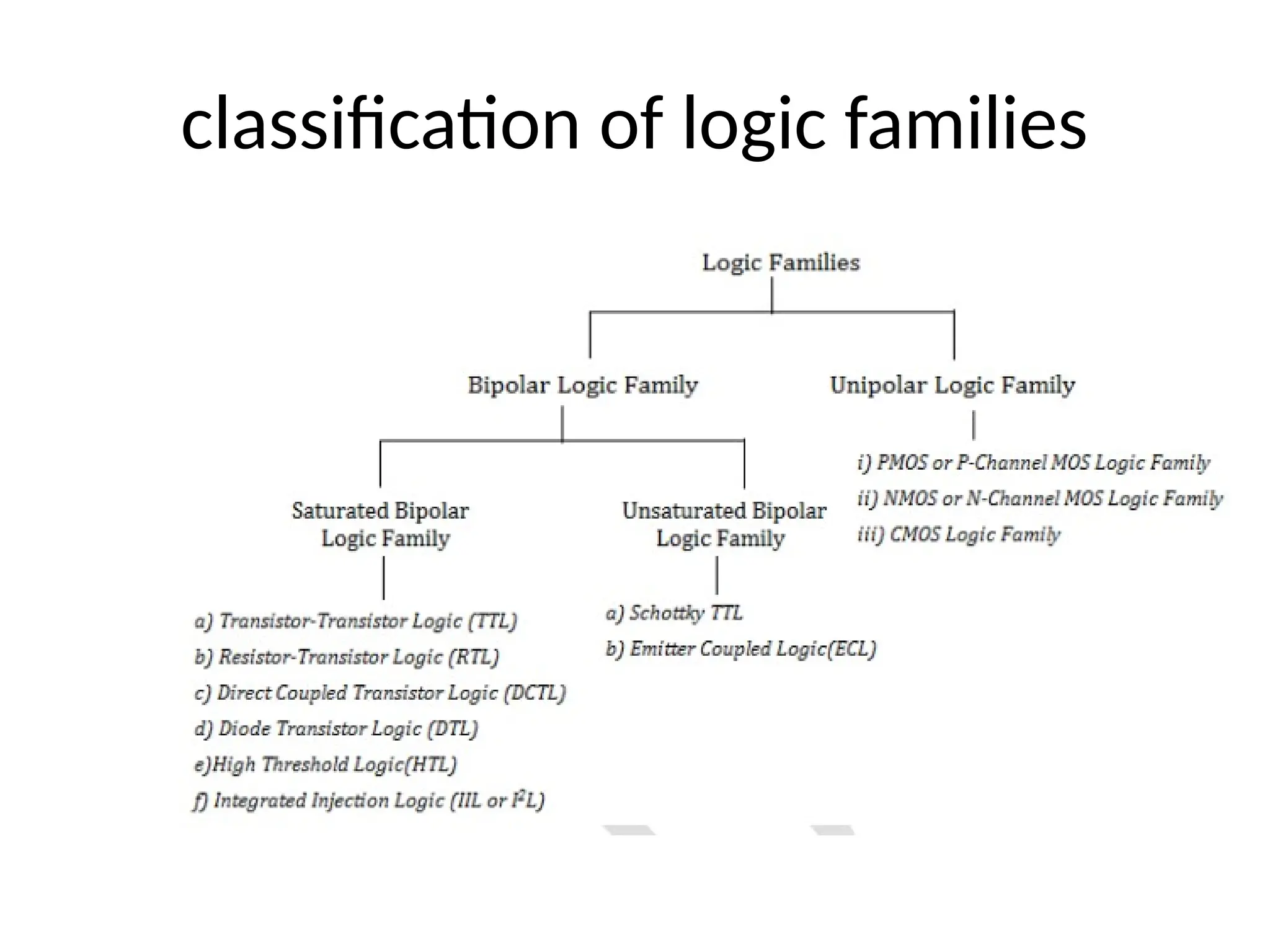
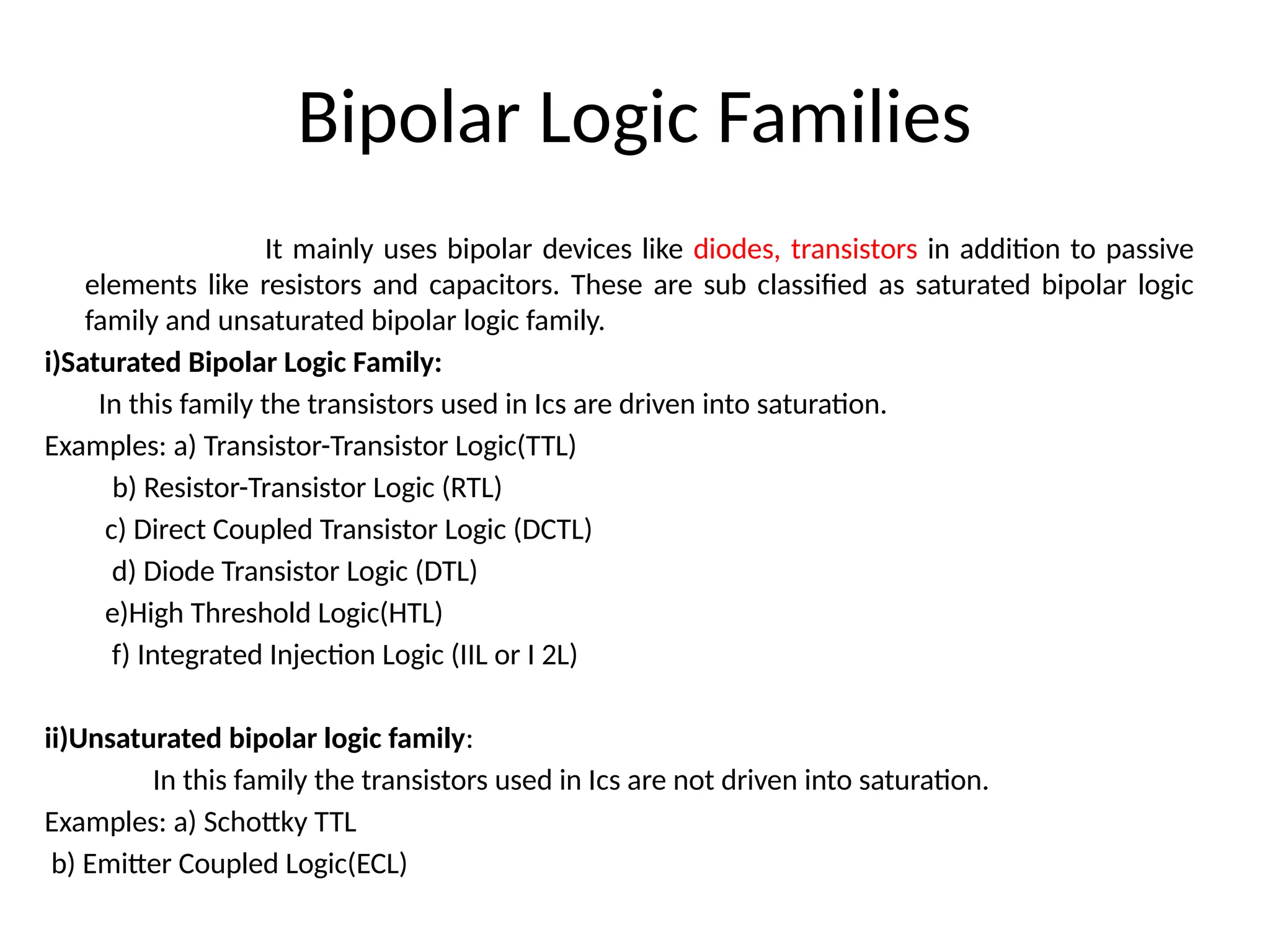
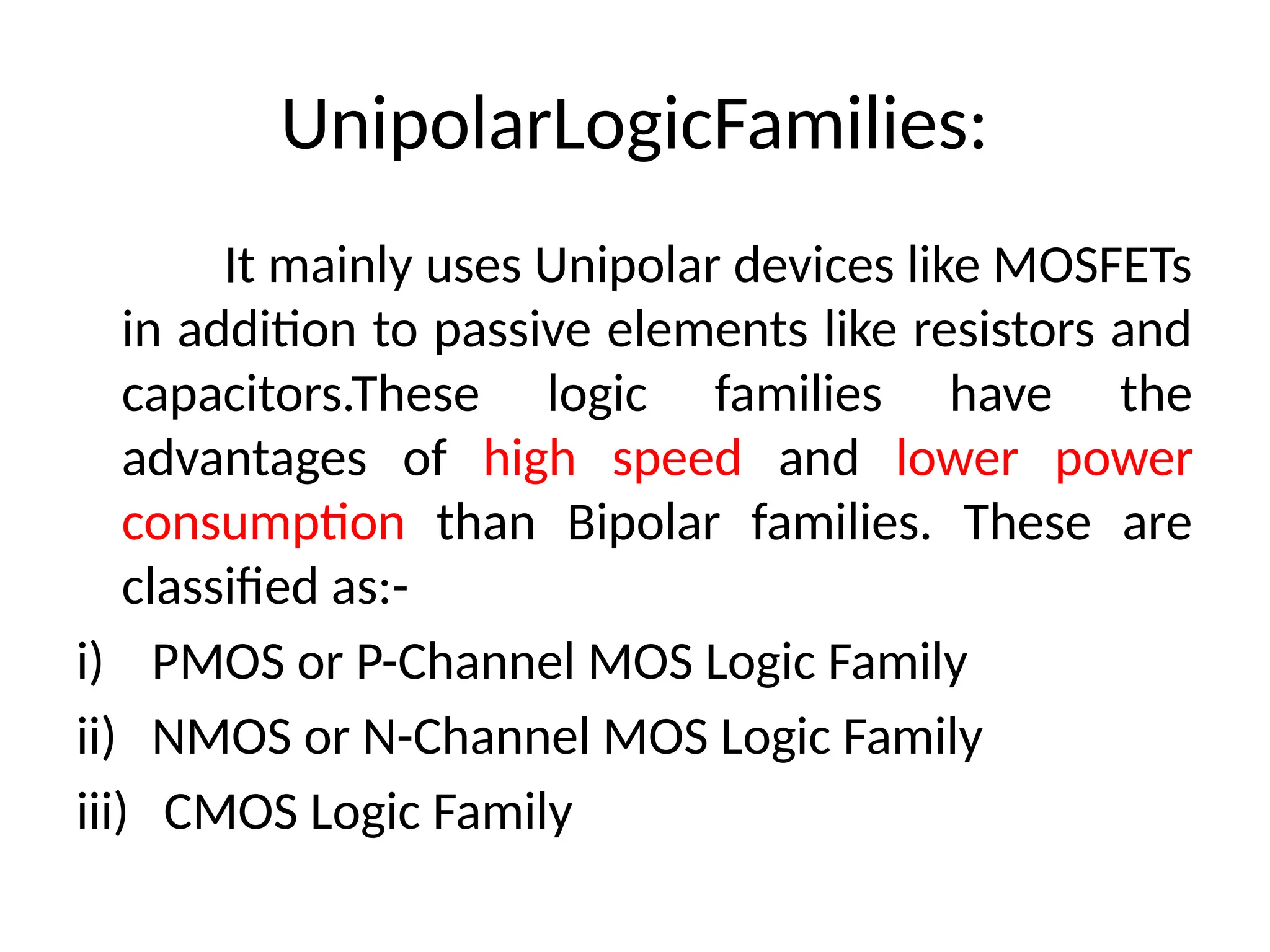
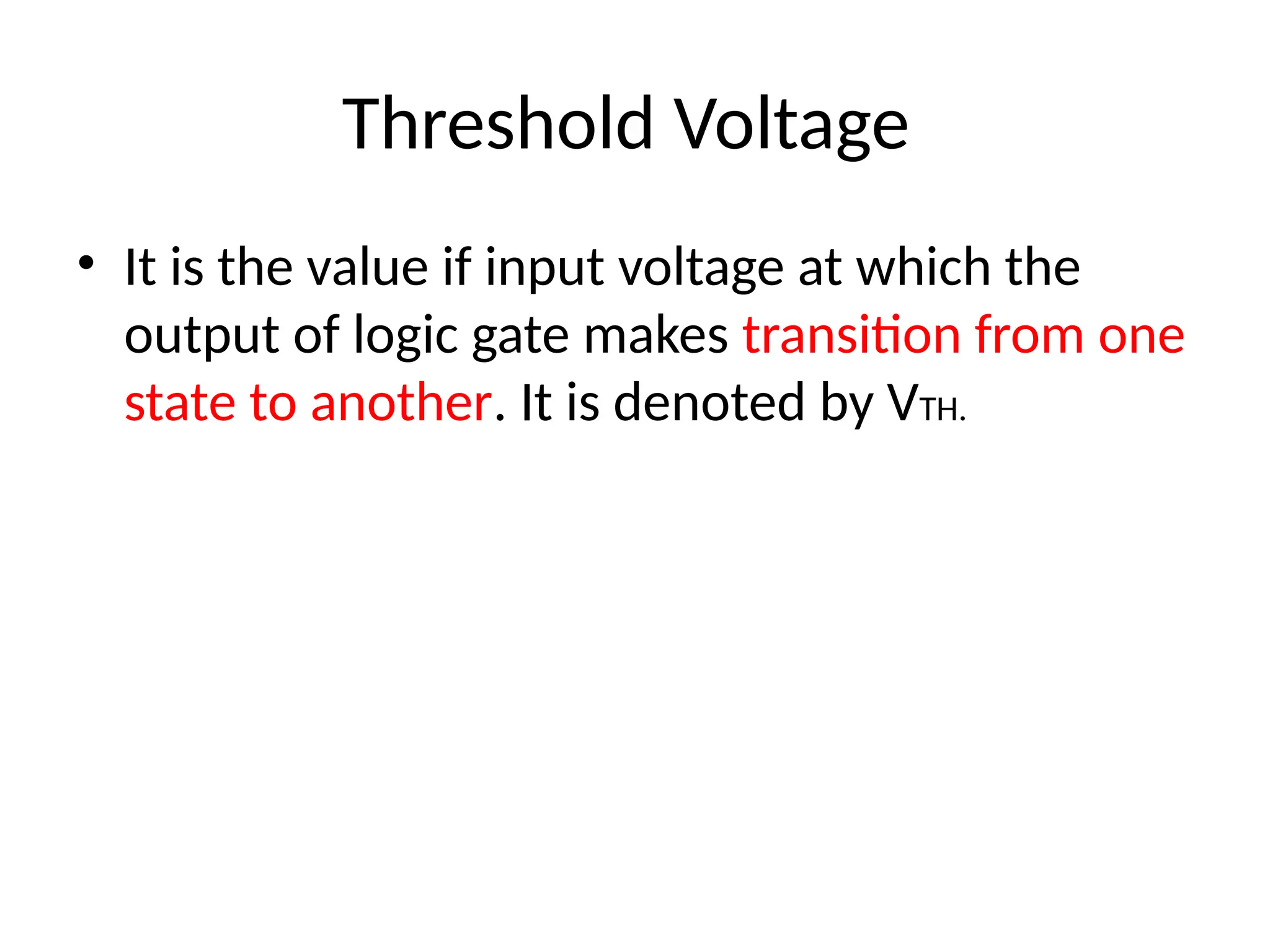
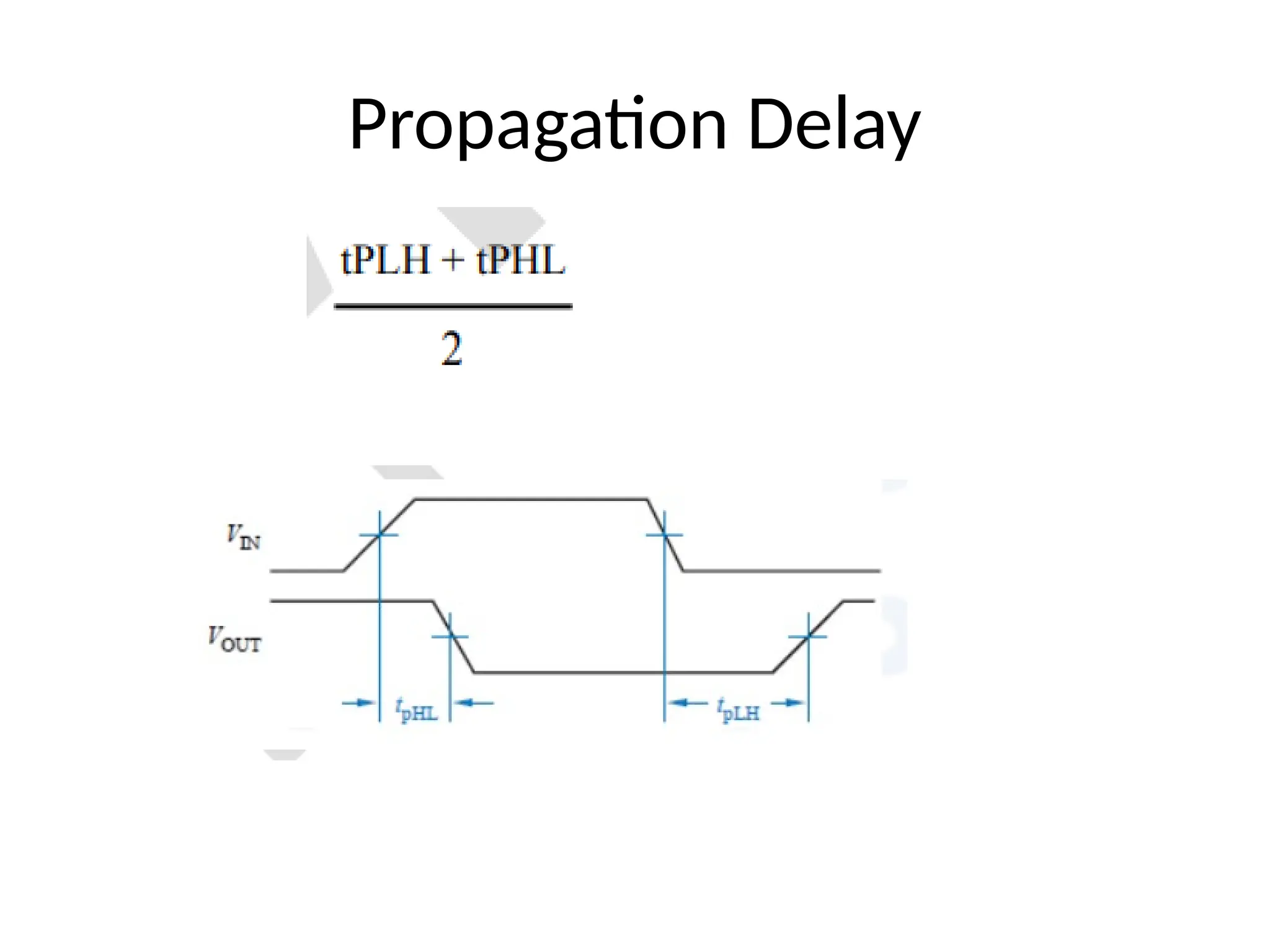
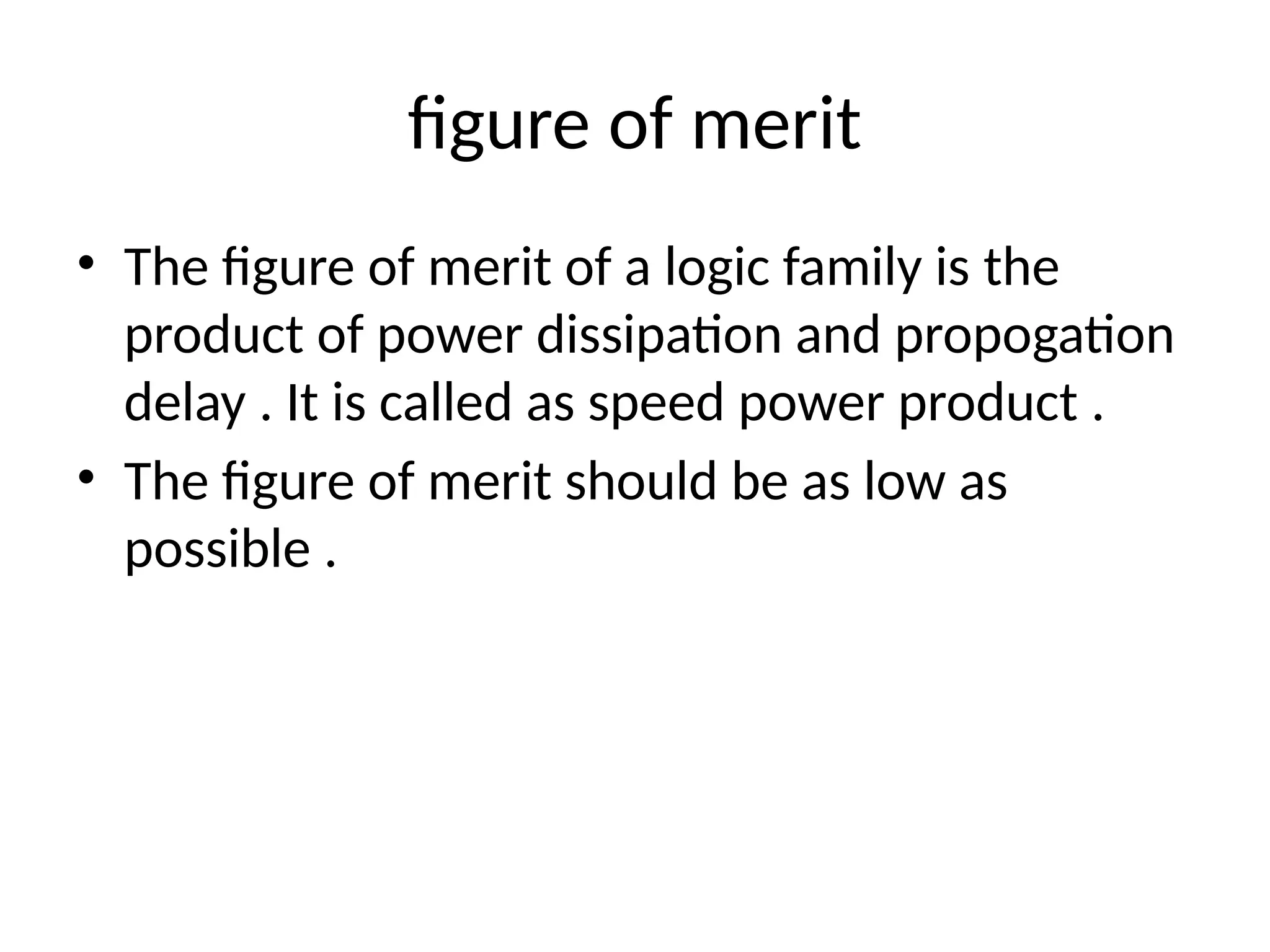
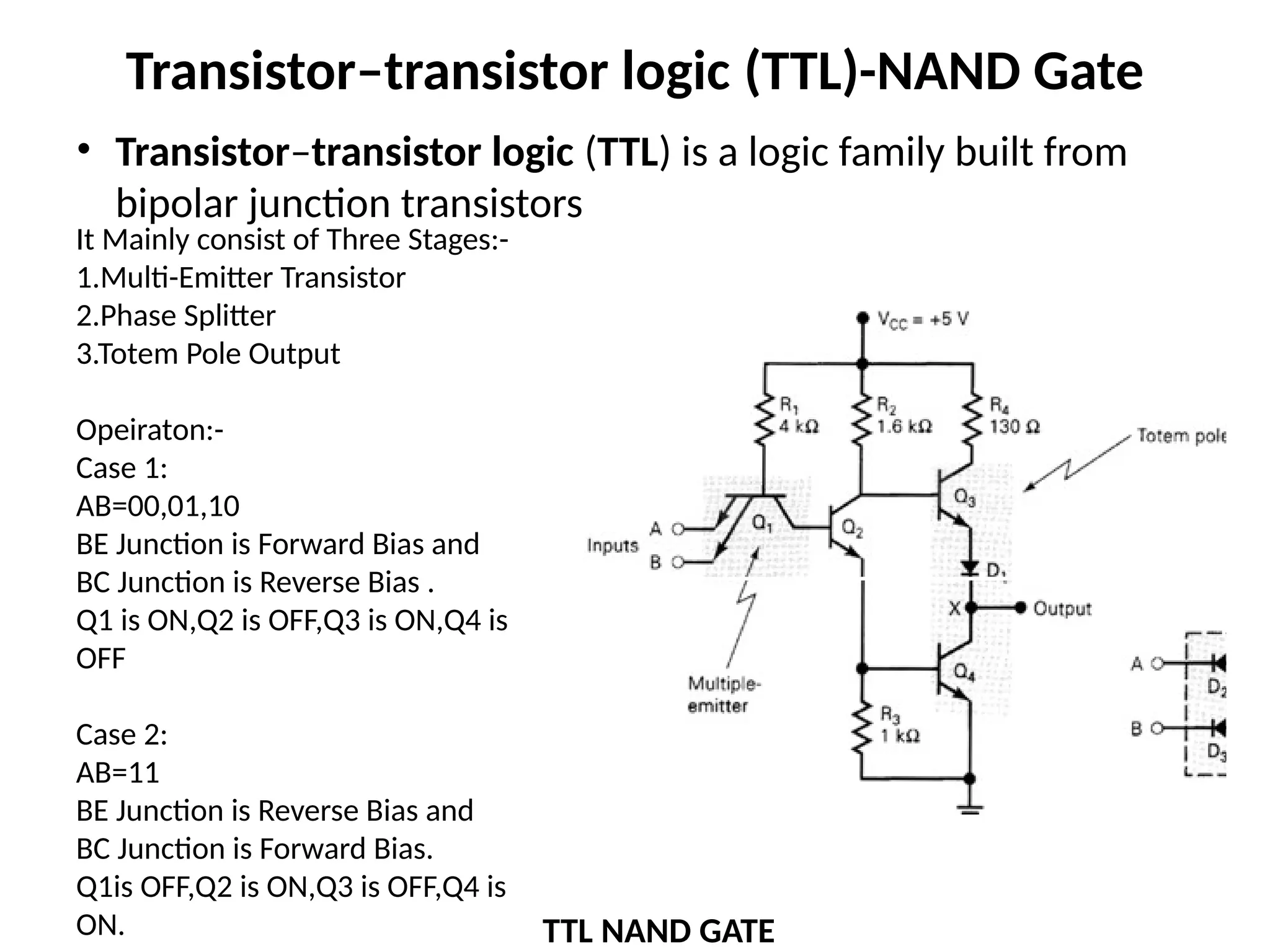
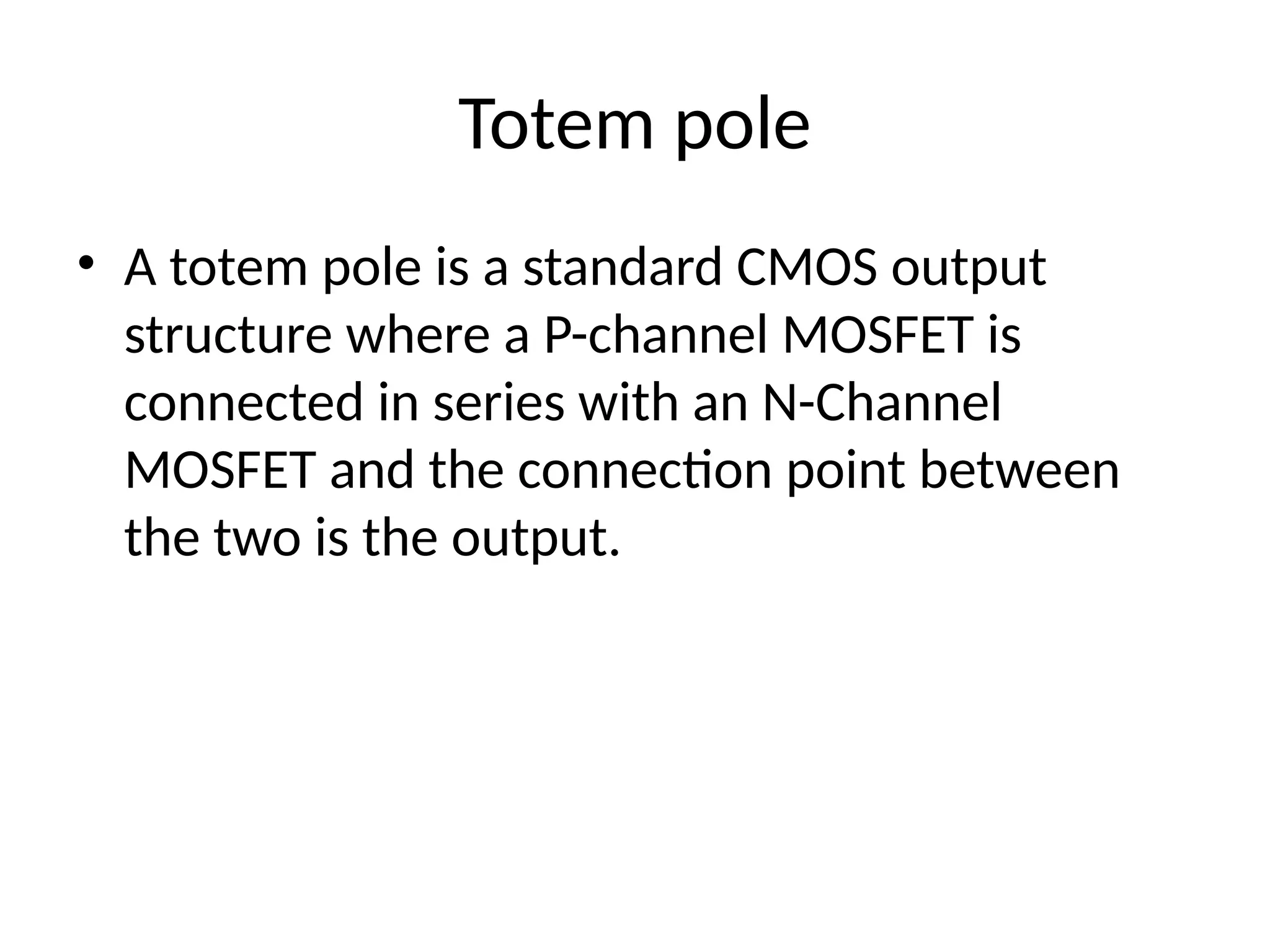
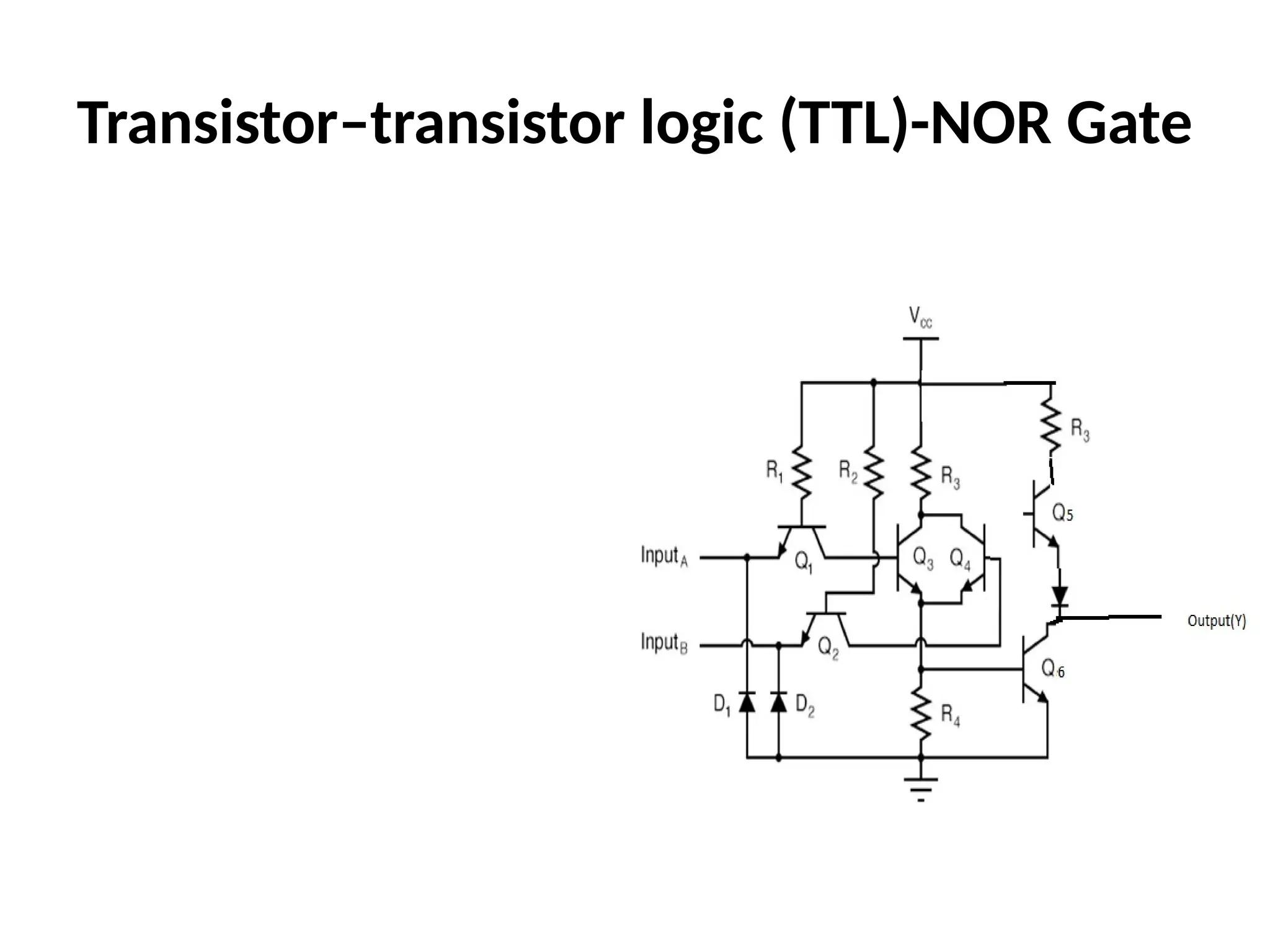
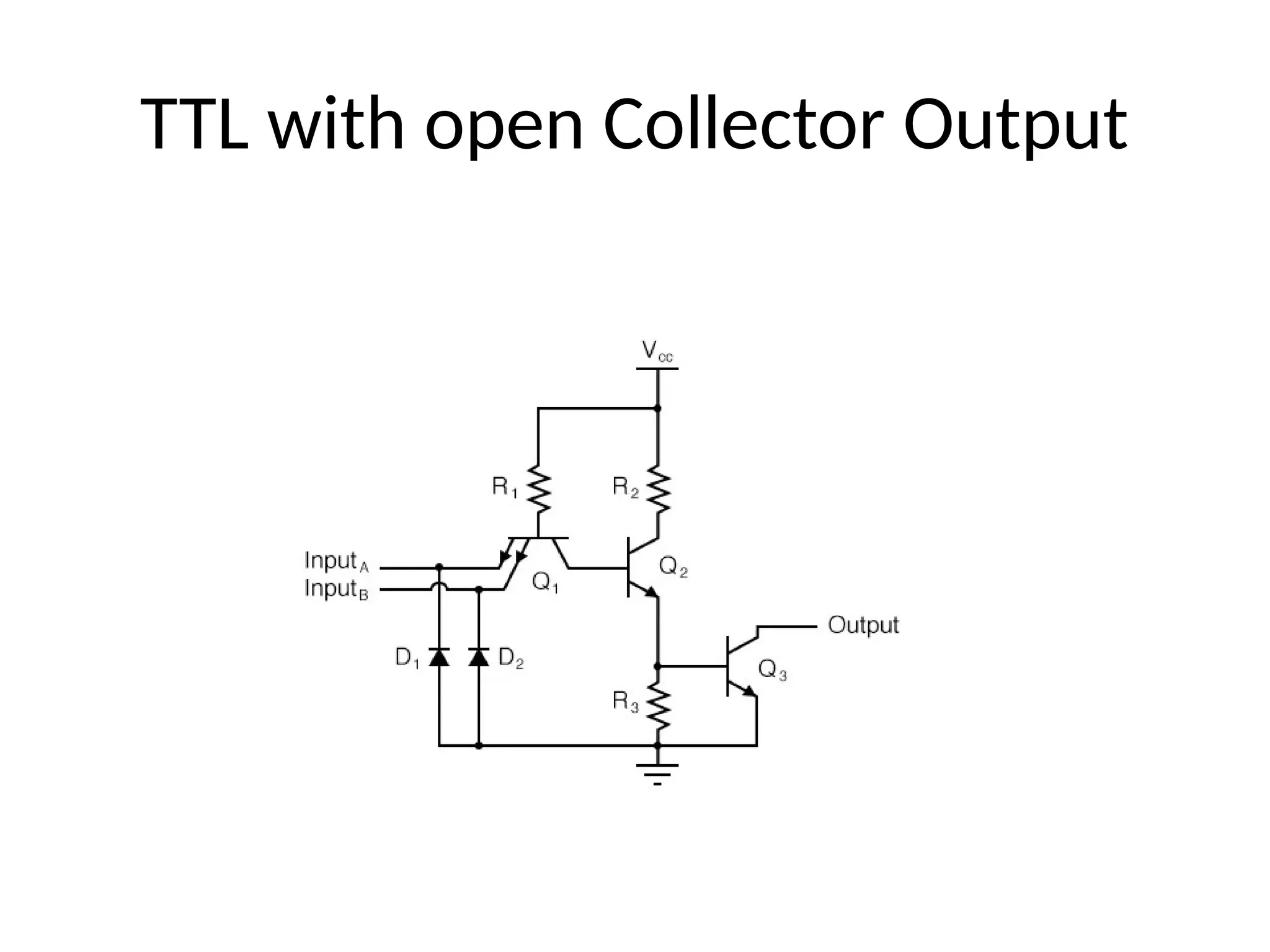
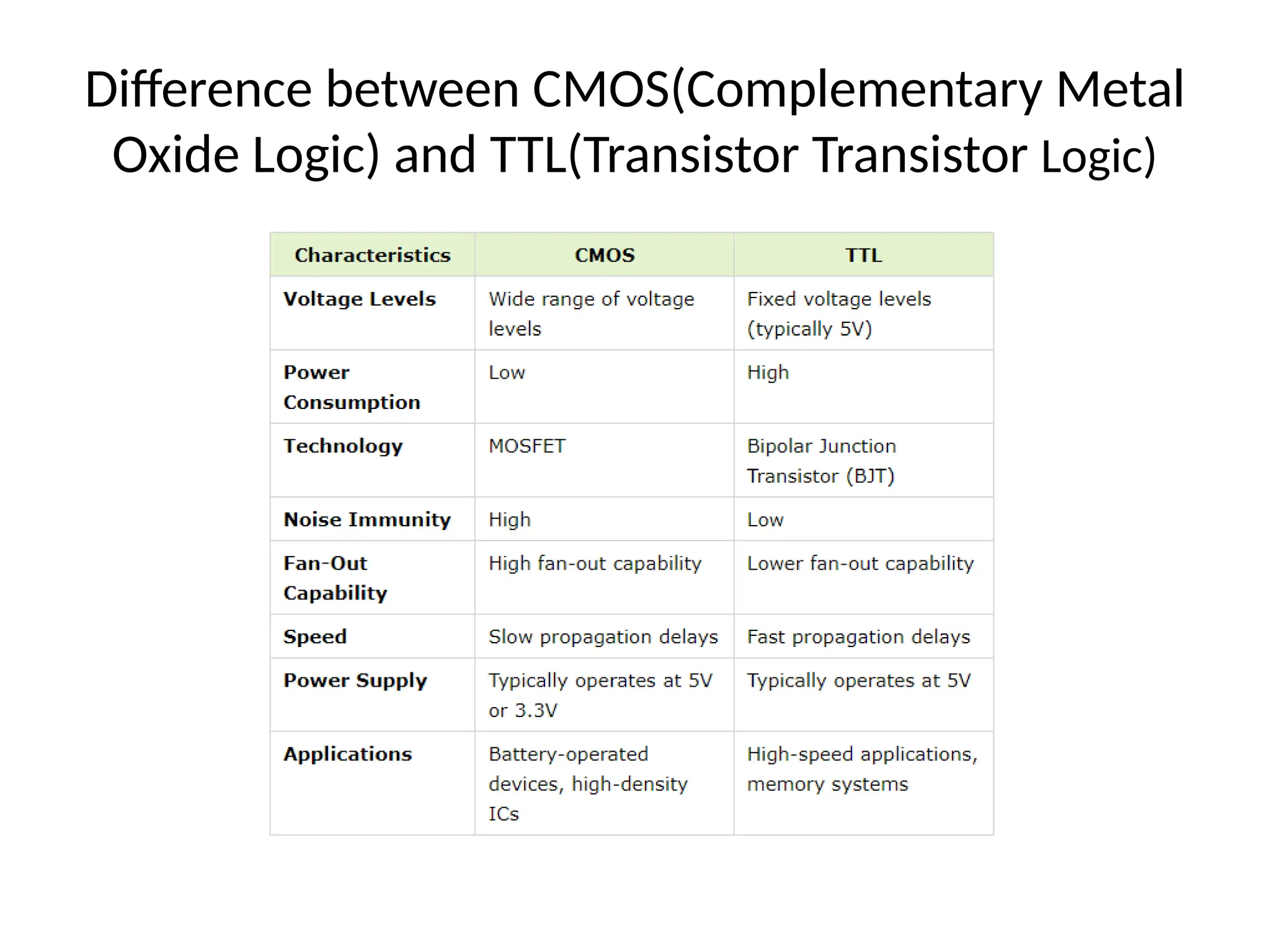
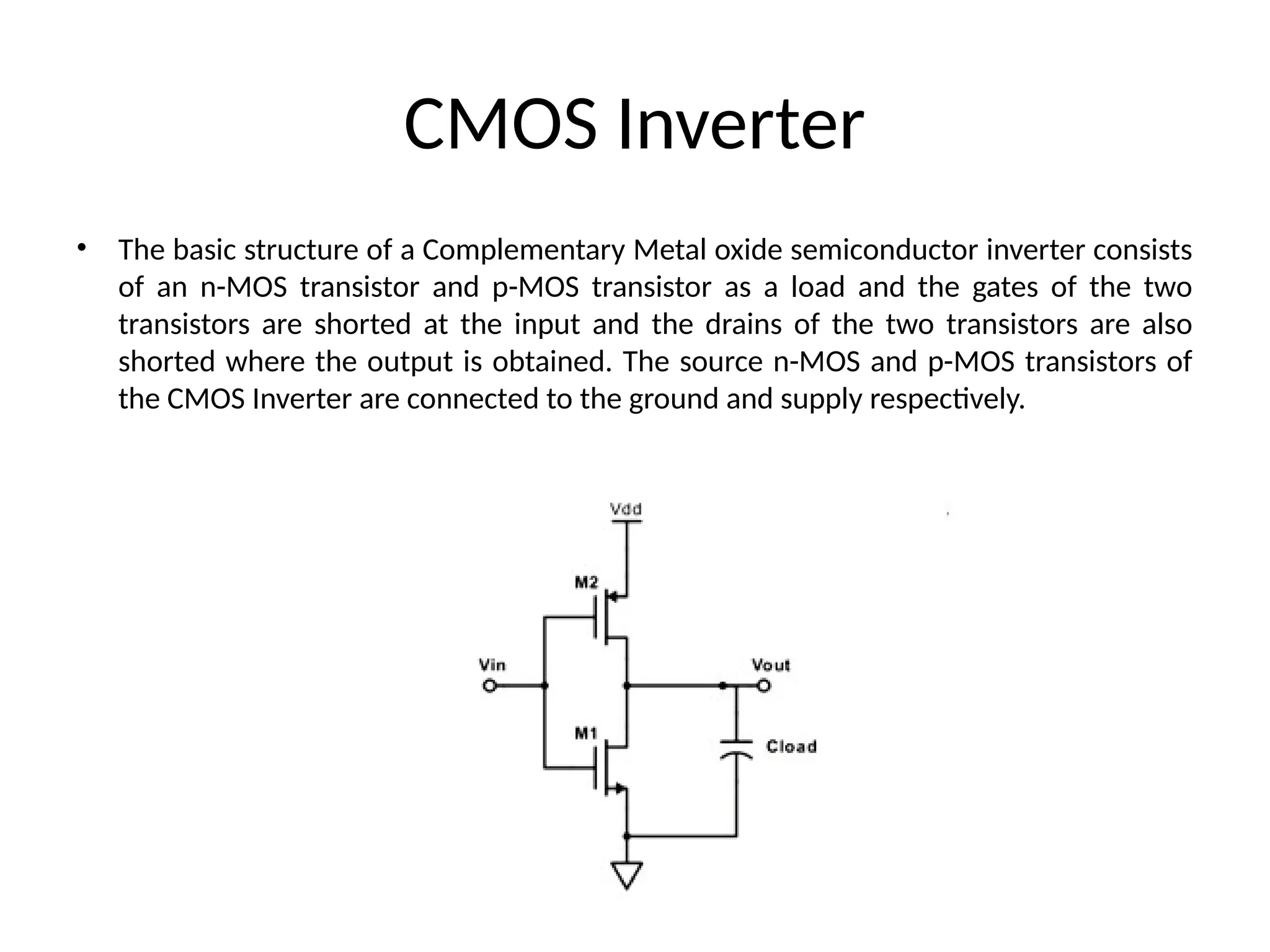
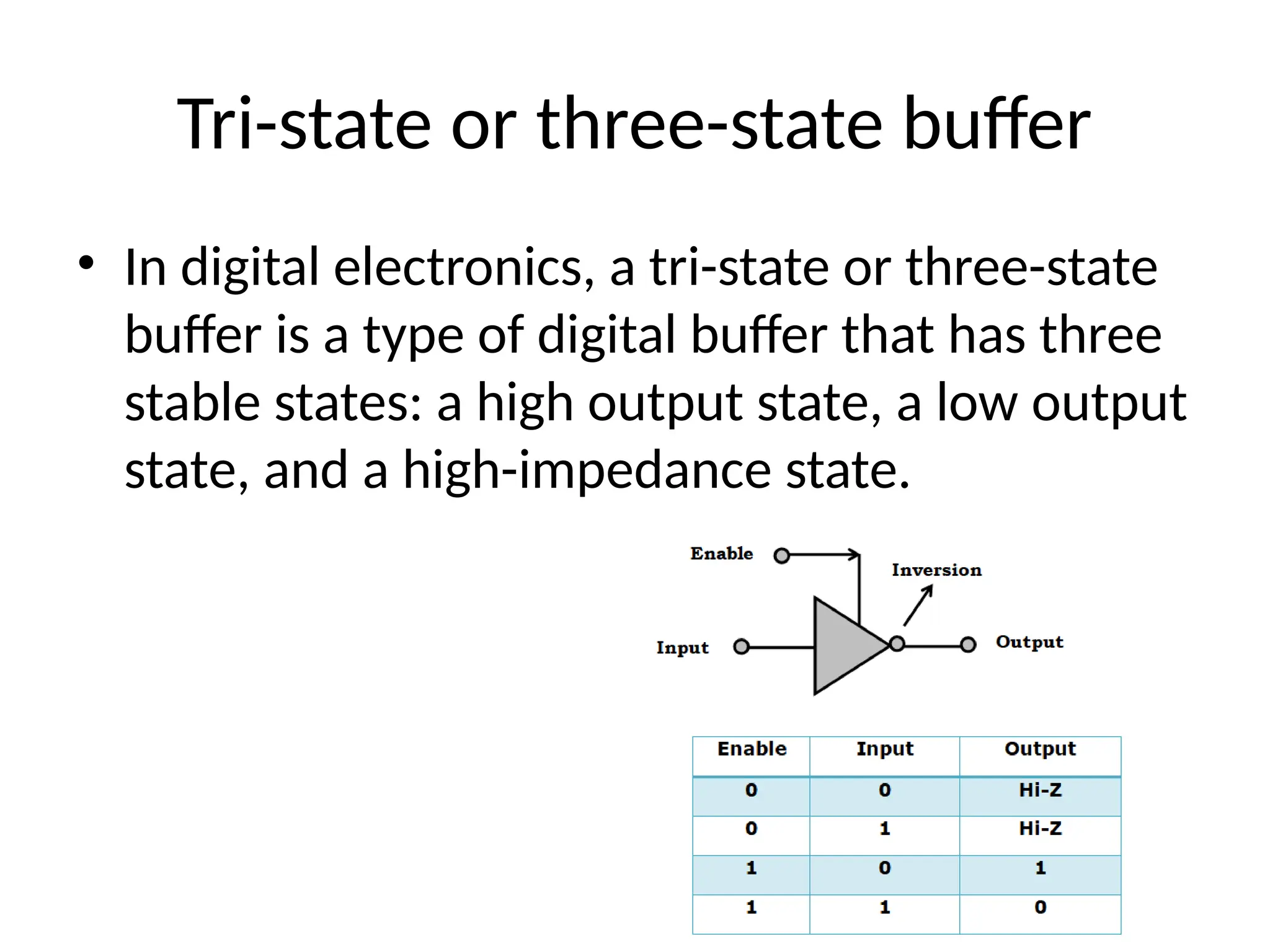
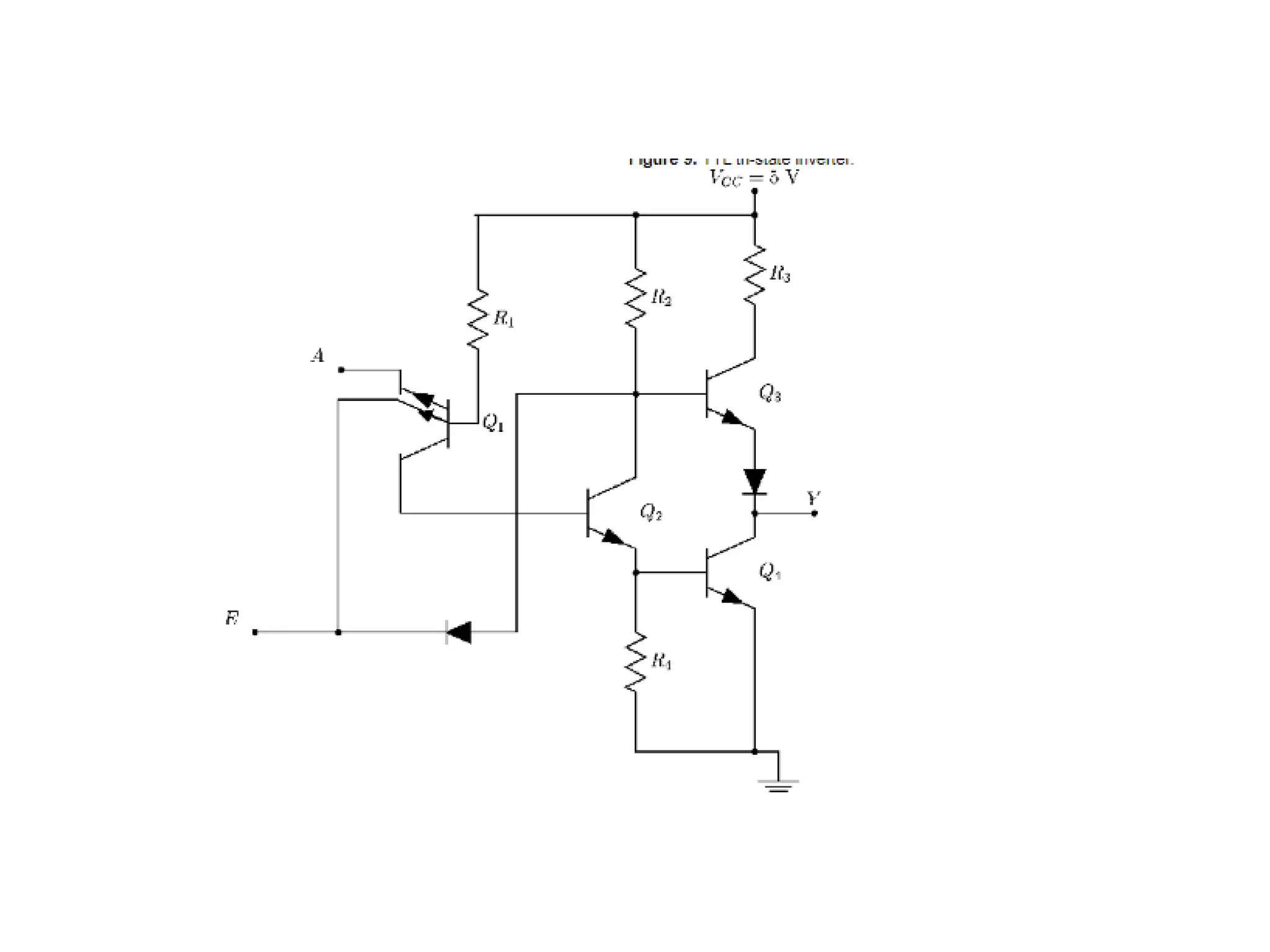
Chapter 4 discusses logic families in digital integrated circuits, classifying them into bipolar and unipolar families, with various examples such as TTL and CMOS. Key characteristics of digital ICs include threshold voltage, propagation delay, voltage and current parameters, power consumption, and noise immunity. The chapter also explains the workings of specific logic families like TTL and CMOS, emphasizing performance factors like fan-in, fan-out, and the figure of merit.