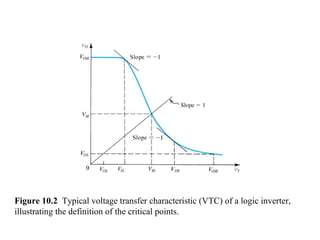
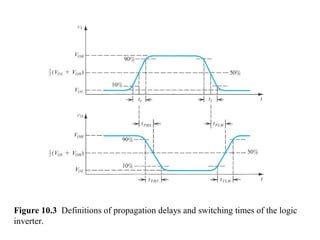
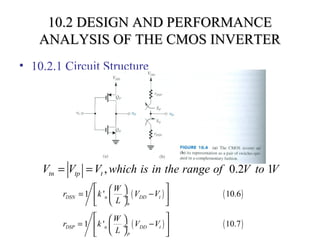
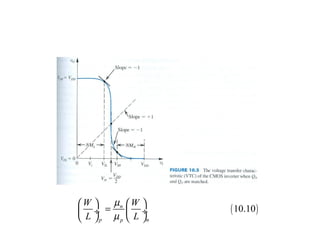
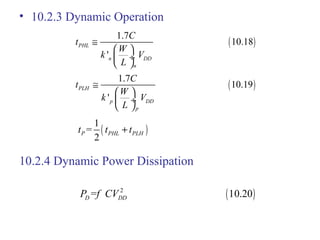
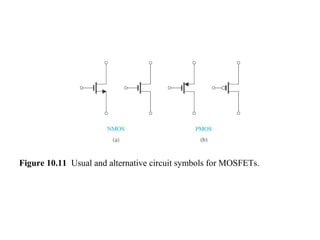
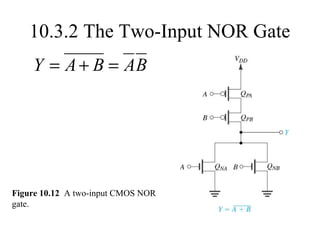
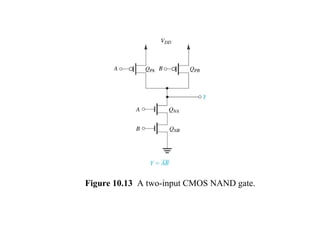
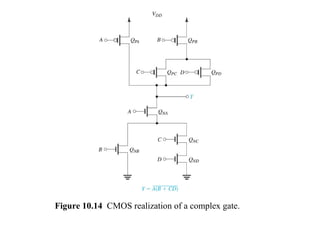
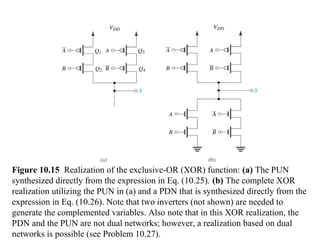
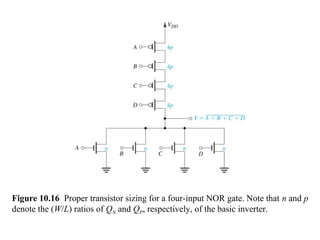
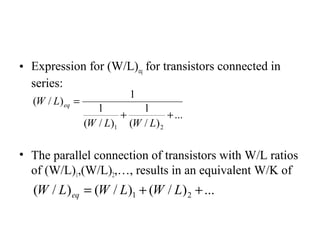
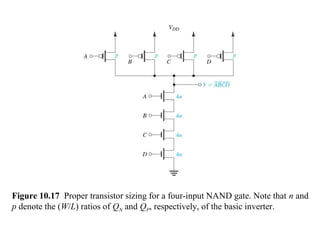
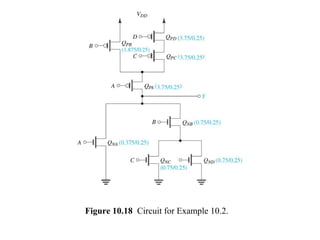
This document discusses CMOS logic circuits. It begins by explaining that CMOS is the dominant technology for digital circuits due to its low power dissipation. It then discusses the structure and operation of the basic CMOS inverter circuit. Key points include that CMOS circuits use complementary NMOS and PMOS transistors to switch the output between power and ground with very low static power. The document also discusses parameters for characterizing logic circuits like propagation delay and noise margins. It describes how to synthesize more complex CMOS gates from their Boolean expressions by constructing pull-down and pull-up networks. Specific gates like NOR, NAND, and XOR are analyzed. Transistor sizing is also covered to ensure adequate driving capability.