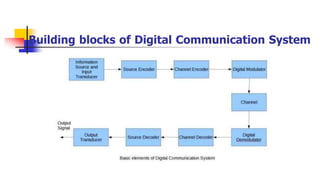
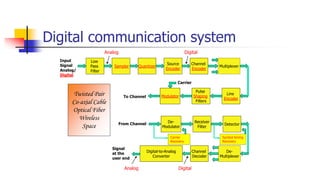
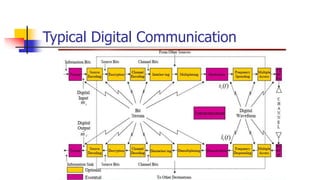
This document provides information about the digital communication course PC601EC. It discusses the prerequisites, course objectives, and units that will be covered in the course. The course aims to familiarize students with digital communication system elements, waveform coding techniques, information theory, channel coding, baseband digital transmission, and spread spectrum communication. Key concepts that will be covered include PCM, source coding, error control codes, digital modulation schemes, and direct sequence and frequency hopping spread spectrum systems.















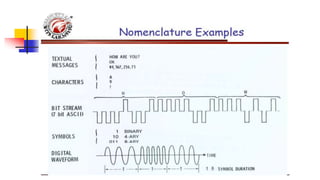
![Basic Digital Communication Nomenclature
Textual Message: information comprised of a sequence of
characters.
Binary Digit (Bit): the fundamental information unit for all
digital systems.
Symbol (mi where i=1,2,…M): for transmission of the bit
stream; groups of k bits are combined to form new symbol
from a finite set of M such symbols; M=2k.
Digital Waveform: voltage or current waveform representing
a digital symbol.
Data Rate: Symbol transmission is associated with a symbol
duration T. Data rate R=k/T [bps].
Baud Rate: number of symbols transmitted per second [baud]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-1-211008052646/85/UNIT-1-Elements-of-Digital-Communication-17-320.jpg)