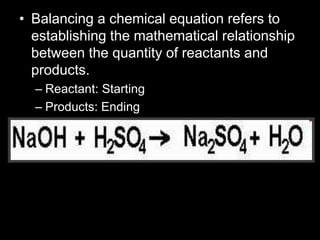
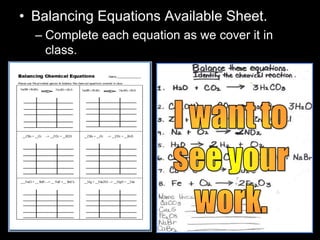
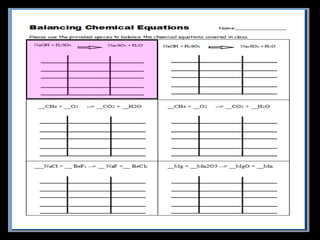
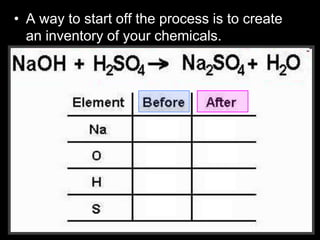
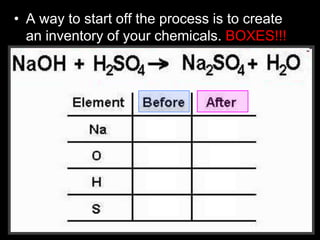
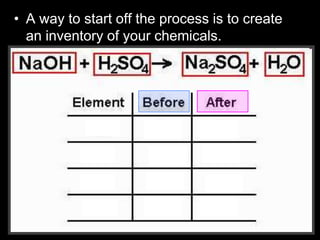
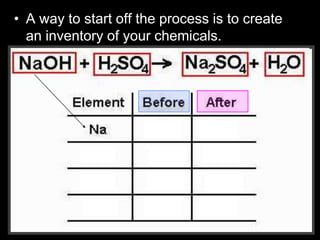
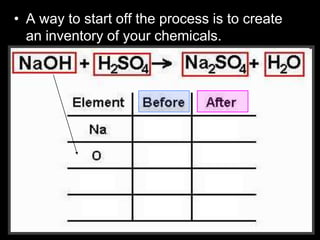
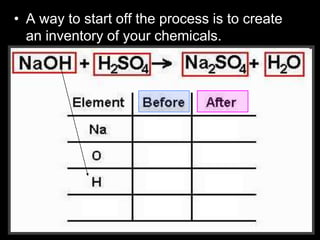
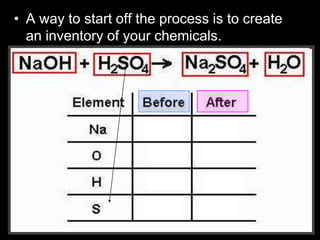
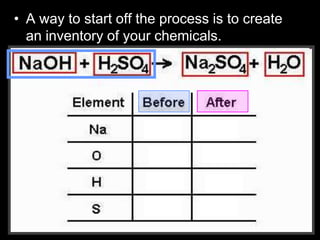
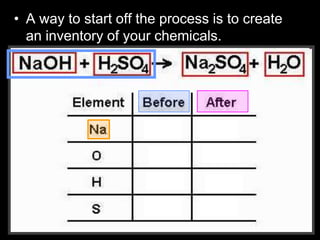
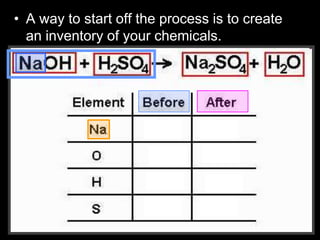
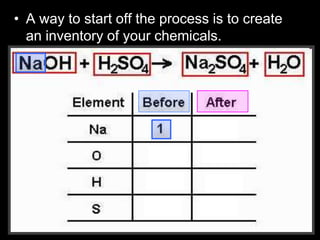
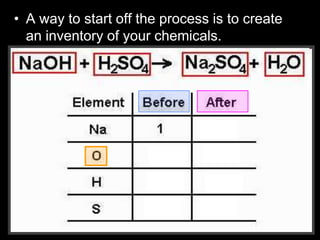
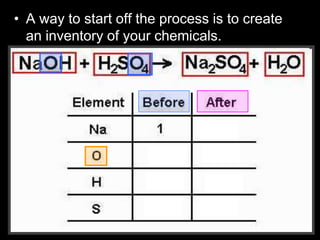
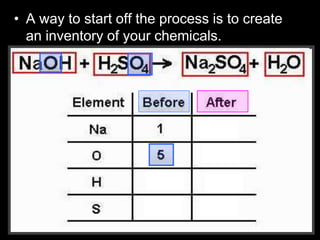
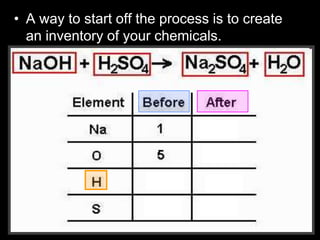
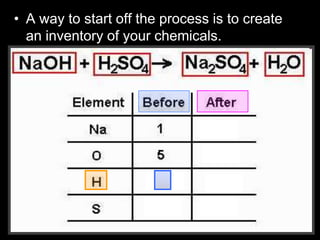
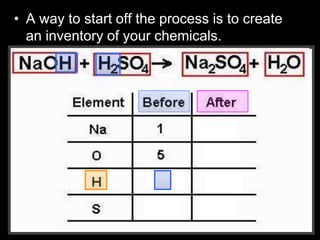
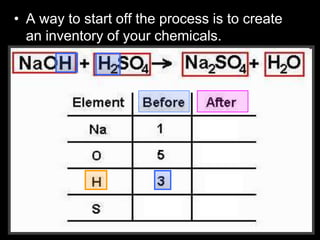
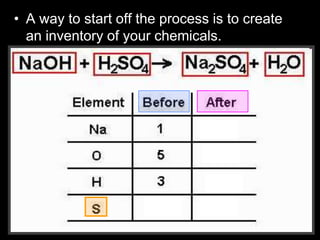
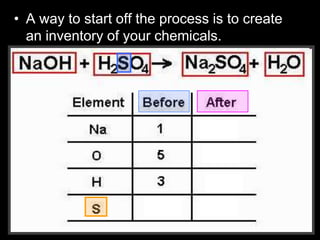
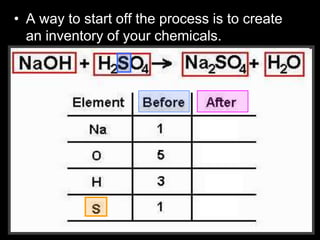
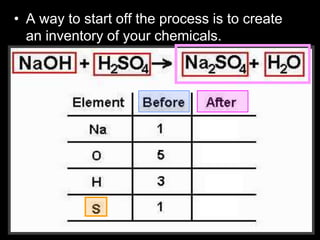
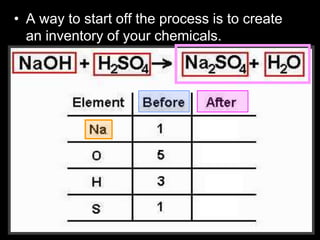
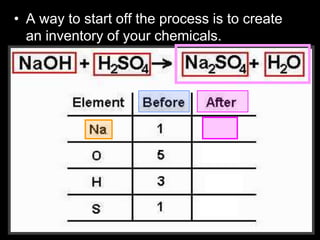
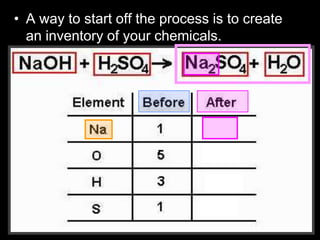
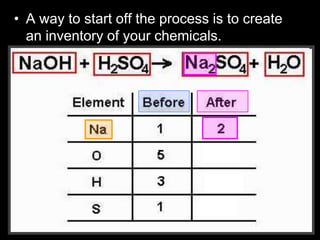
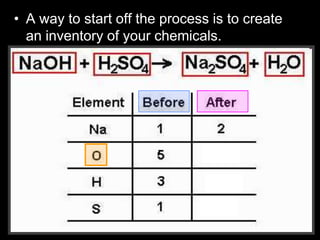
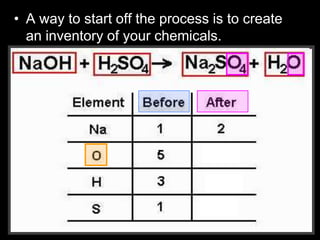
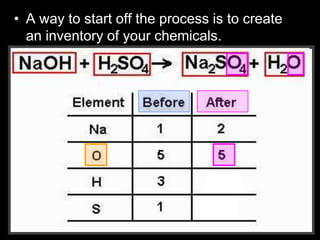
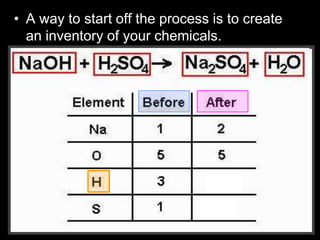
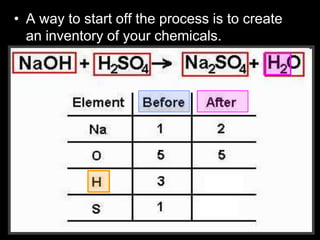
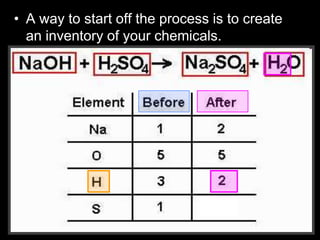
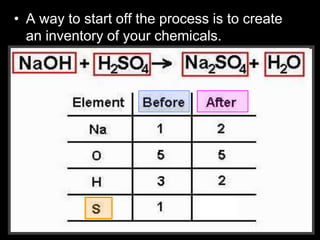
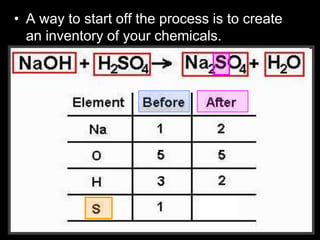
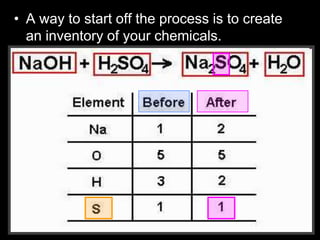
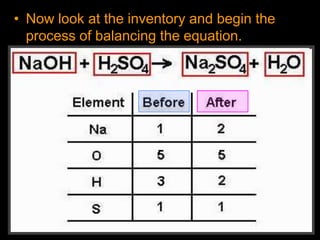
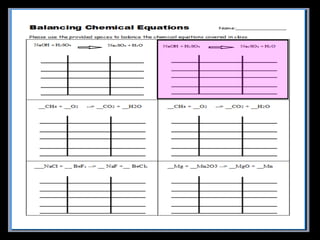
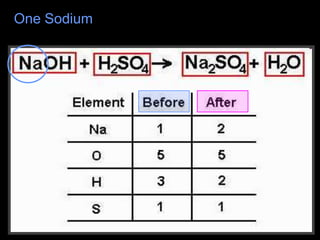
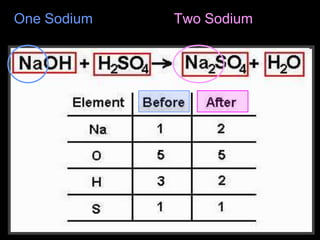
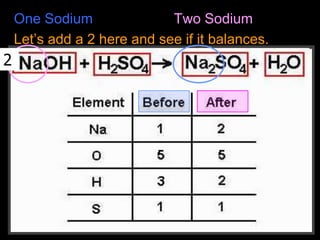
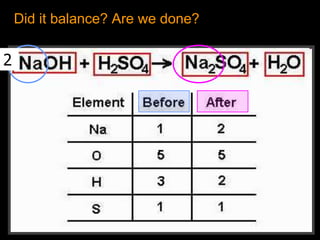
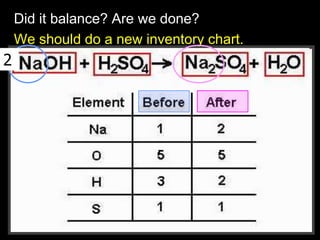
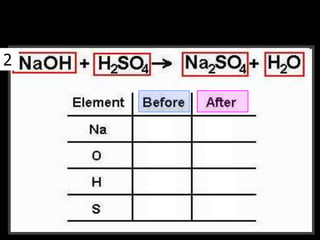
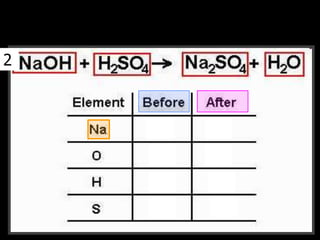
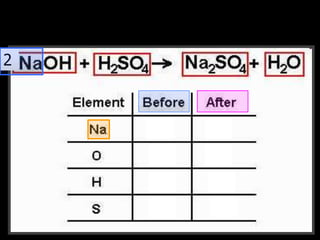
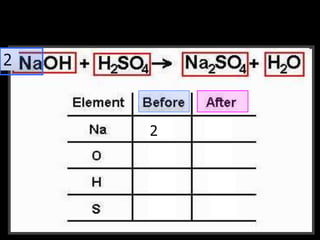
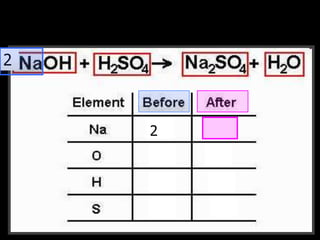
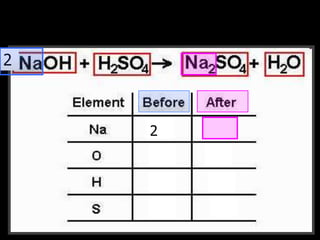
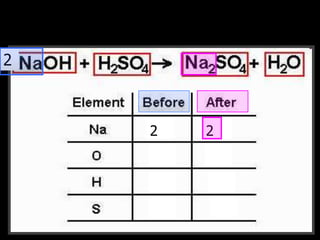
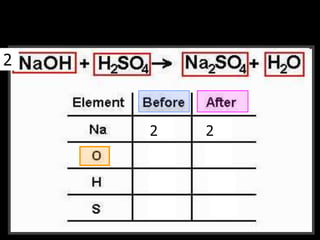
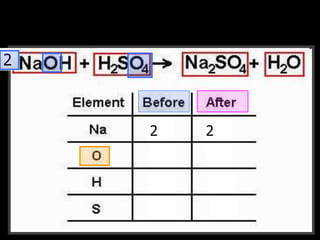
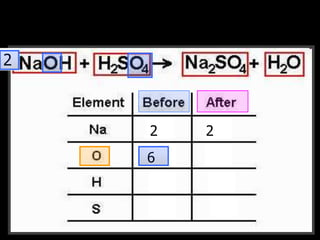
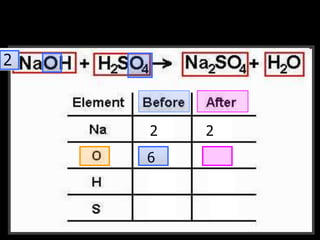
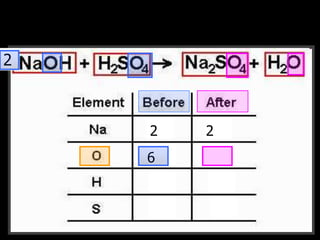
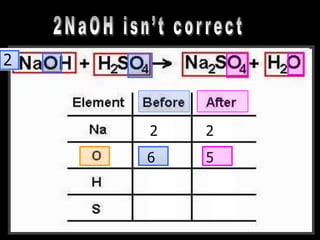
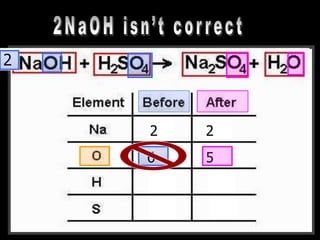
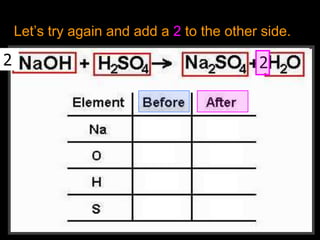
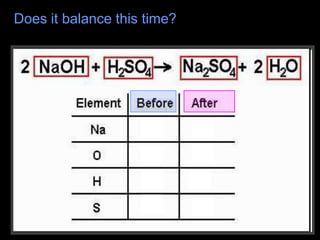
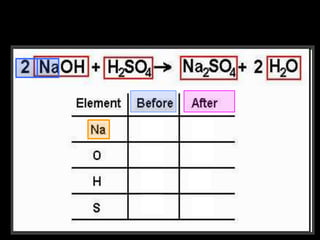
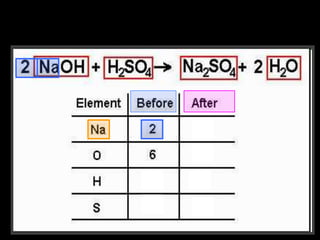
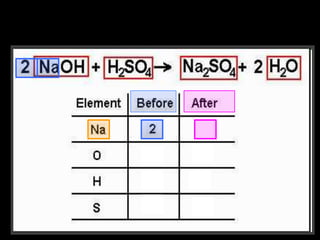
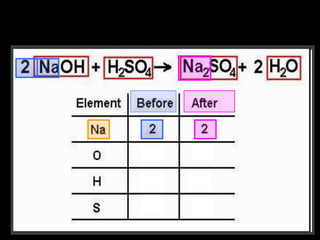
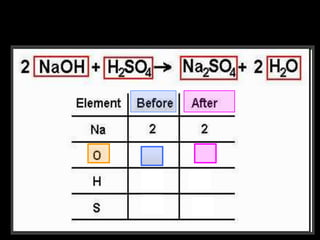
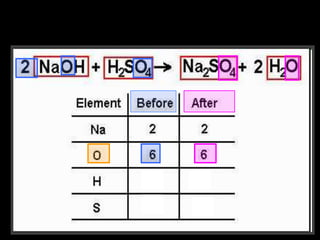
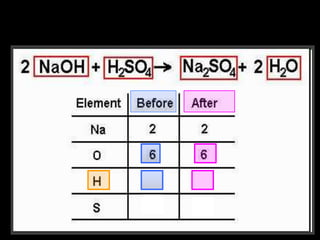
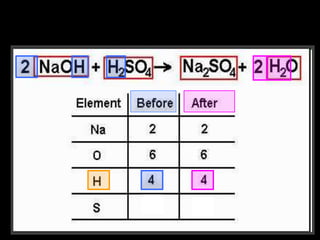
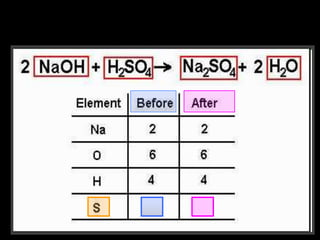
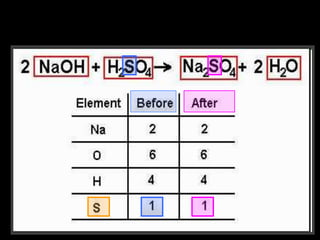
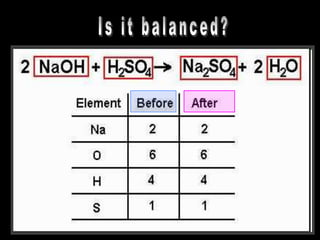
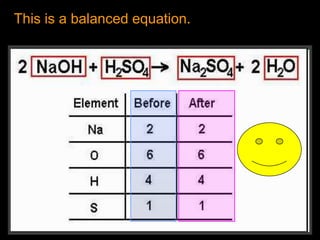
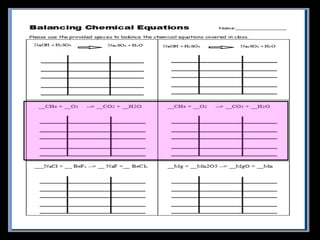
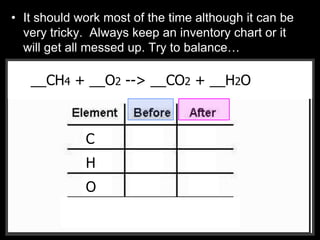
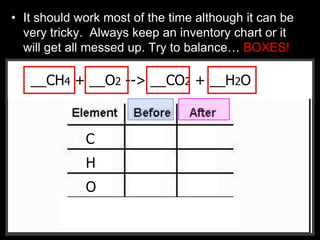
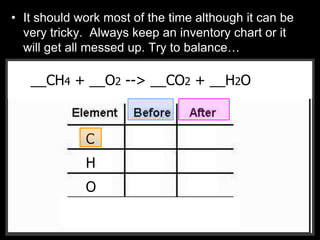
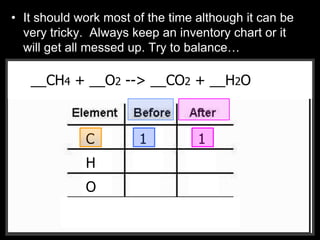
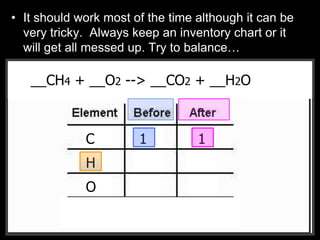
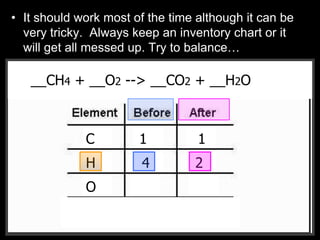
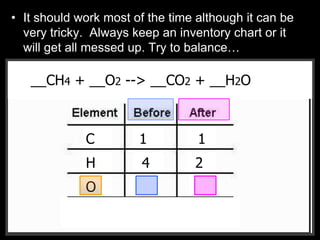
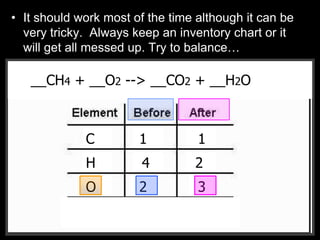
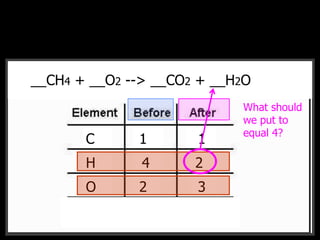
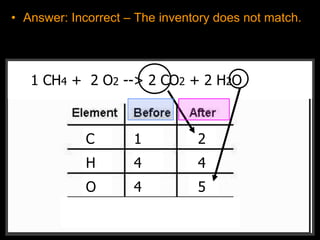
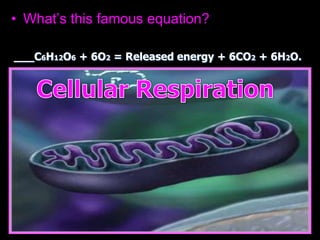
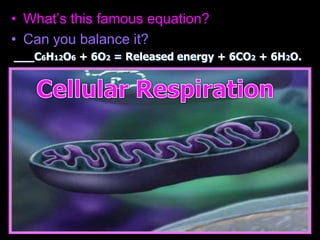
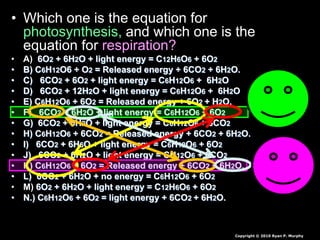
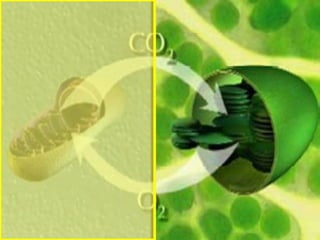
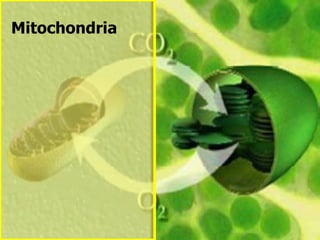
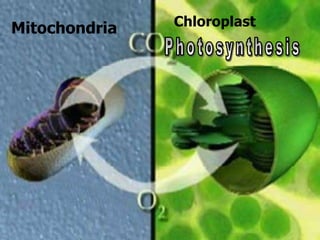
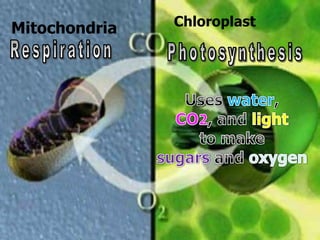
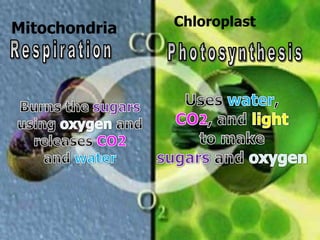
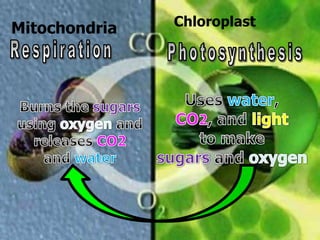
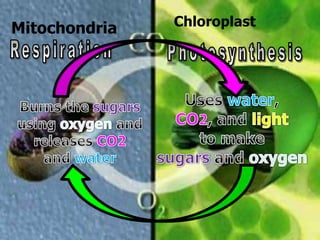
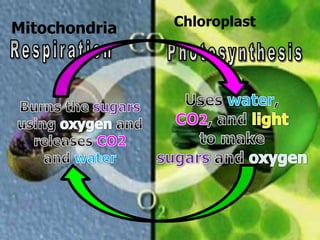
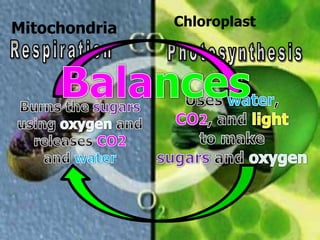
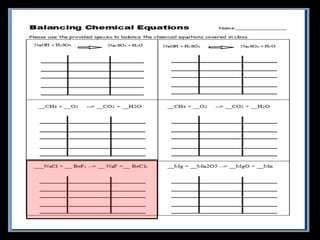
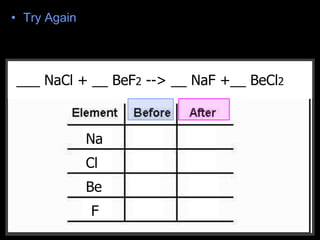
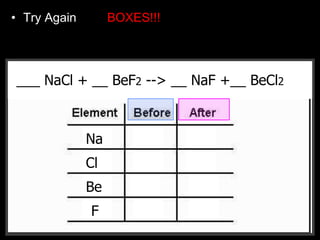
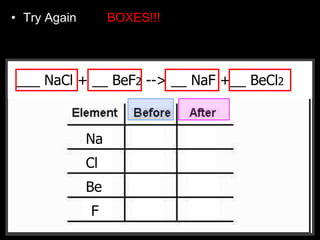
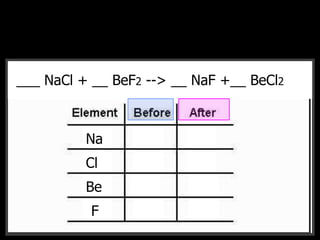
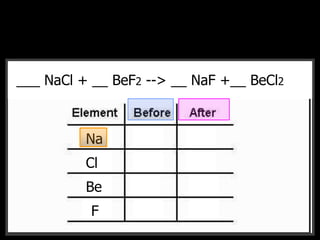
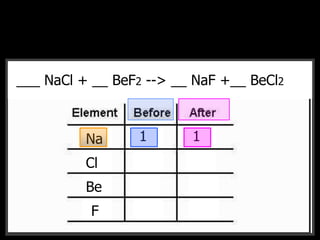
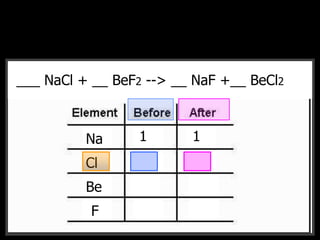
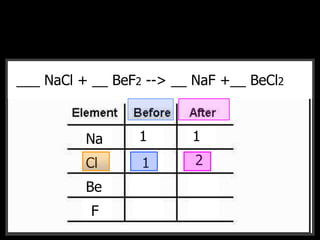
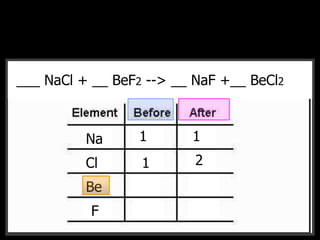
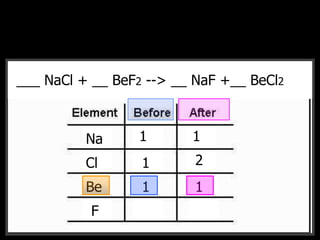
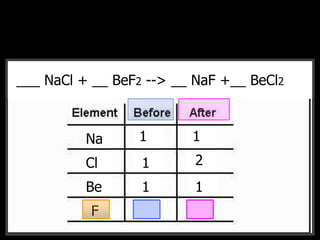
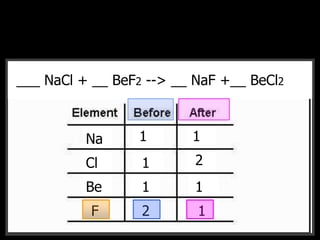
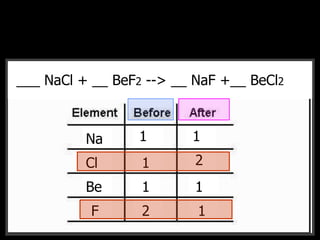
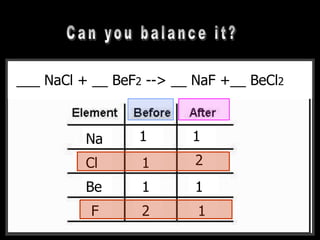
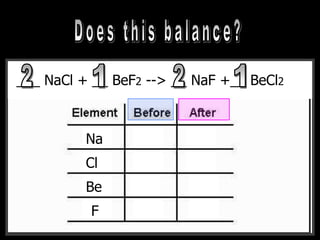
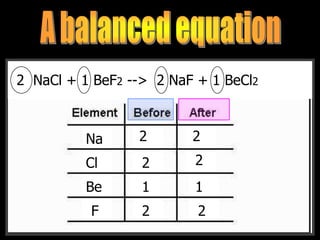
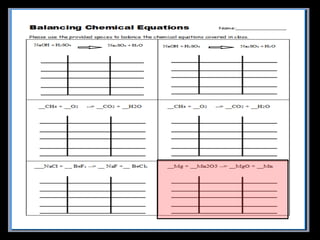
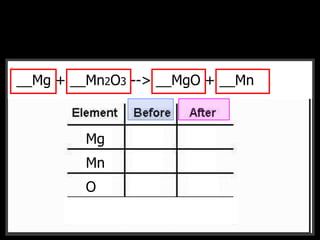
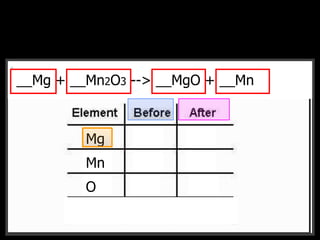
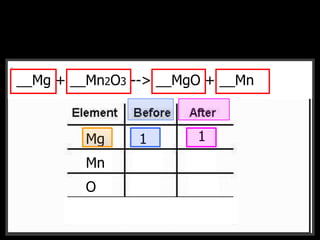
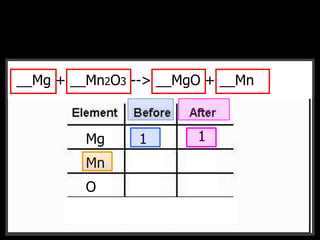
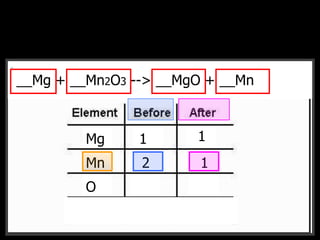
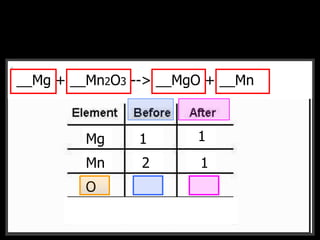
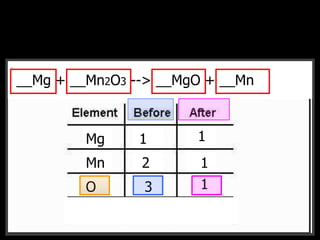
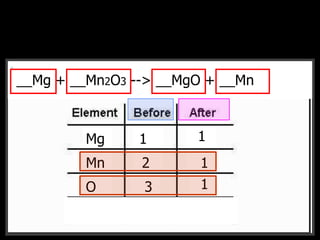
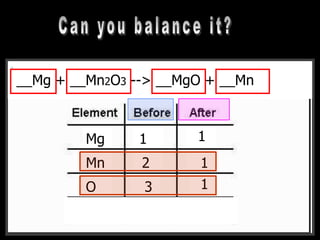
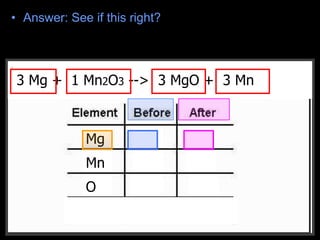
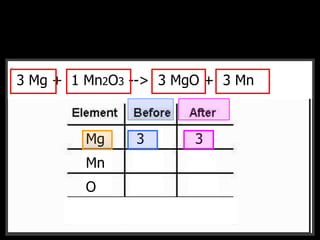
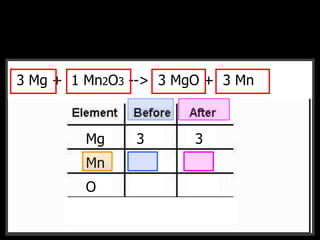
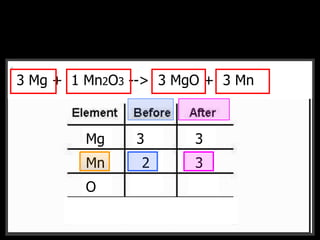
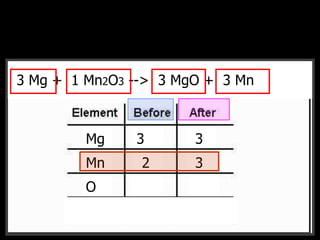
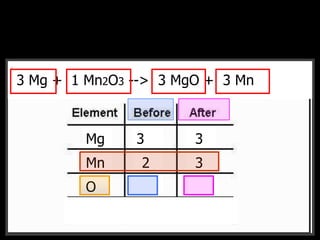
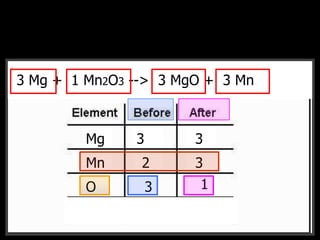
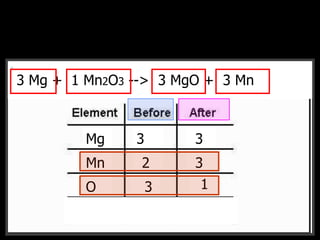
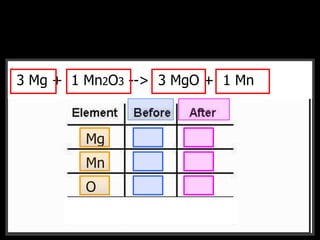
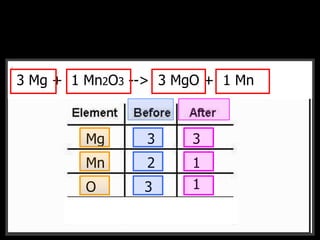
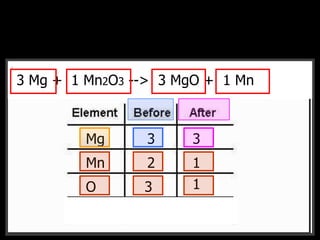
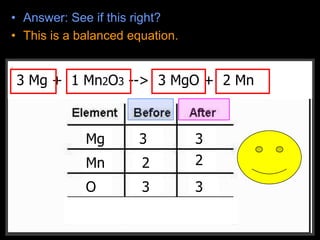
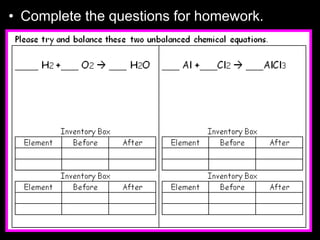
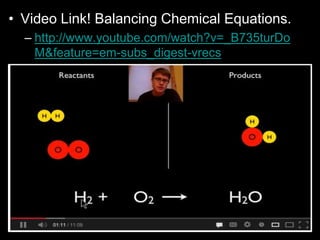
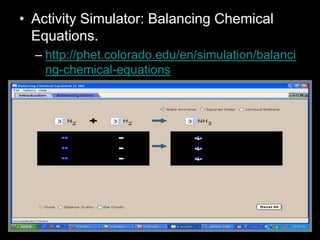
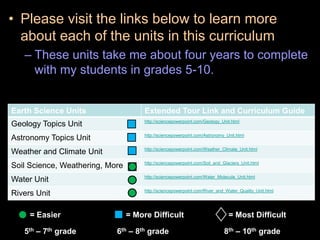
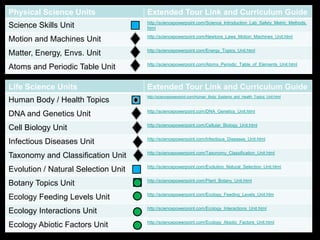
The document covers the process of balancing chemical equations, emphasizing the importance of maintaining the same amount of reactants and products as dictated by the law of conservation of mass. It provides strategies for balancing equations, such as creating an inventory of chemicals and methodically adjusting coefficients without changing subscripts. Additionally, it discusses the relationship between matter and energy in chemical reactions, particularly in relation to processes like photosynthesis.