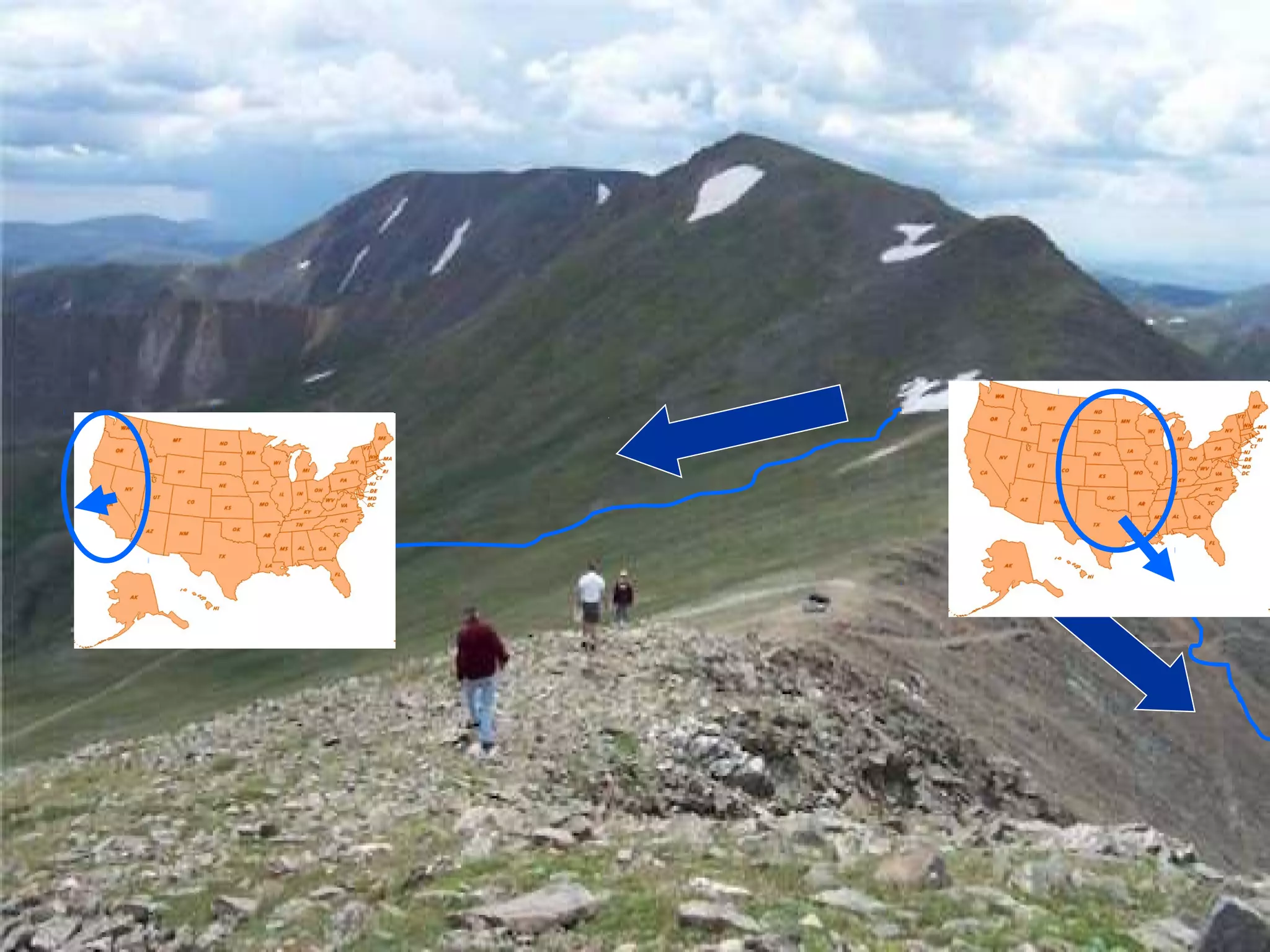
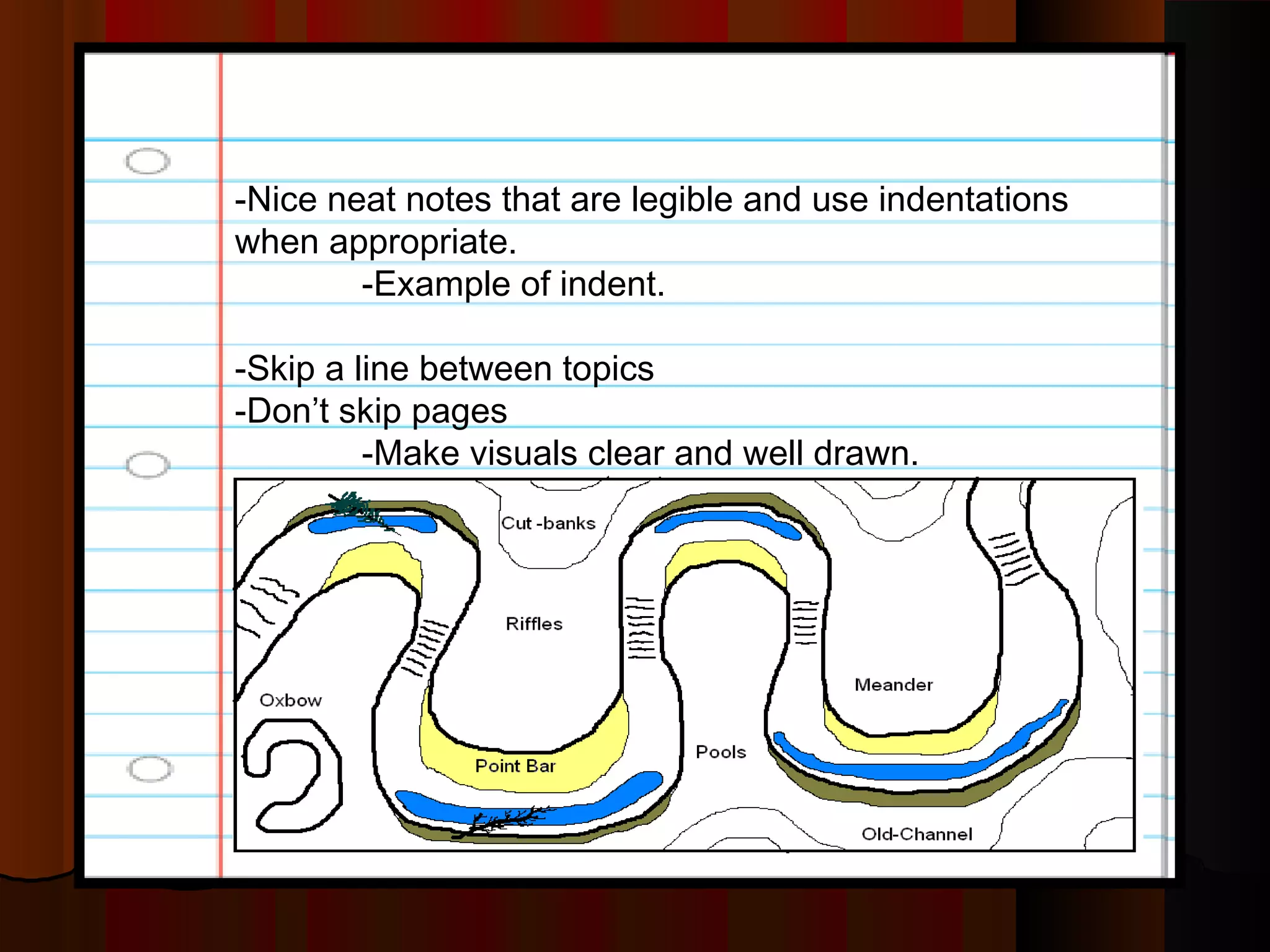
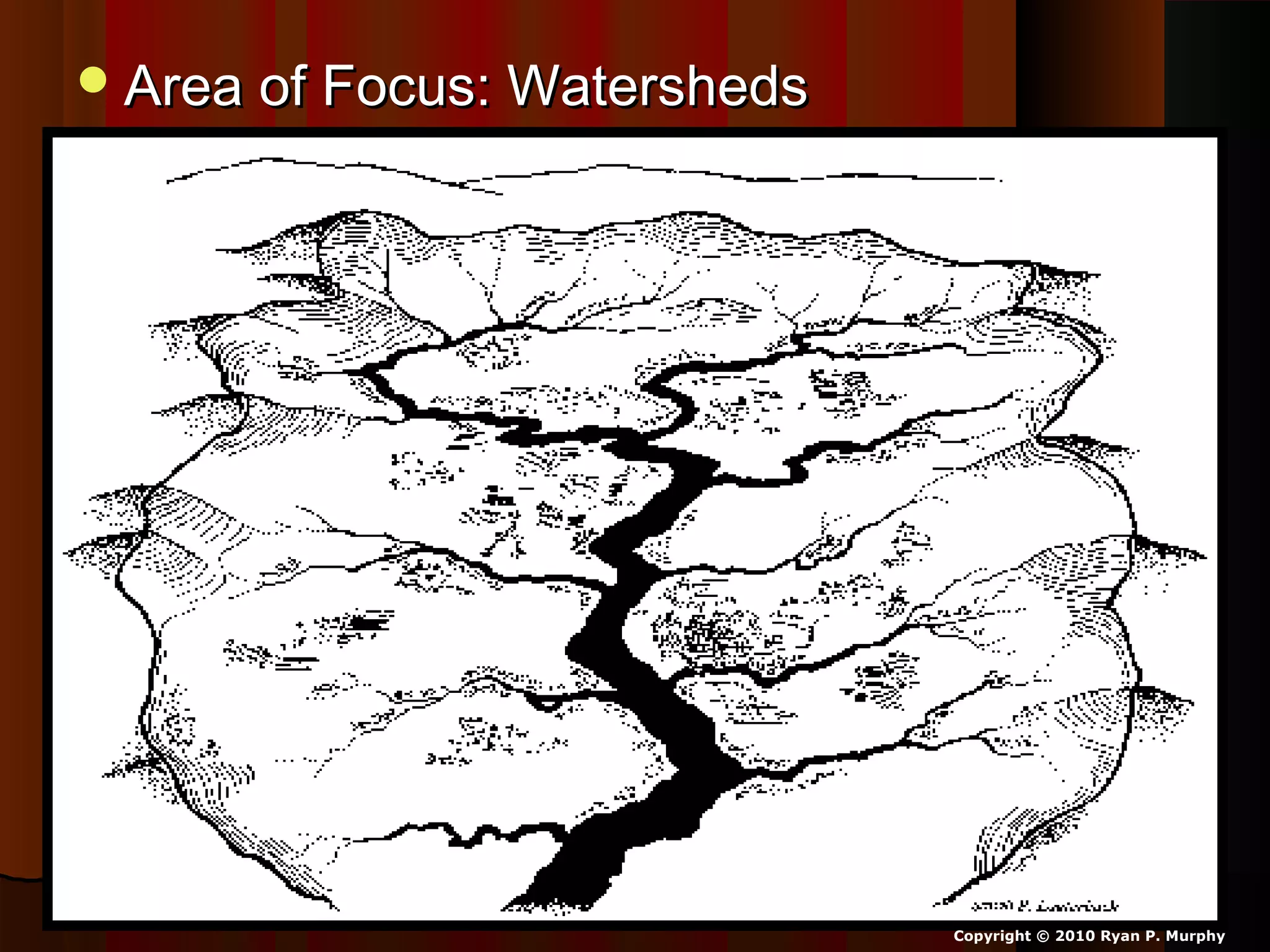
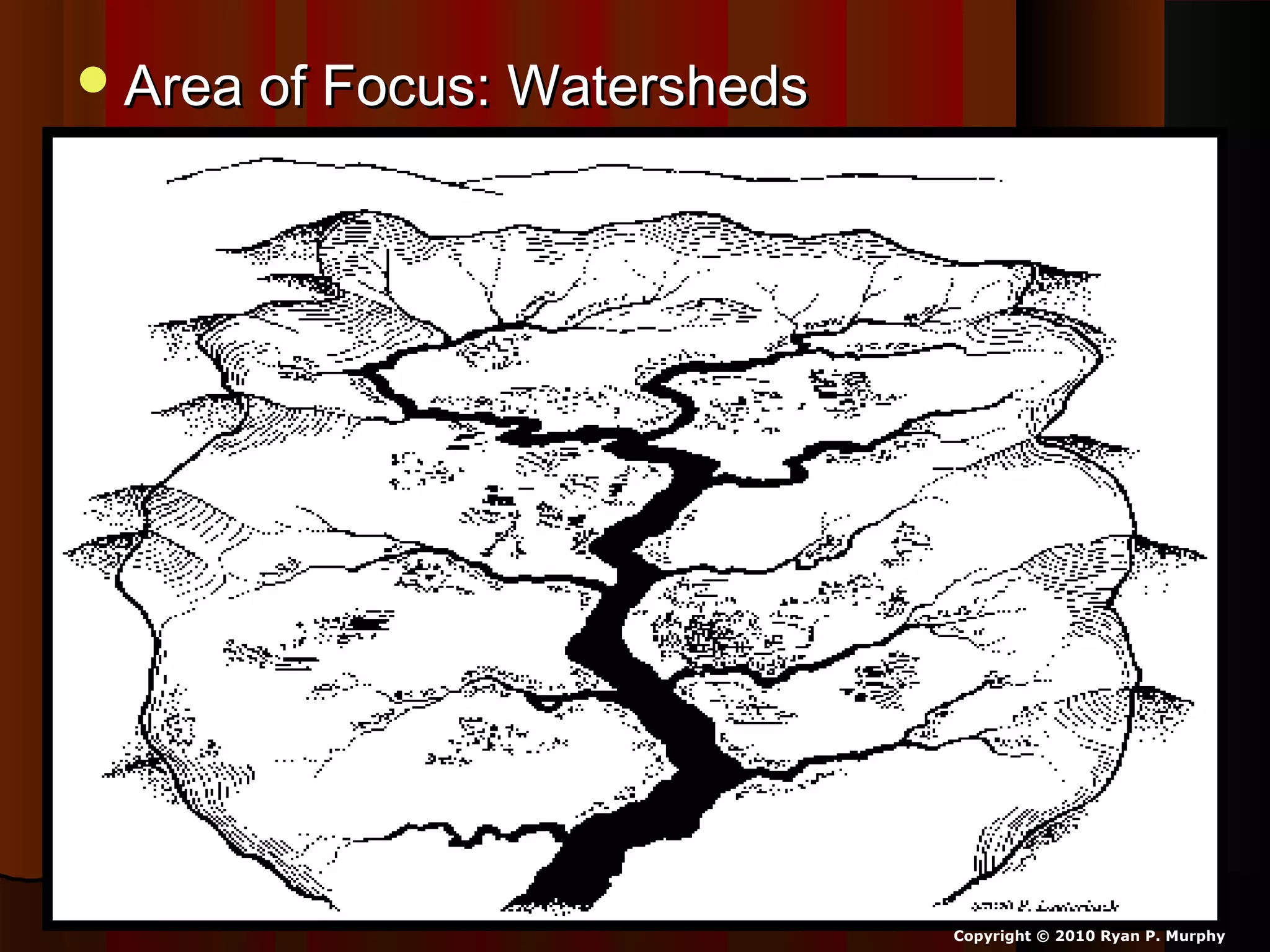
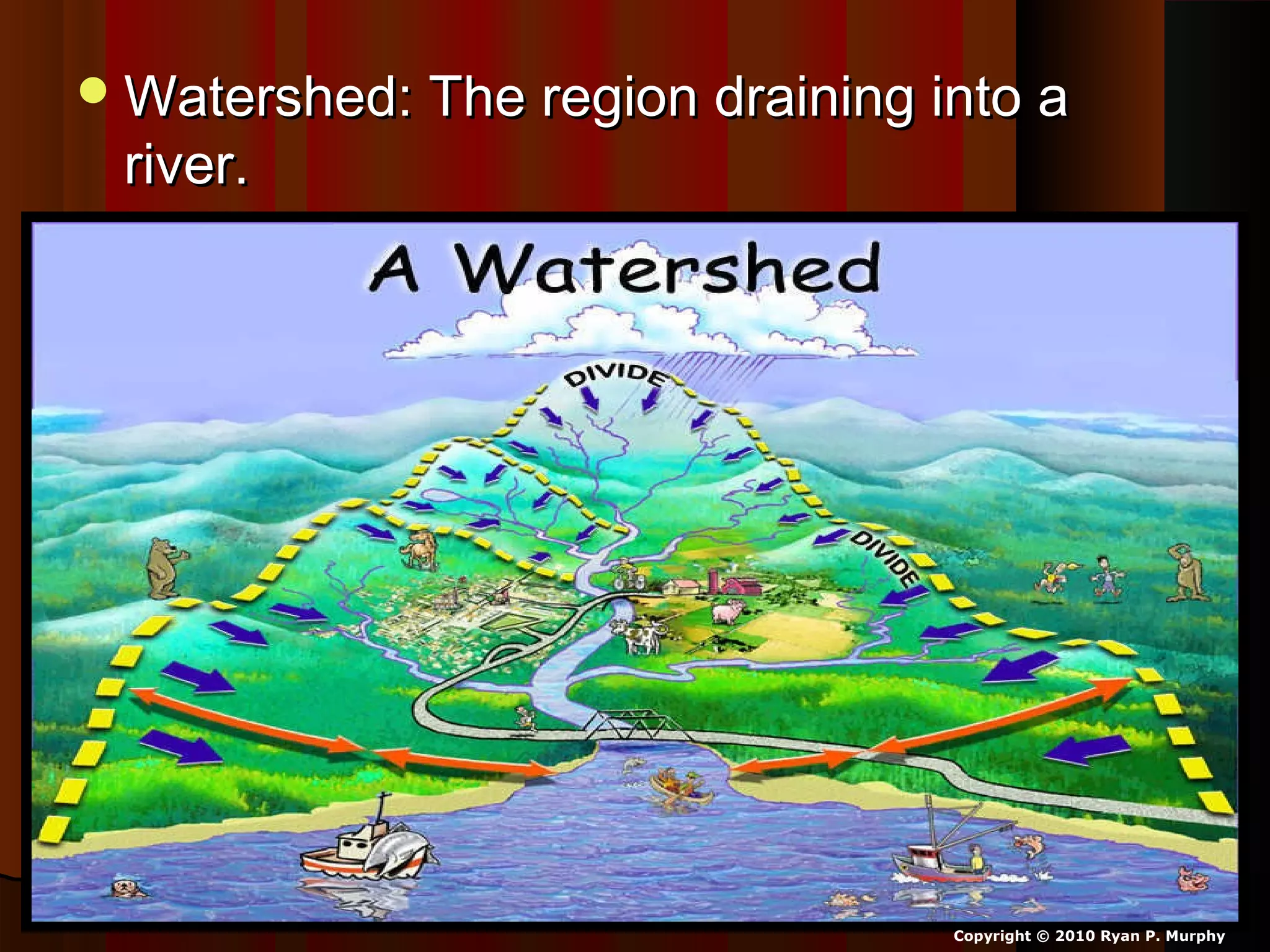
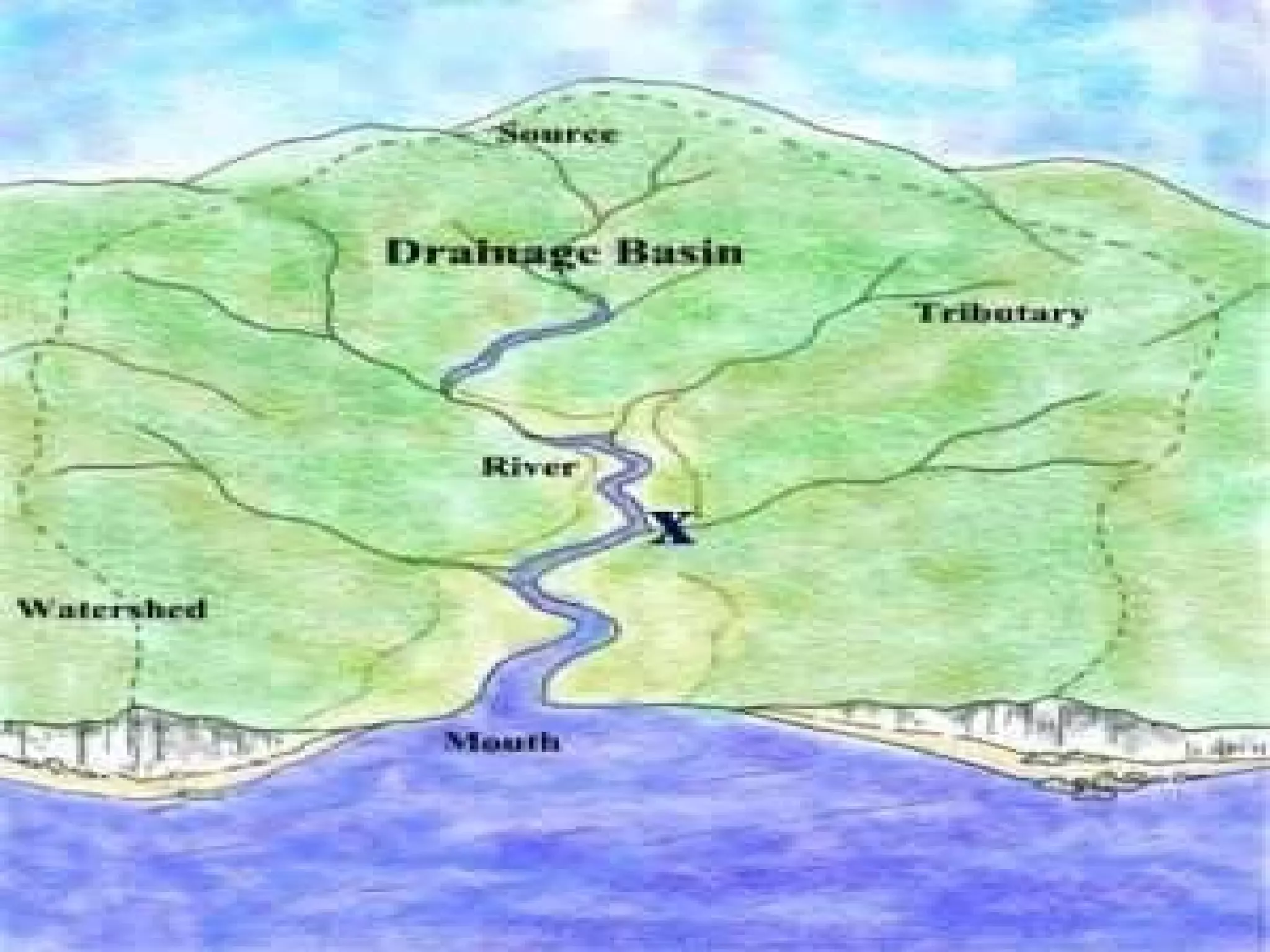
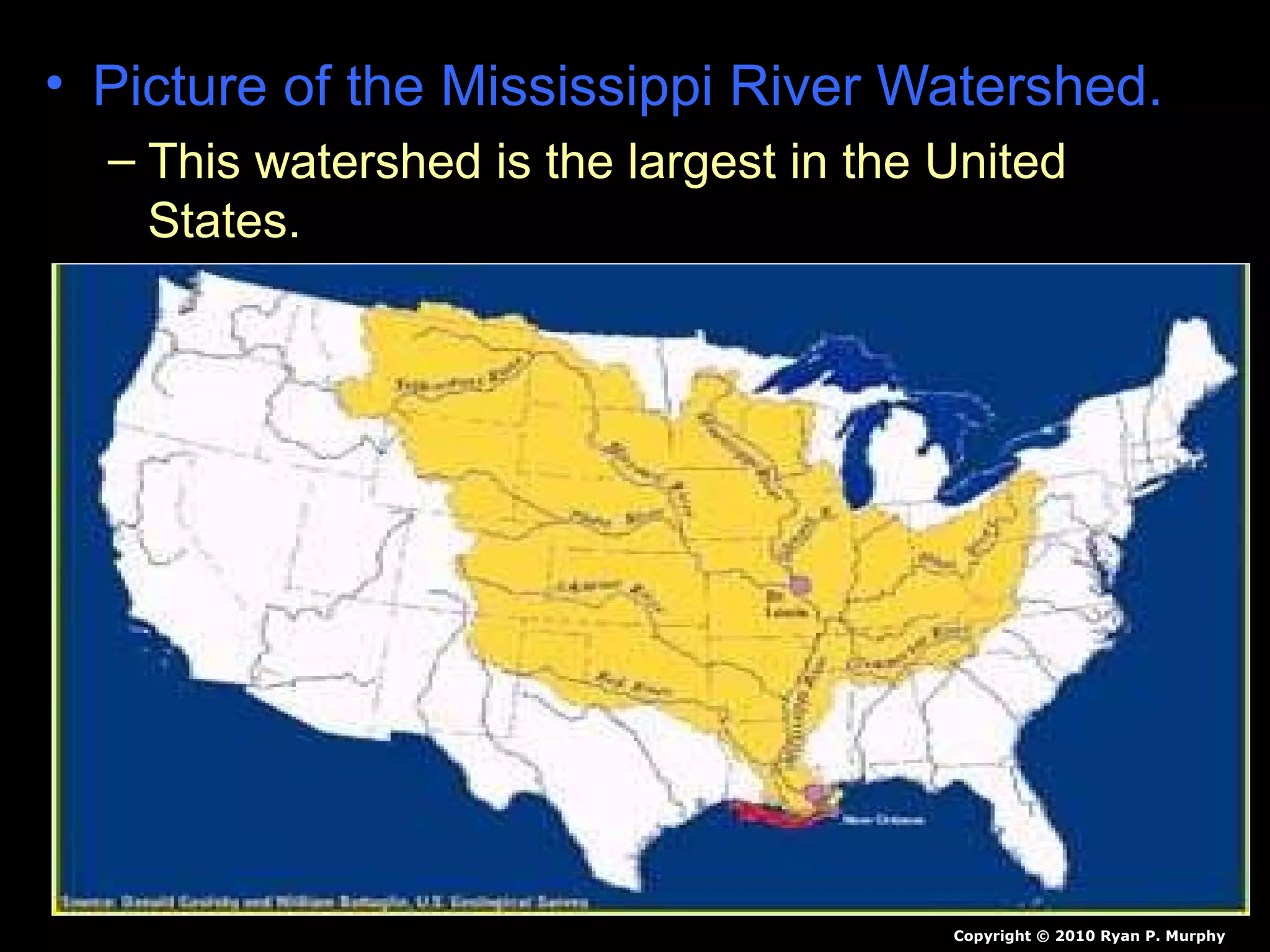
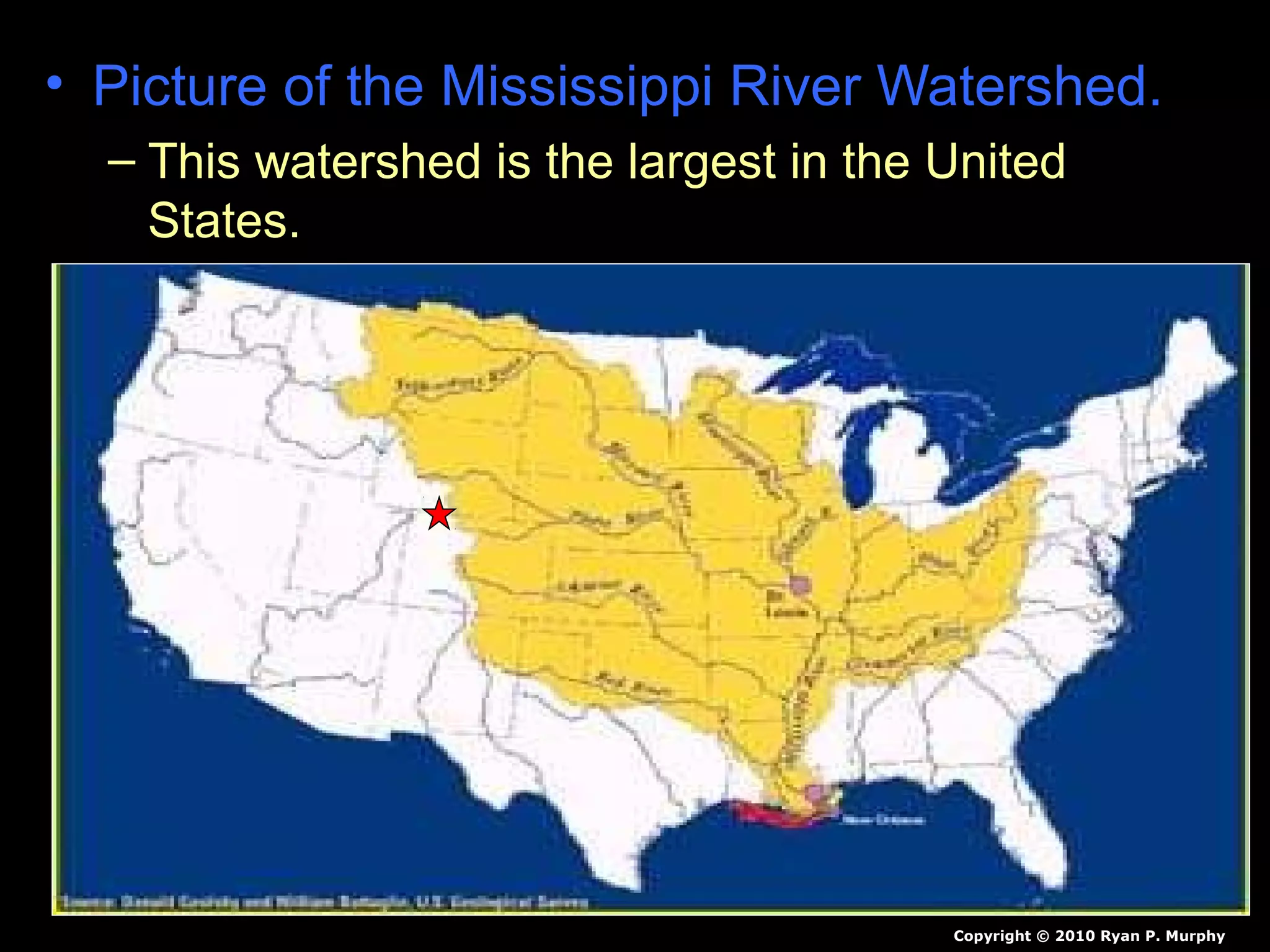
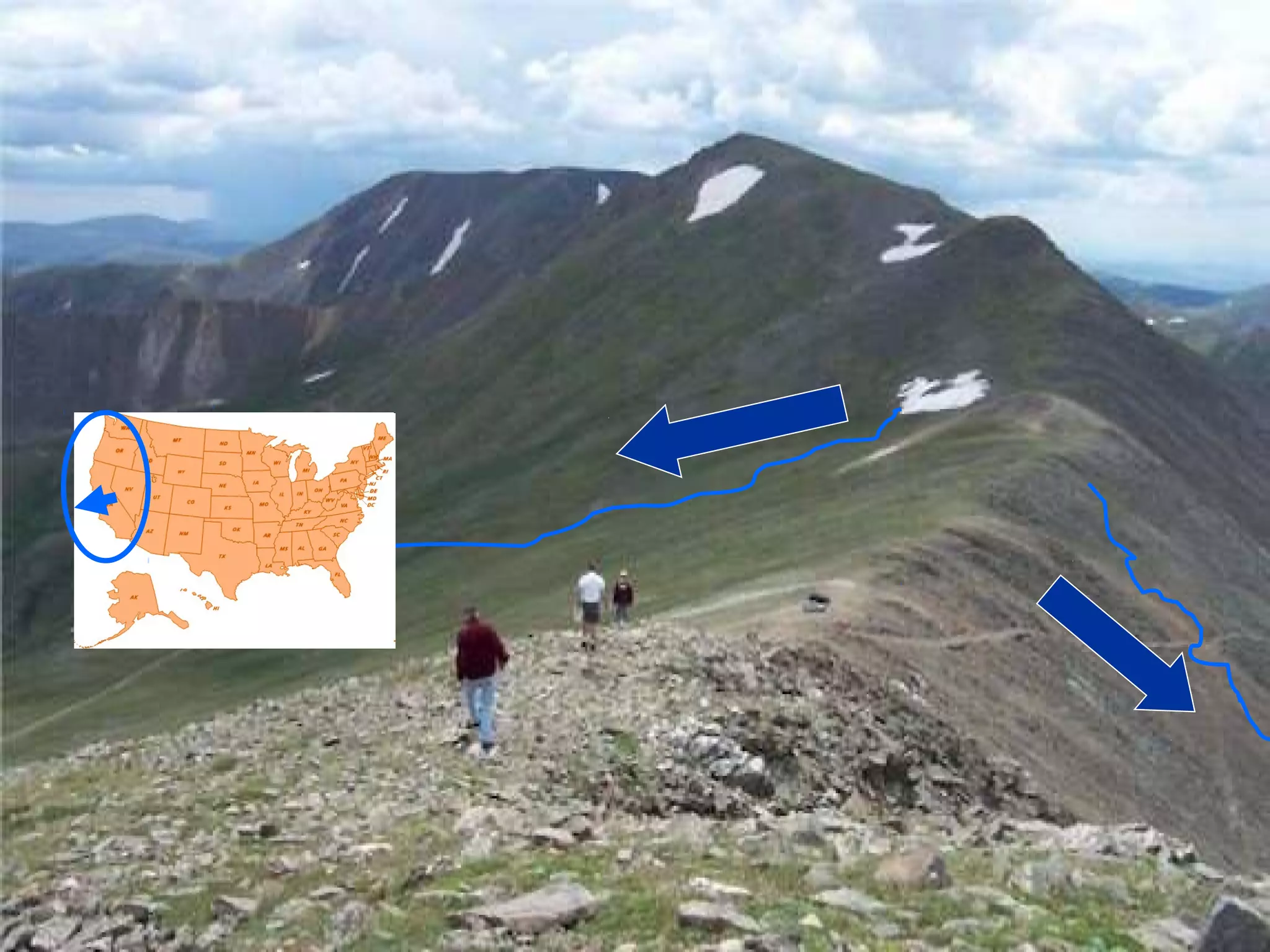
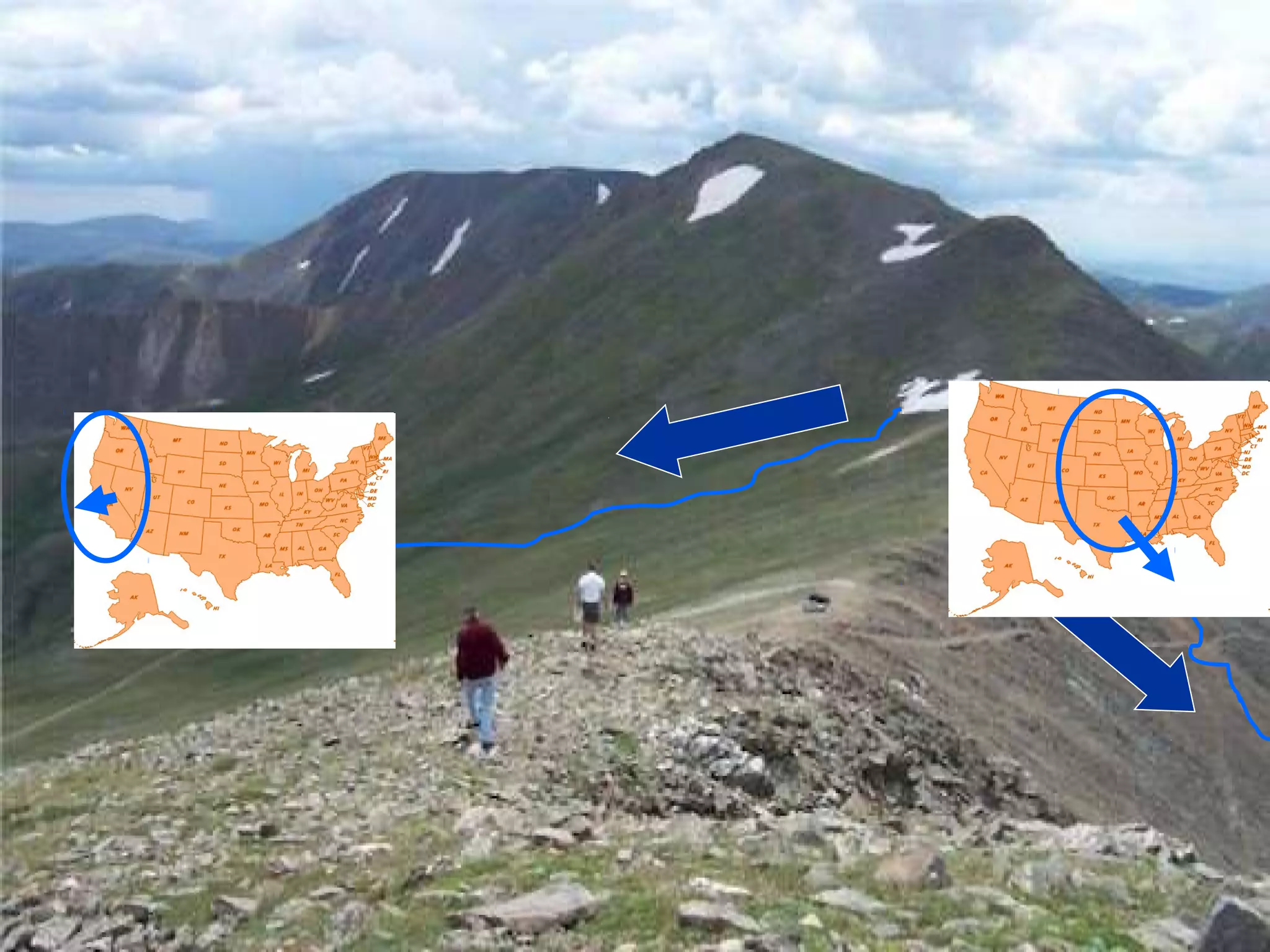
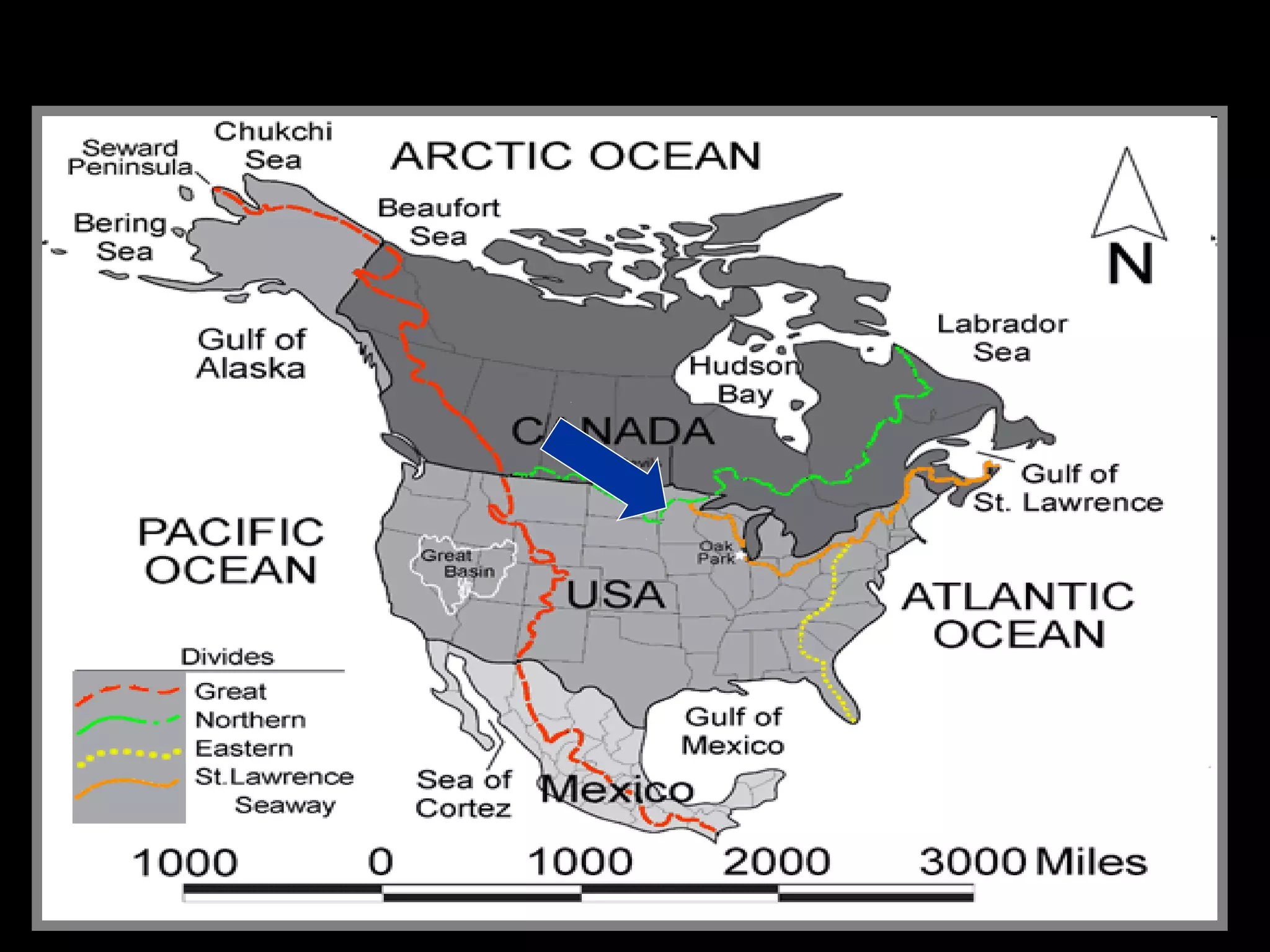
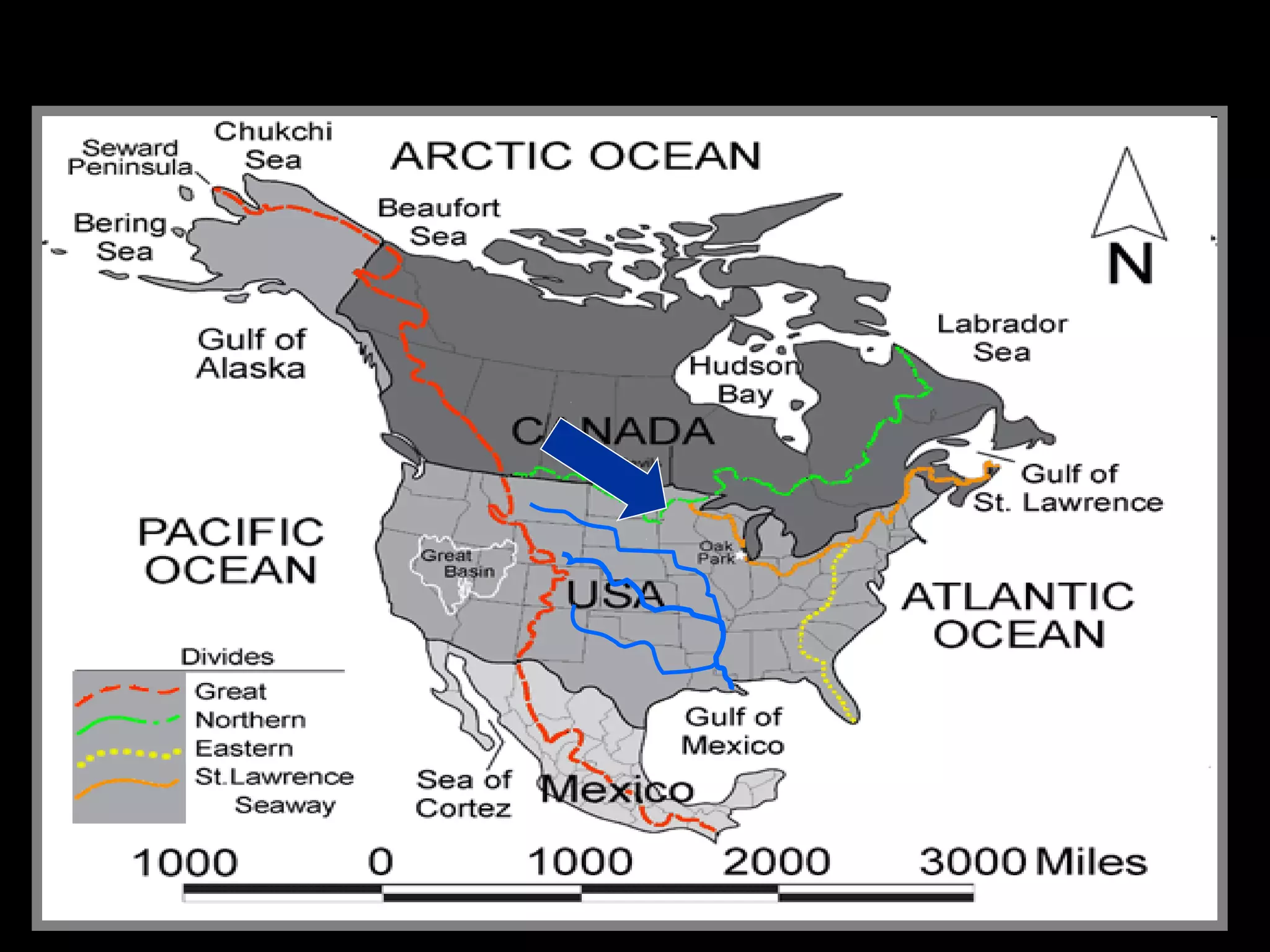
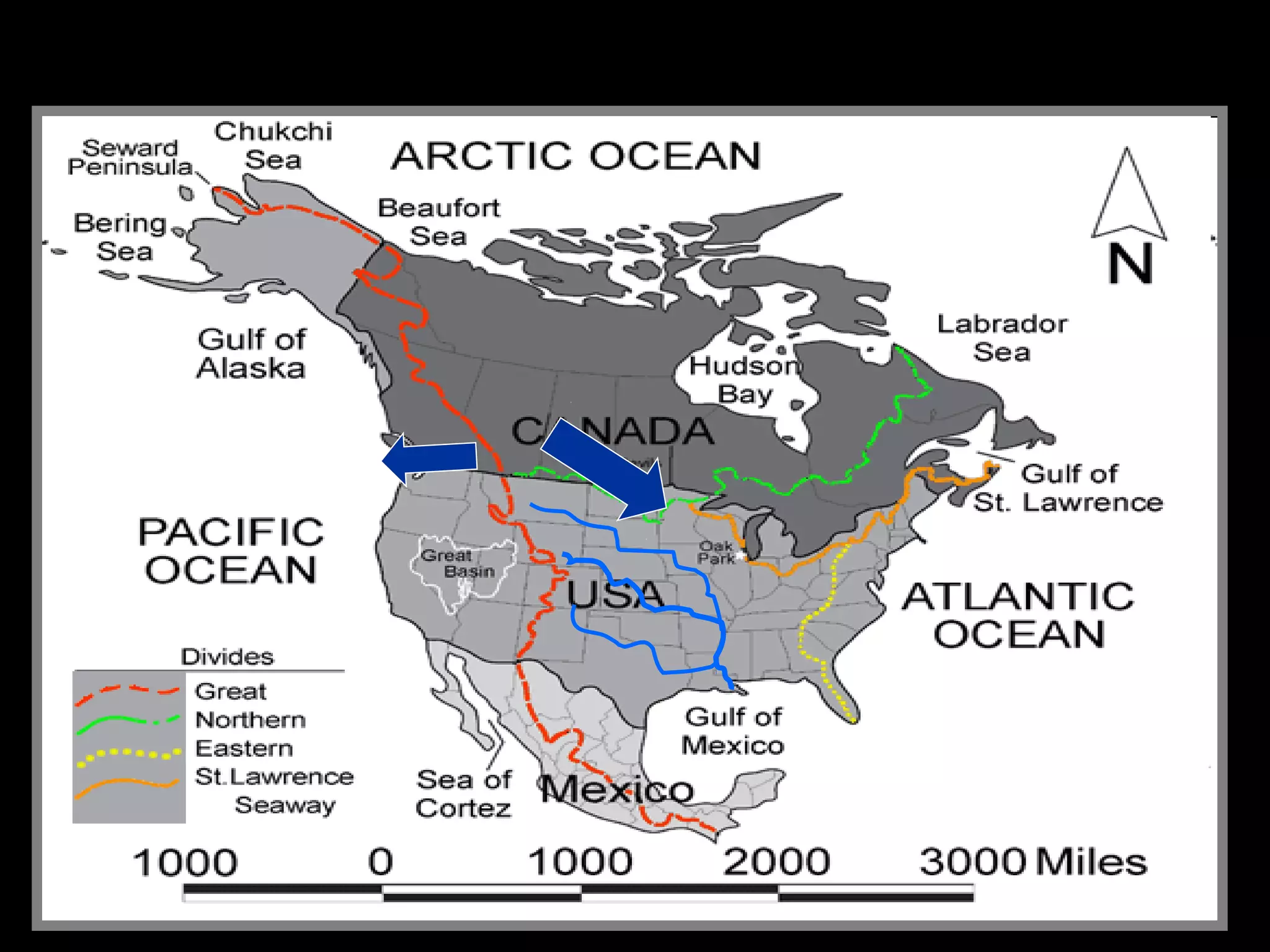
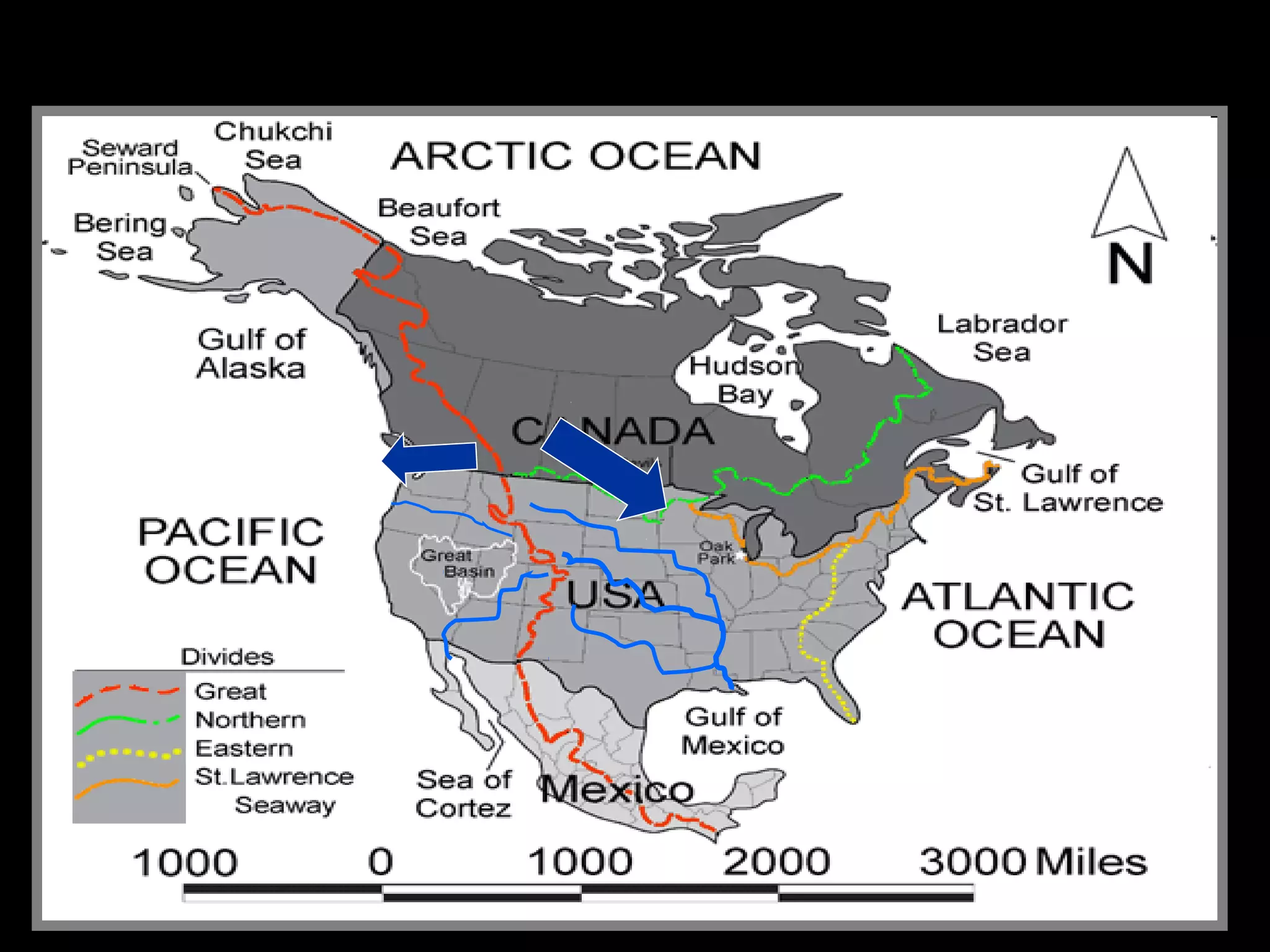
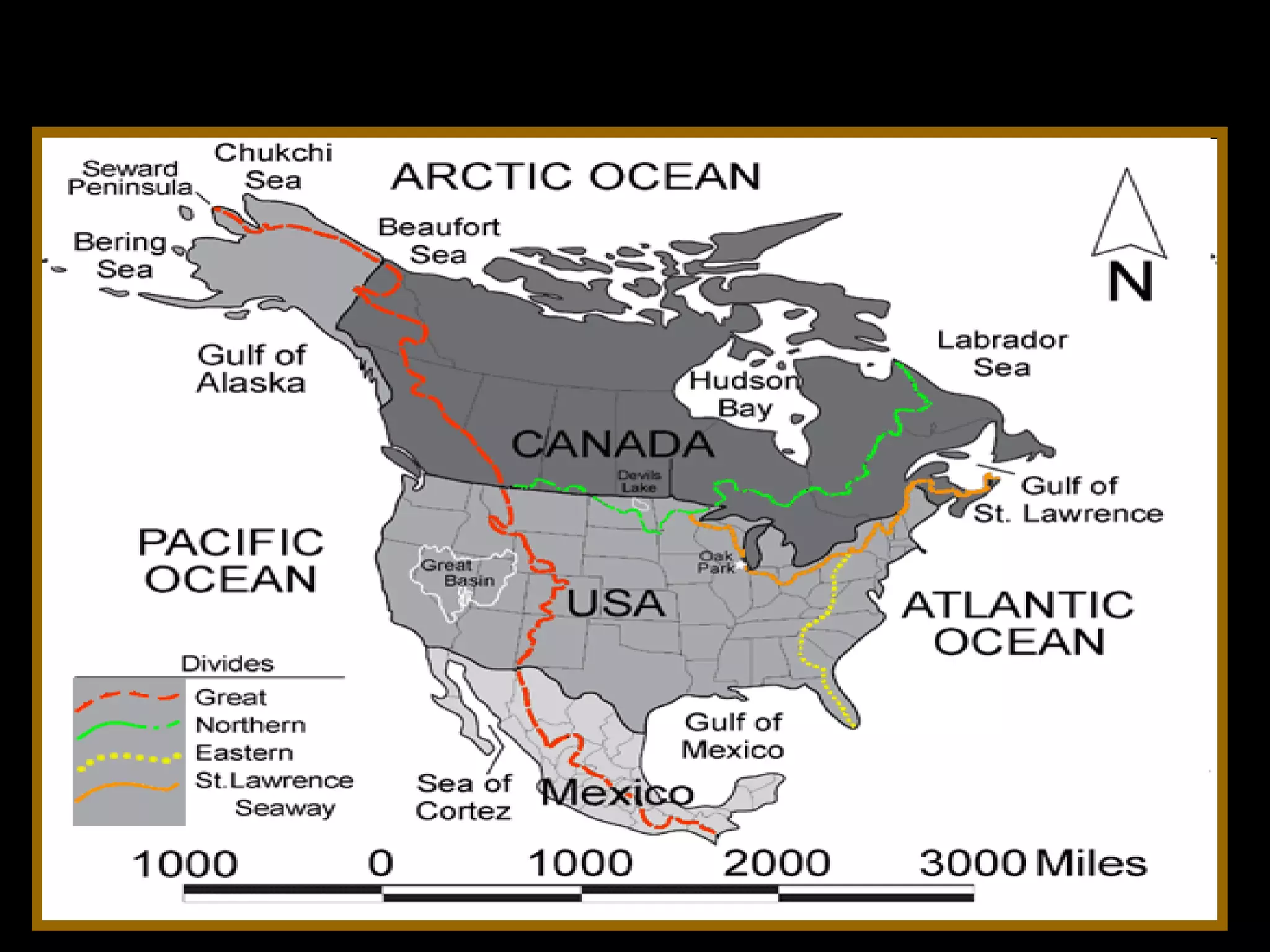
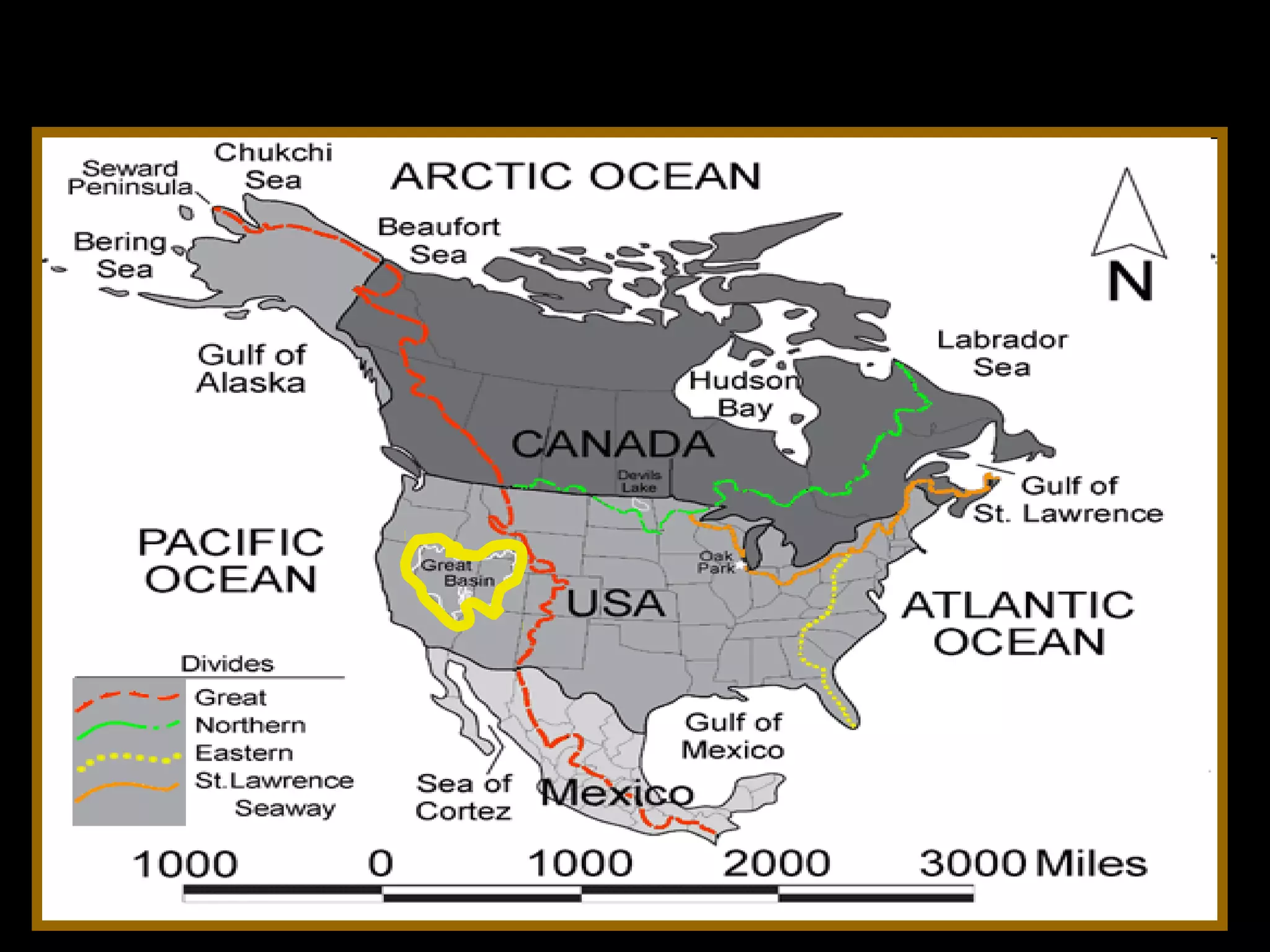
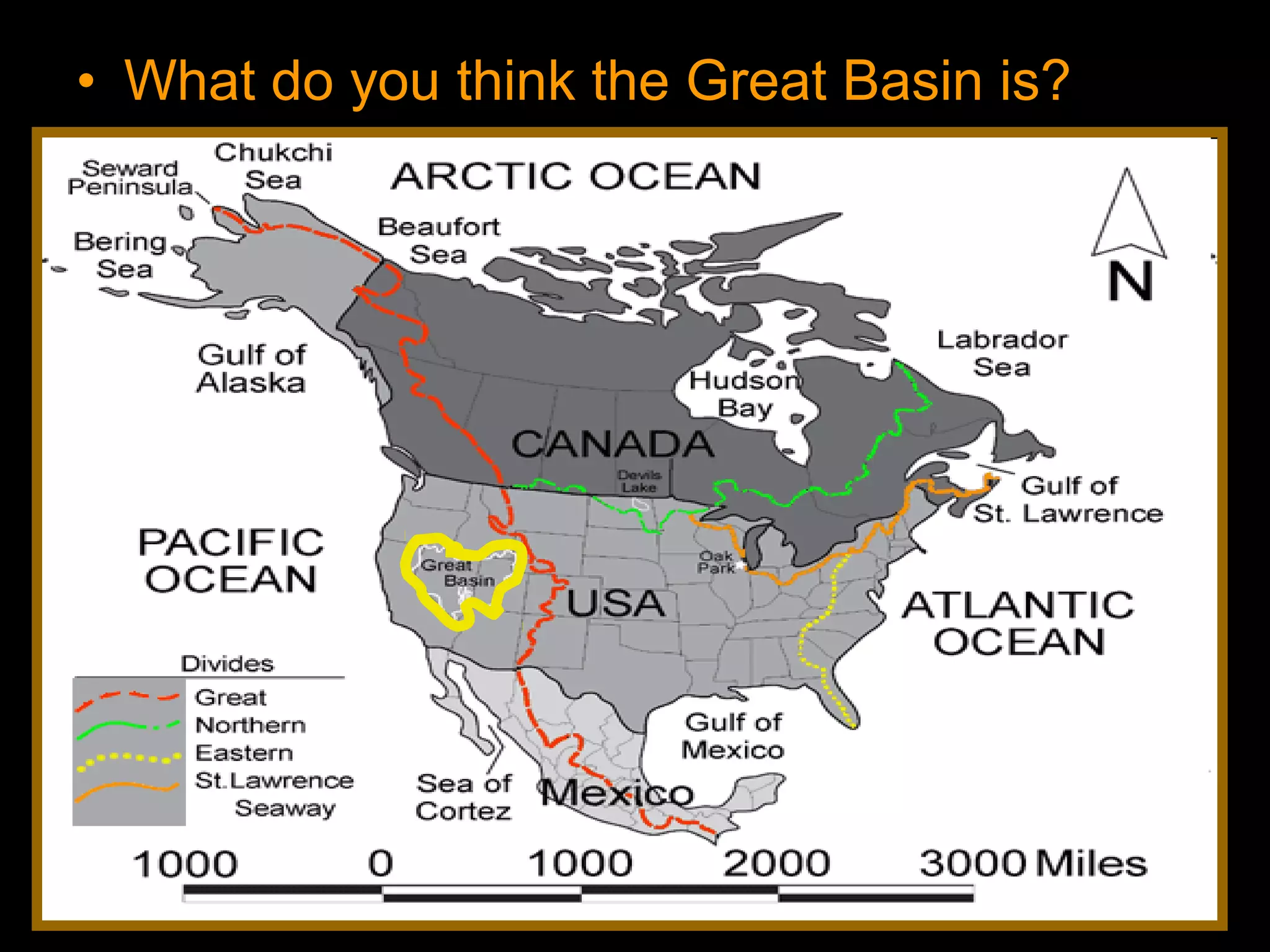
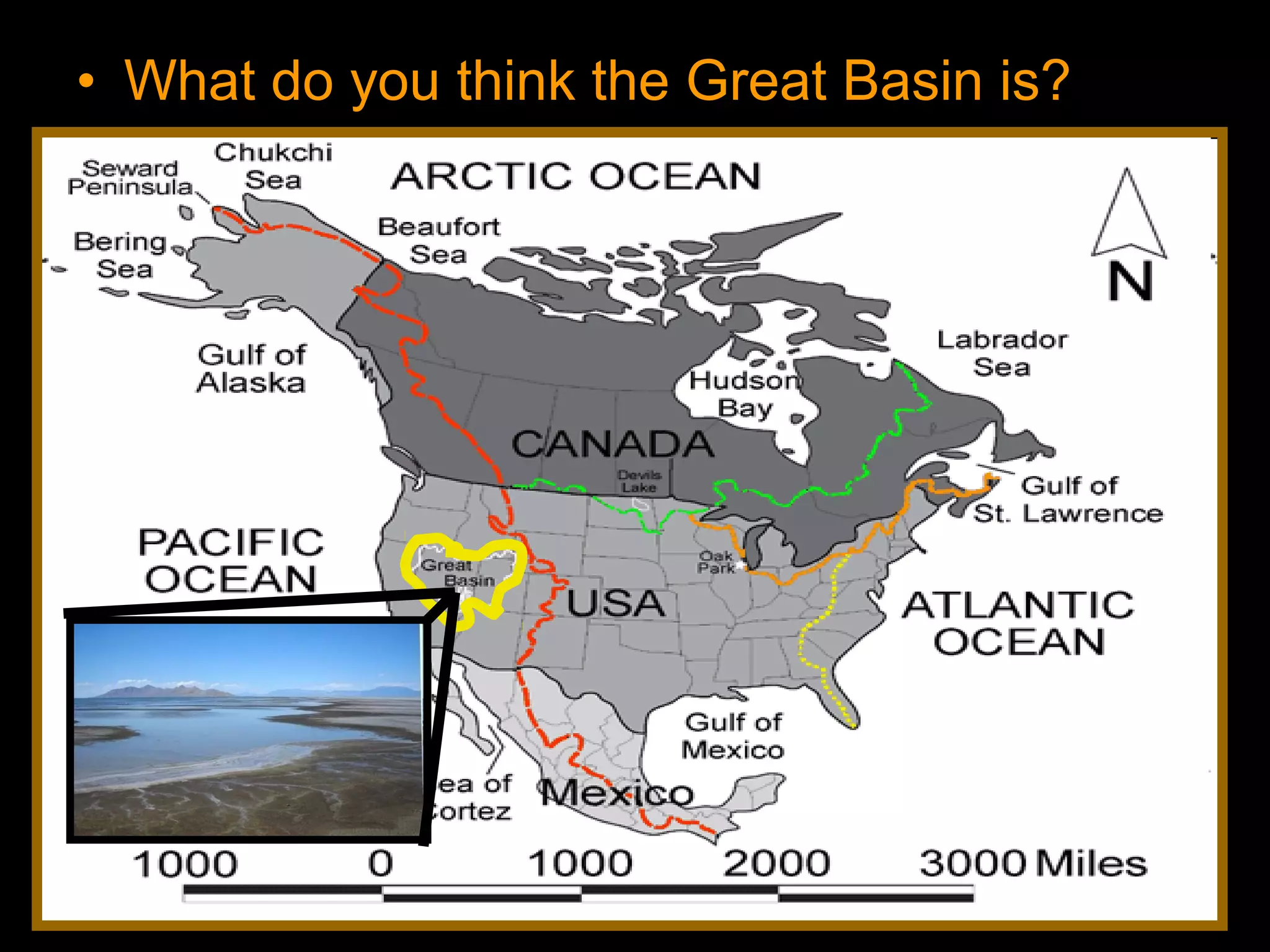
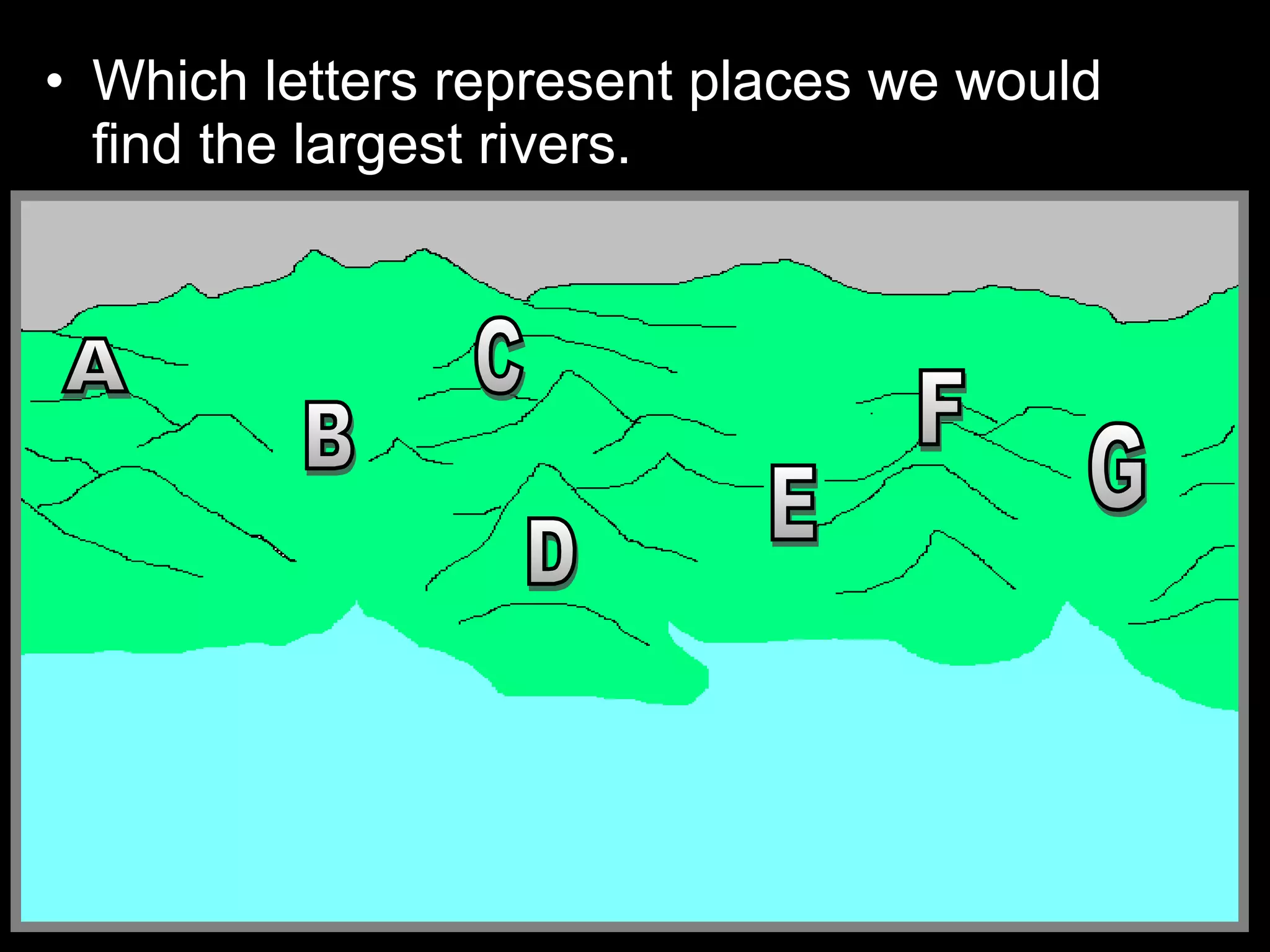
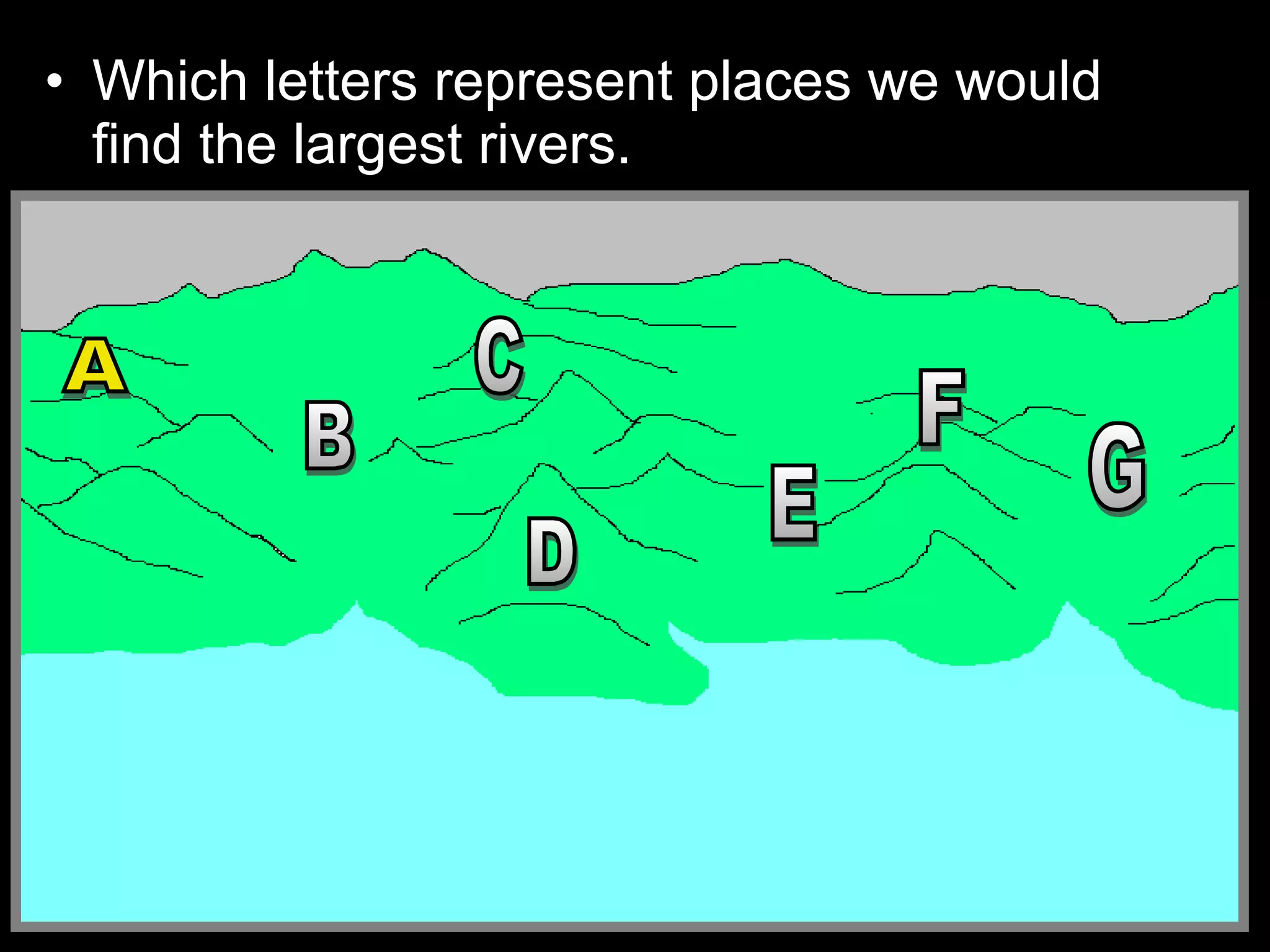
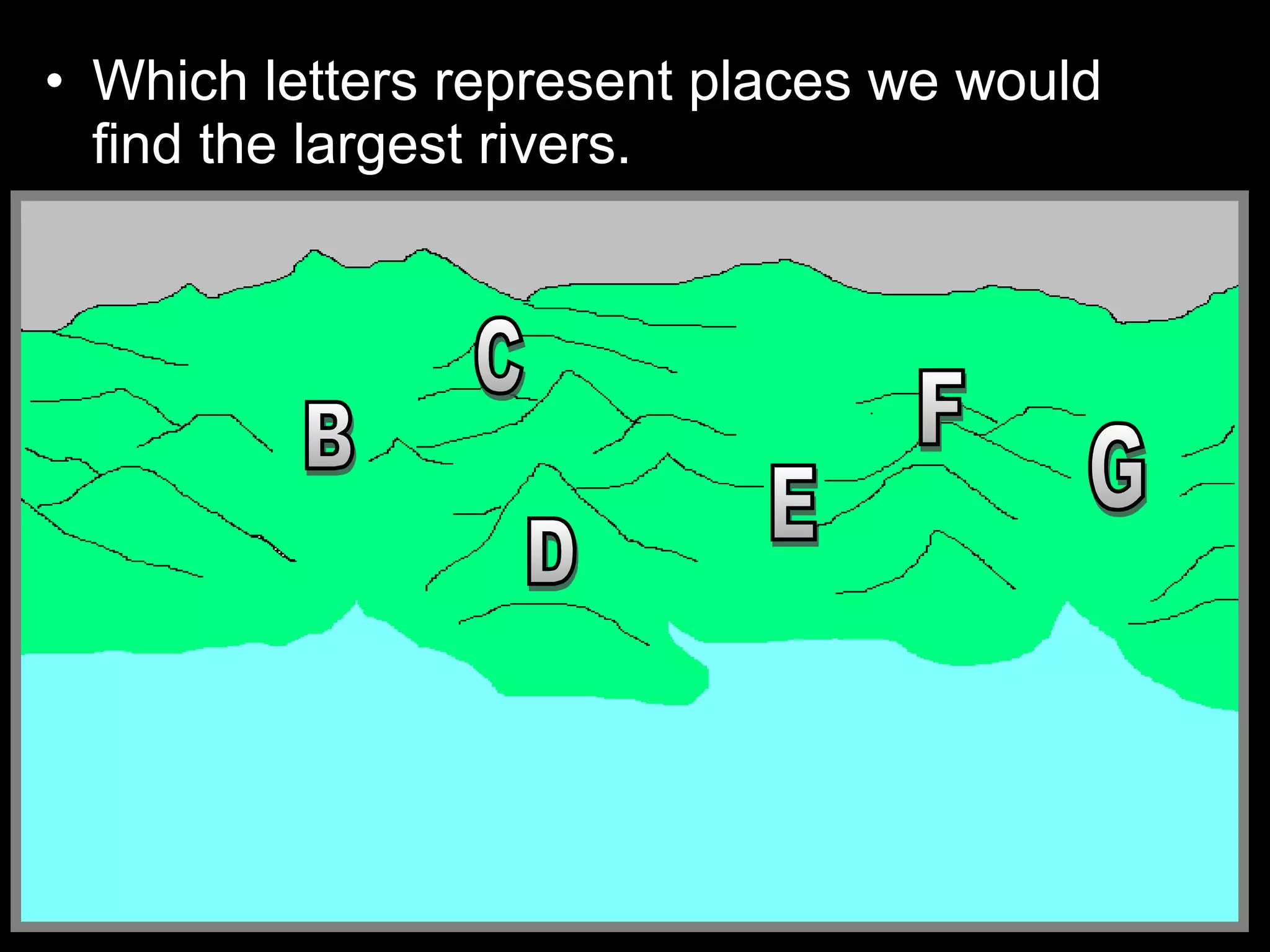
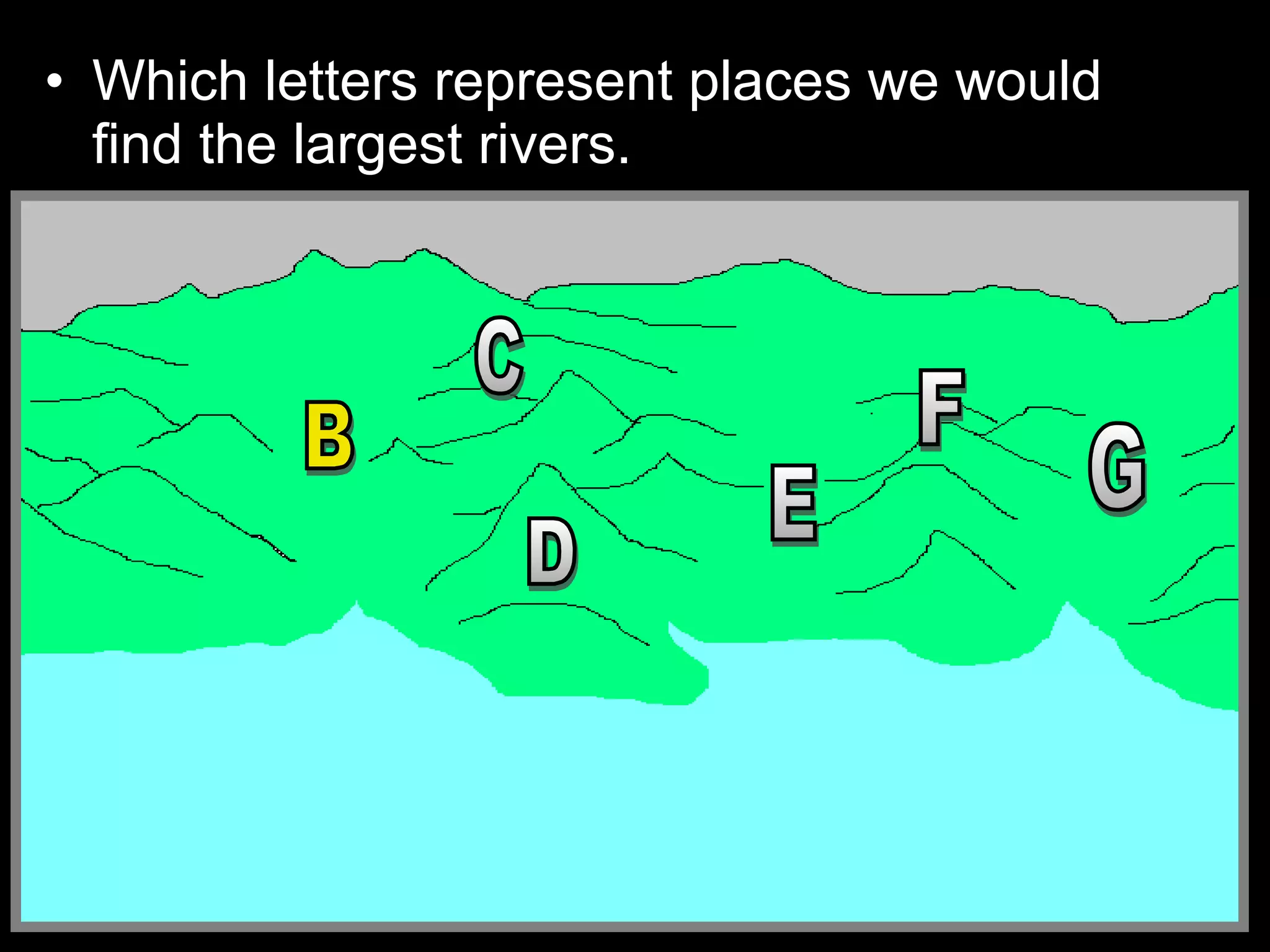
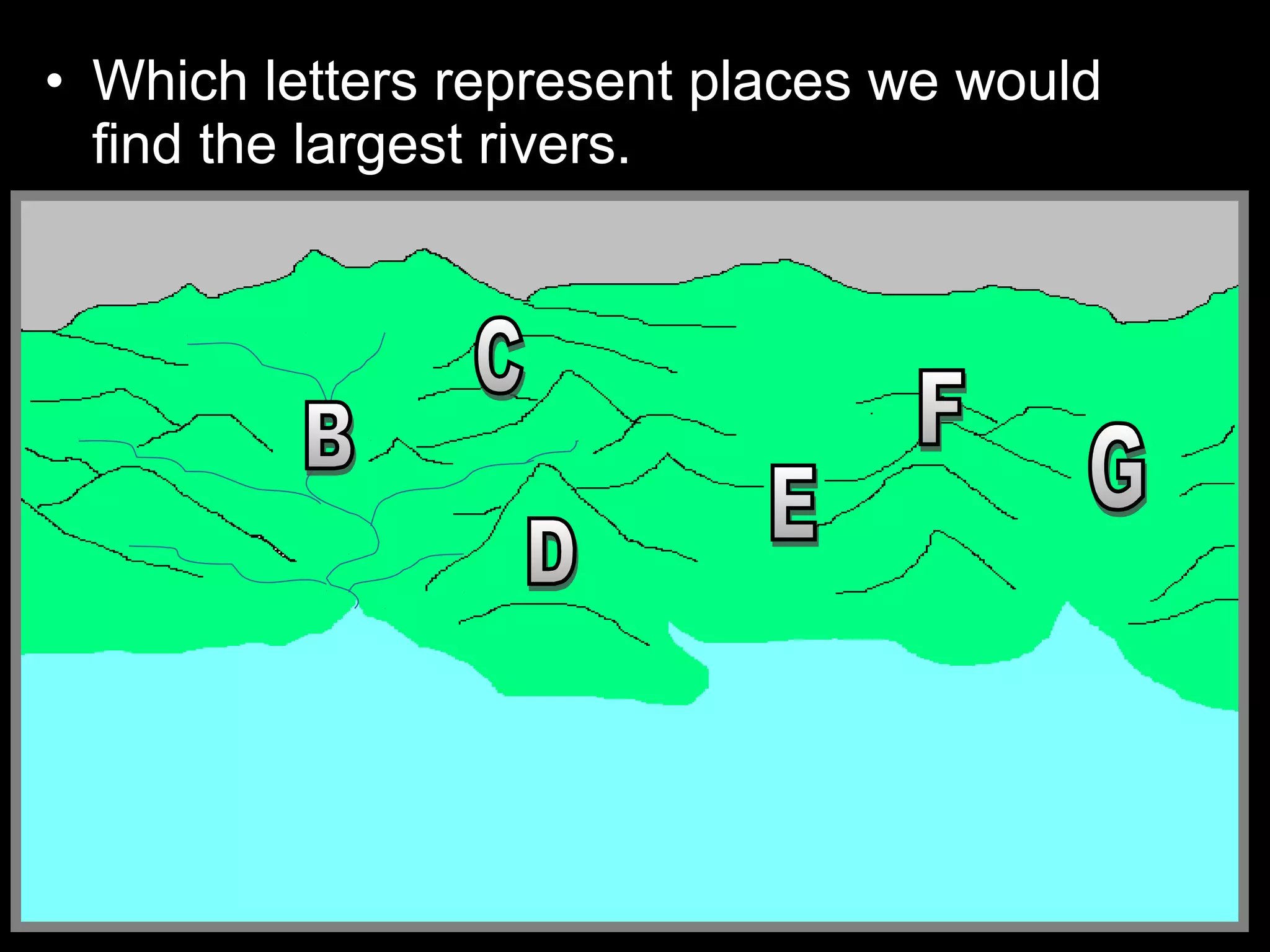
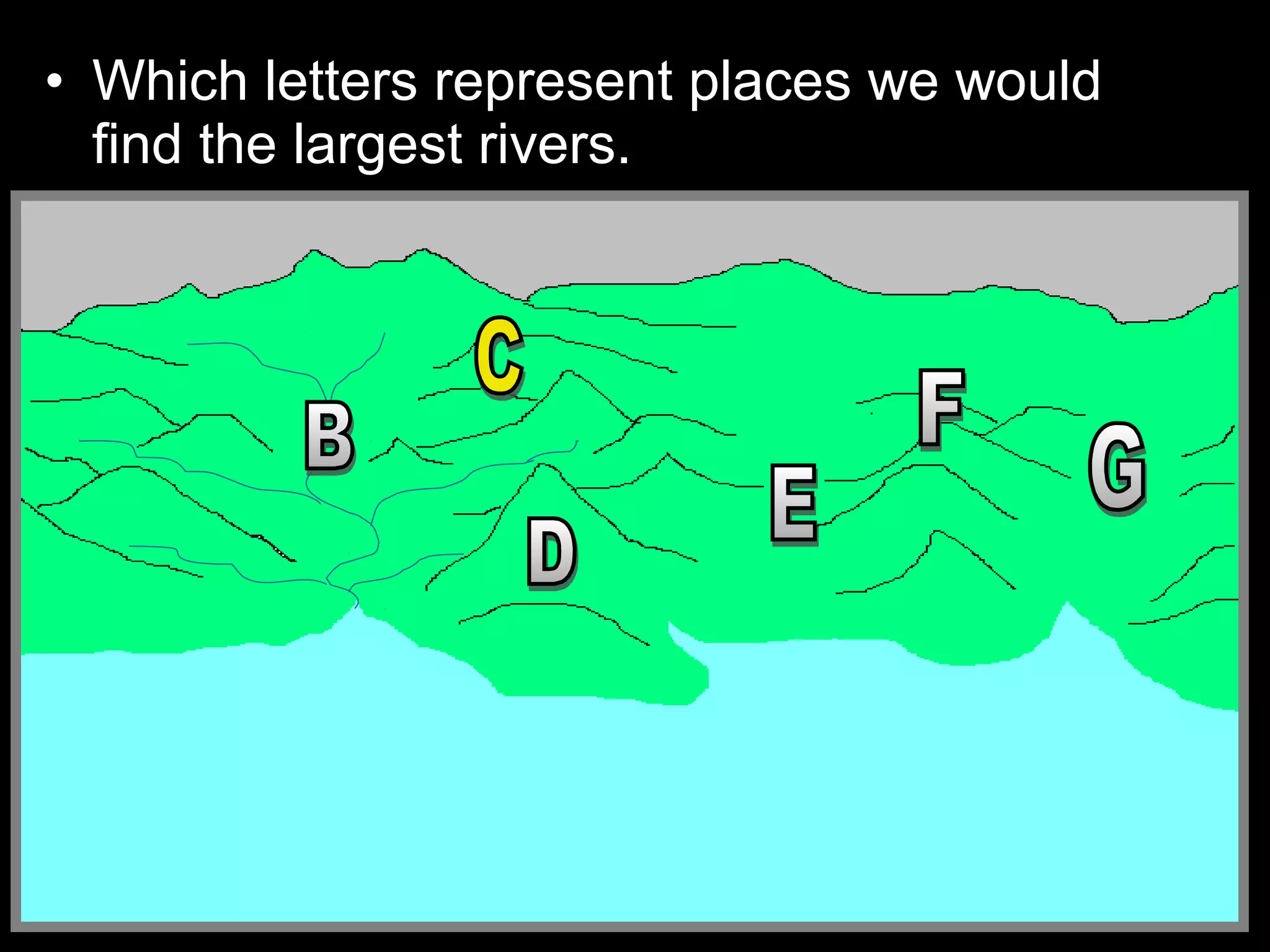
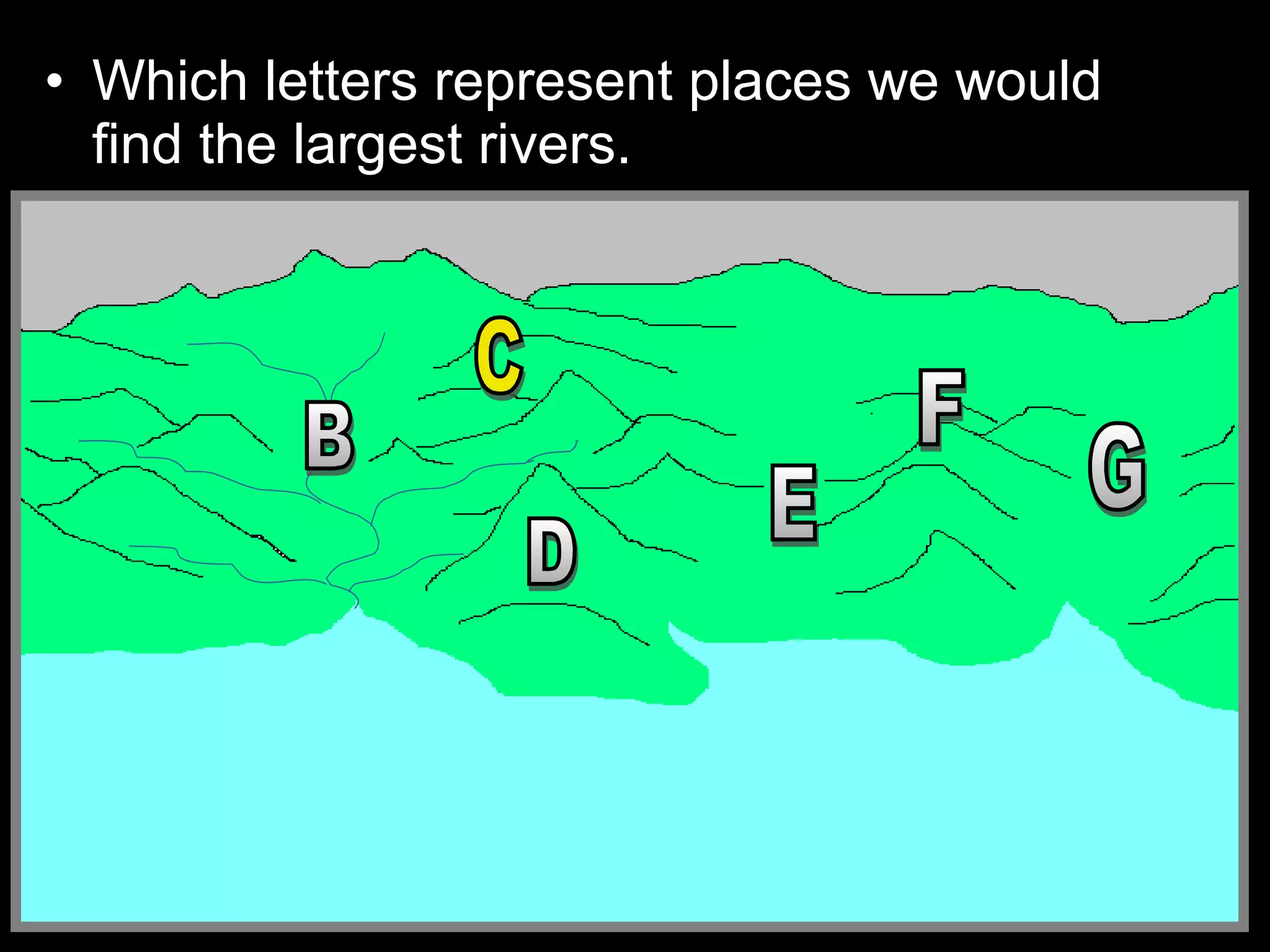
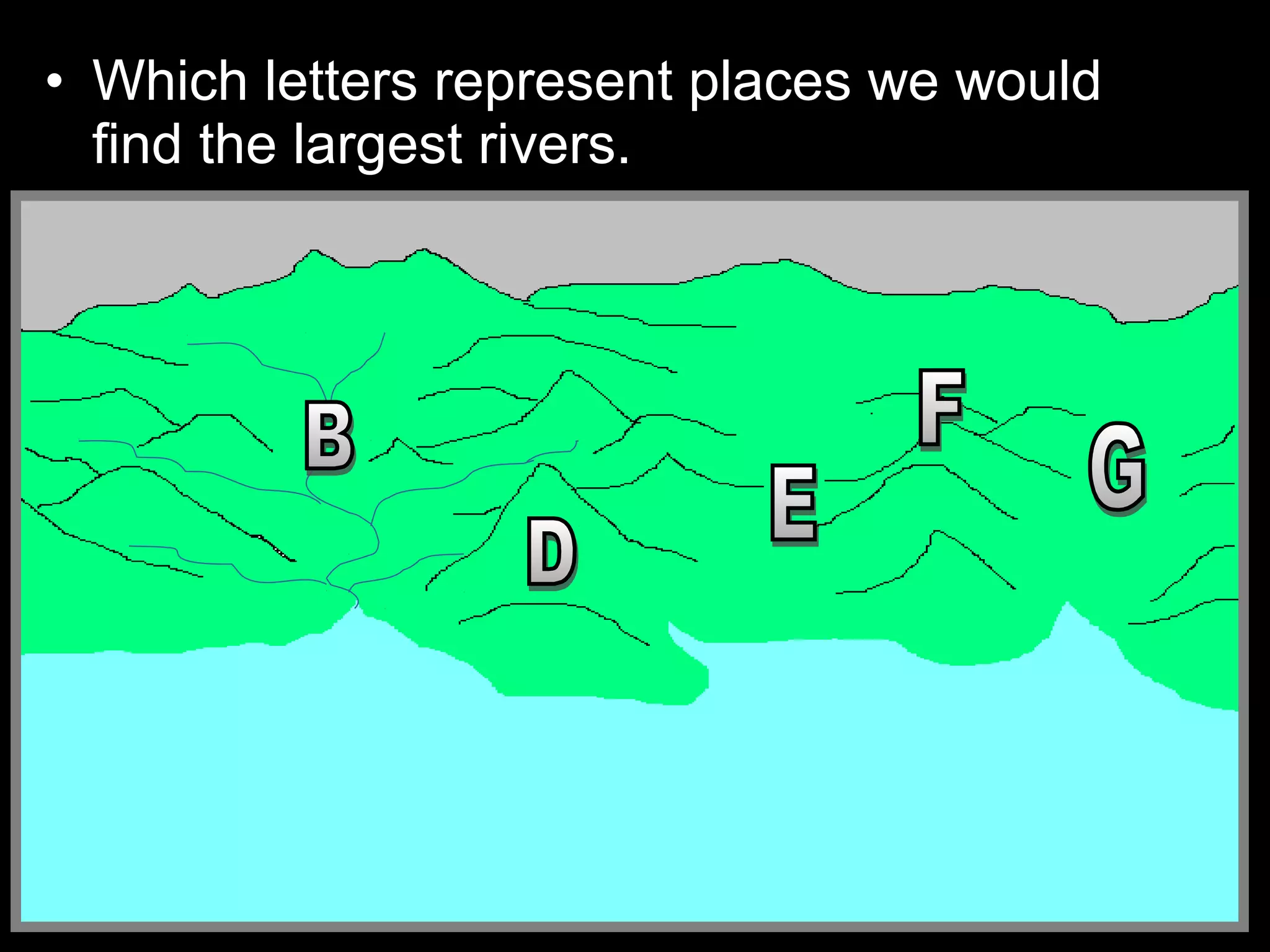
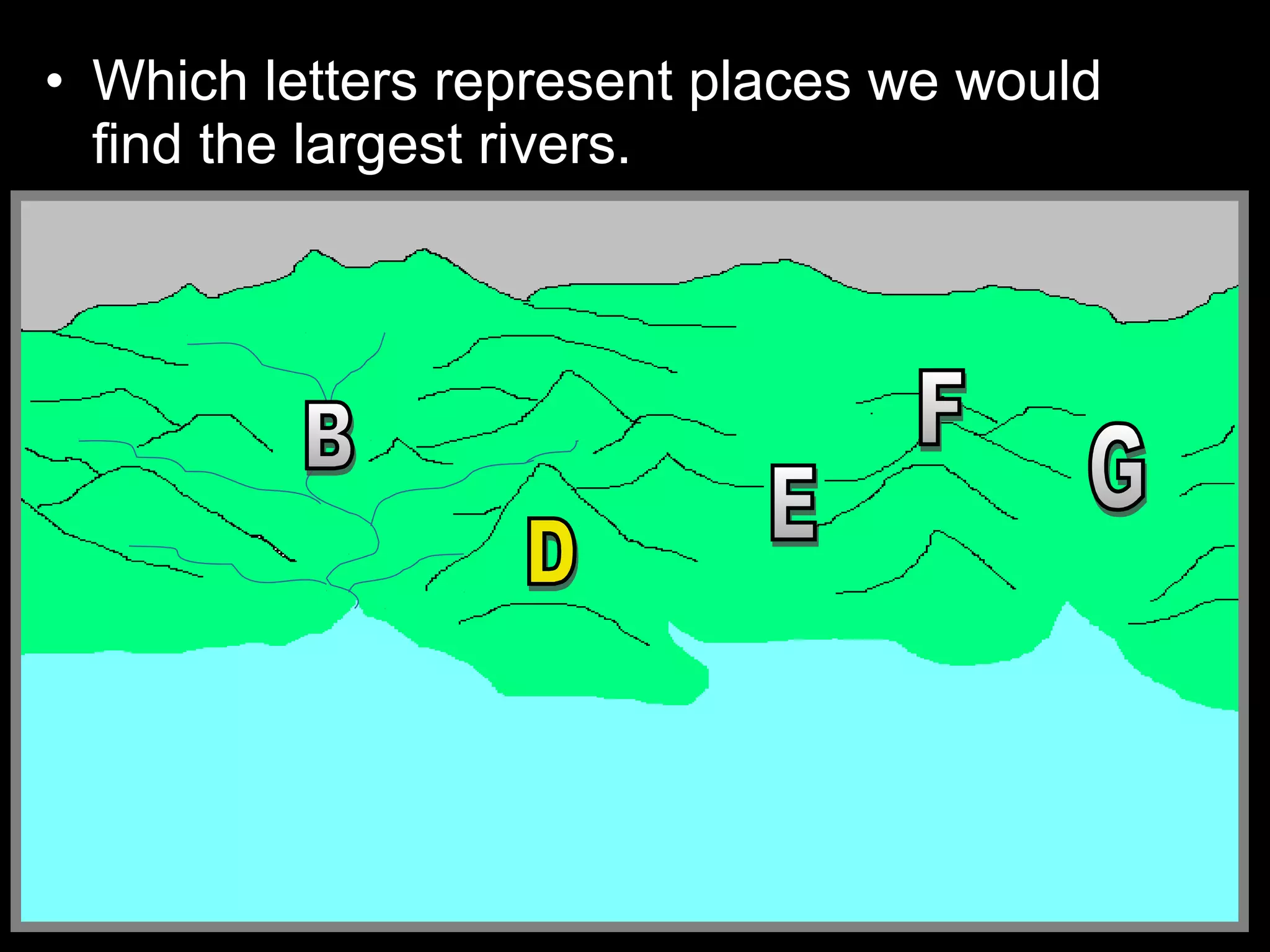
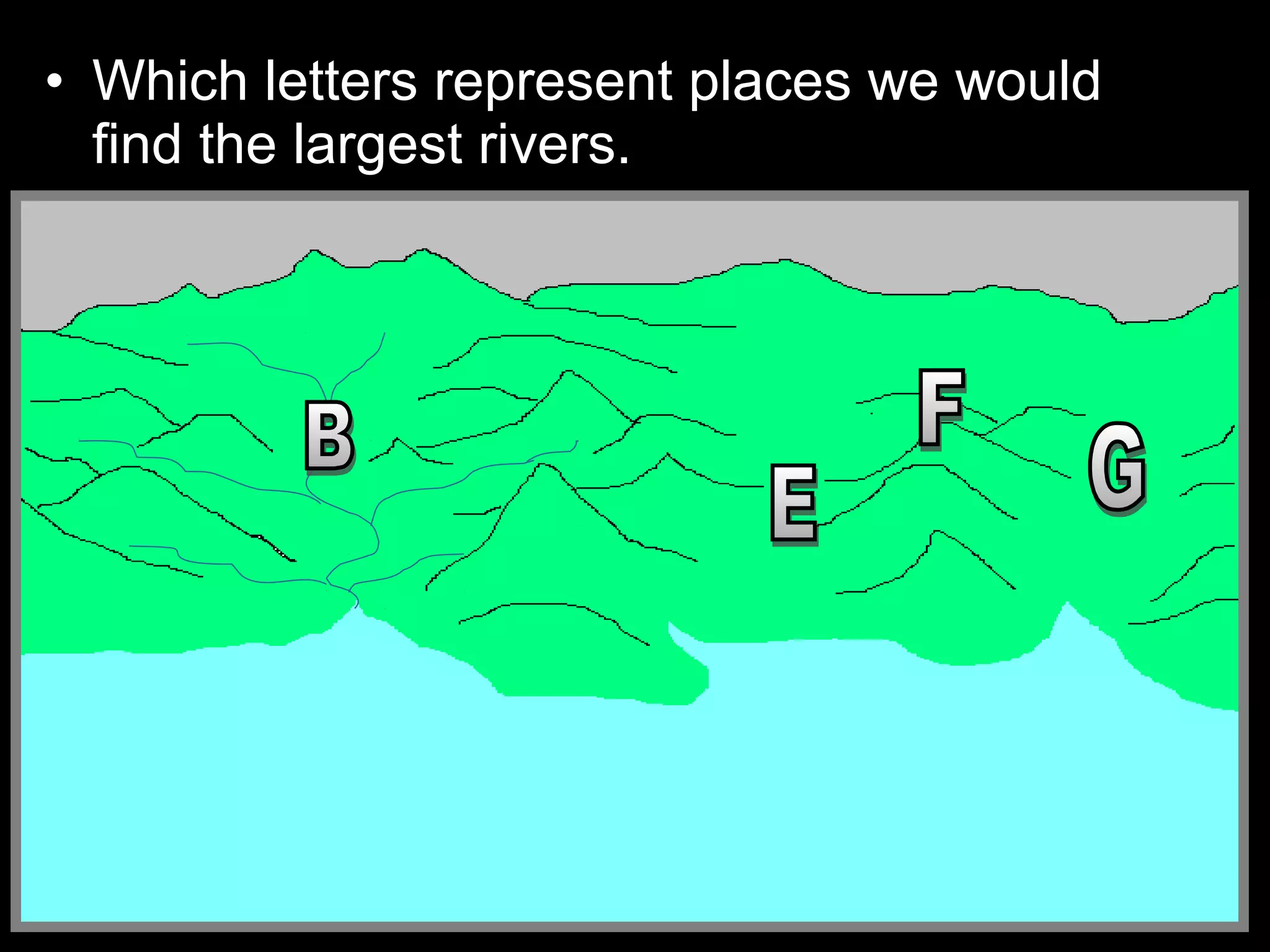
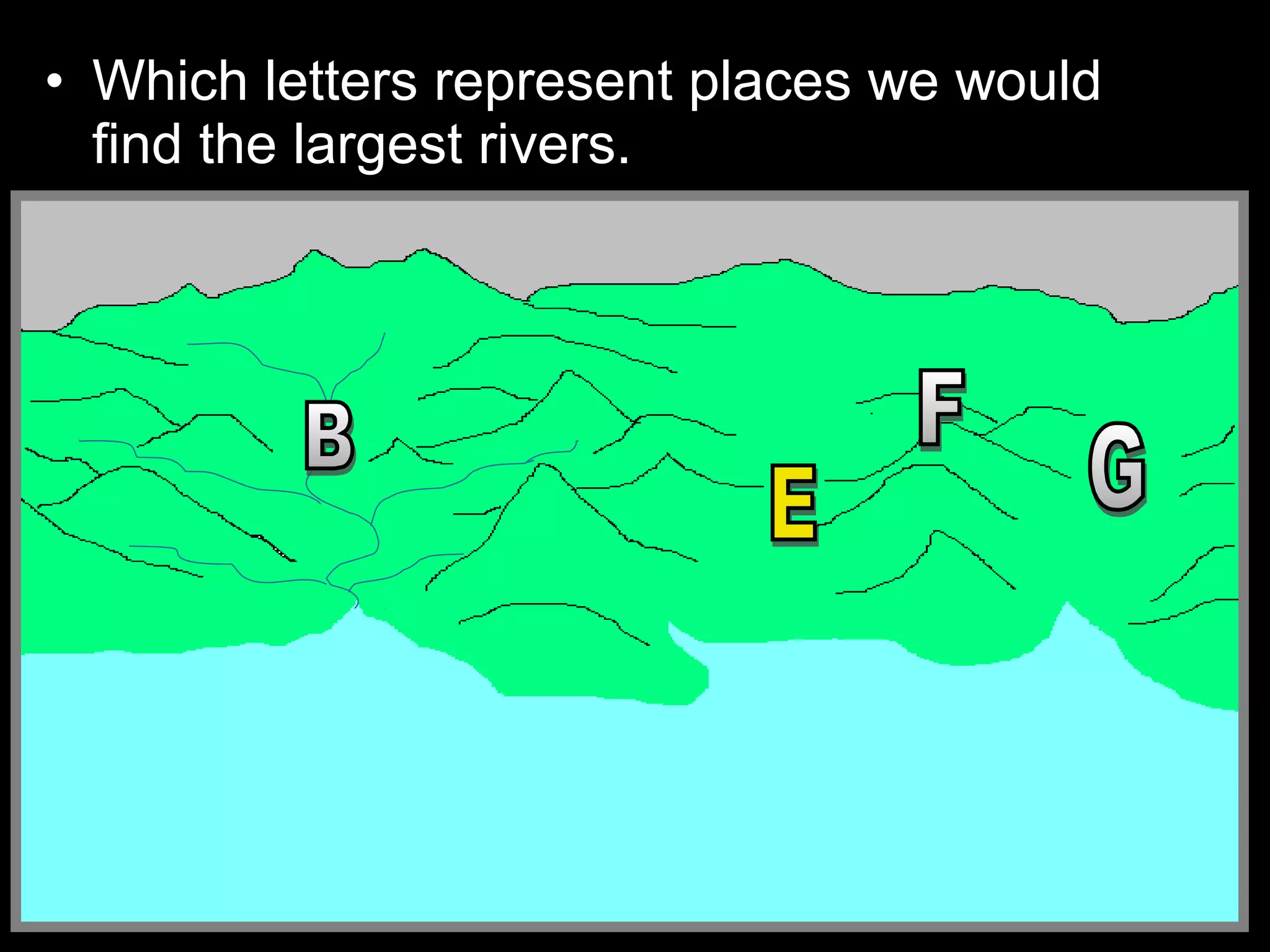
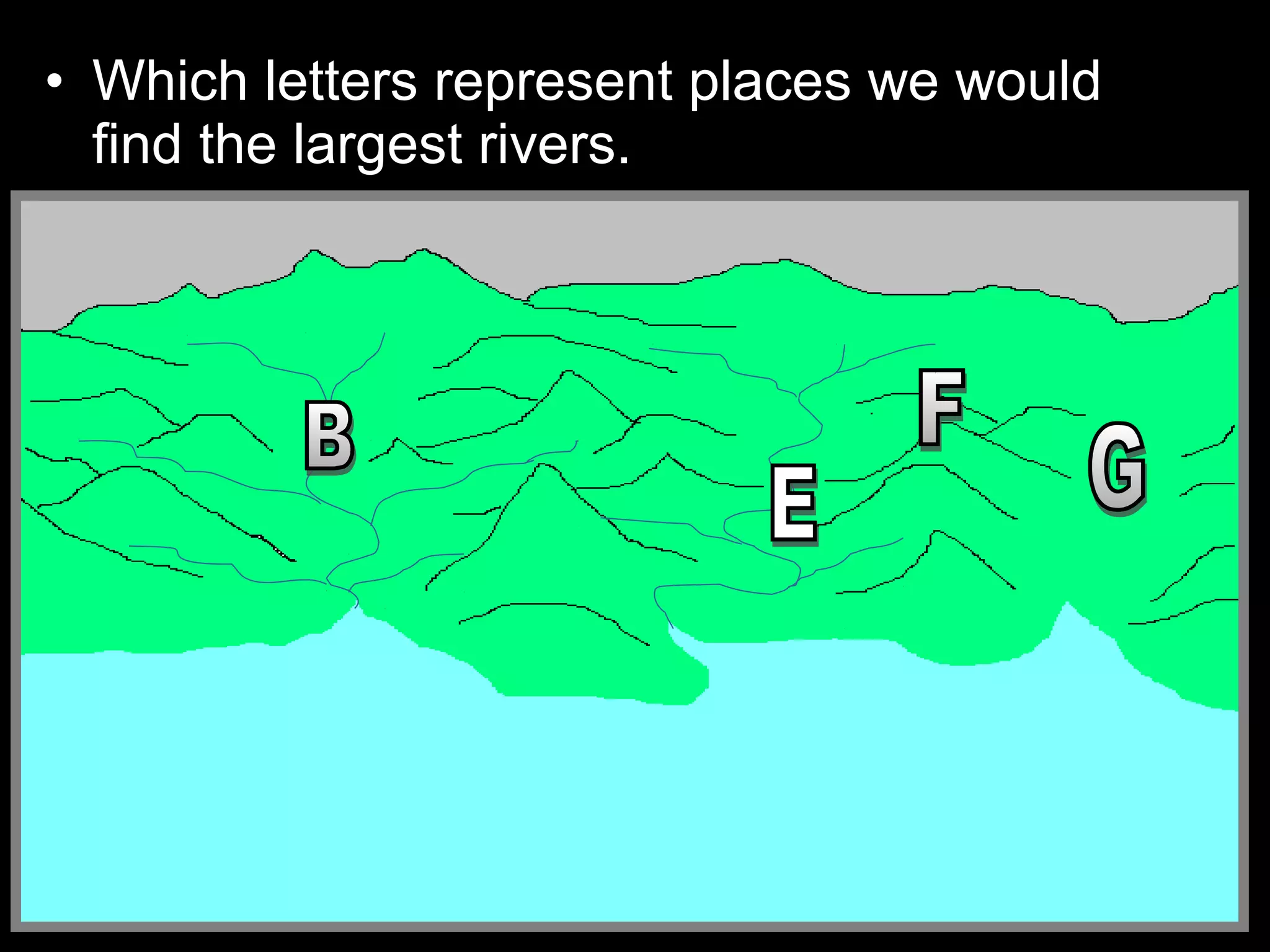
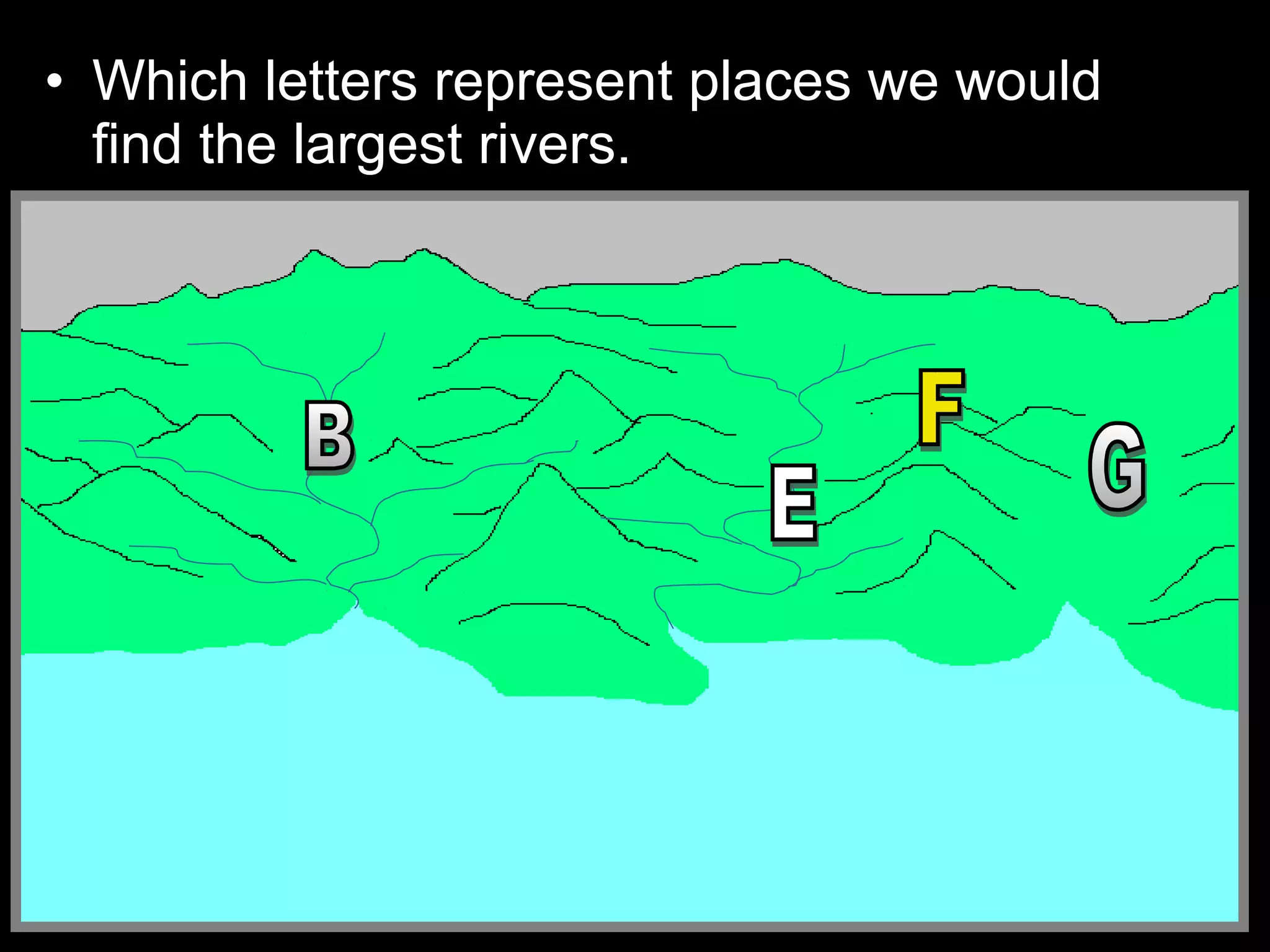
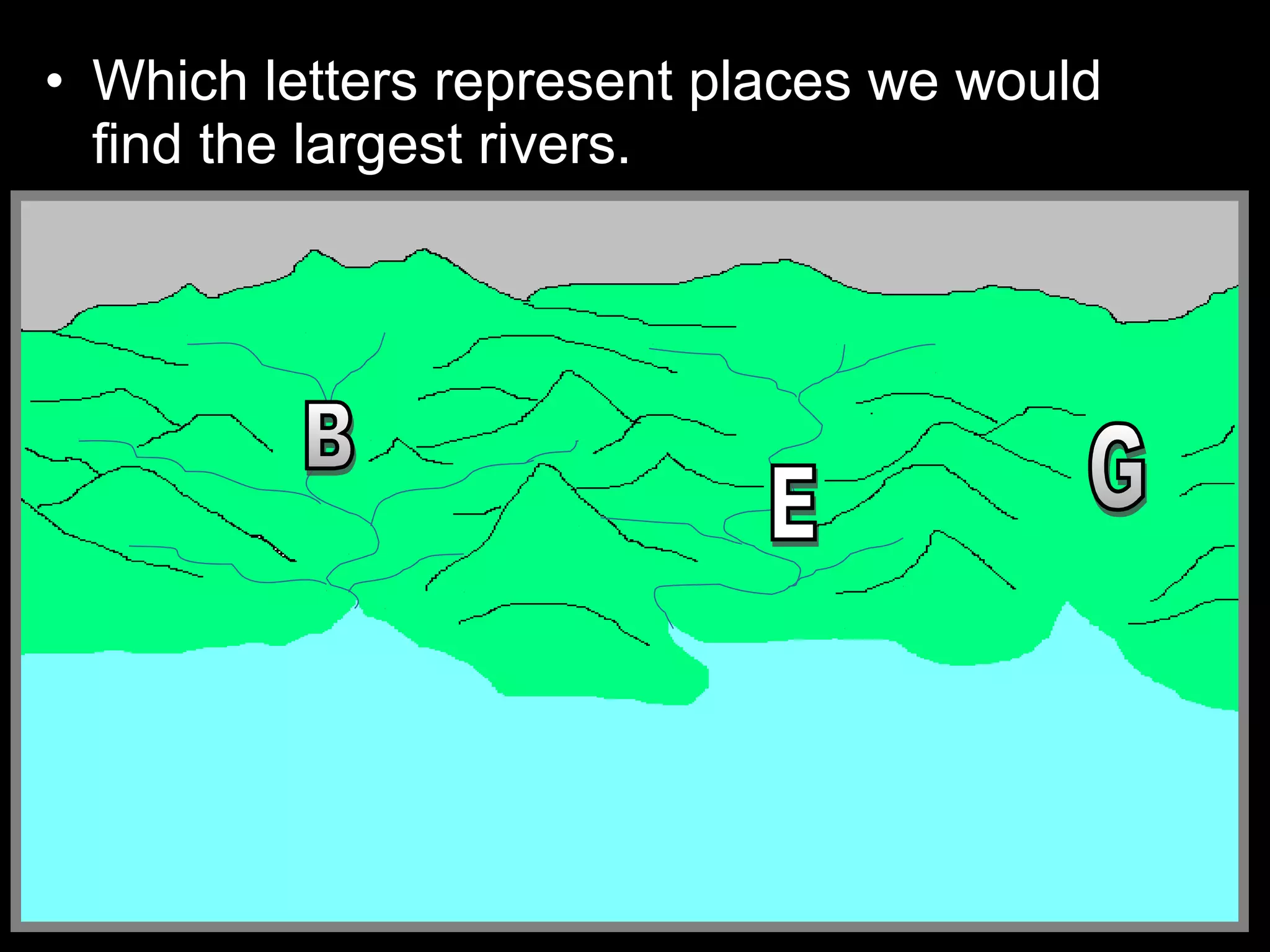
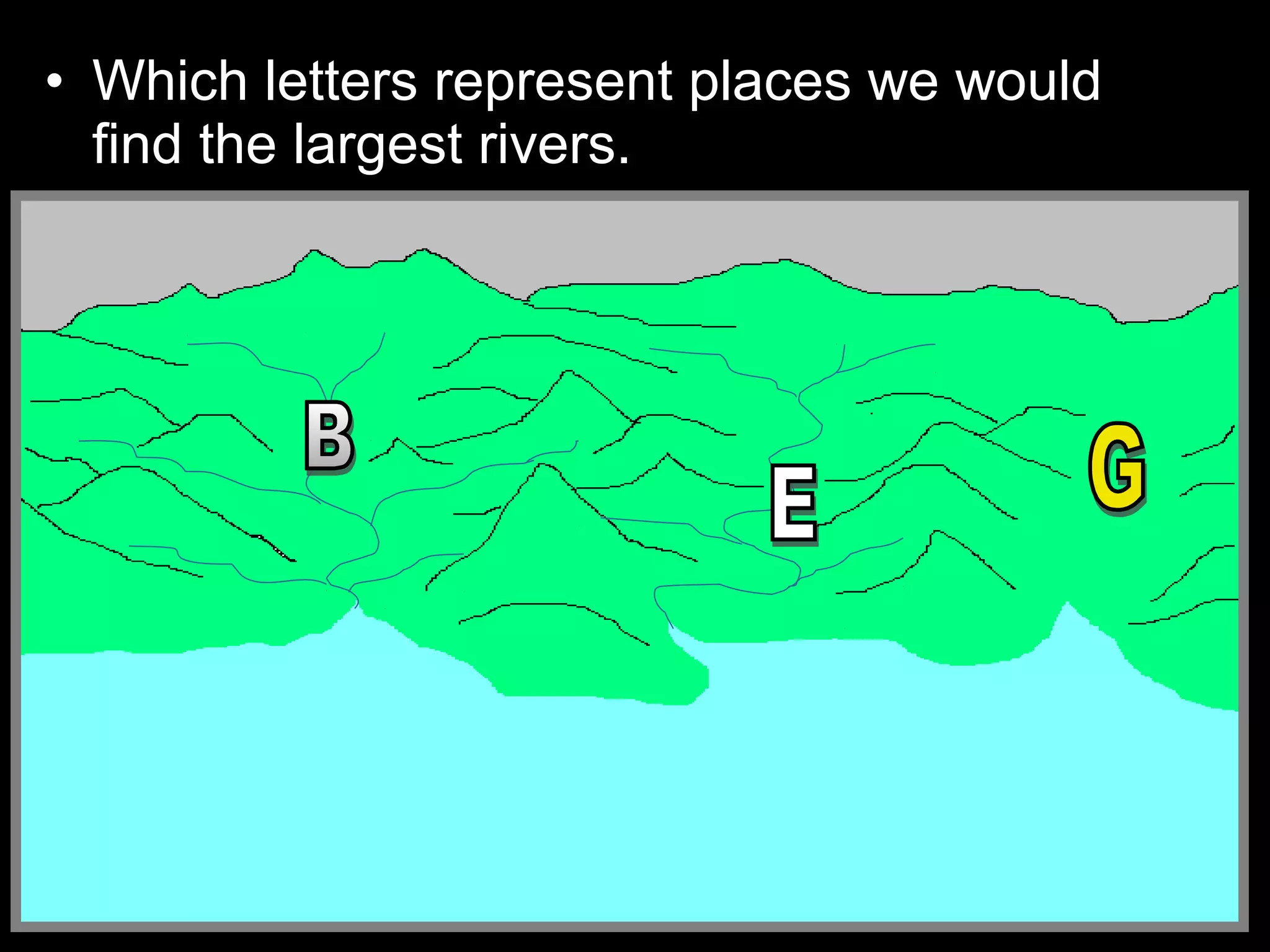
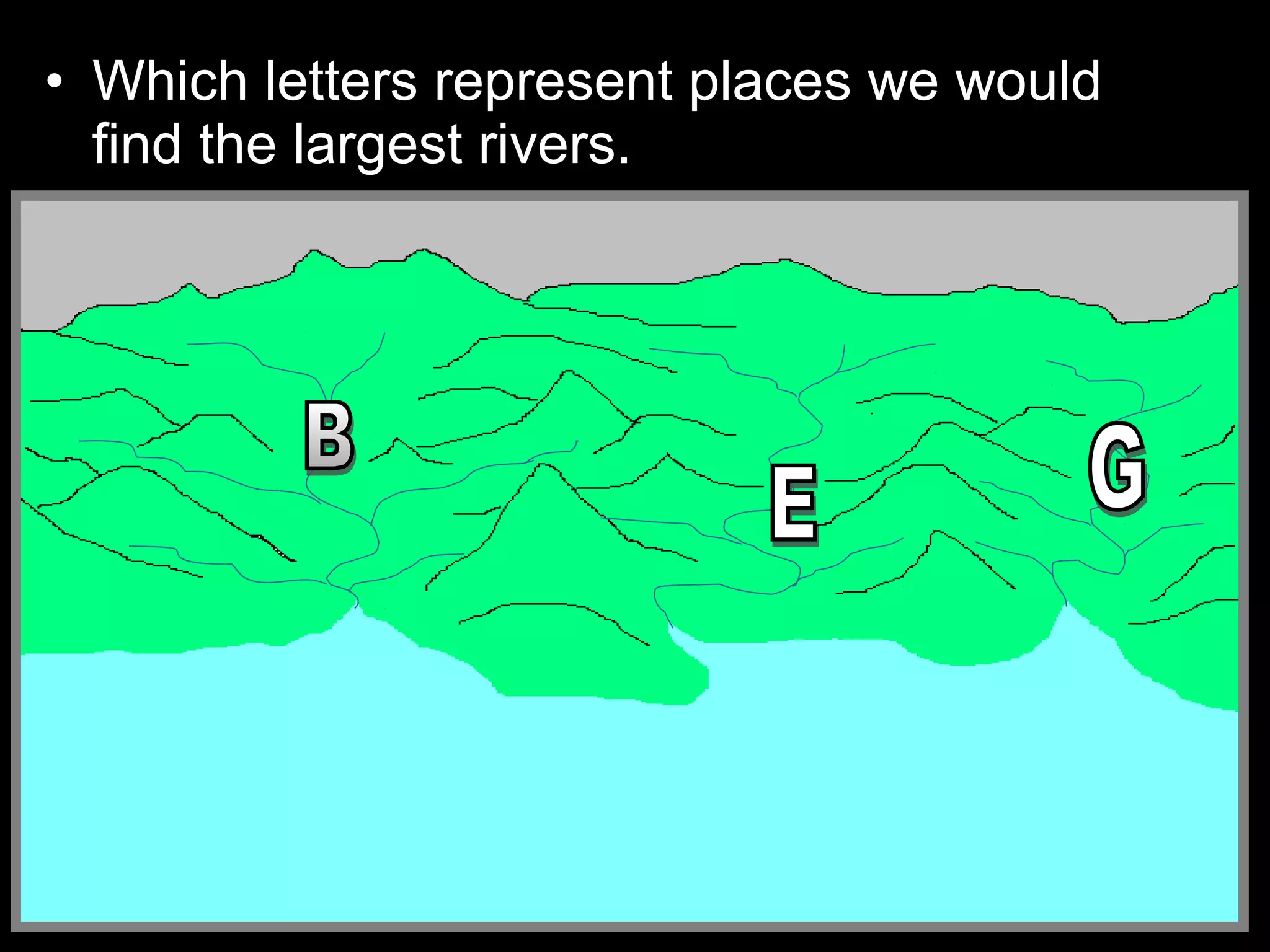
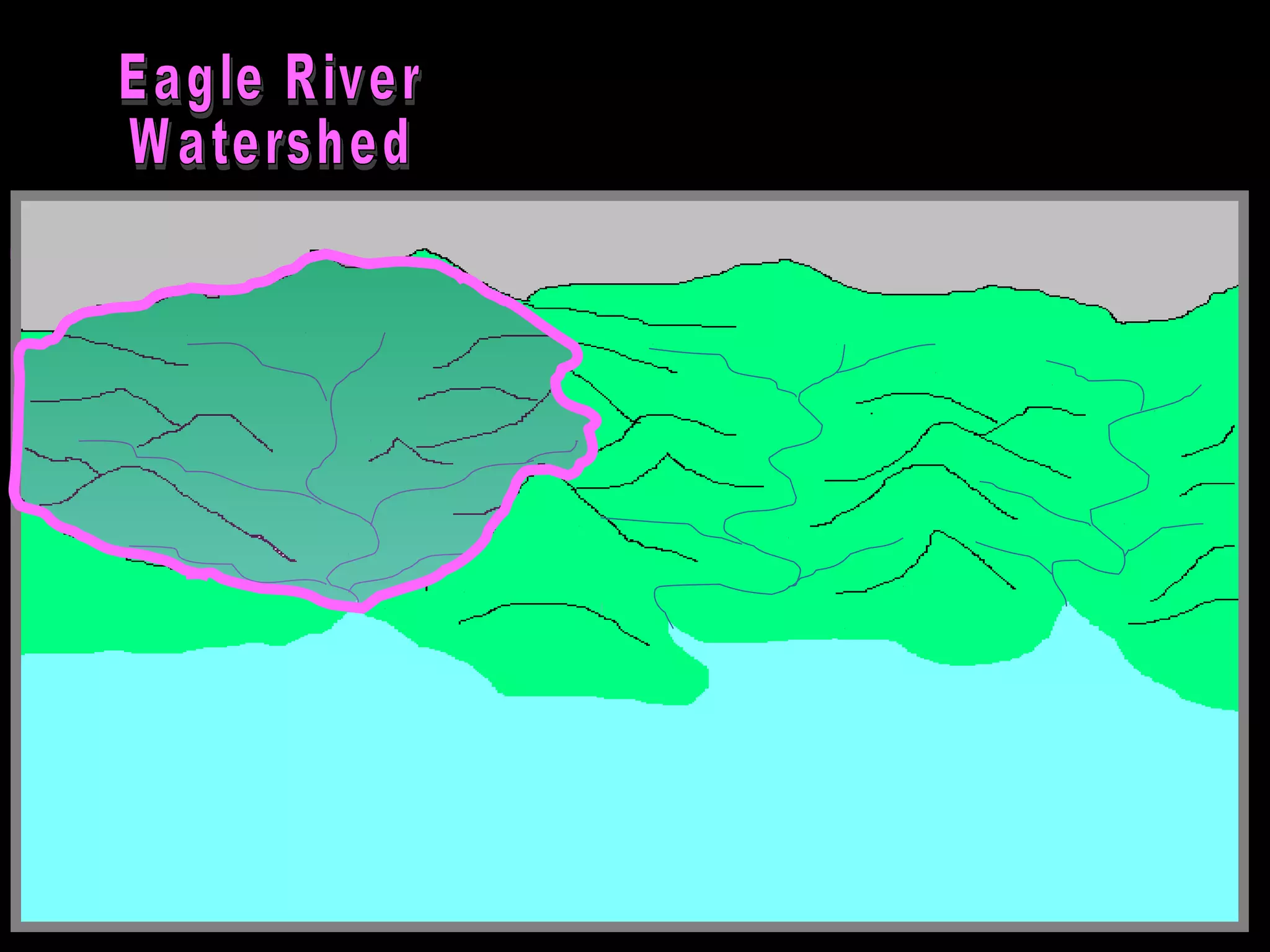
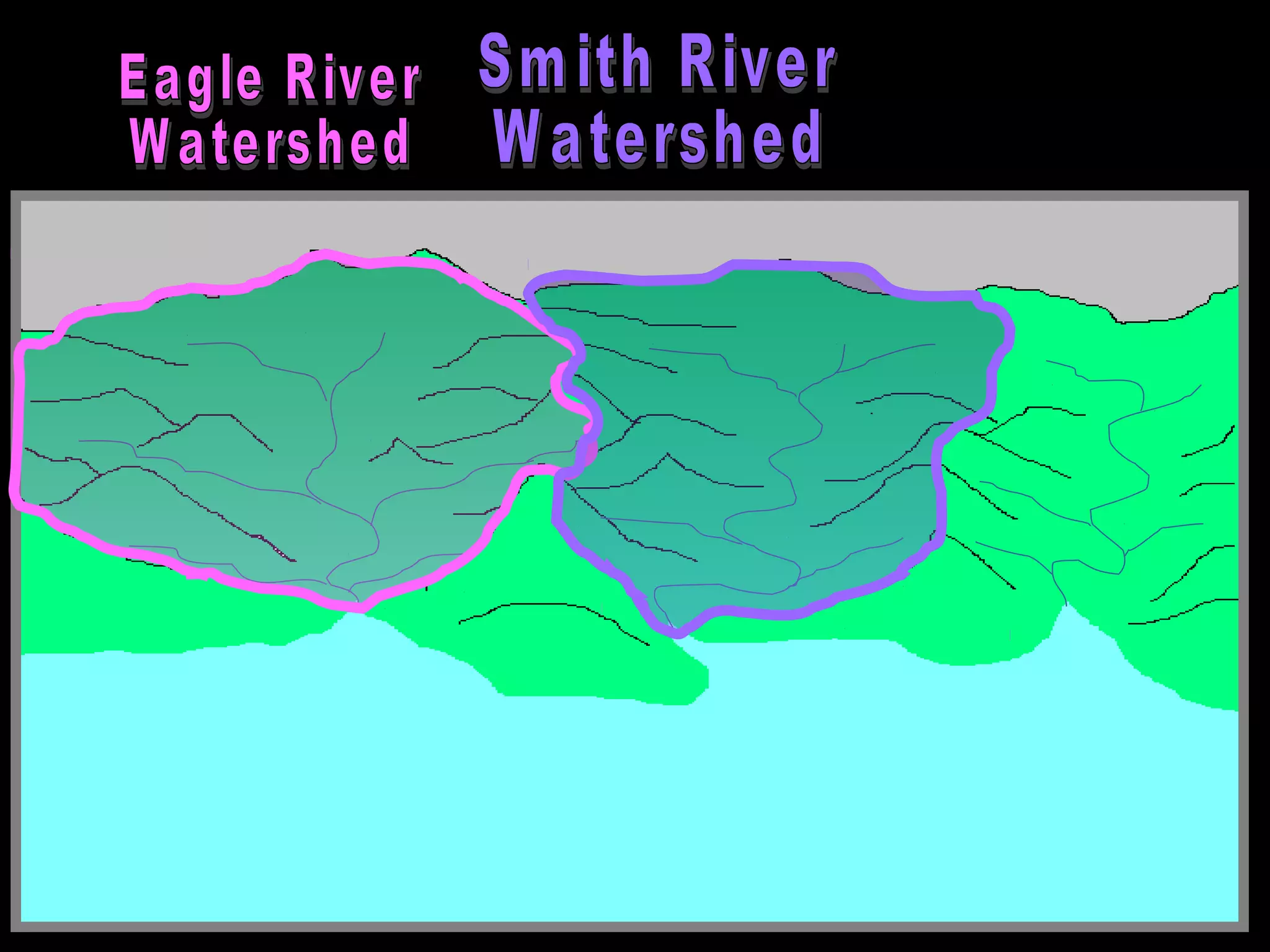
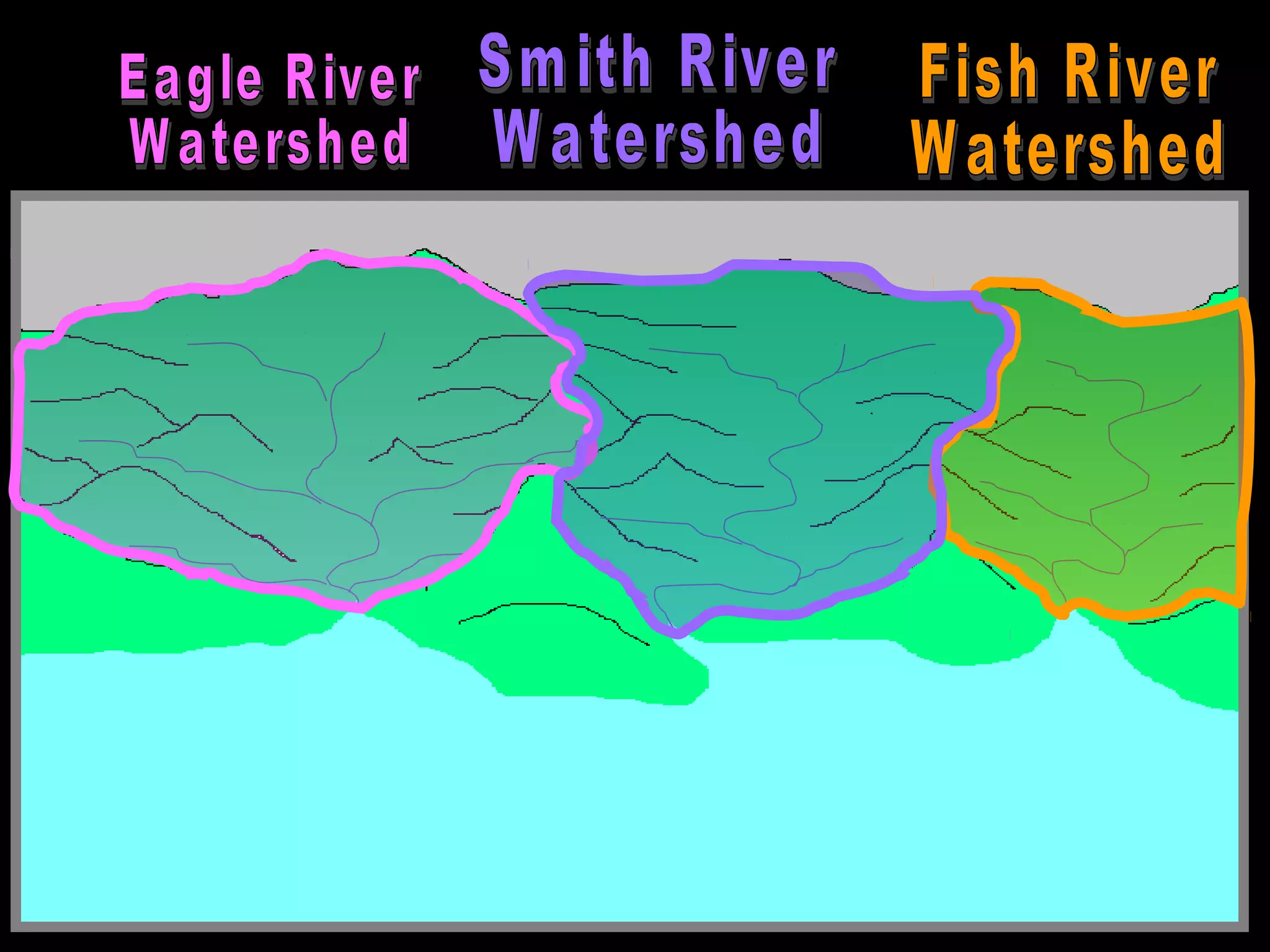
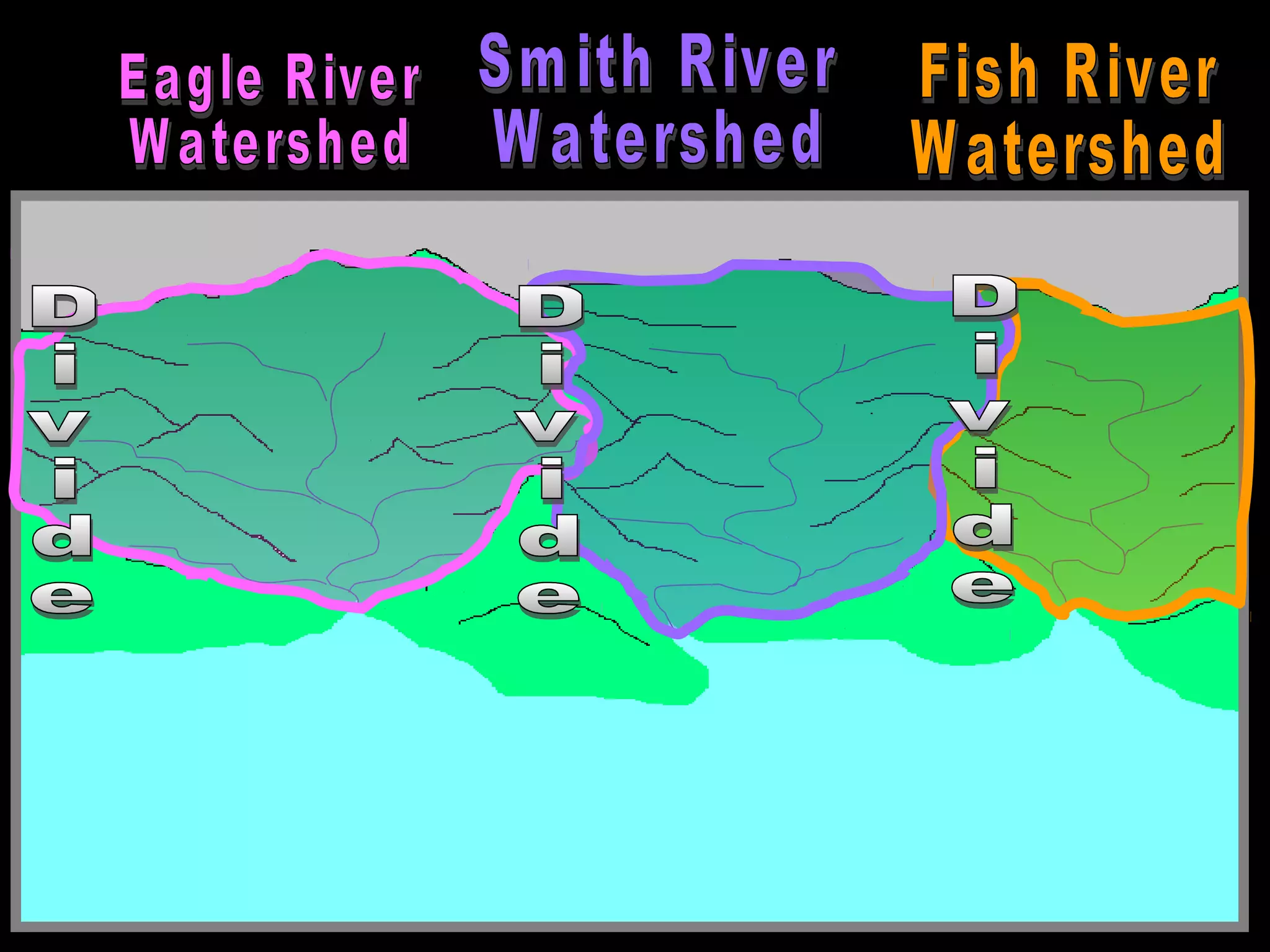
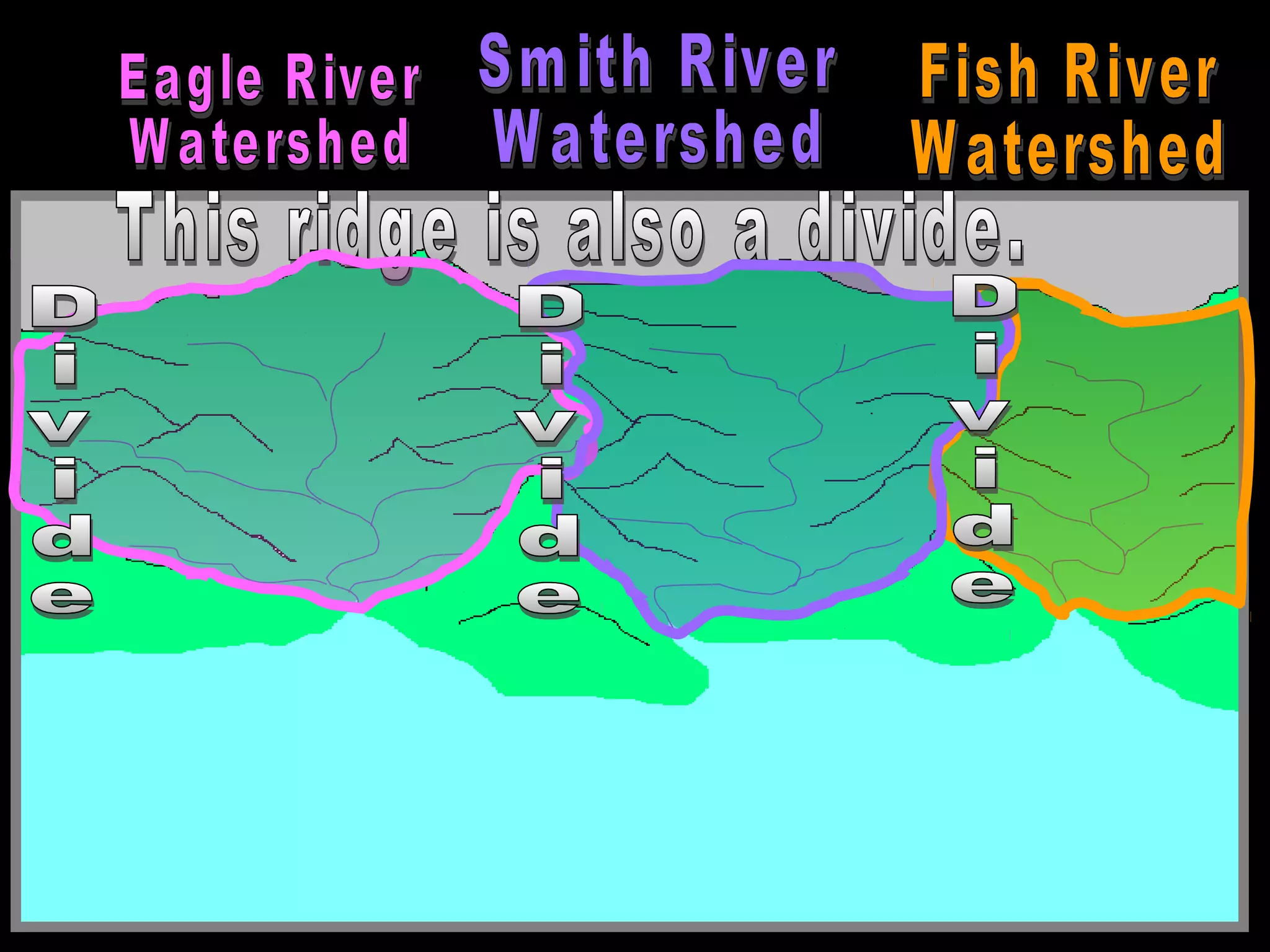
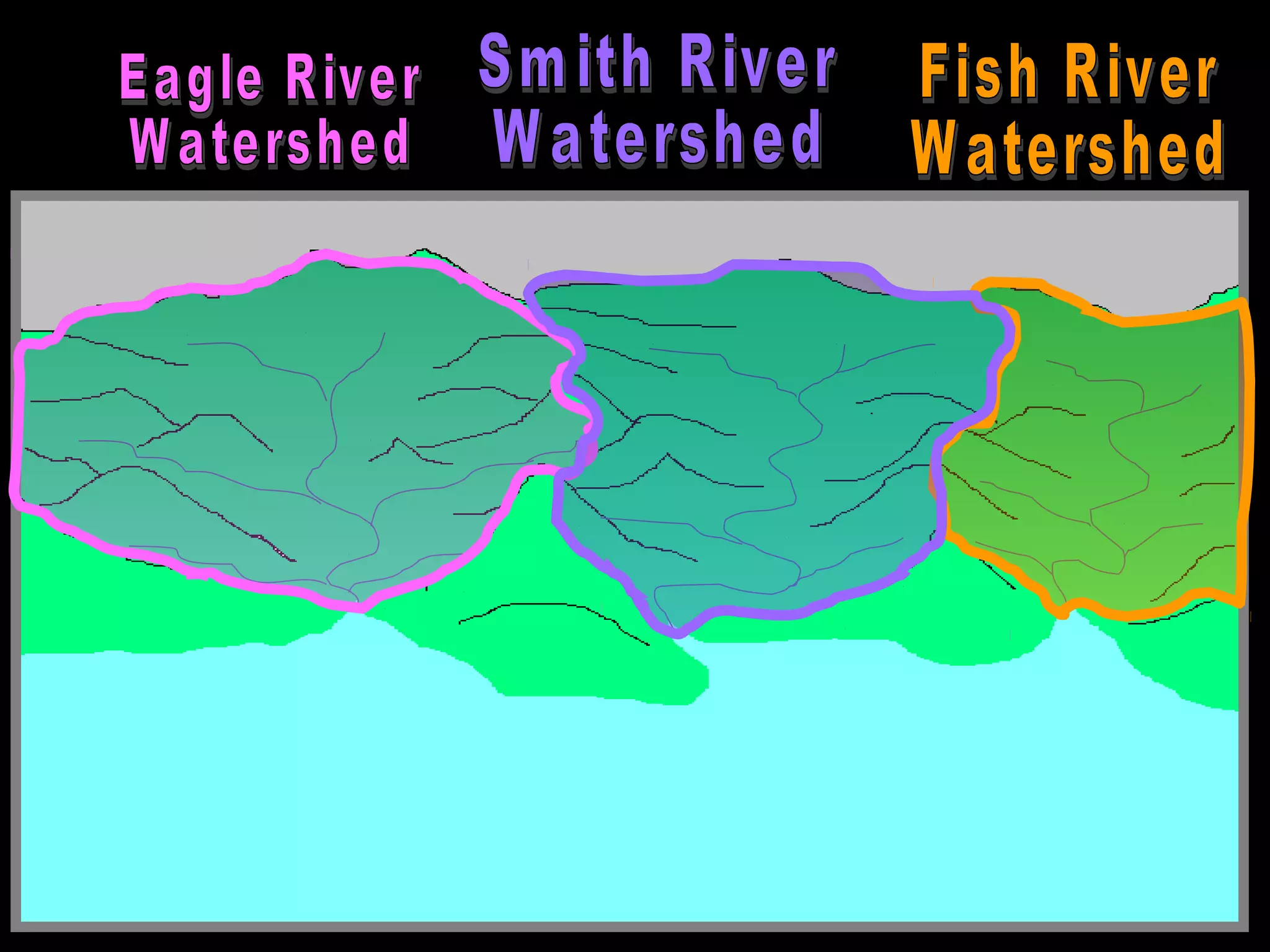
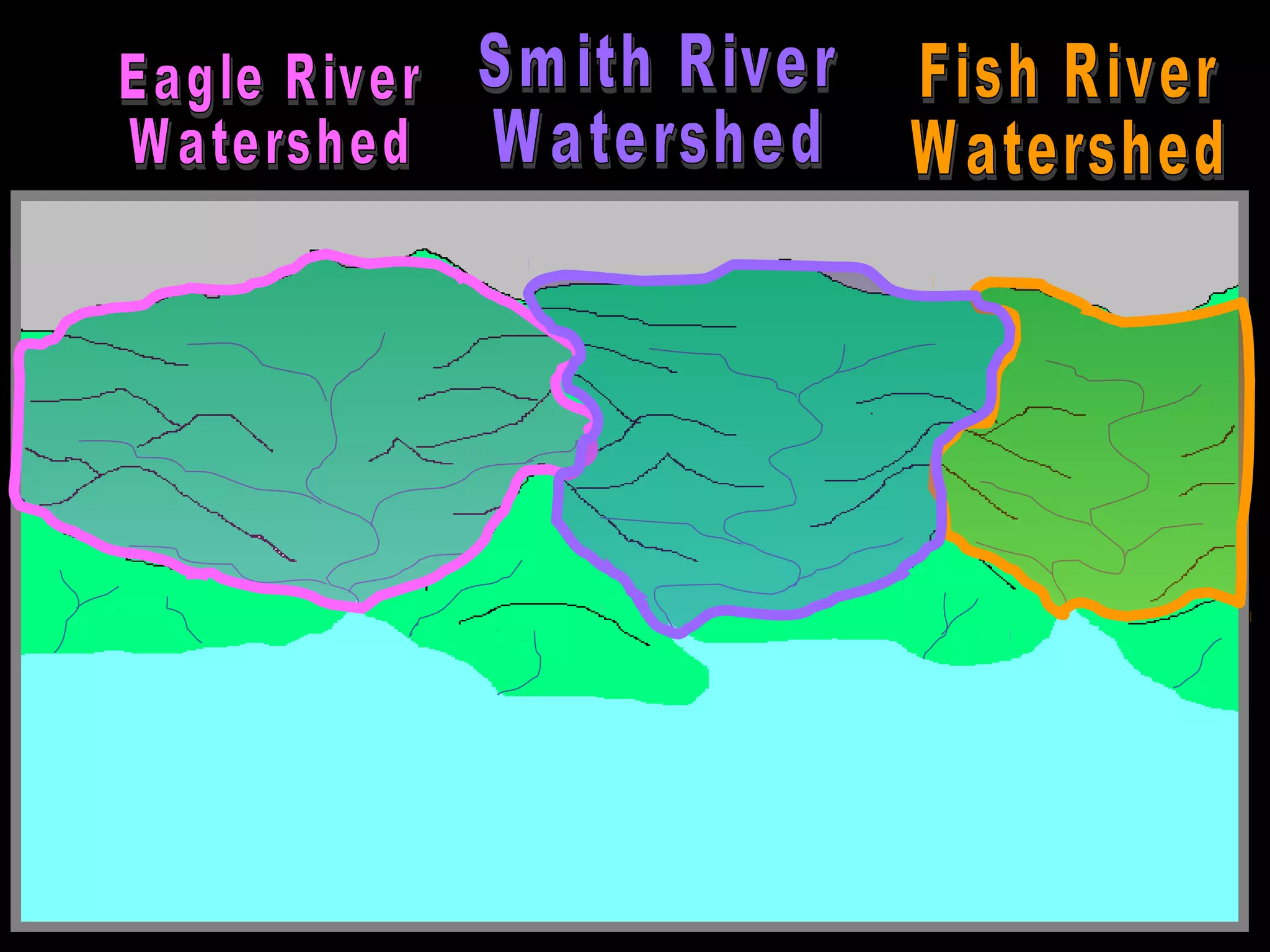
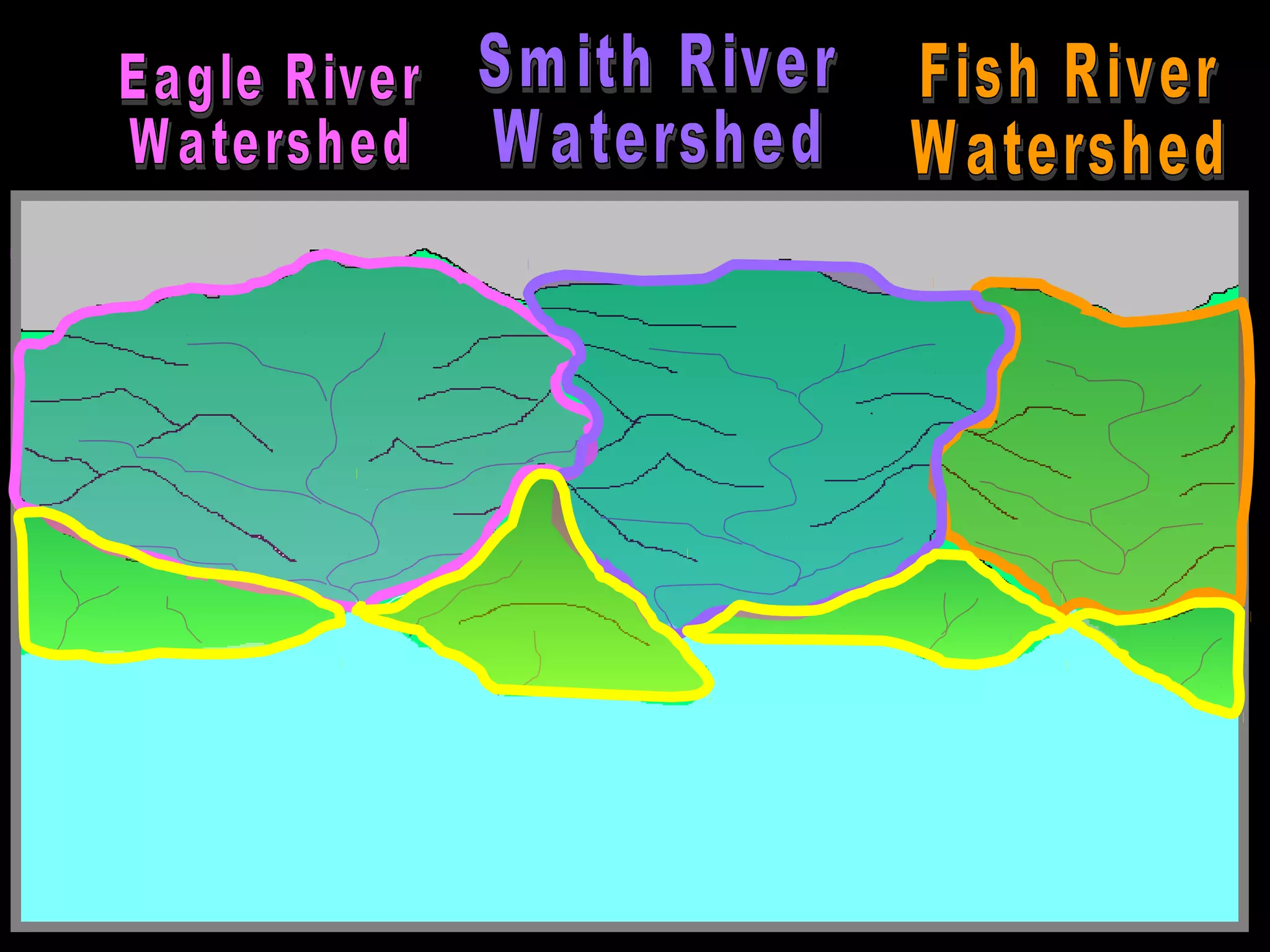
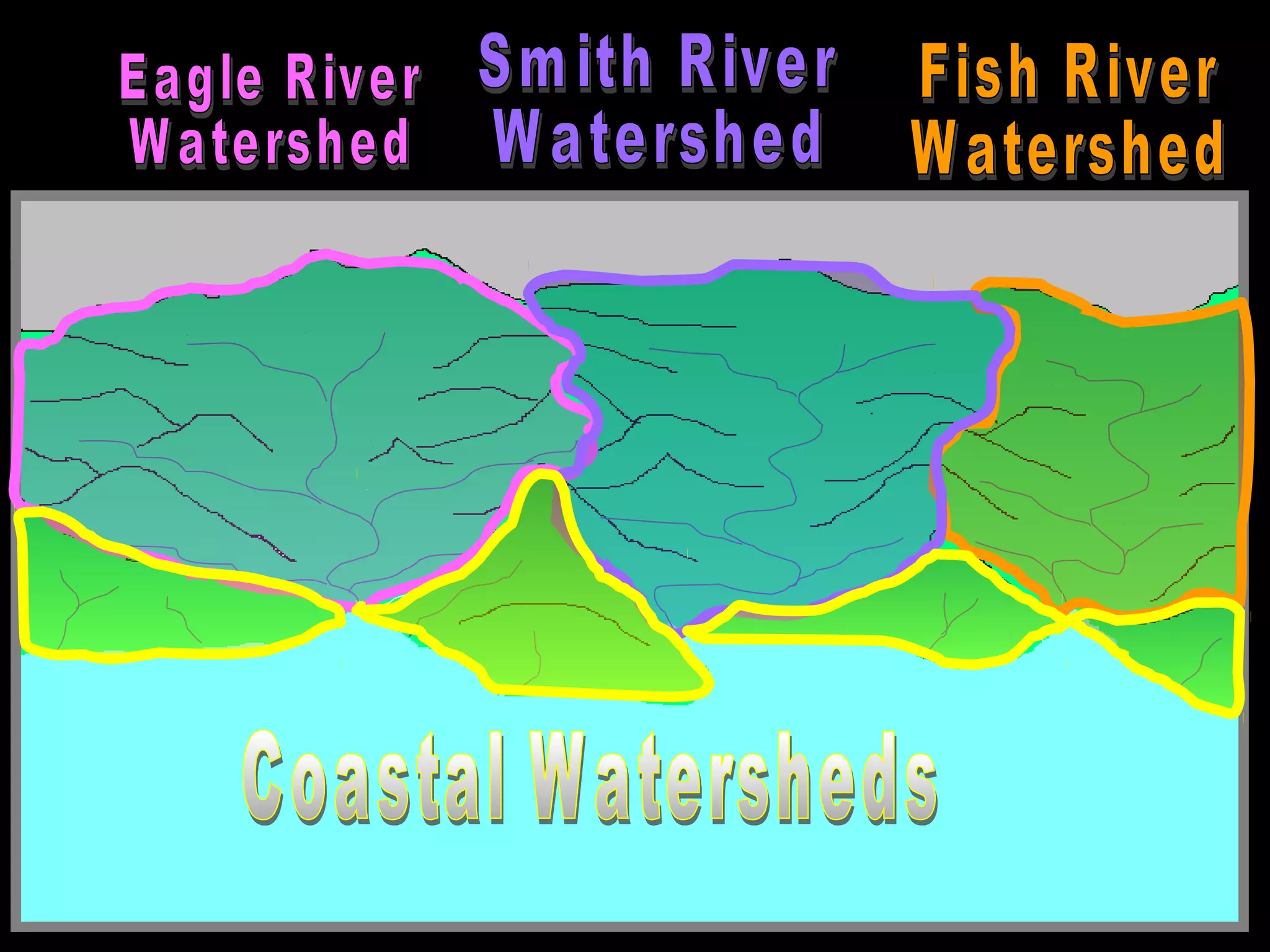
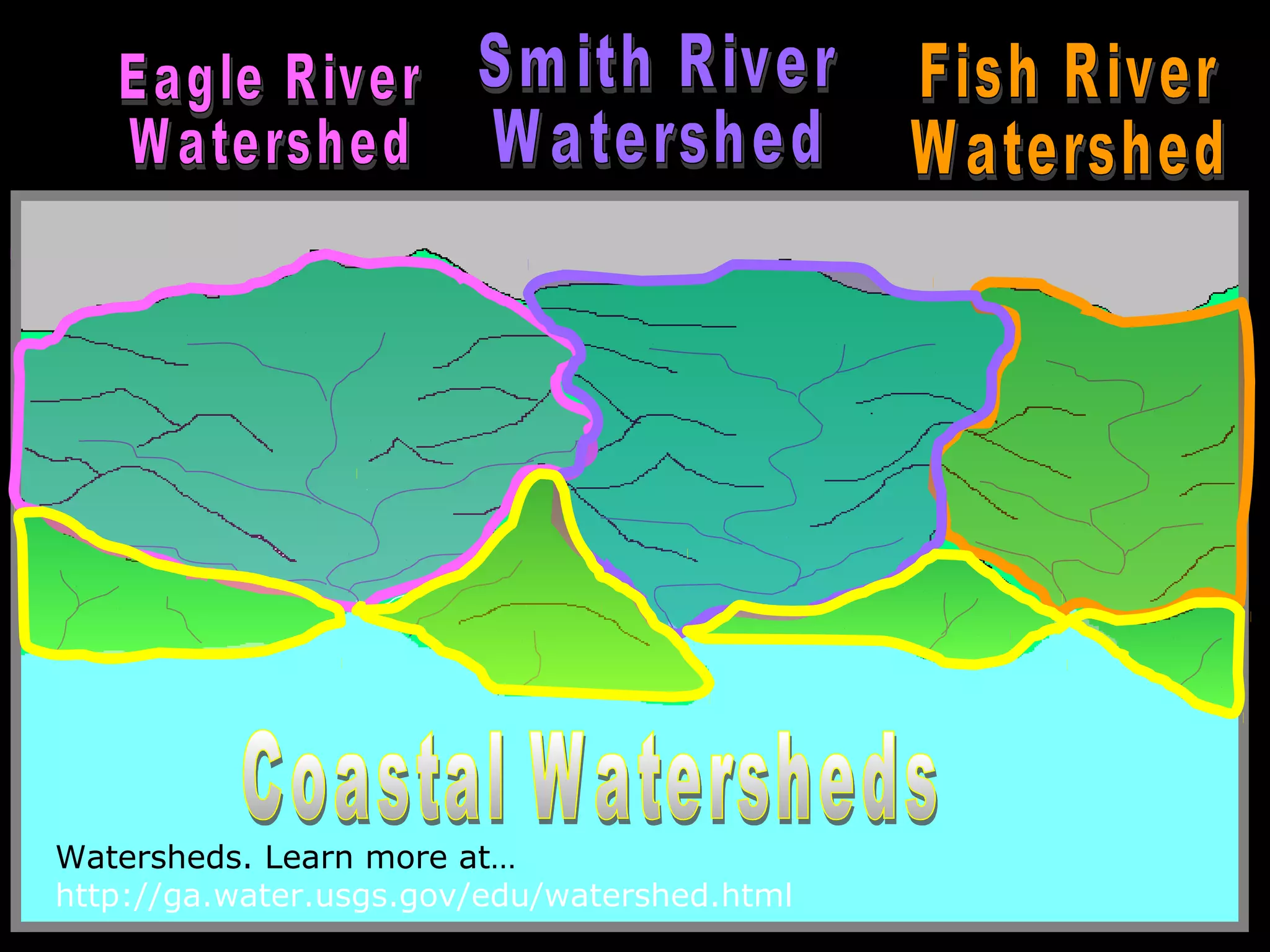
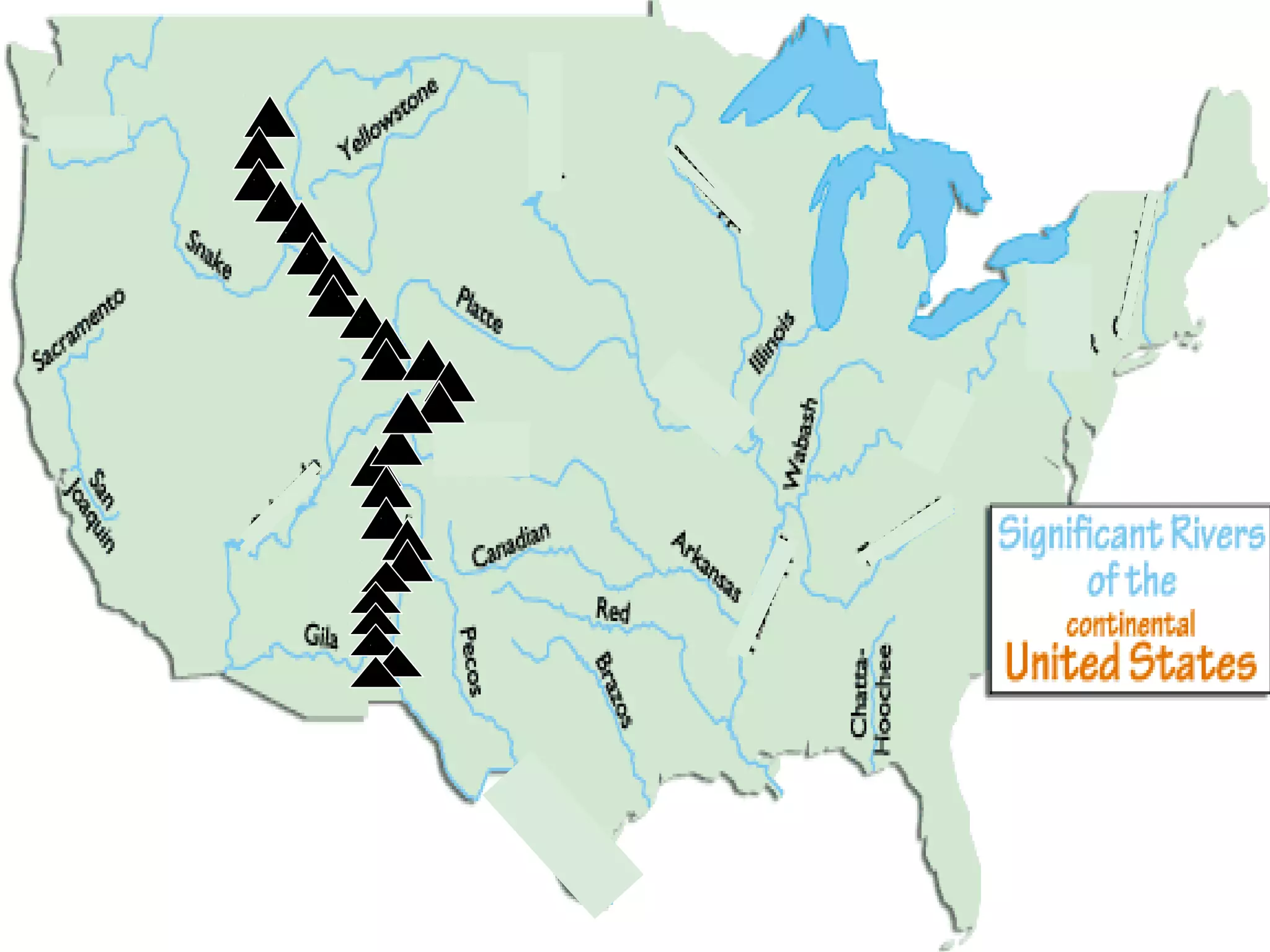
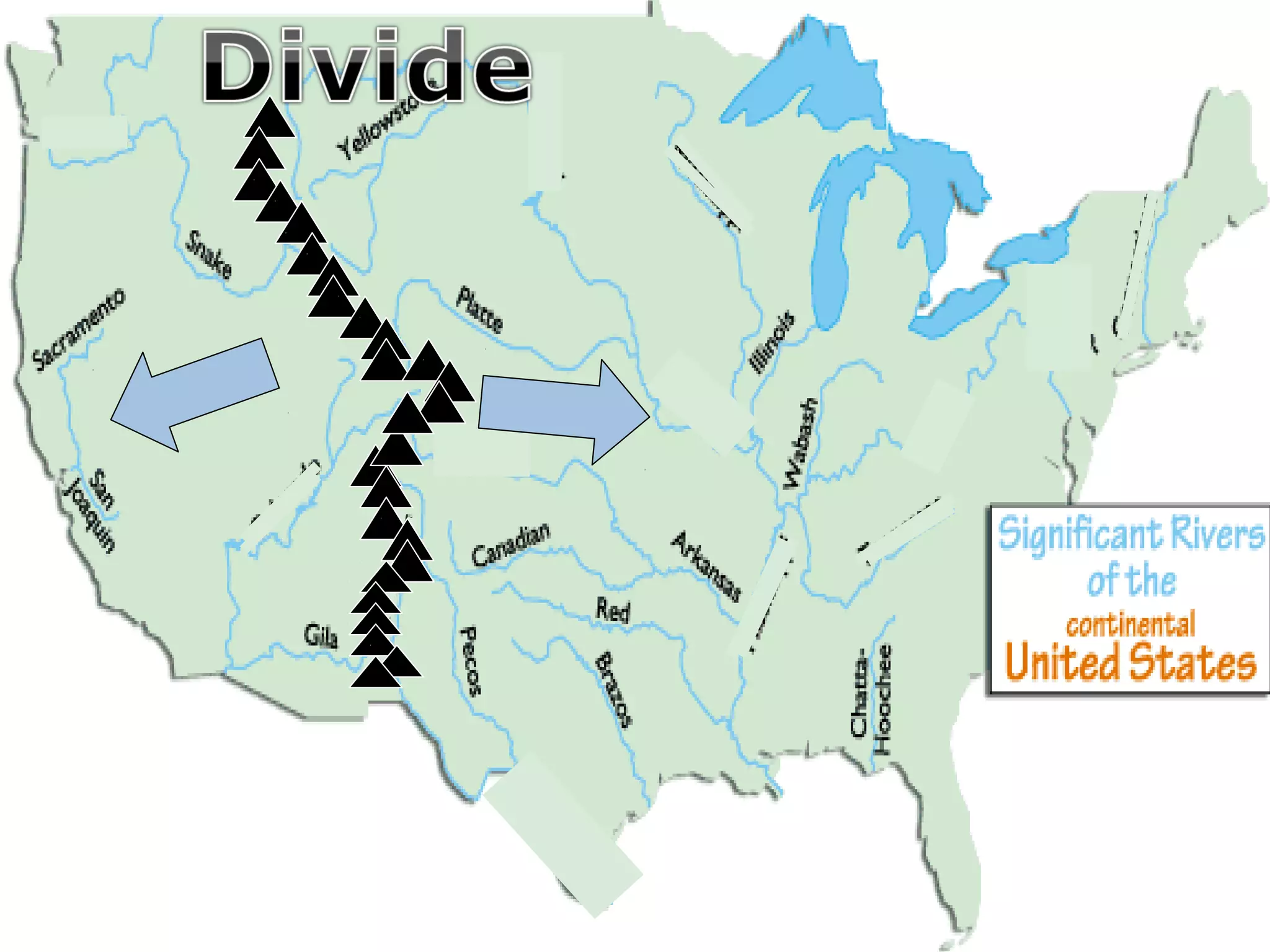
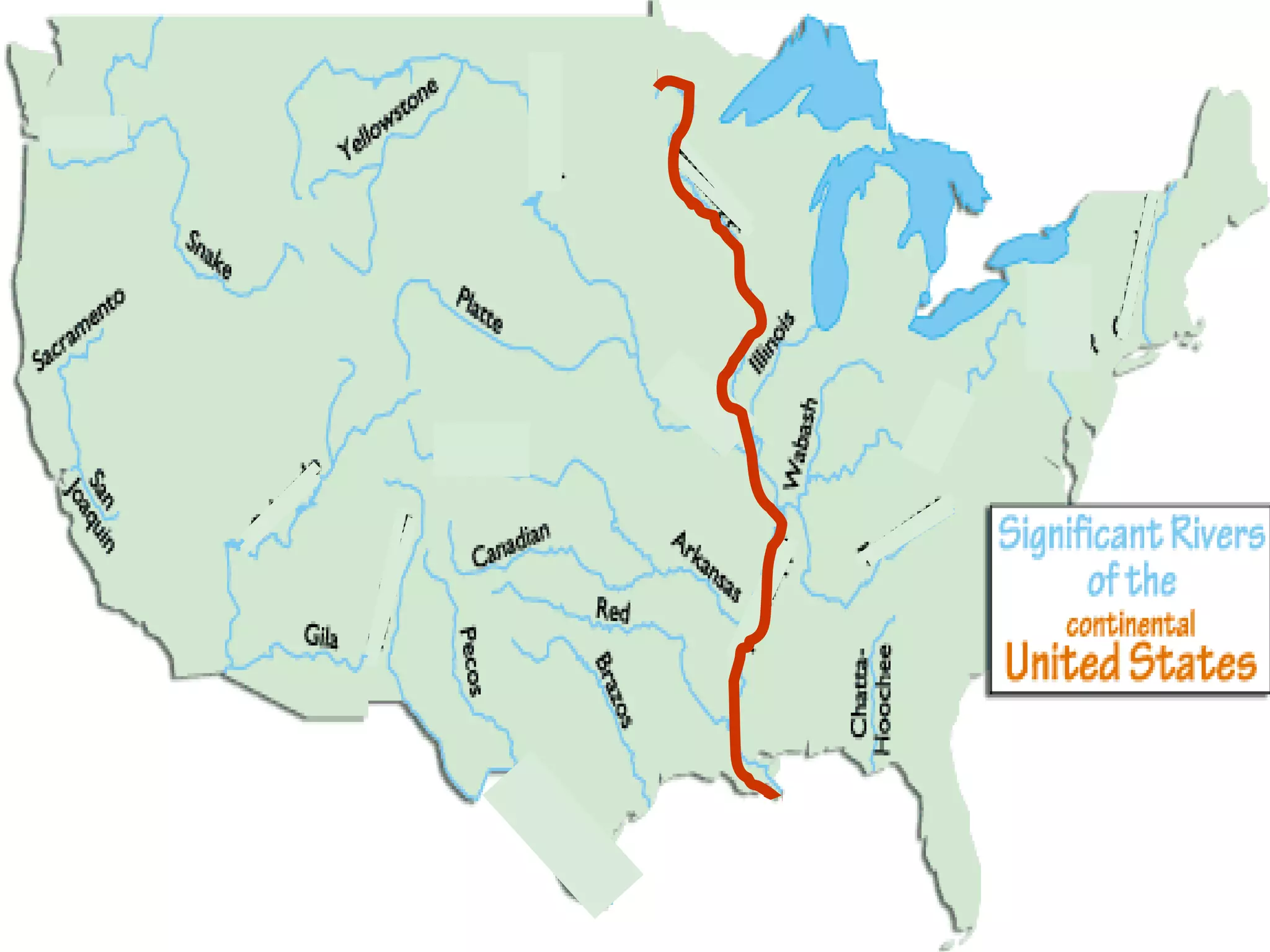
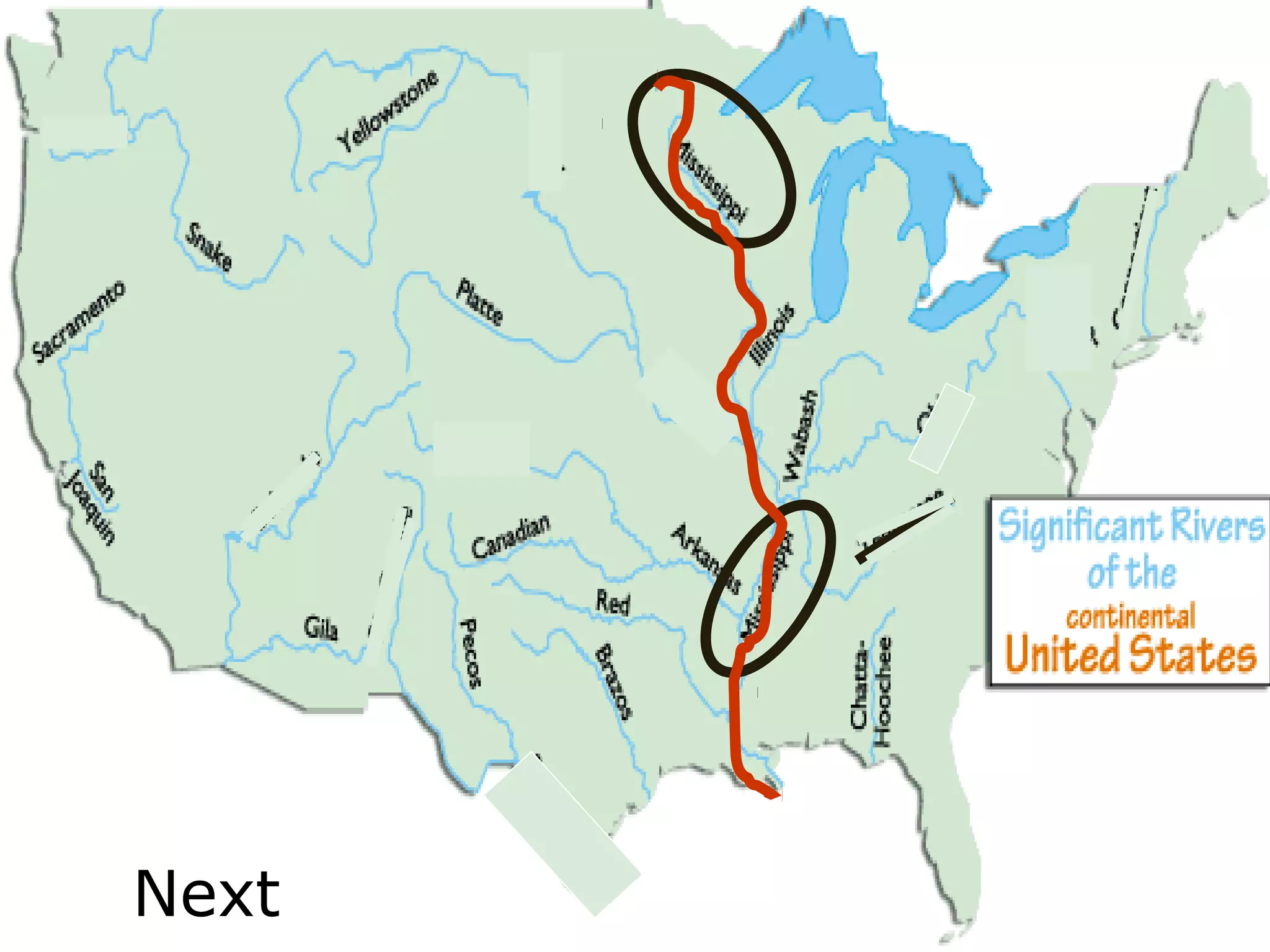
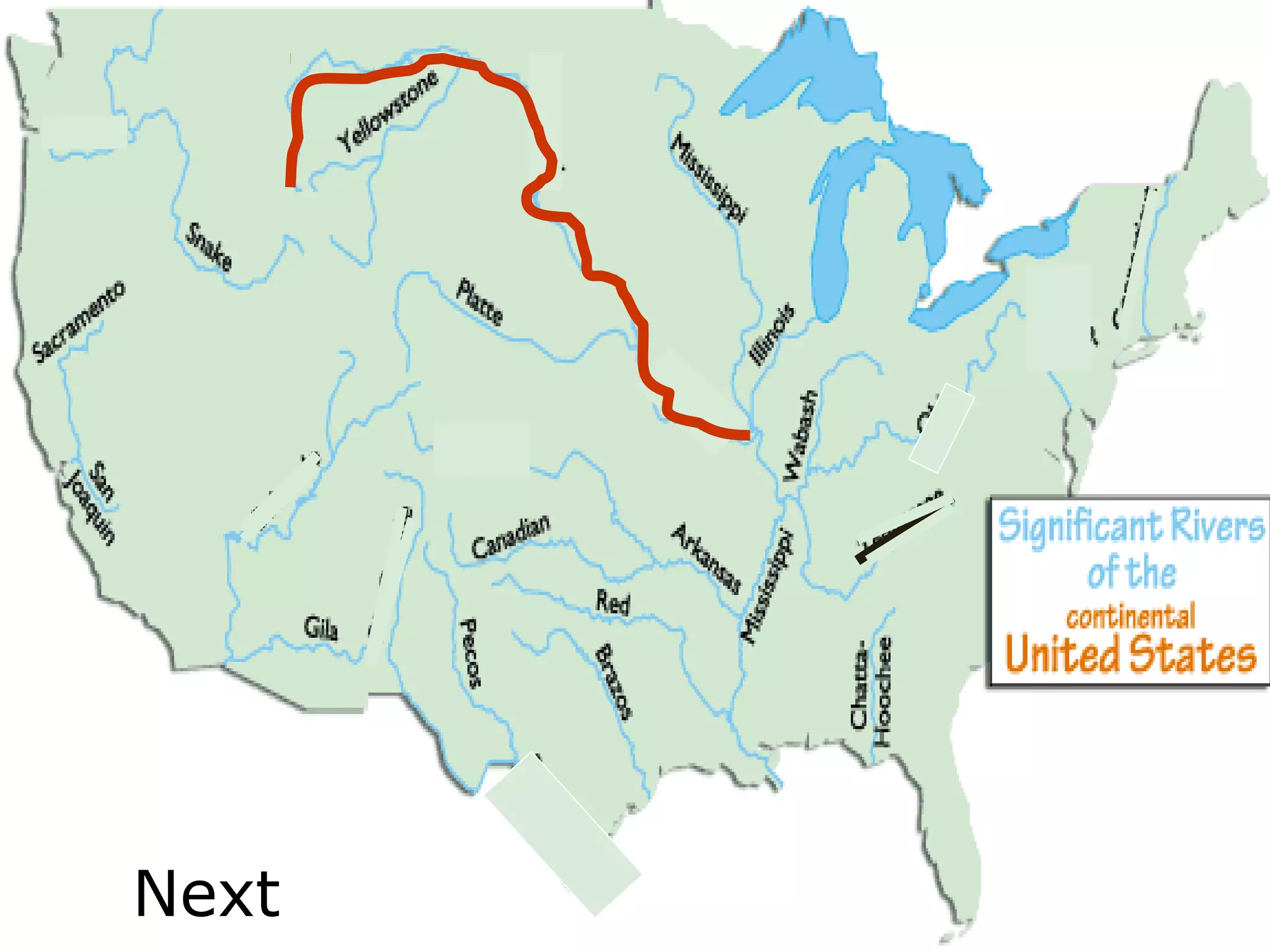
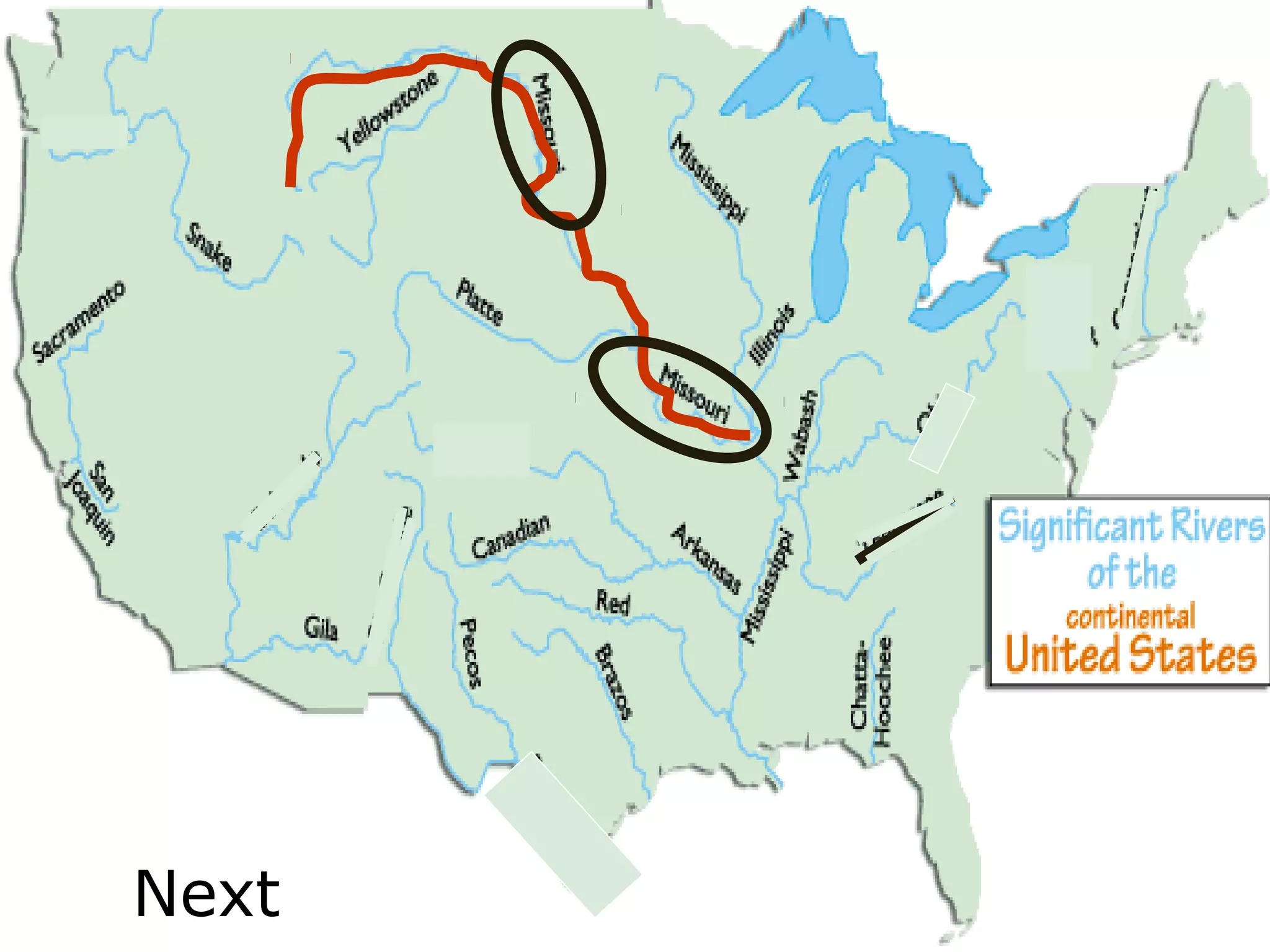
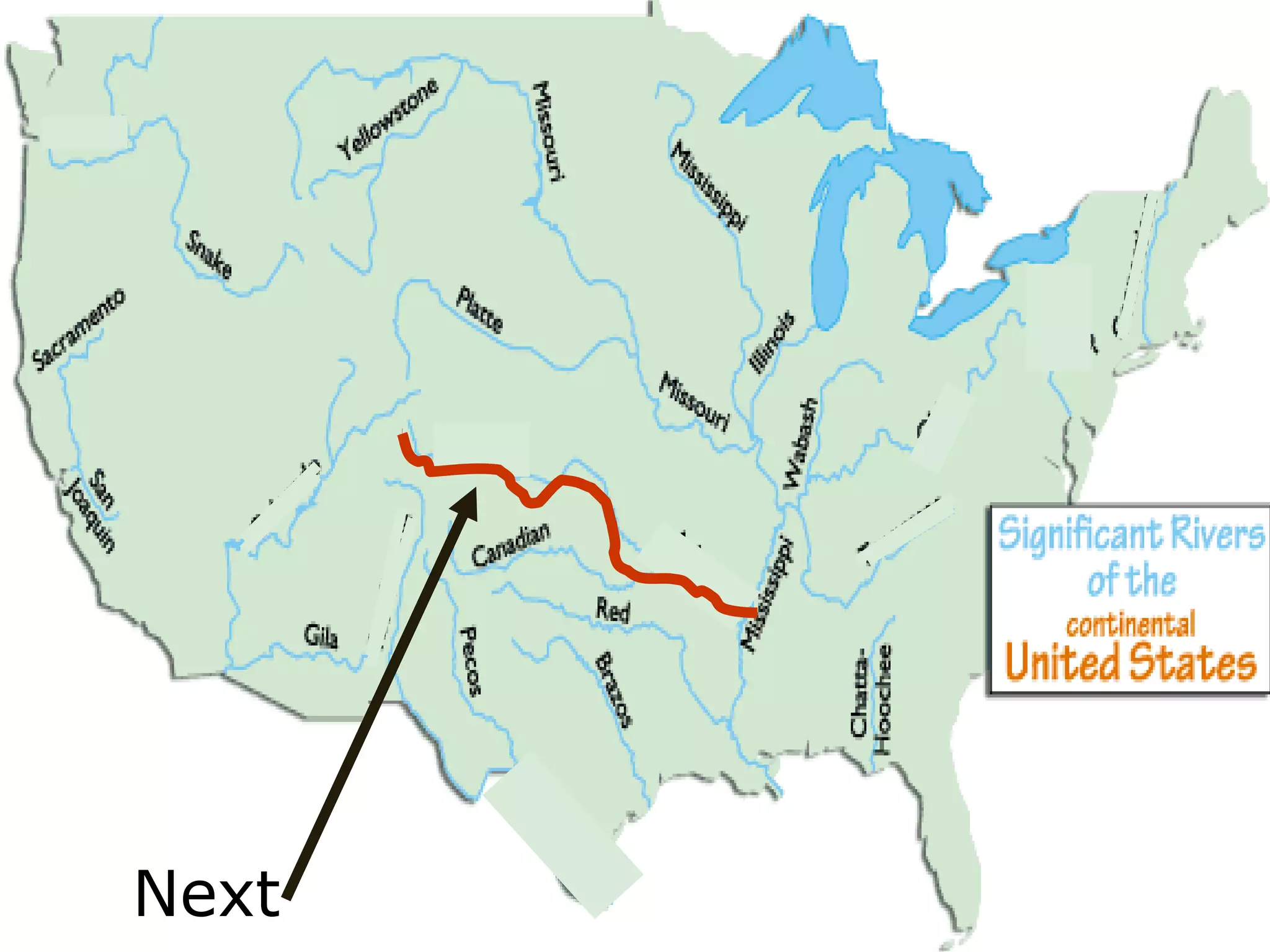
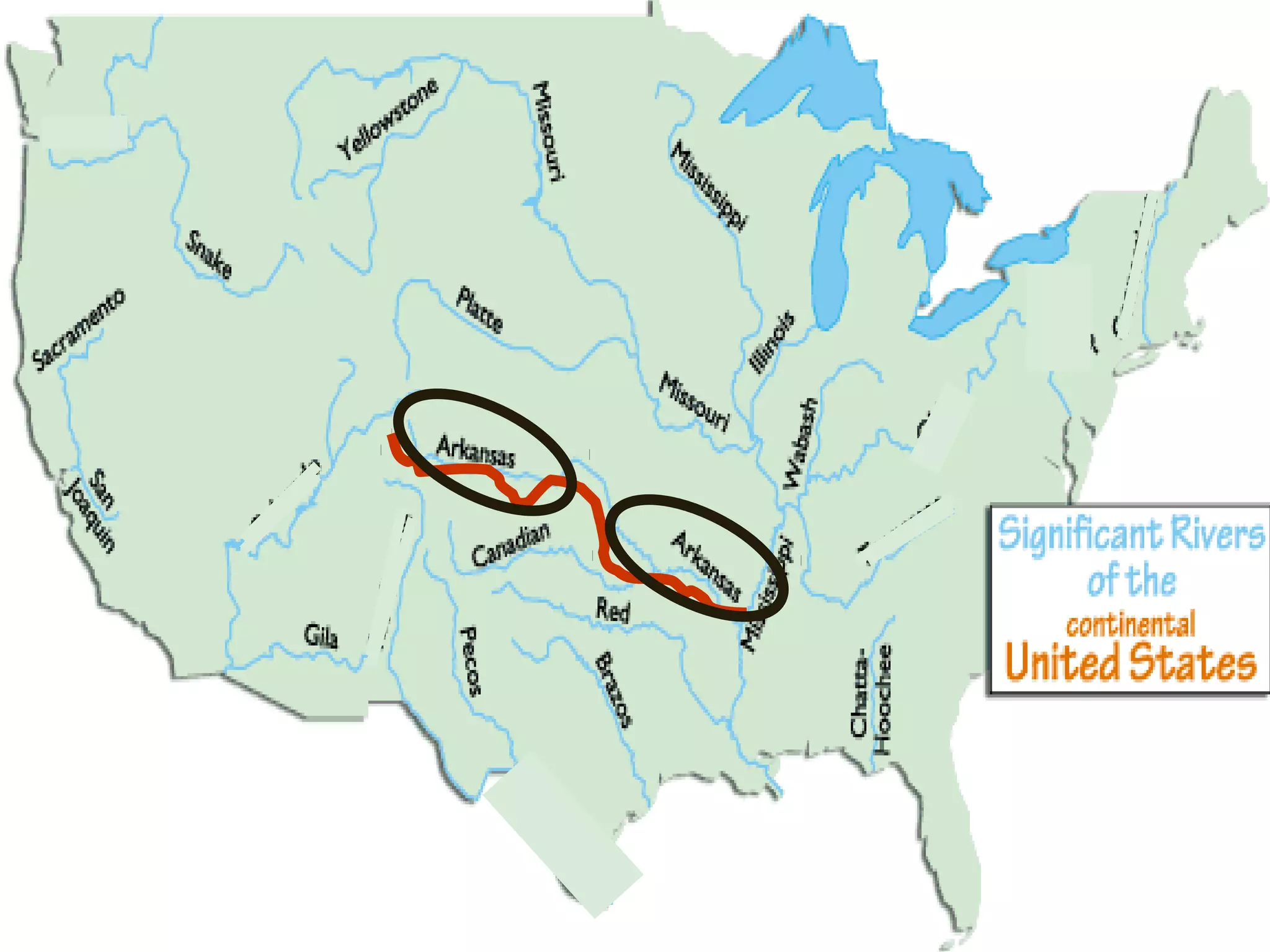
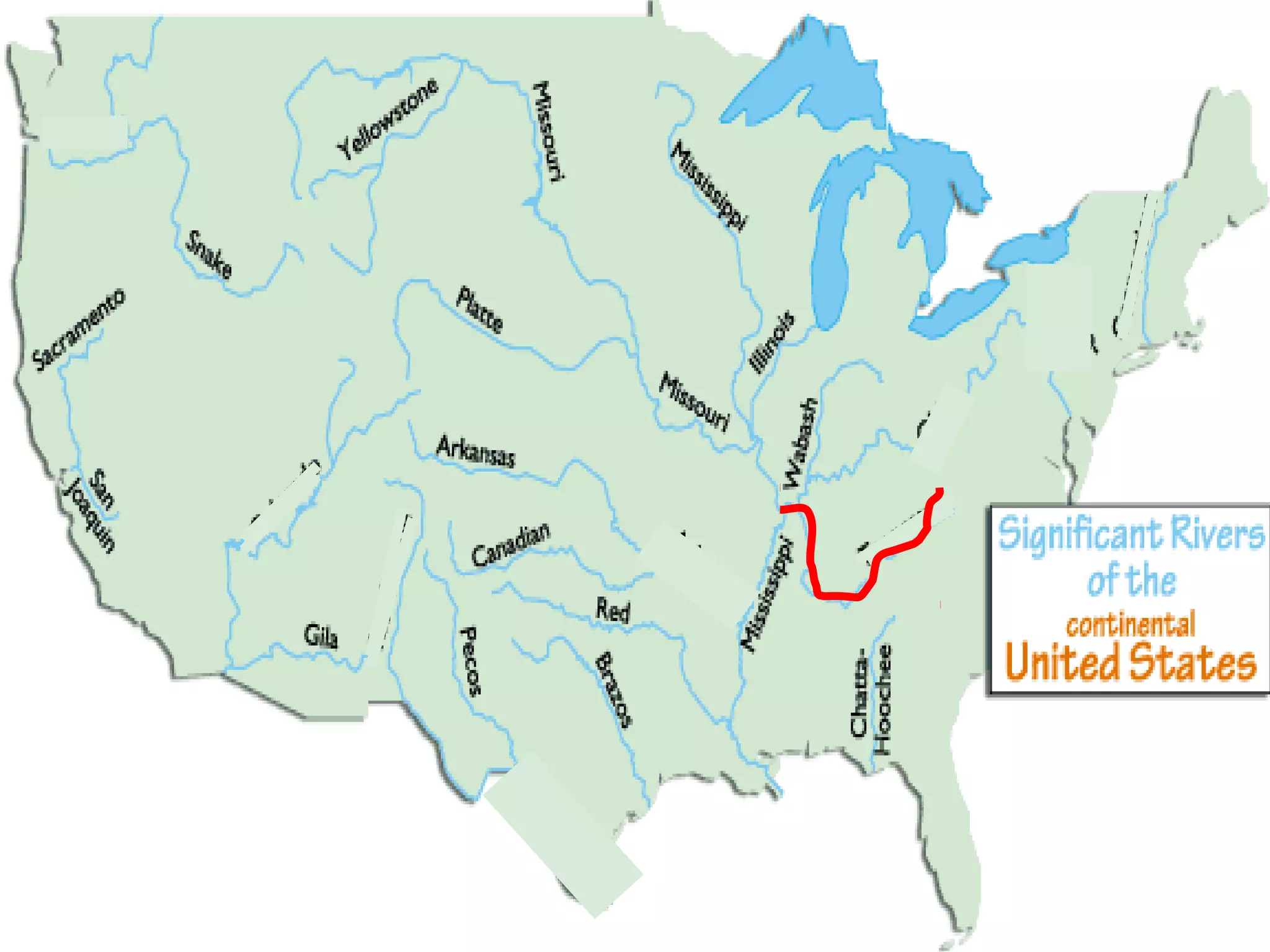
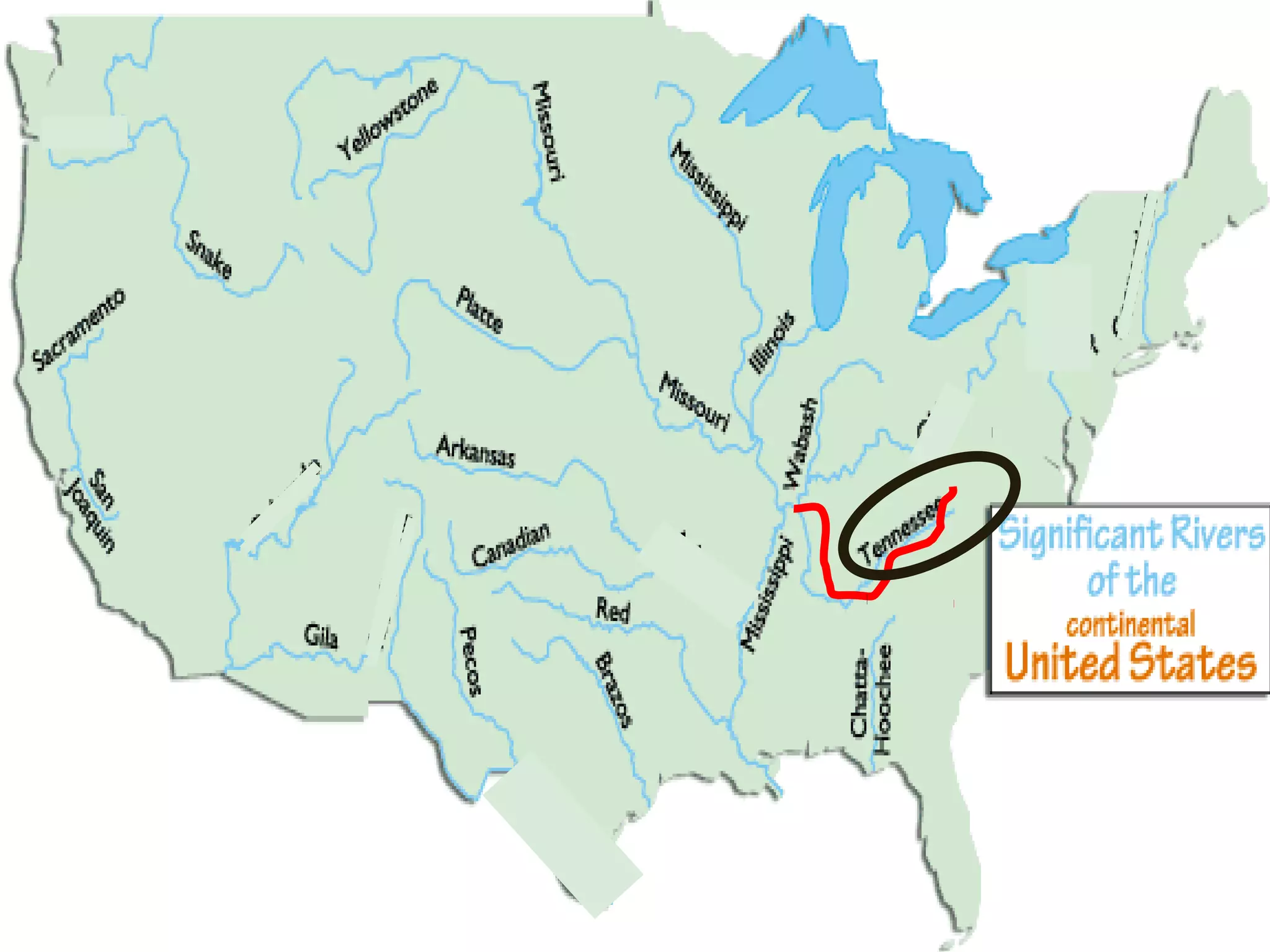
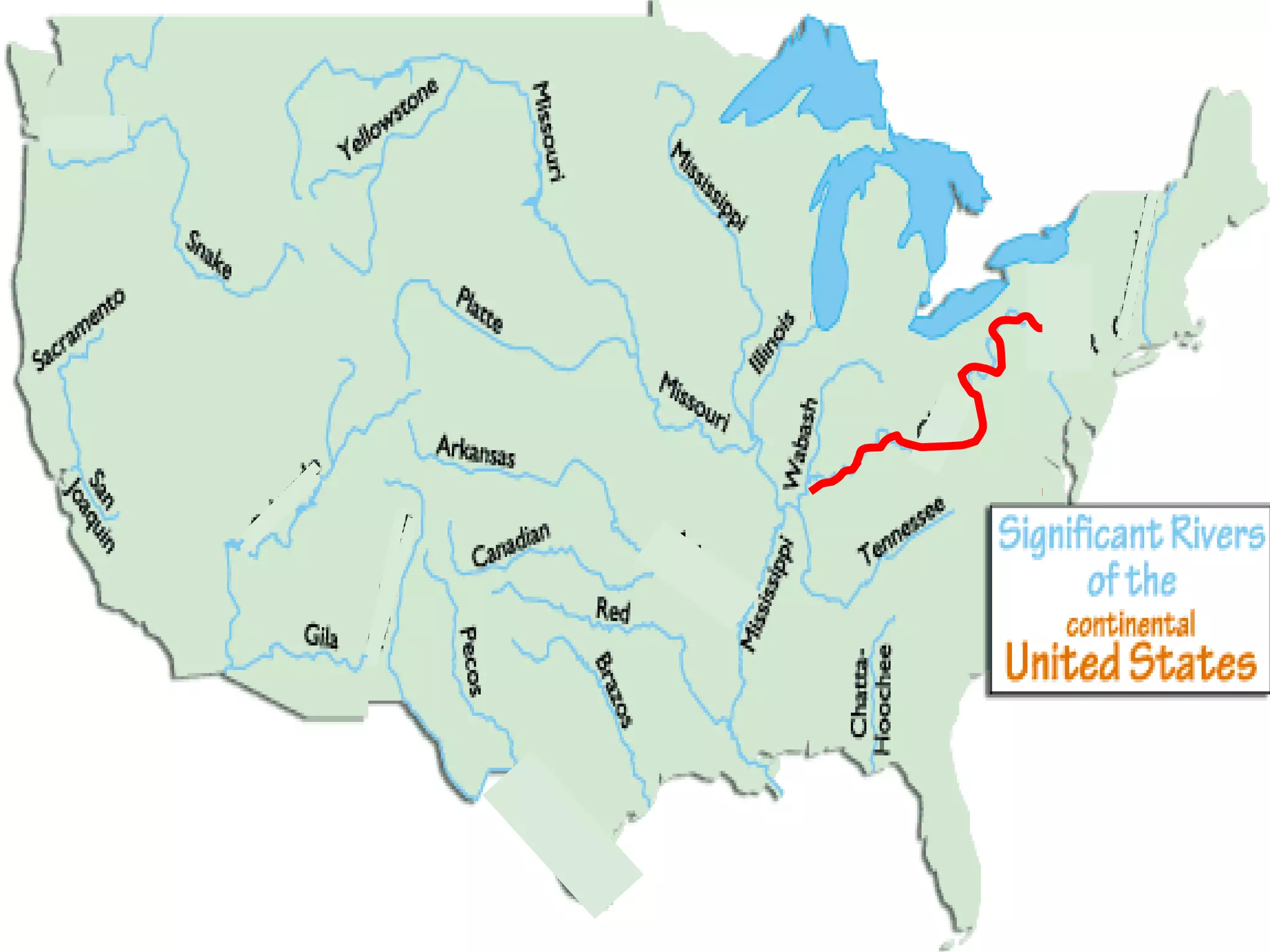
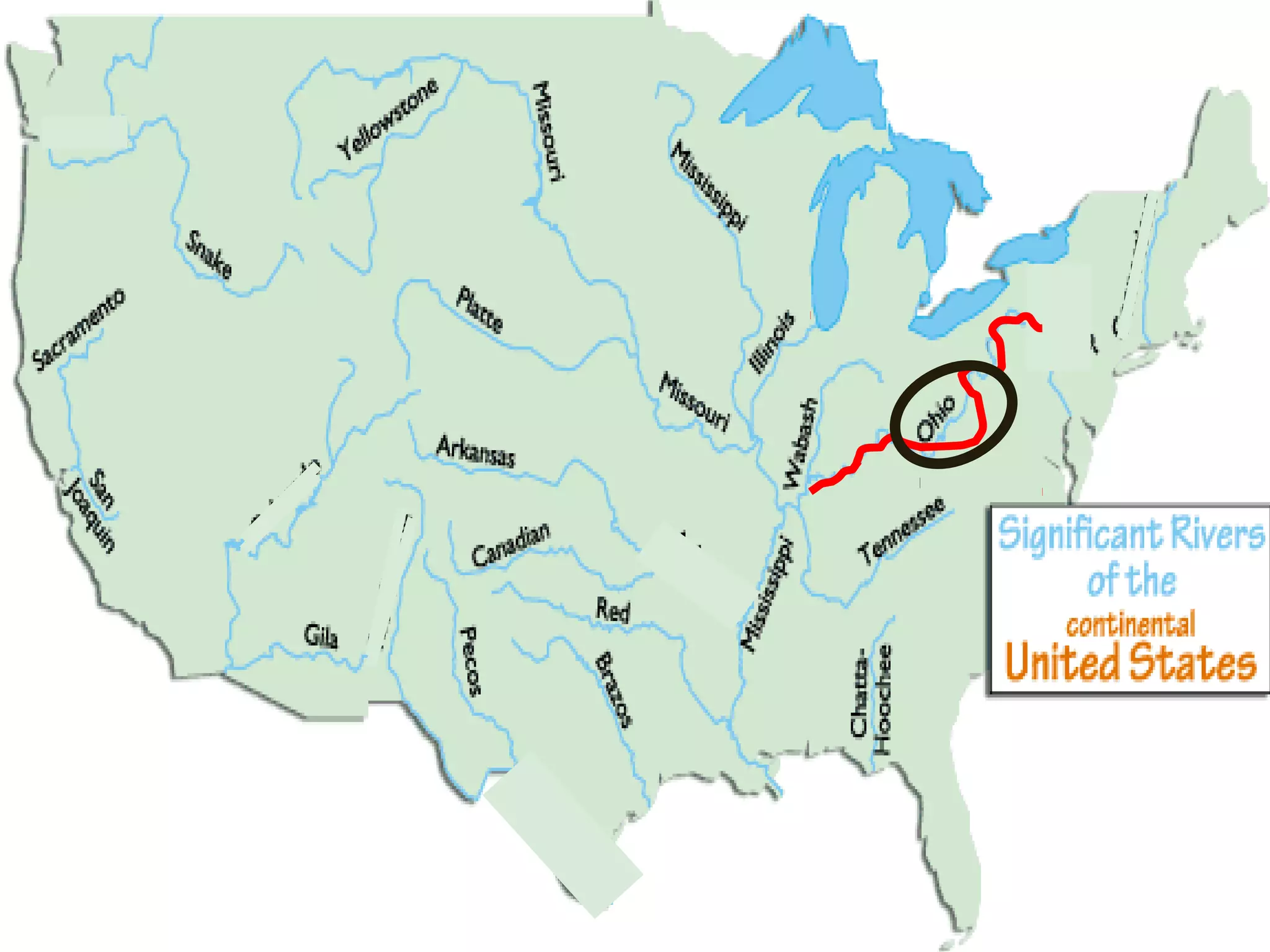
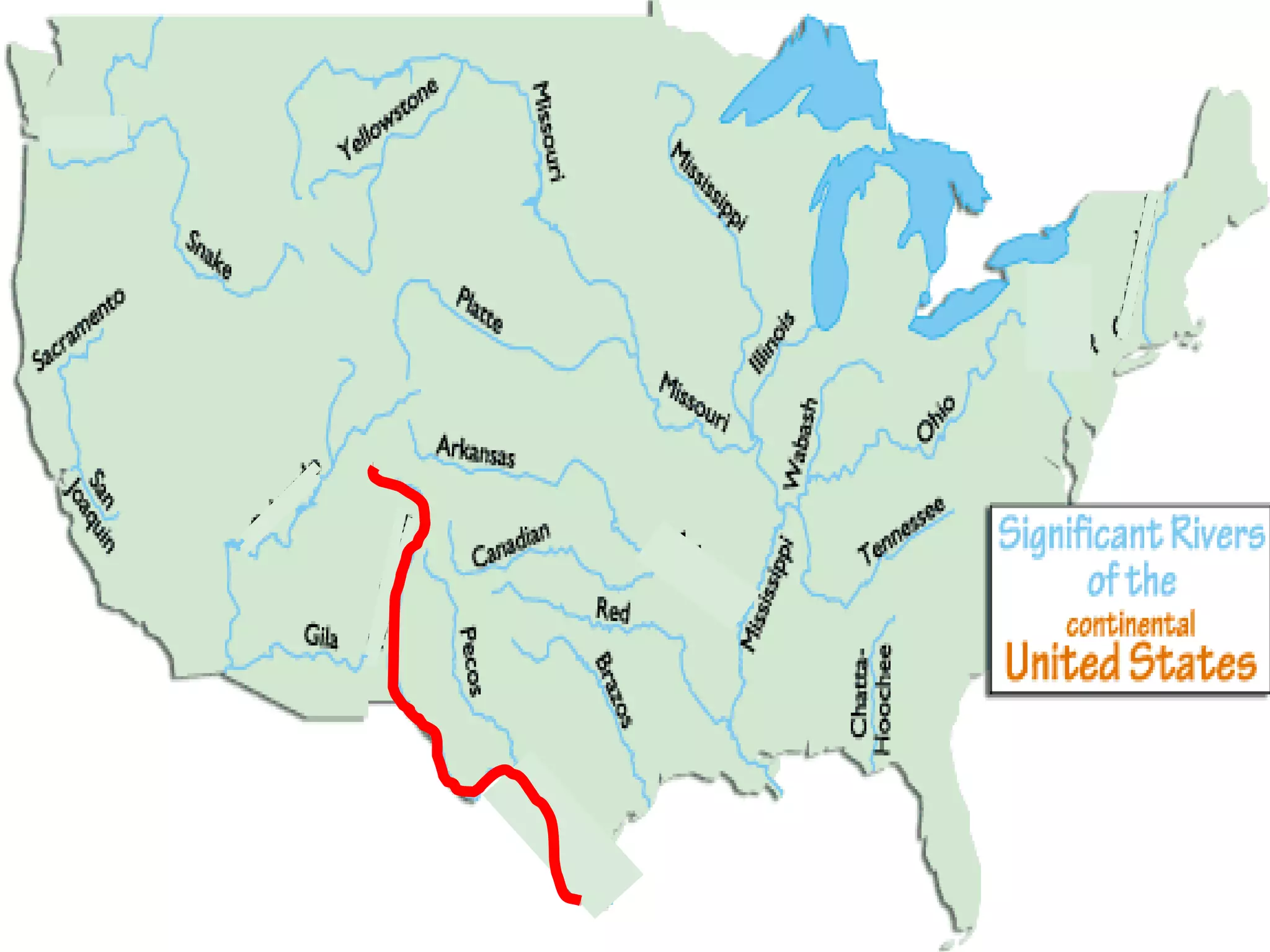
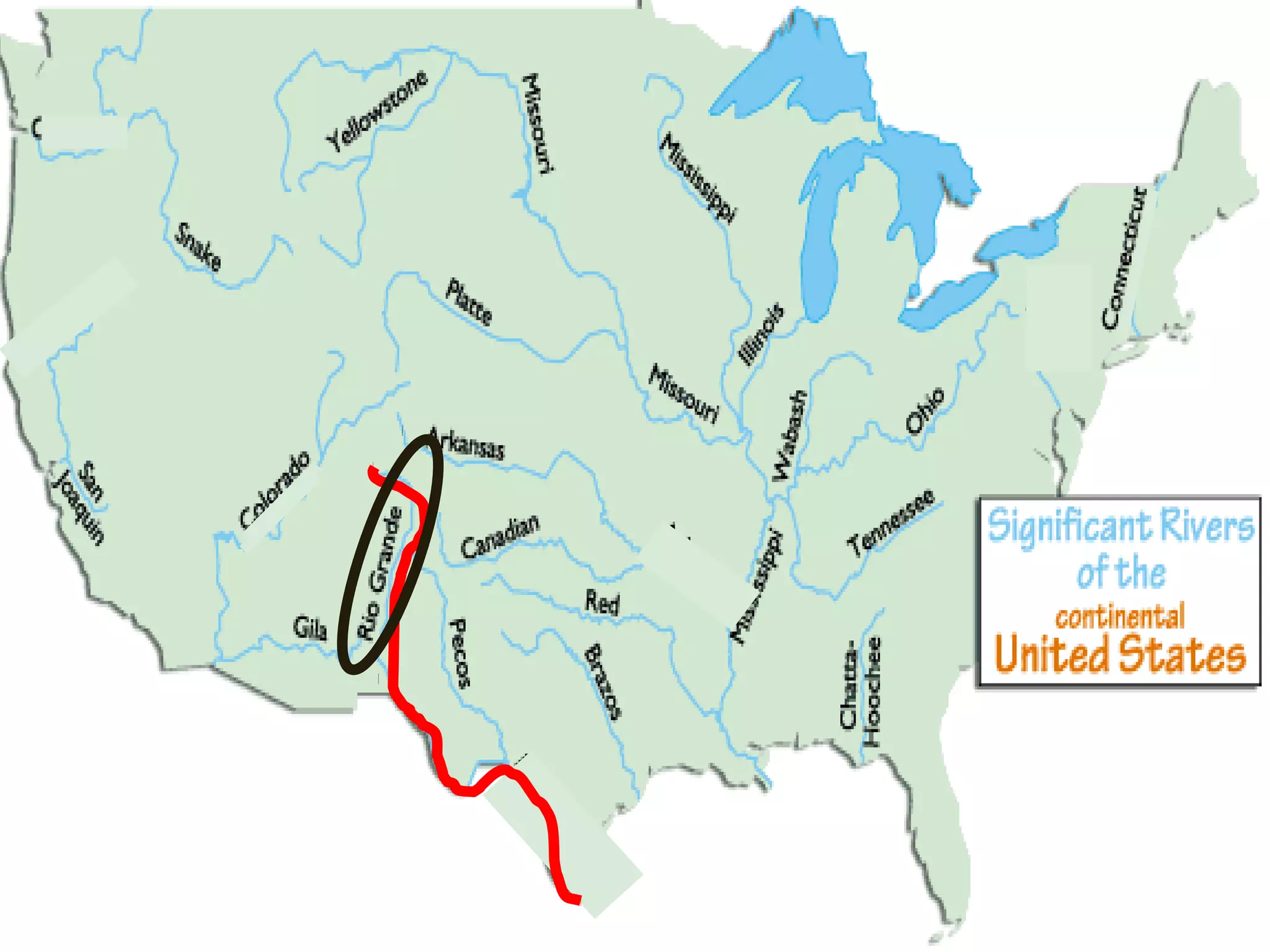
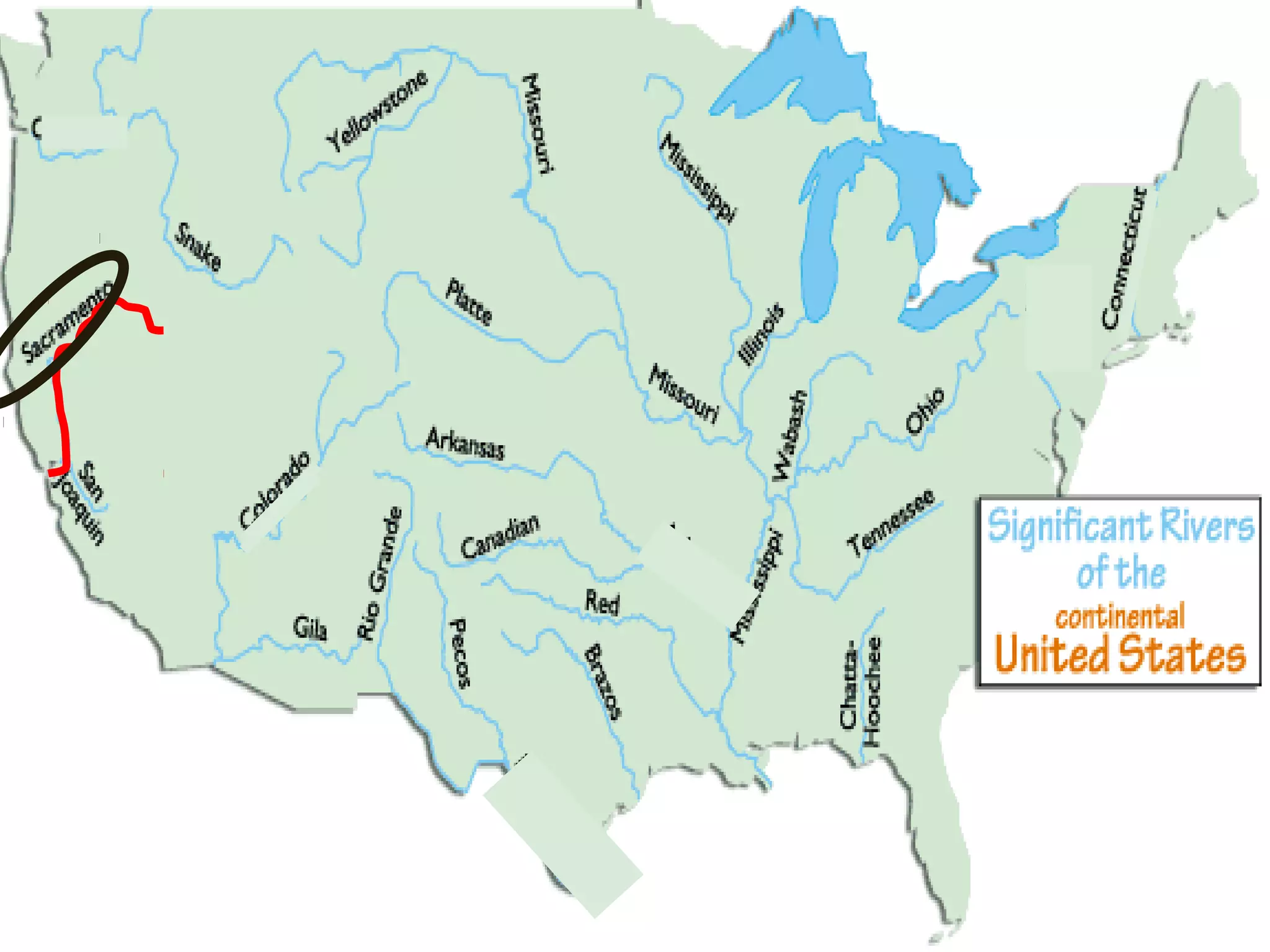
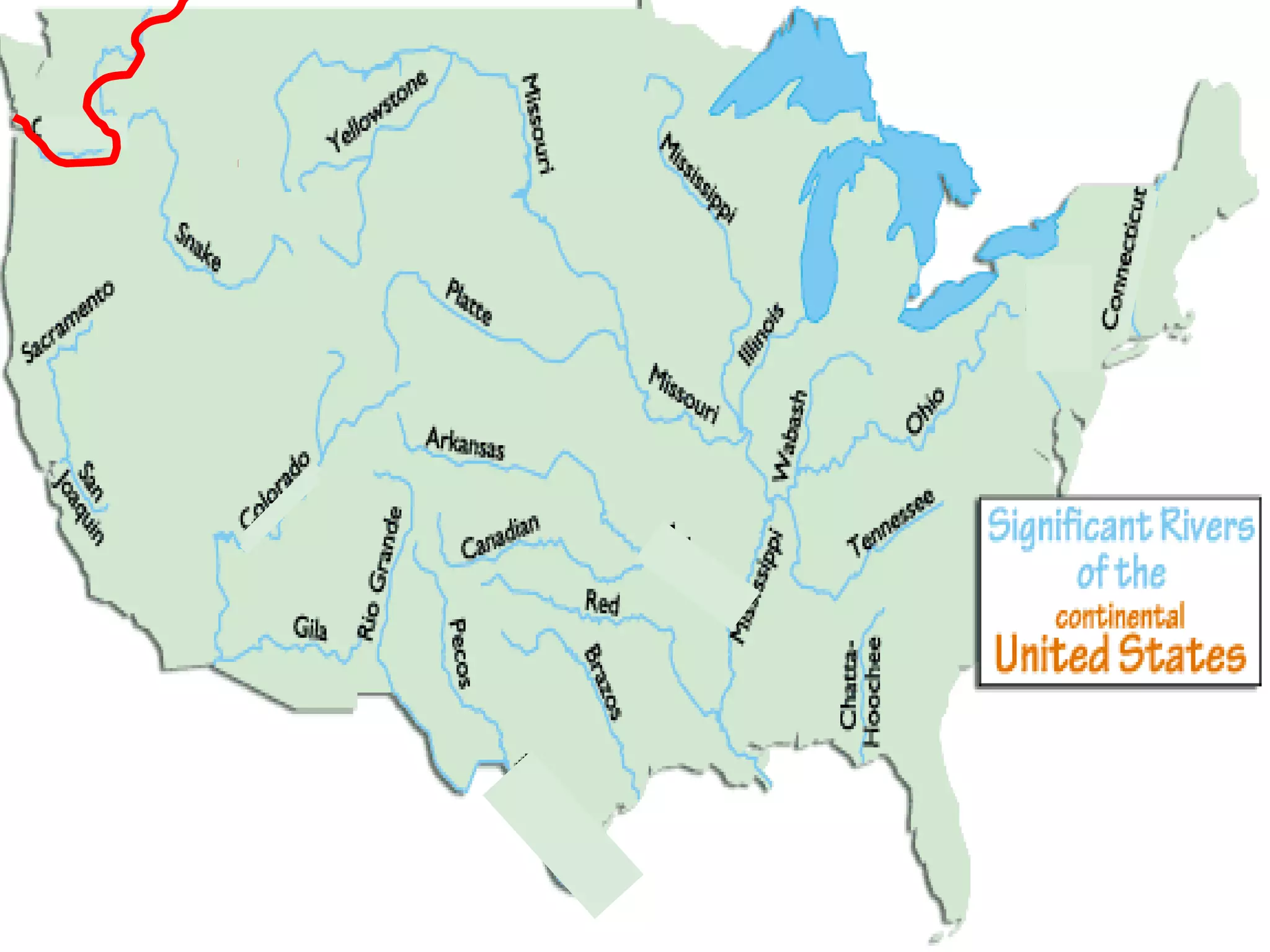
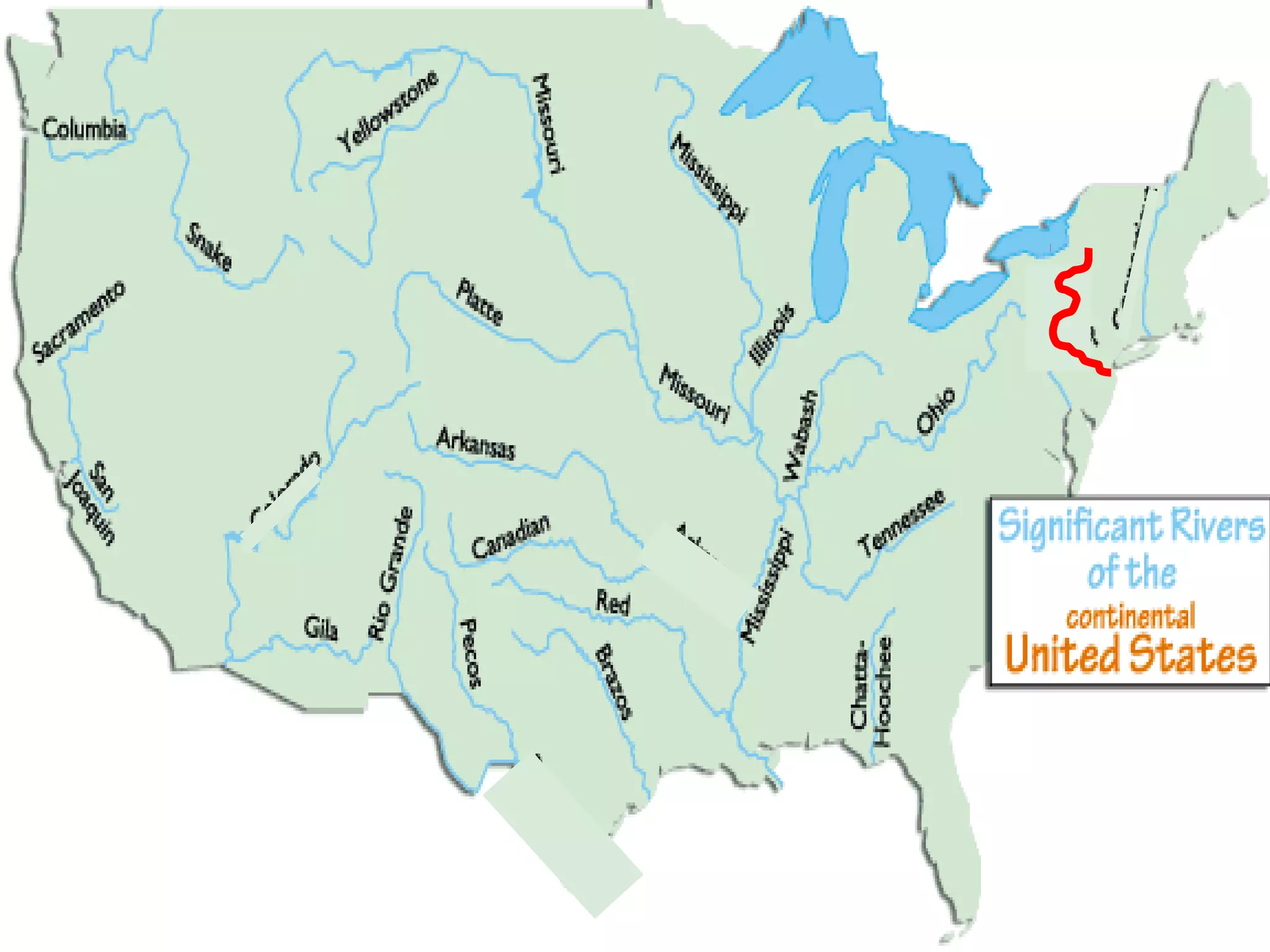
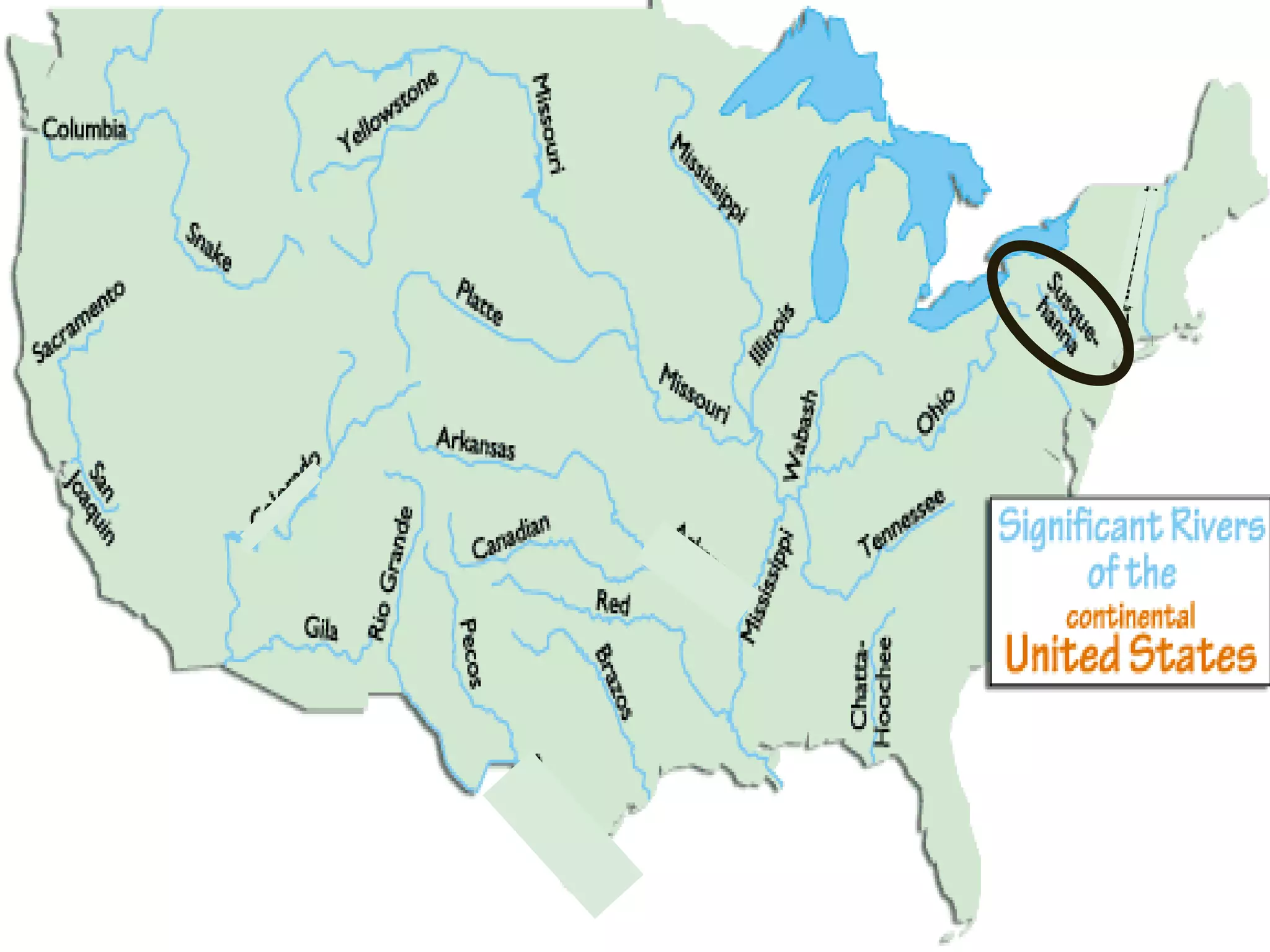
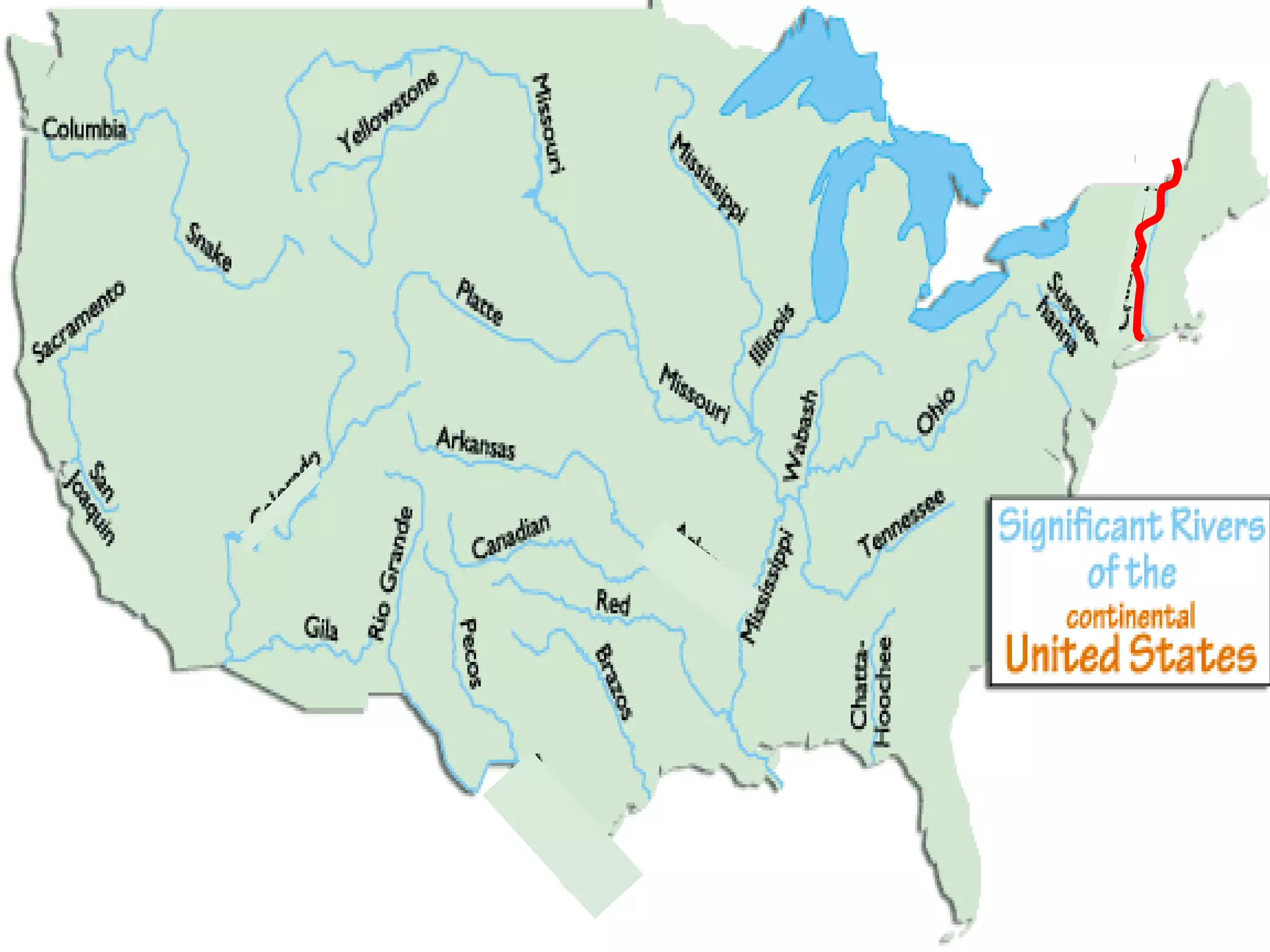
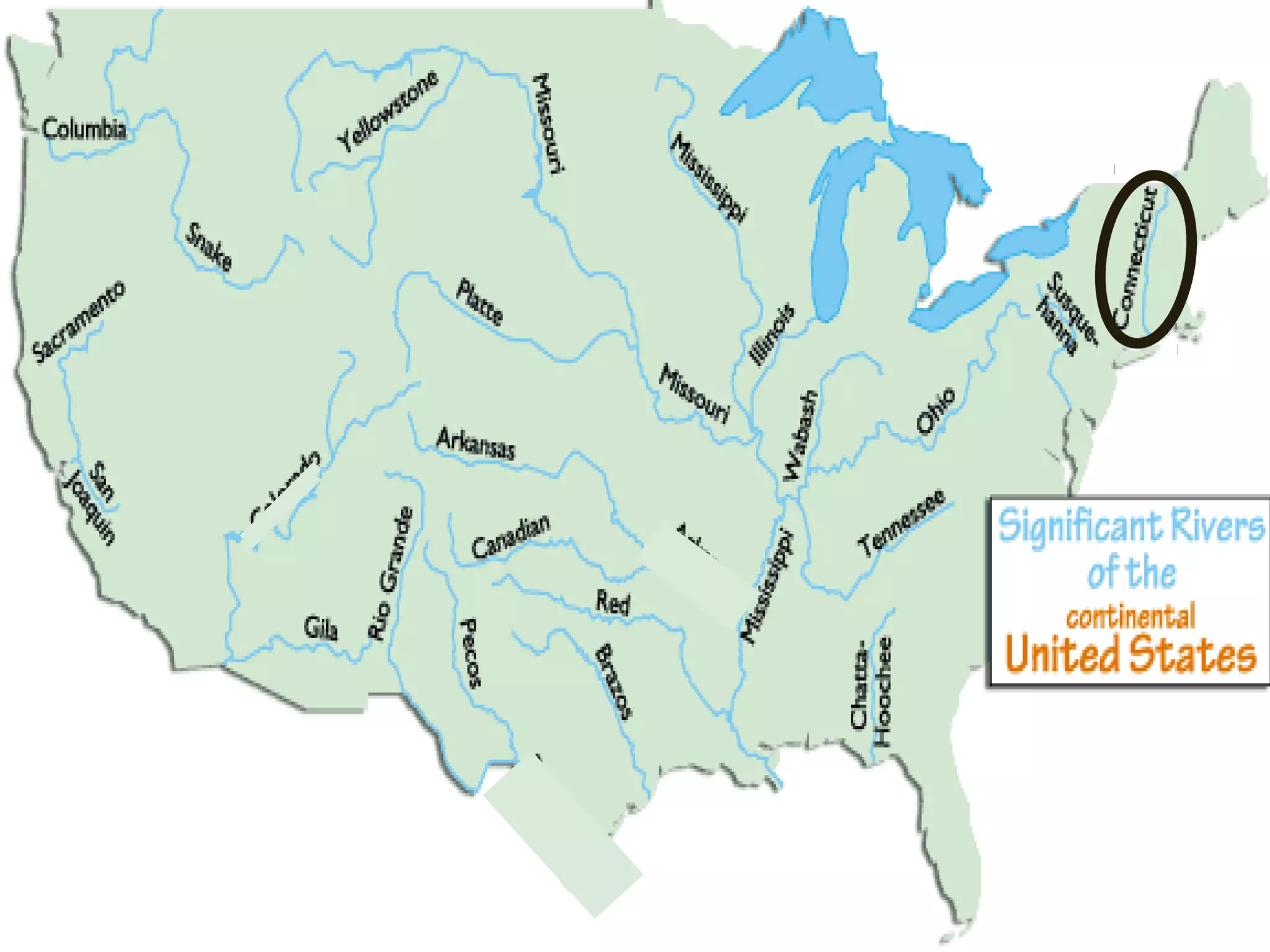
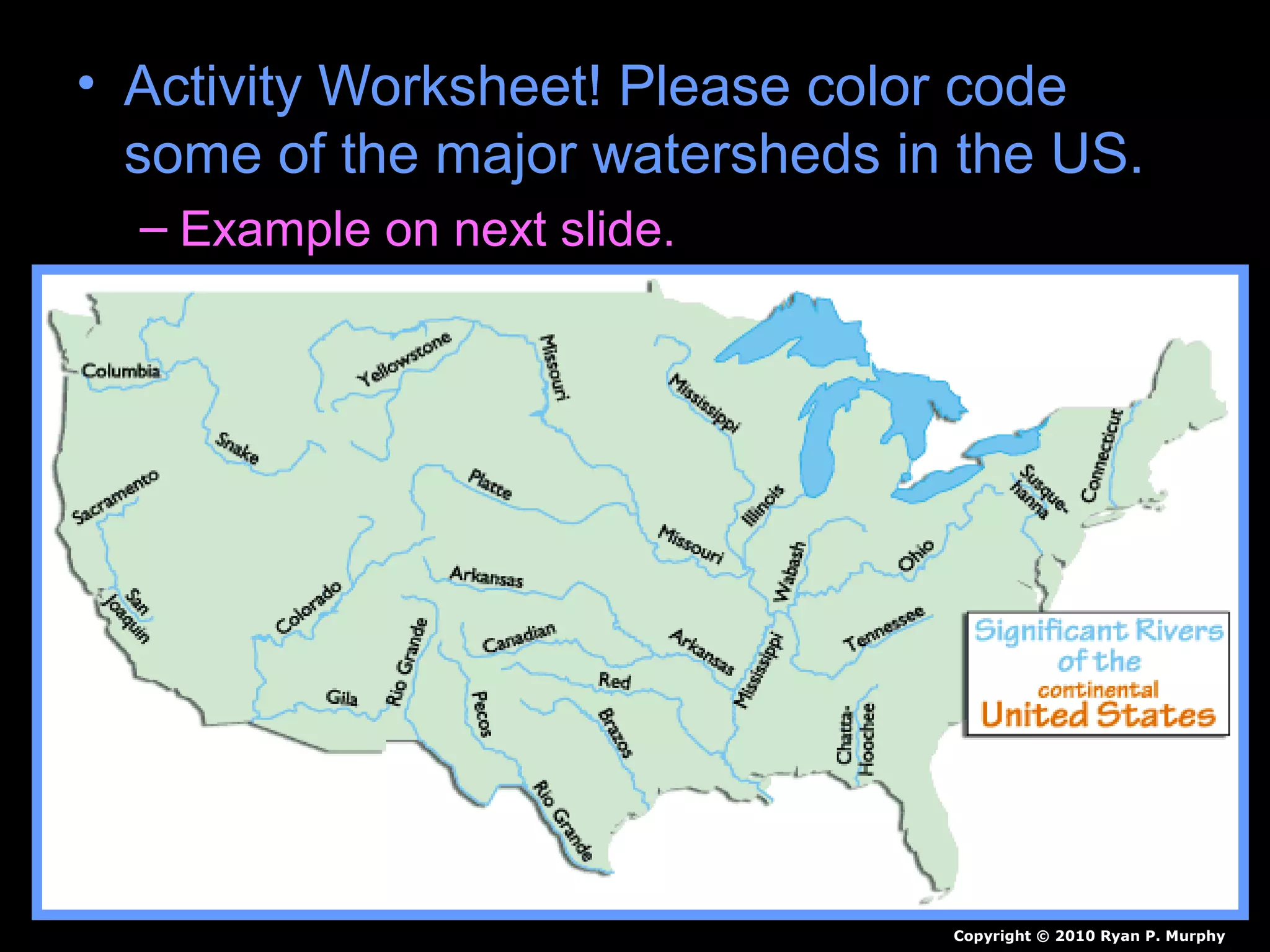
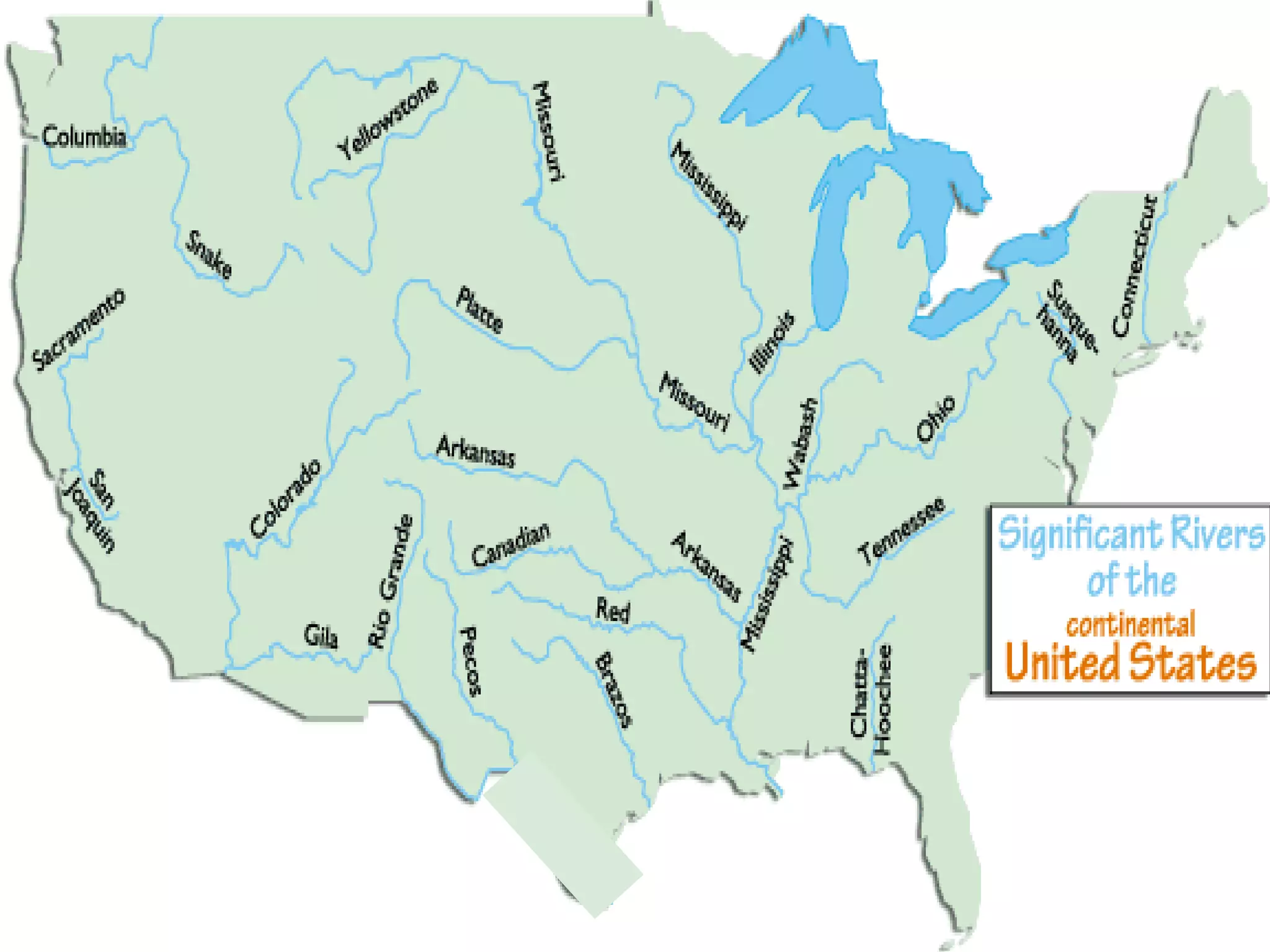
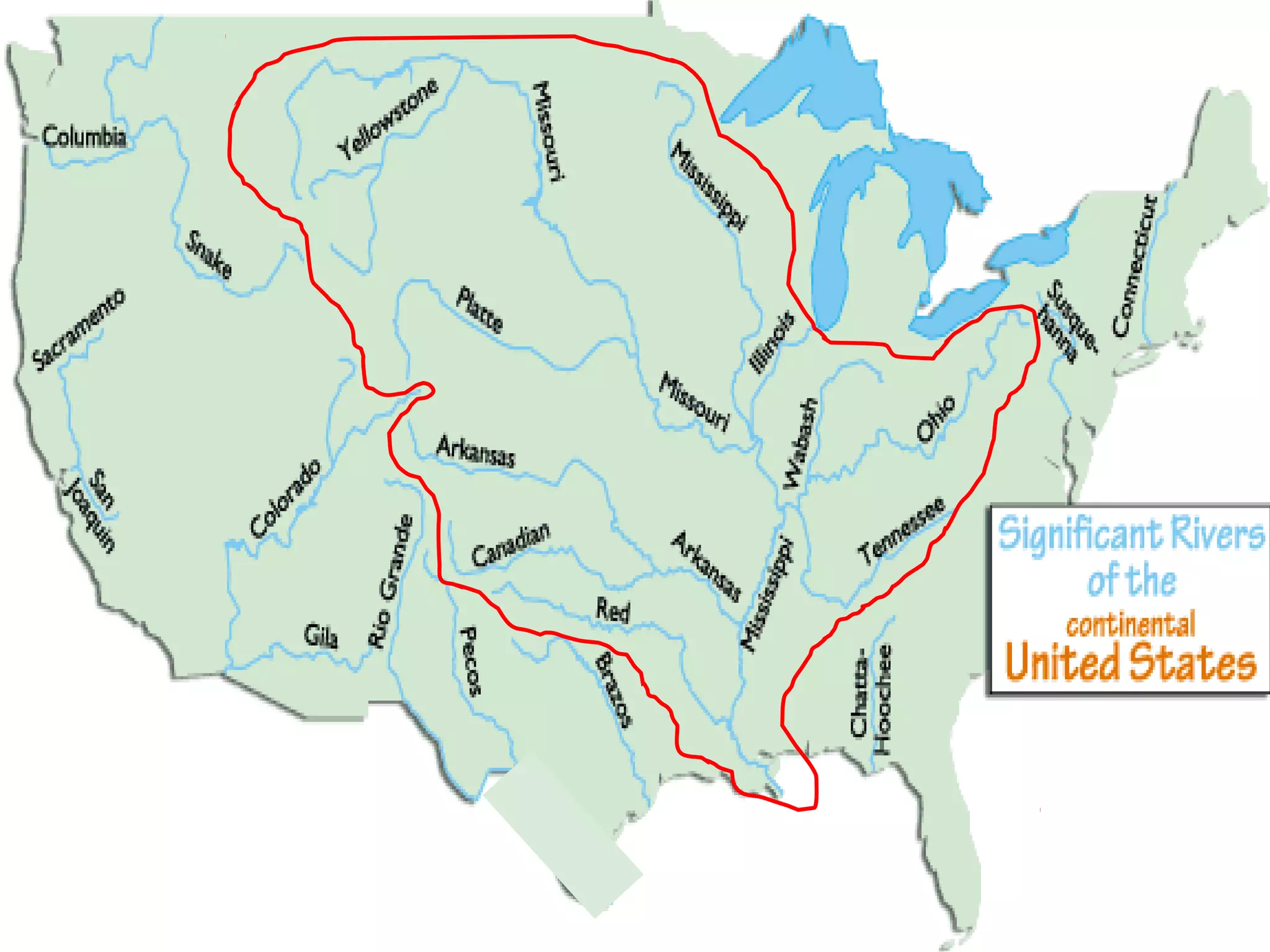
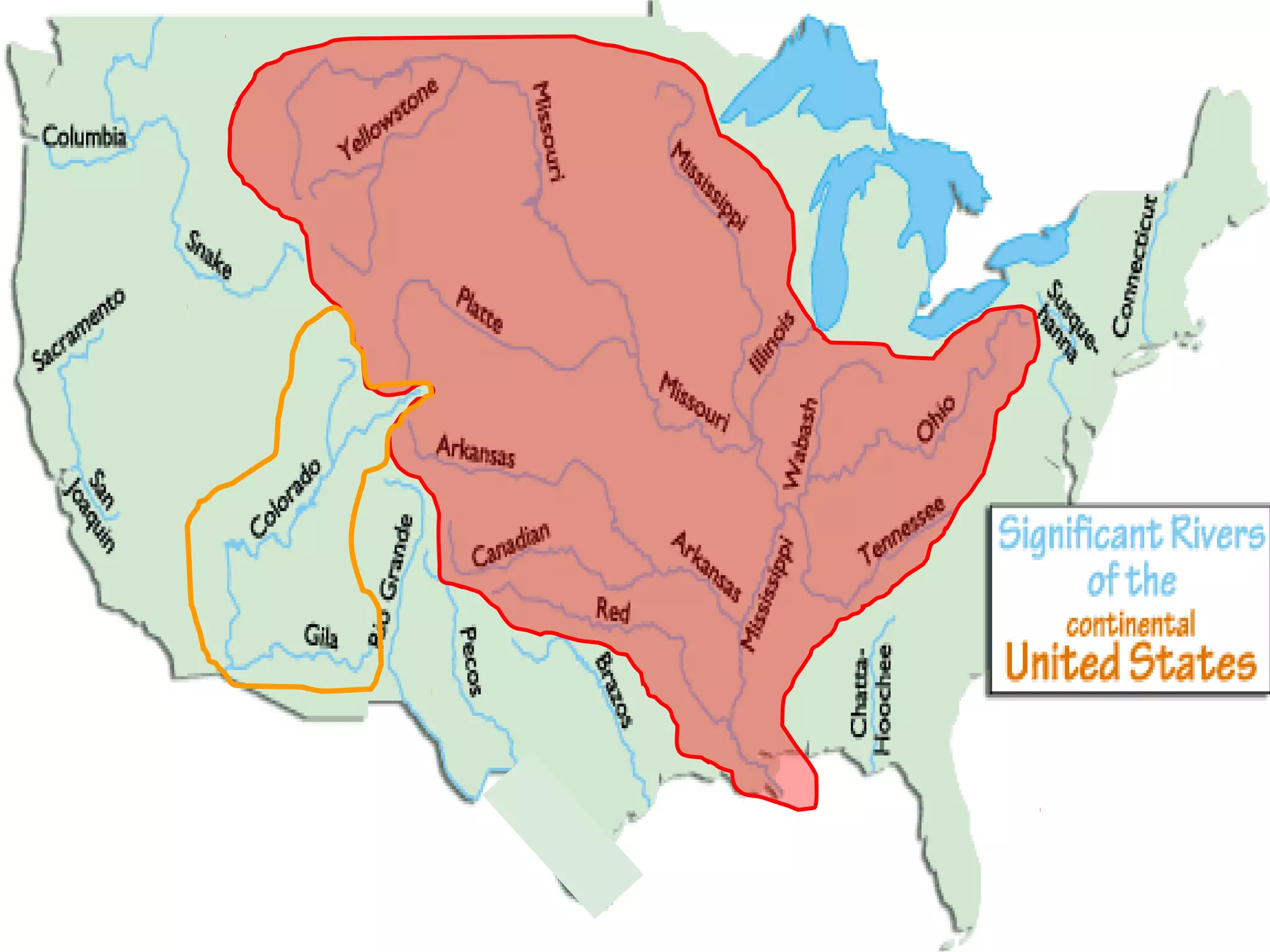
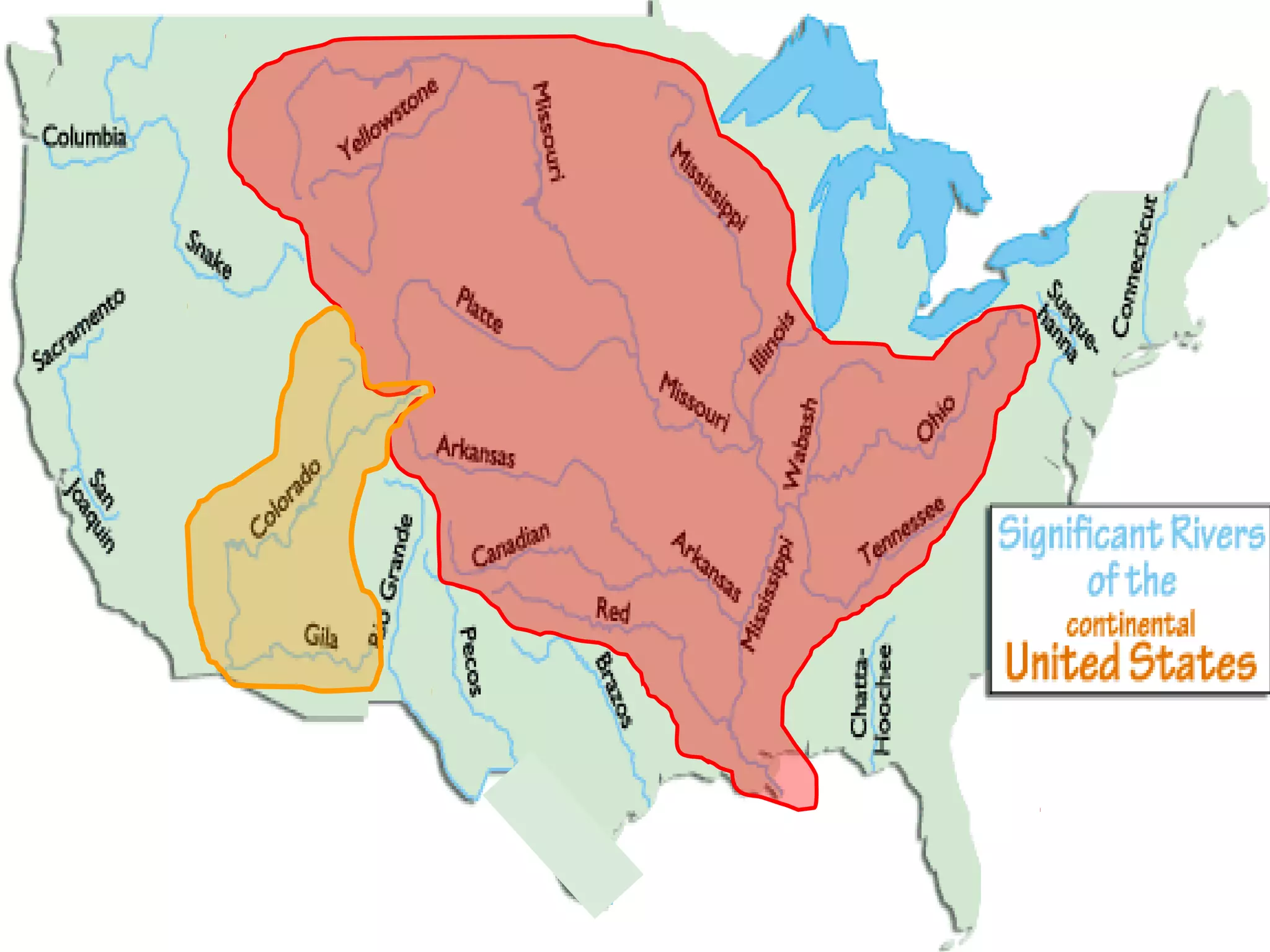
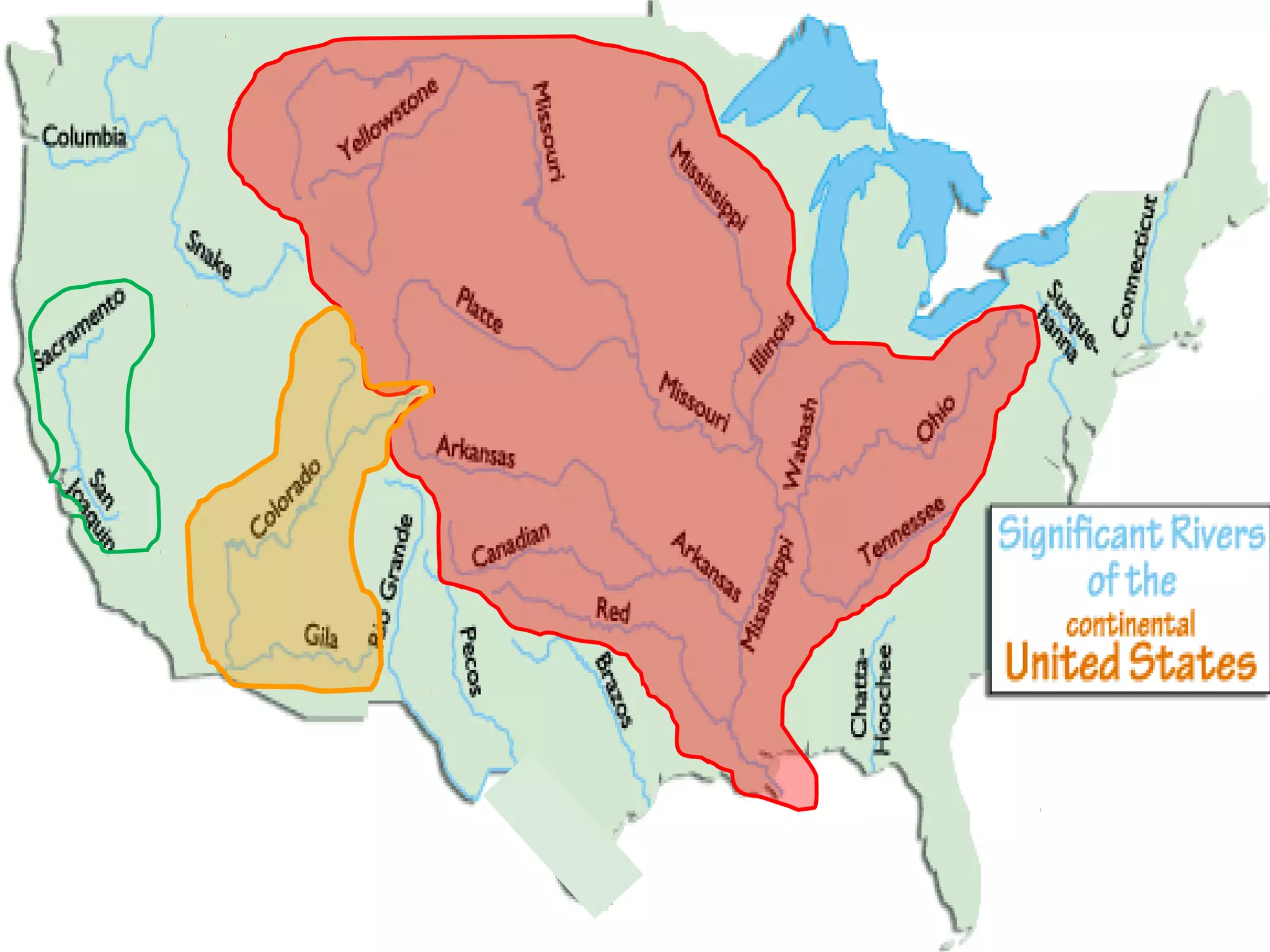
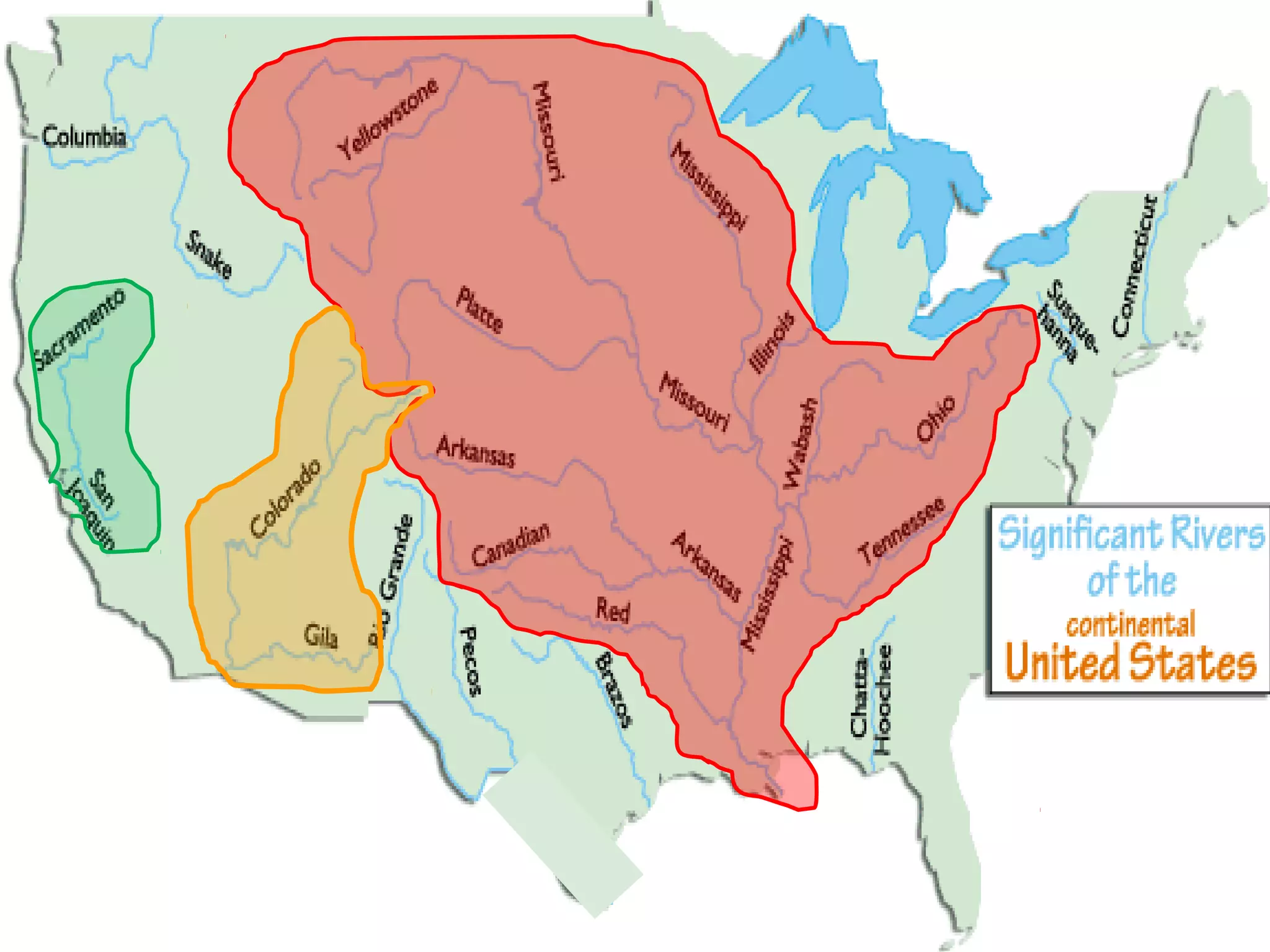
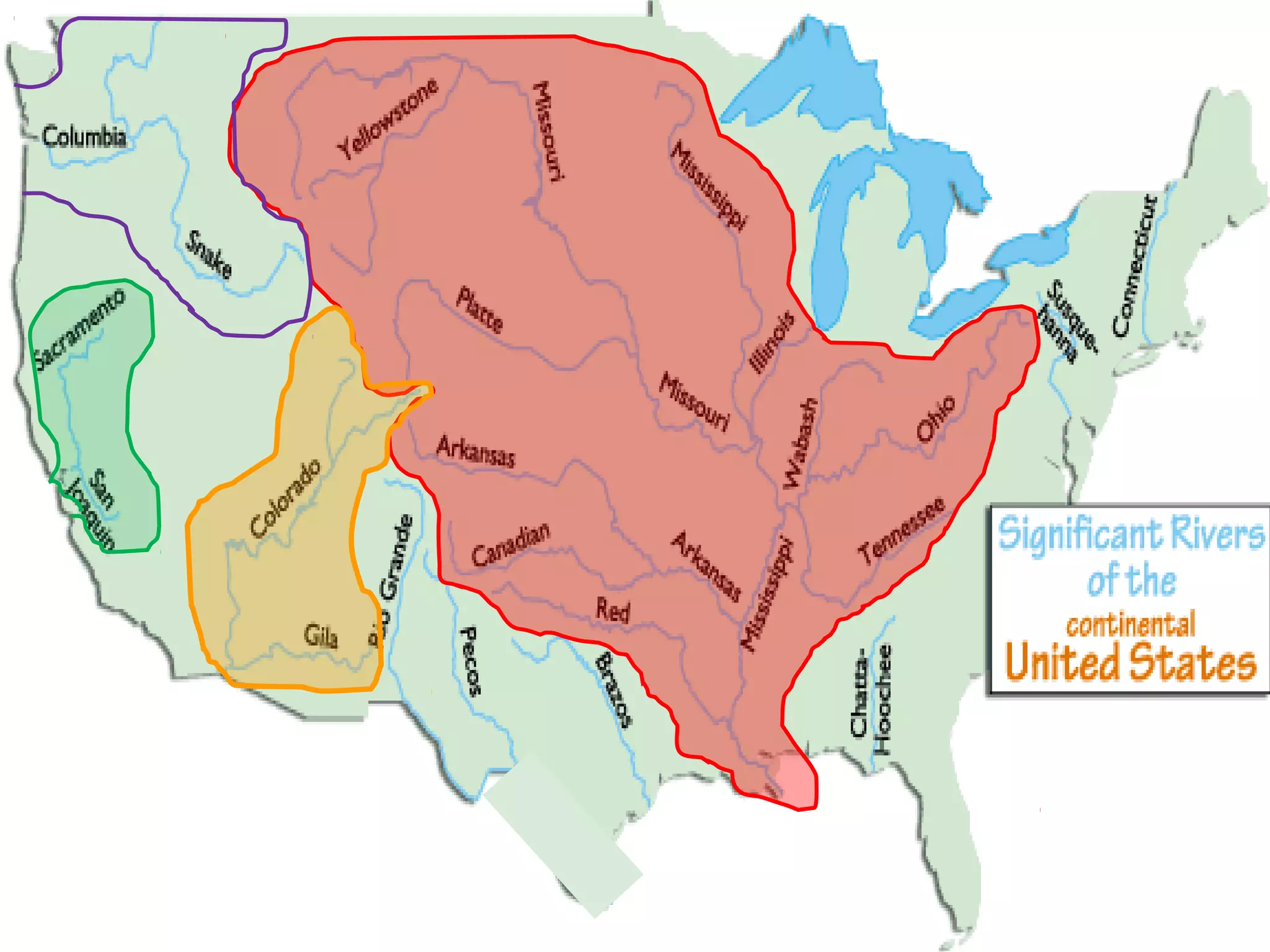
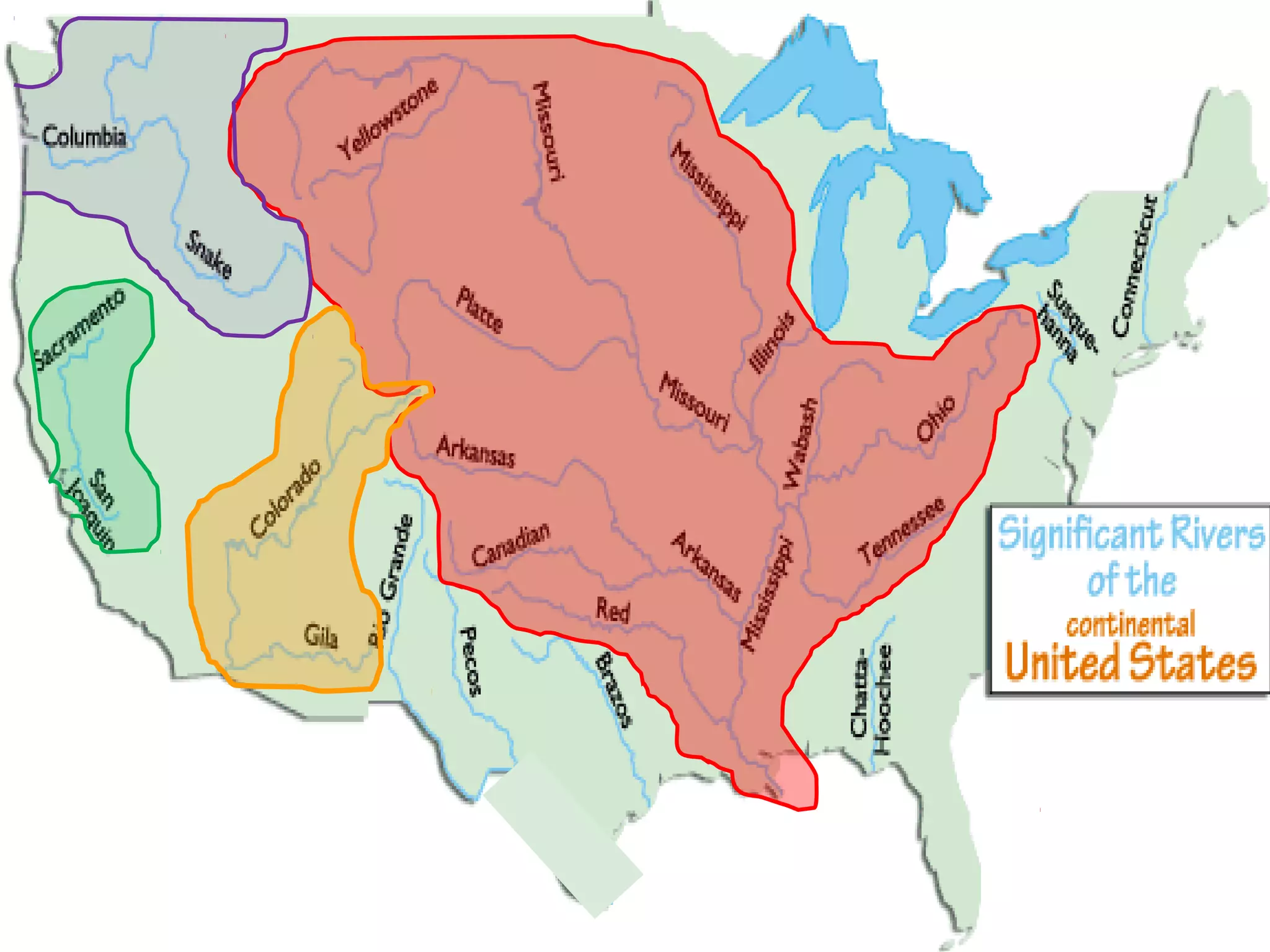
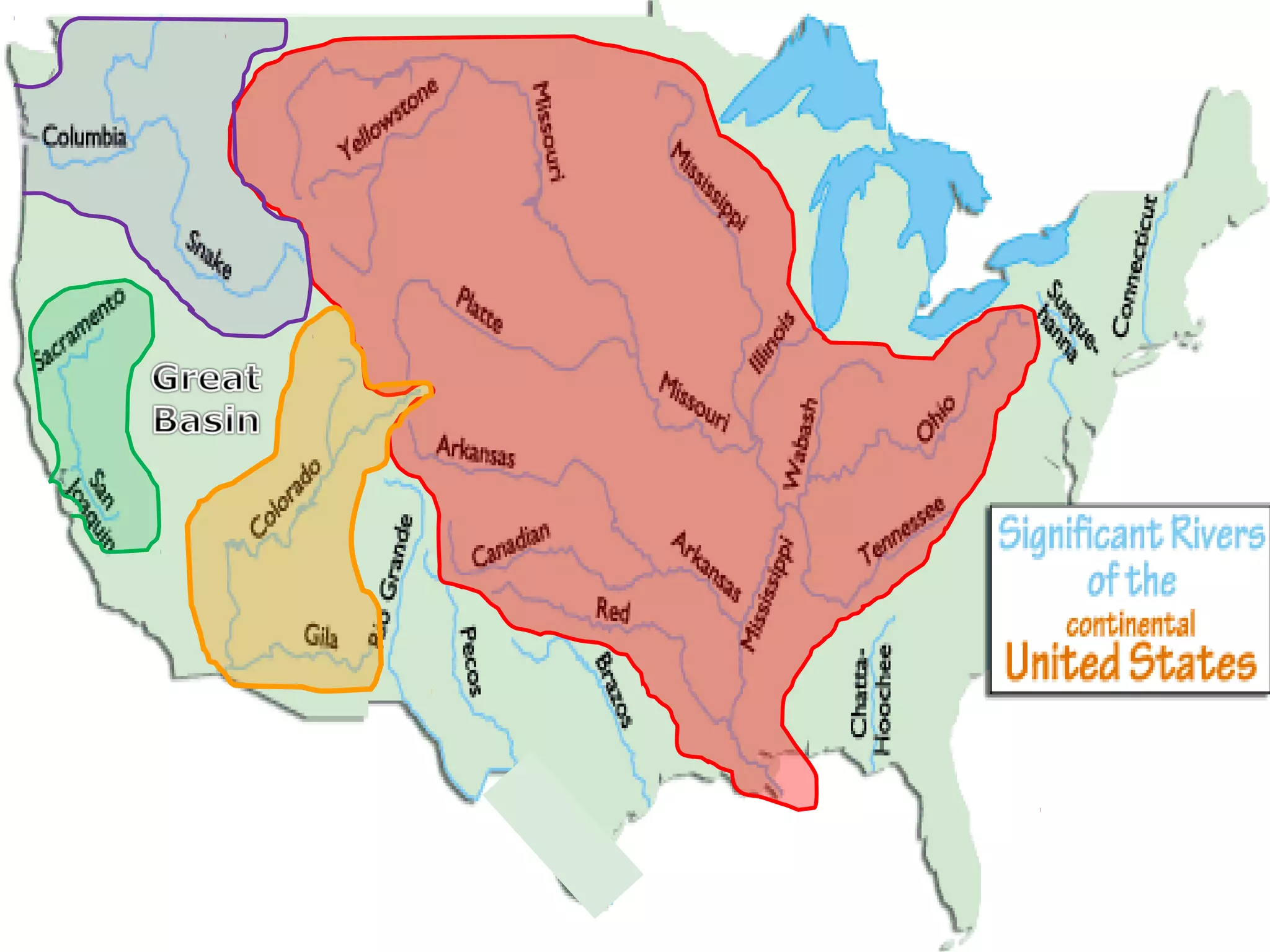
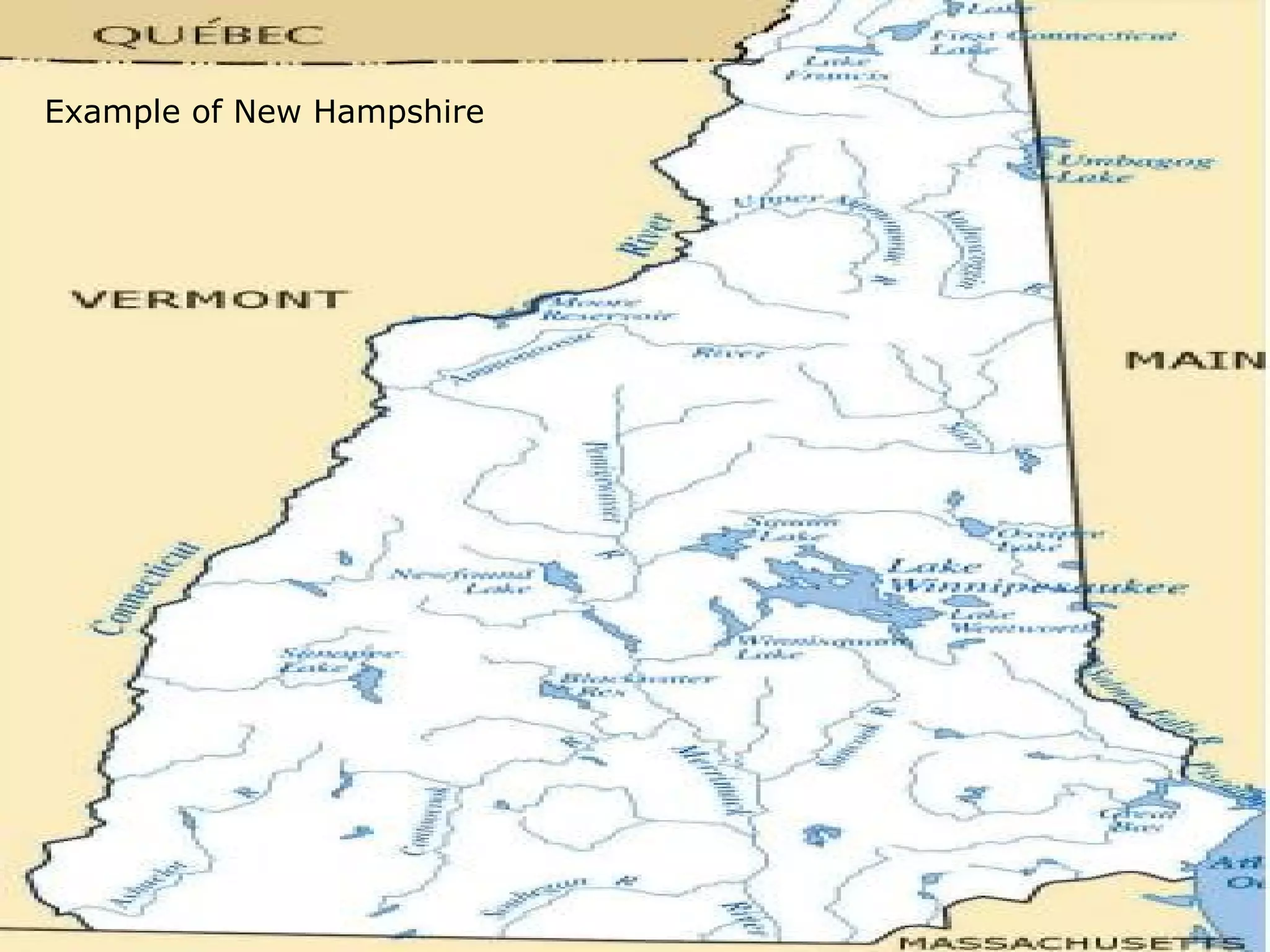
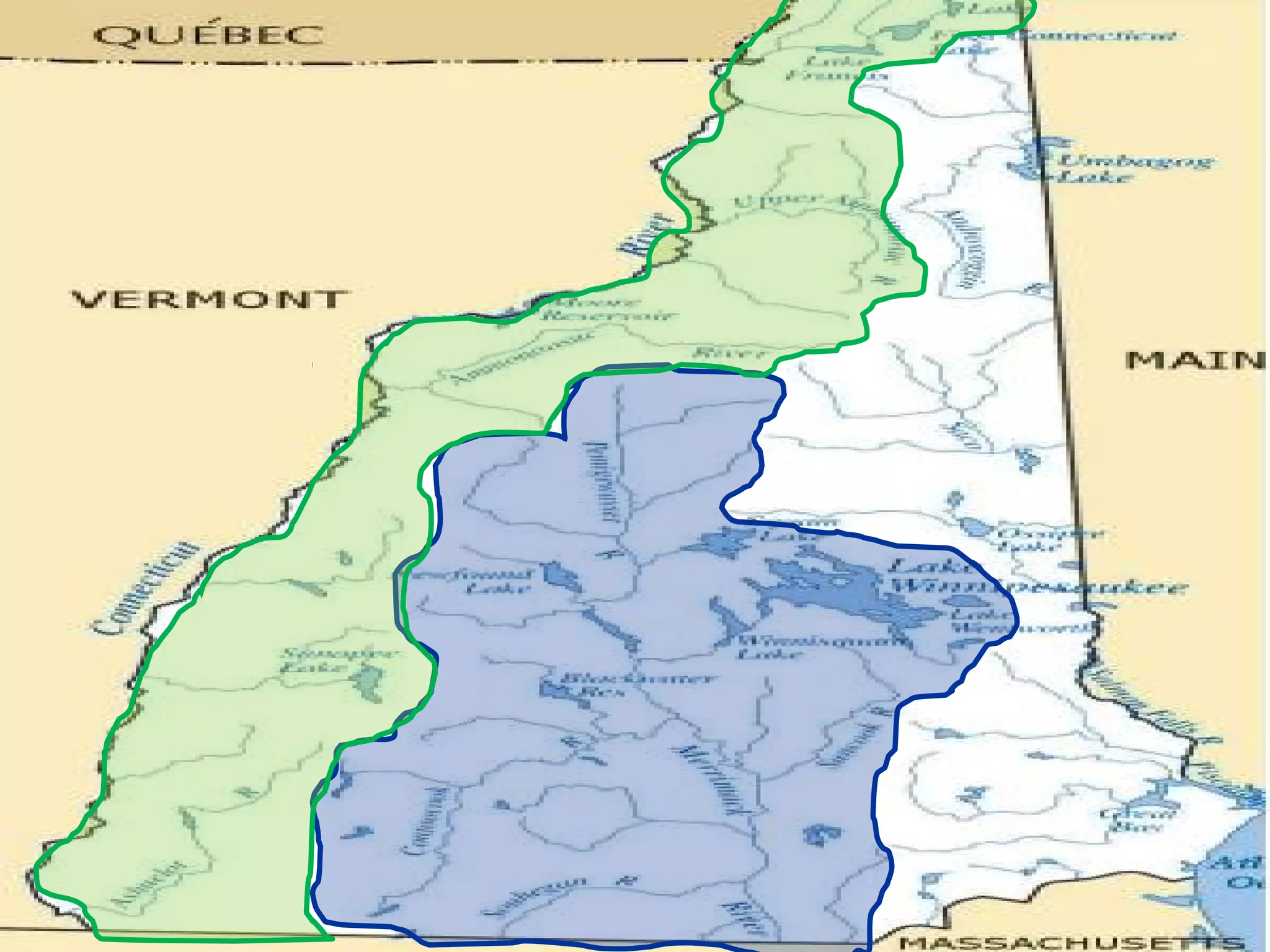
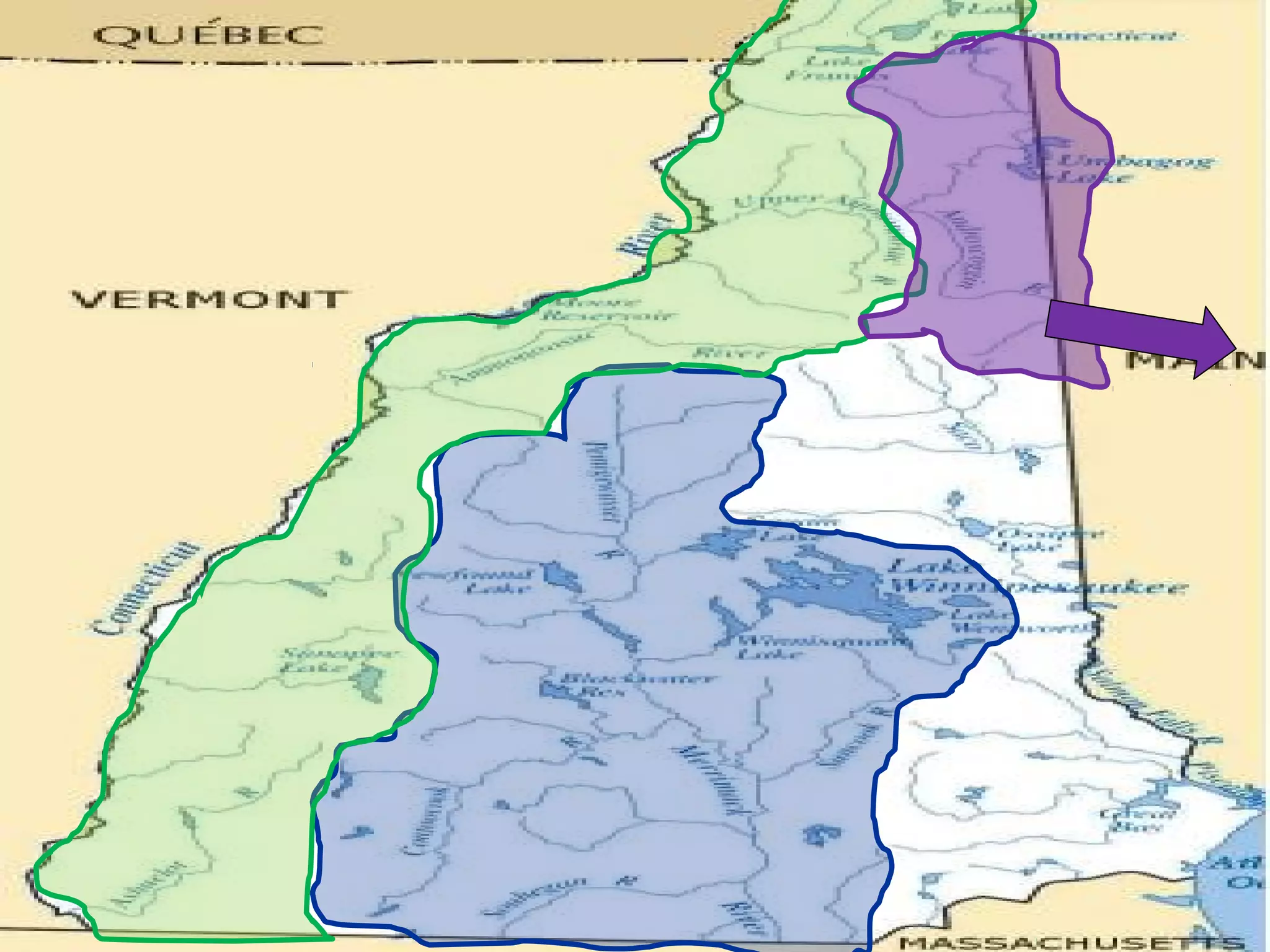
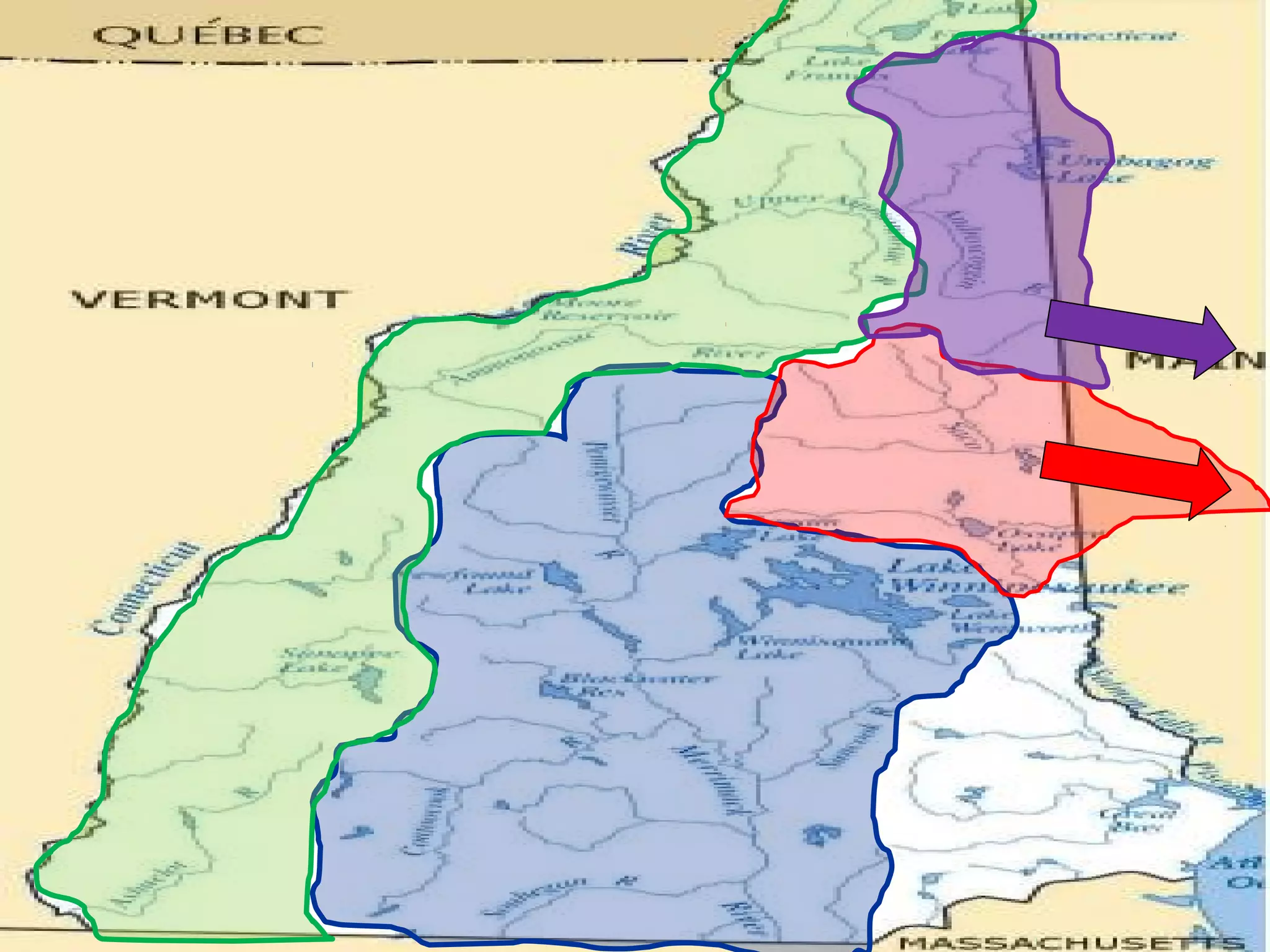
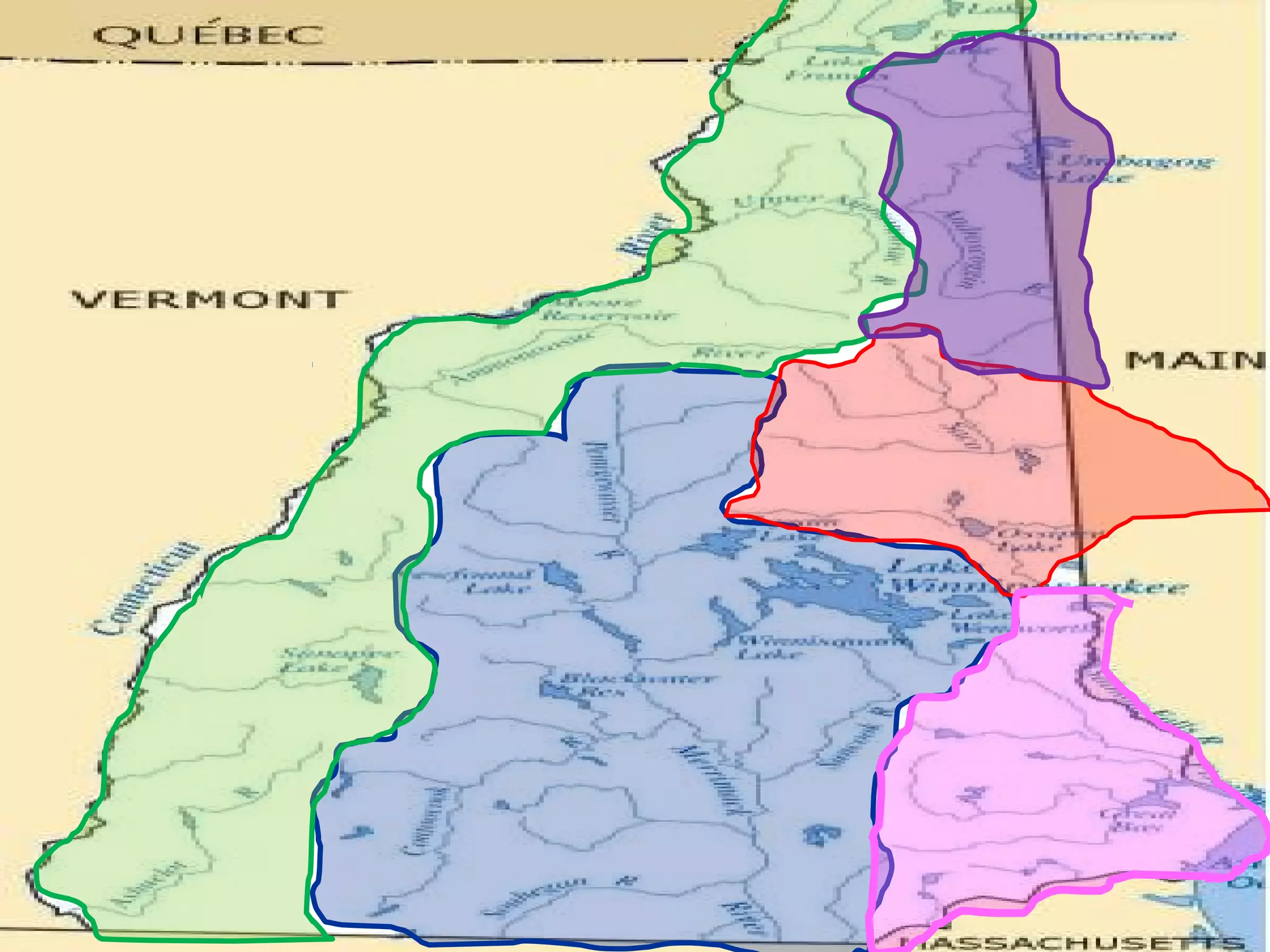
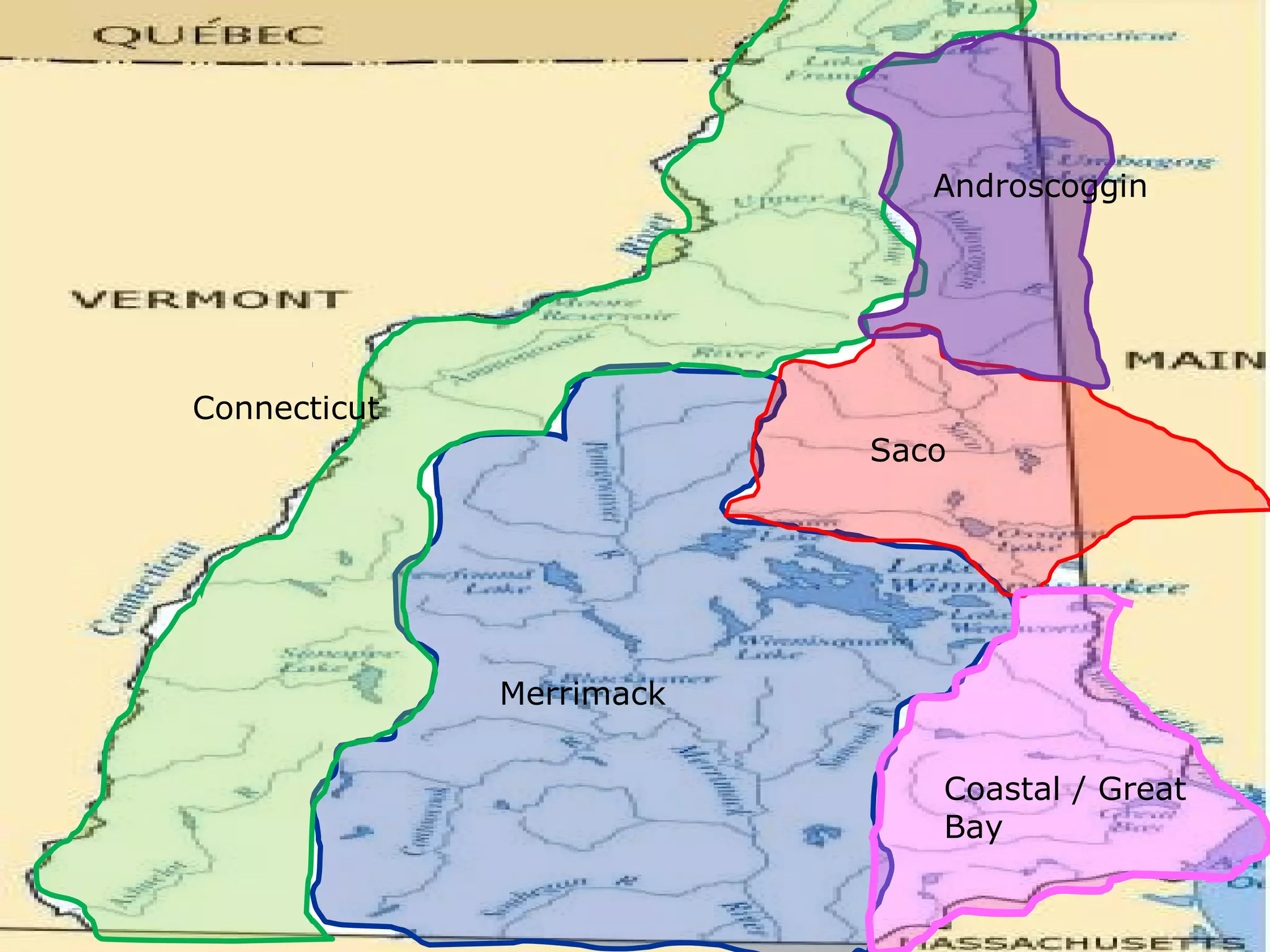
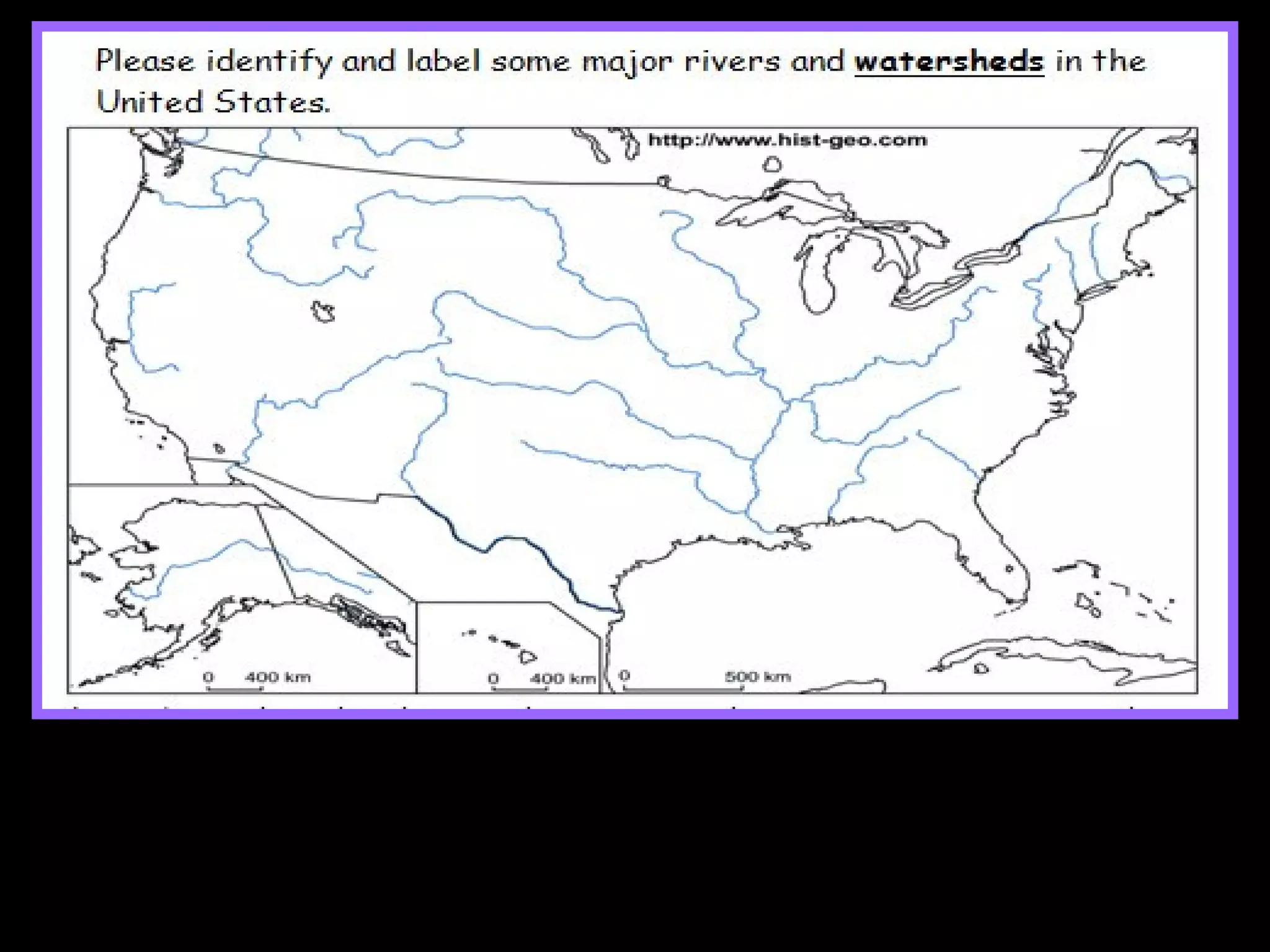
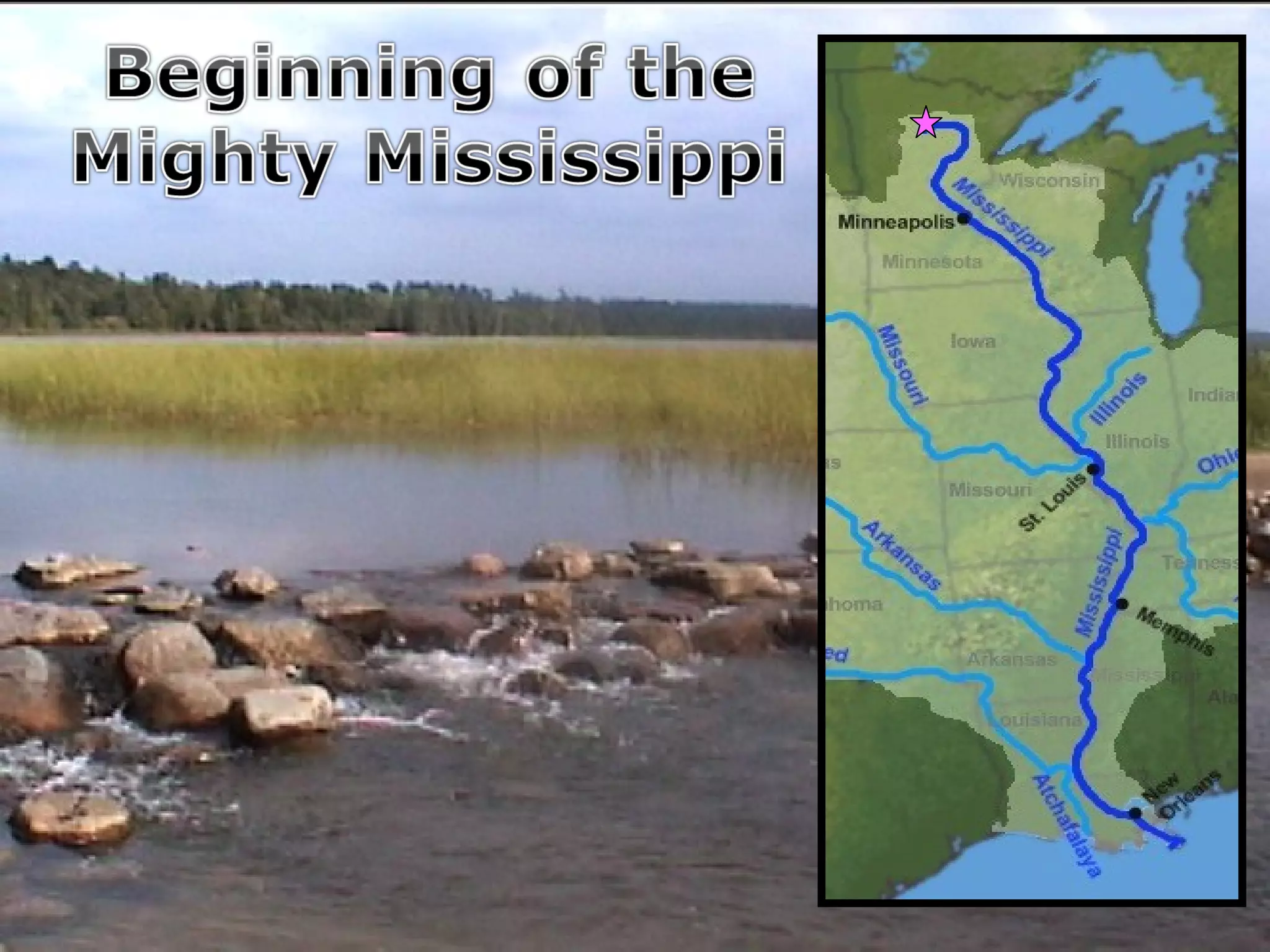
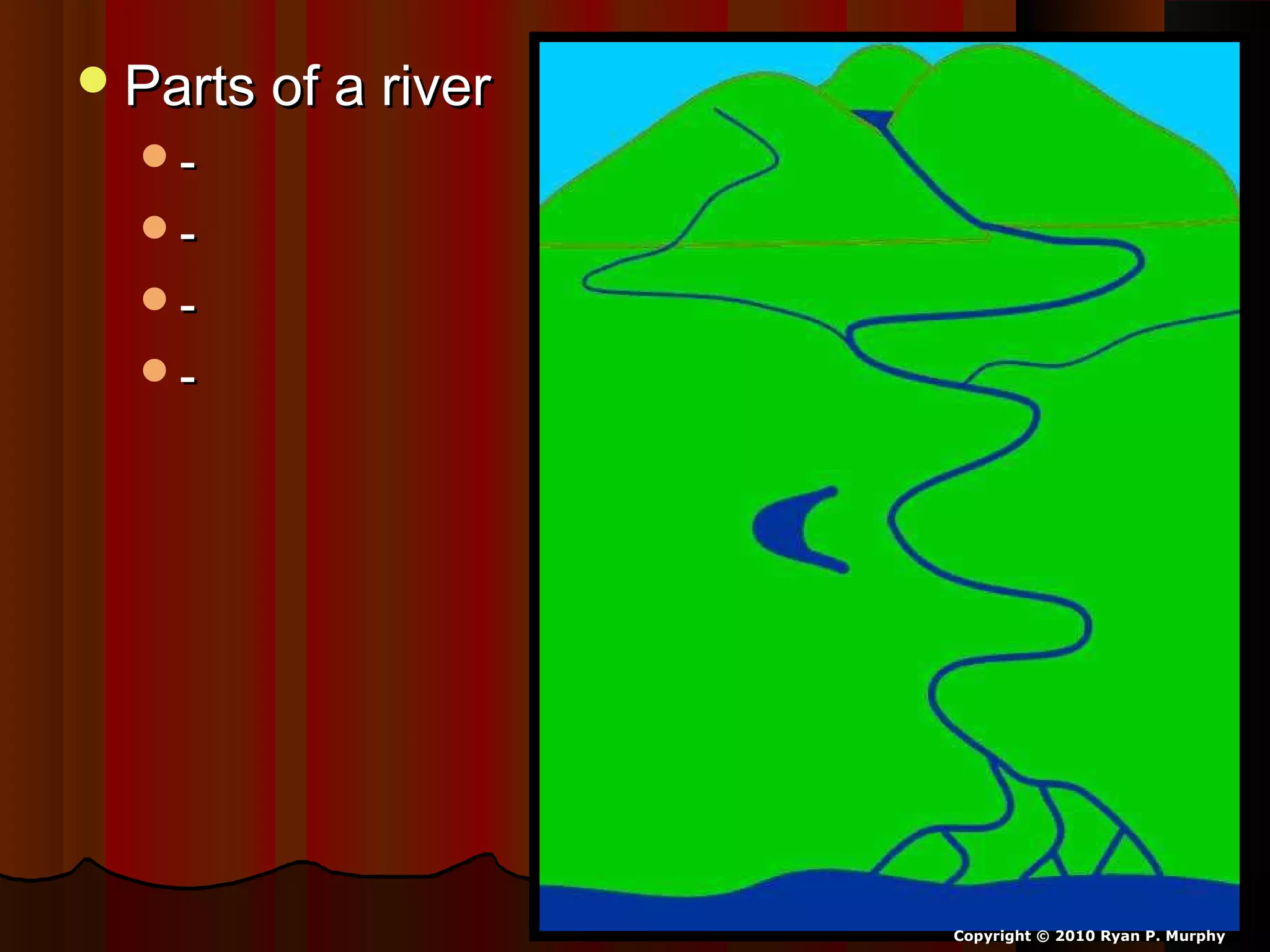
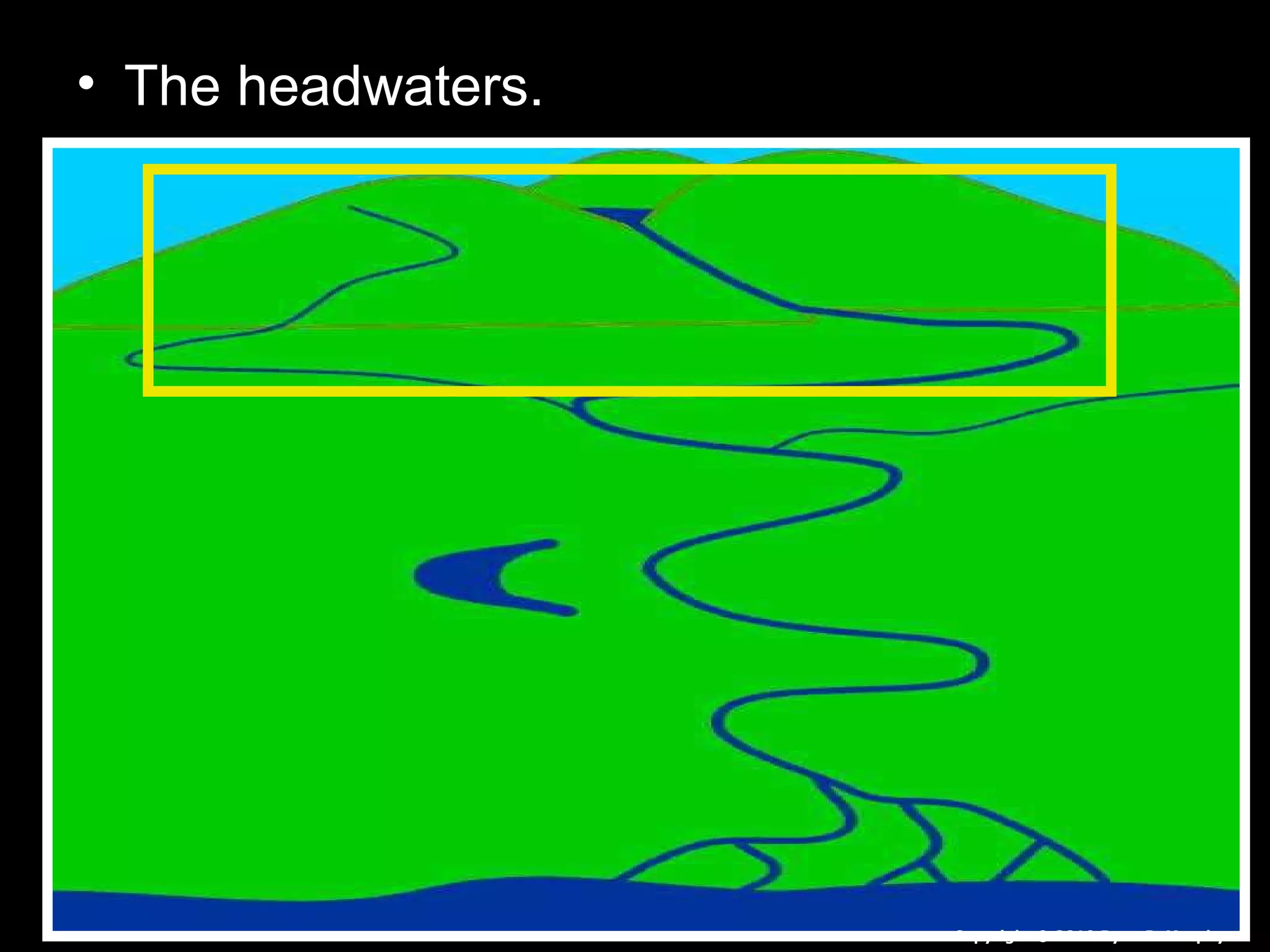
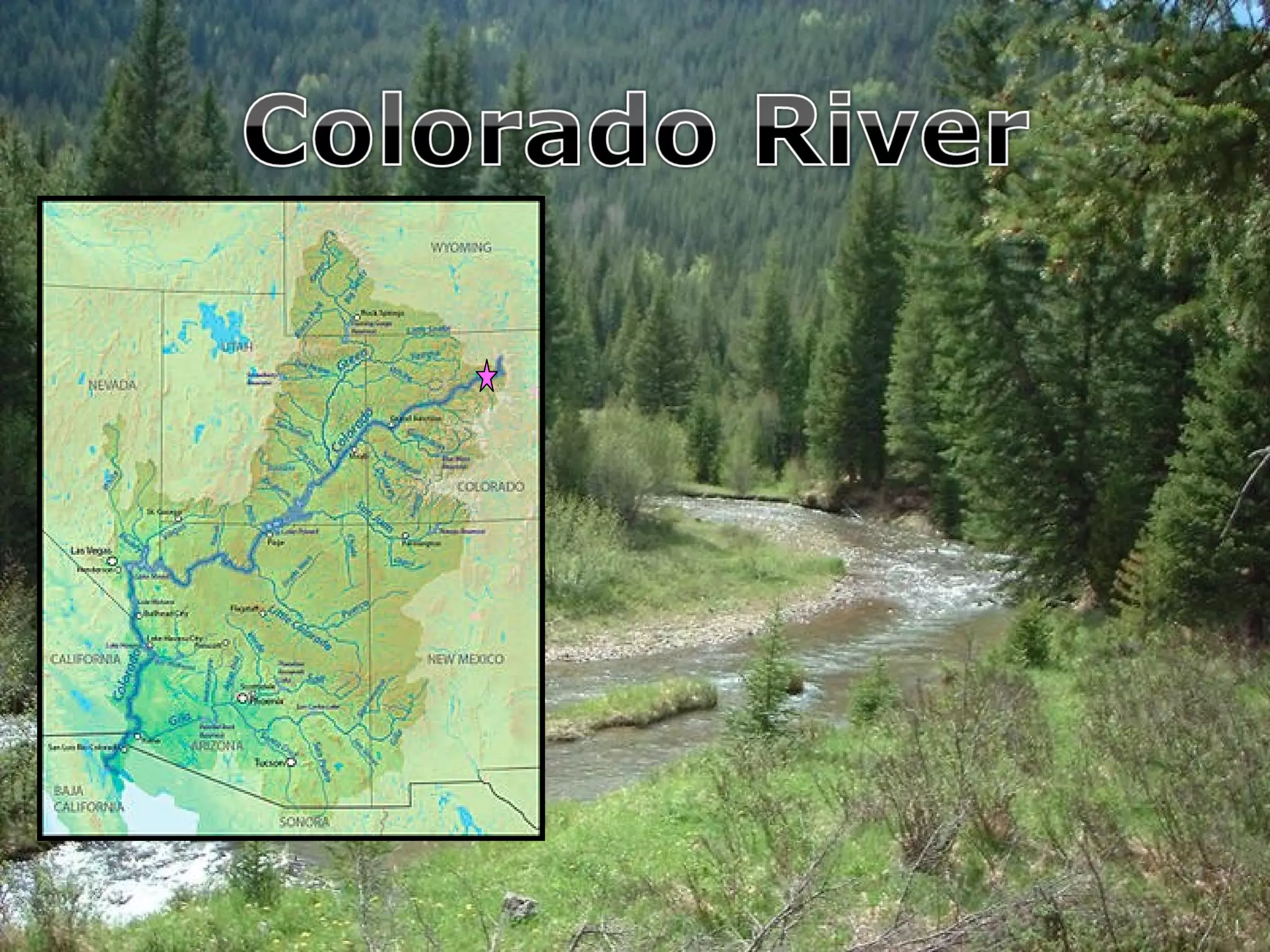
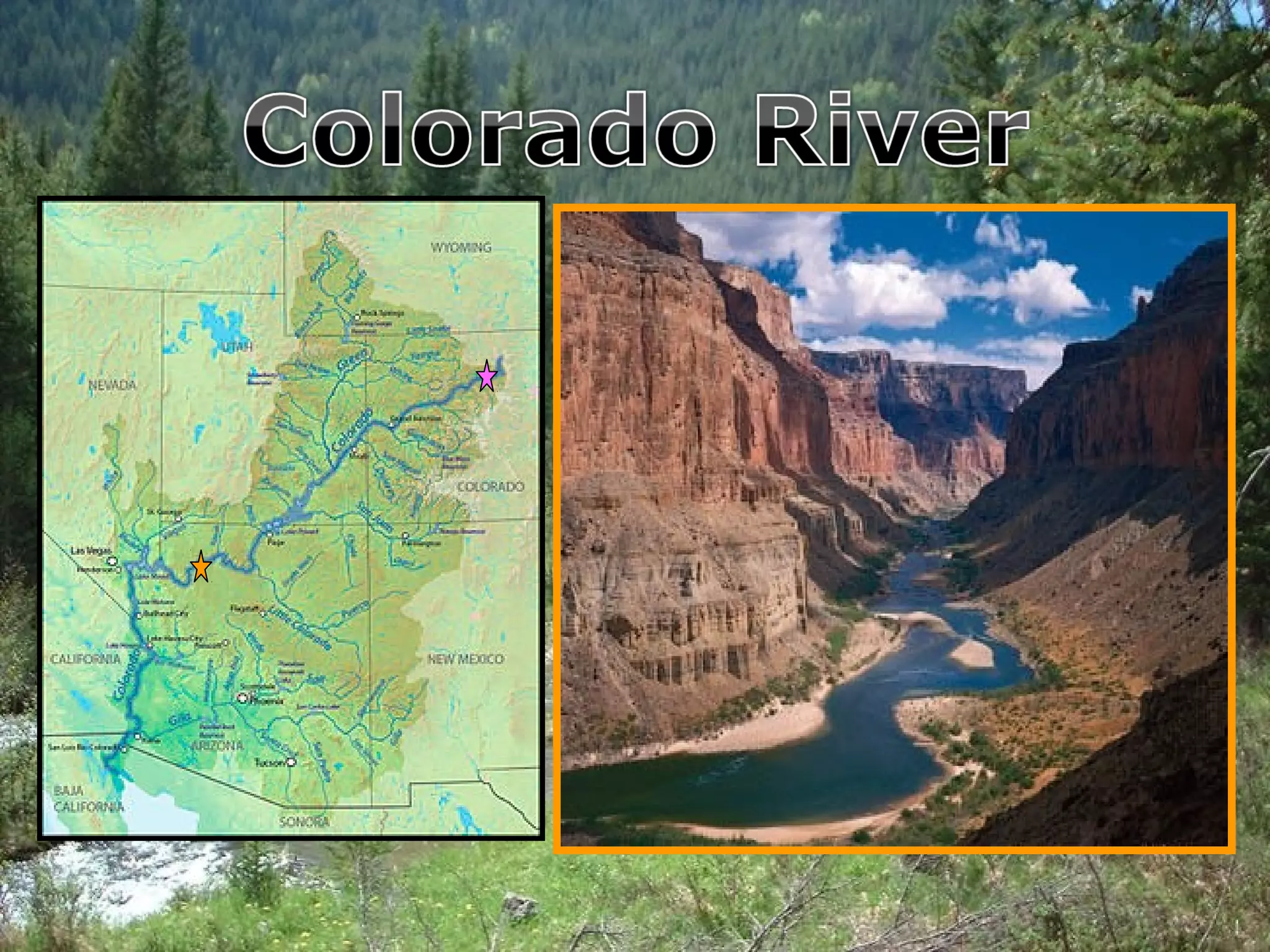
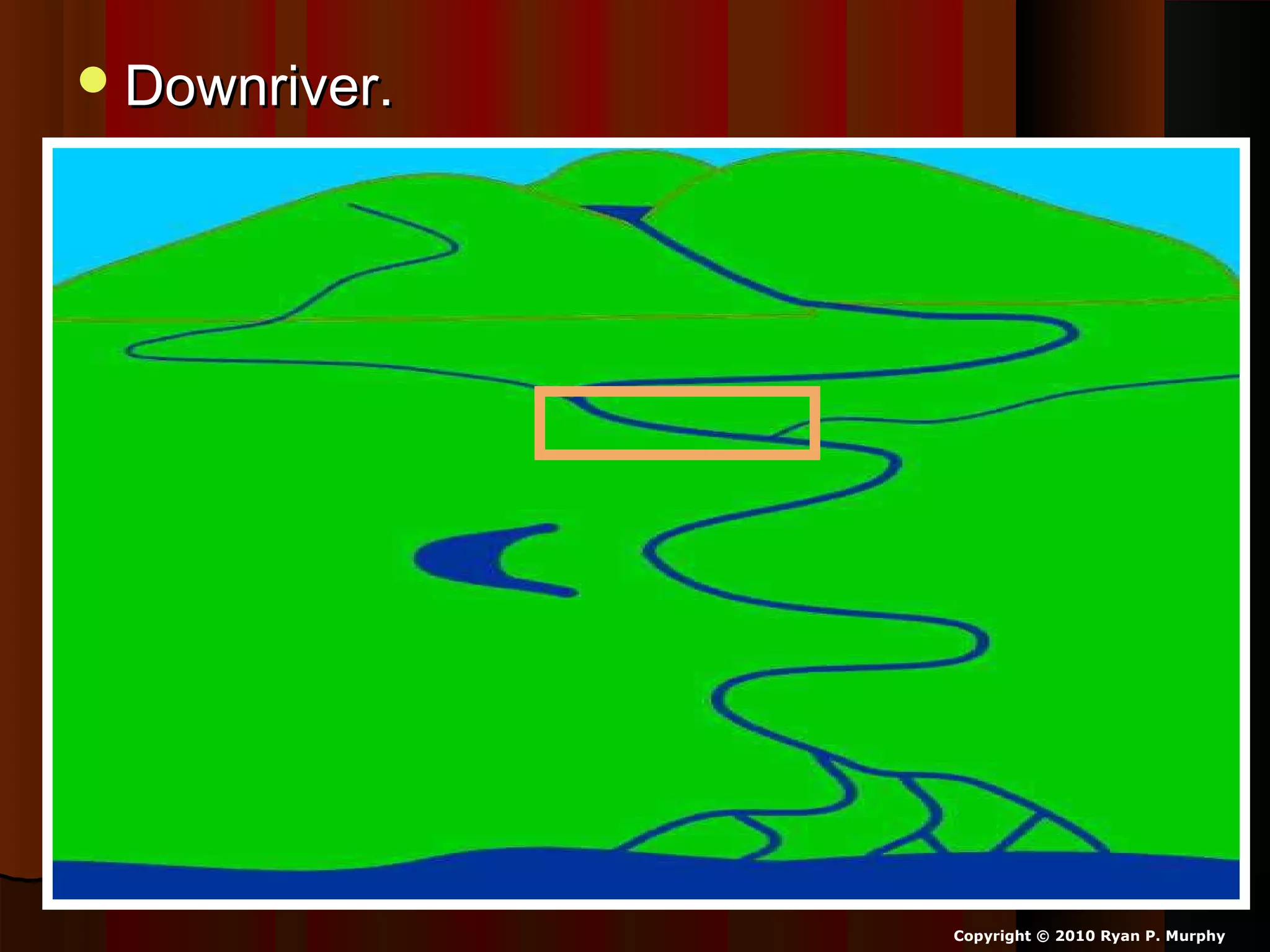
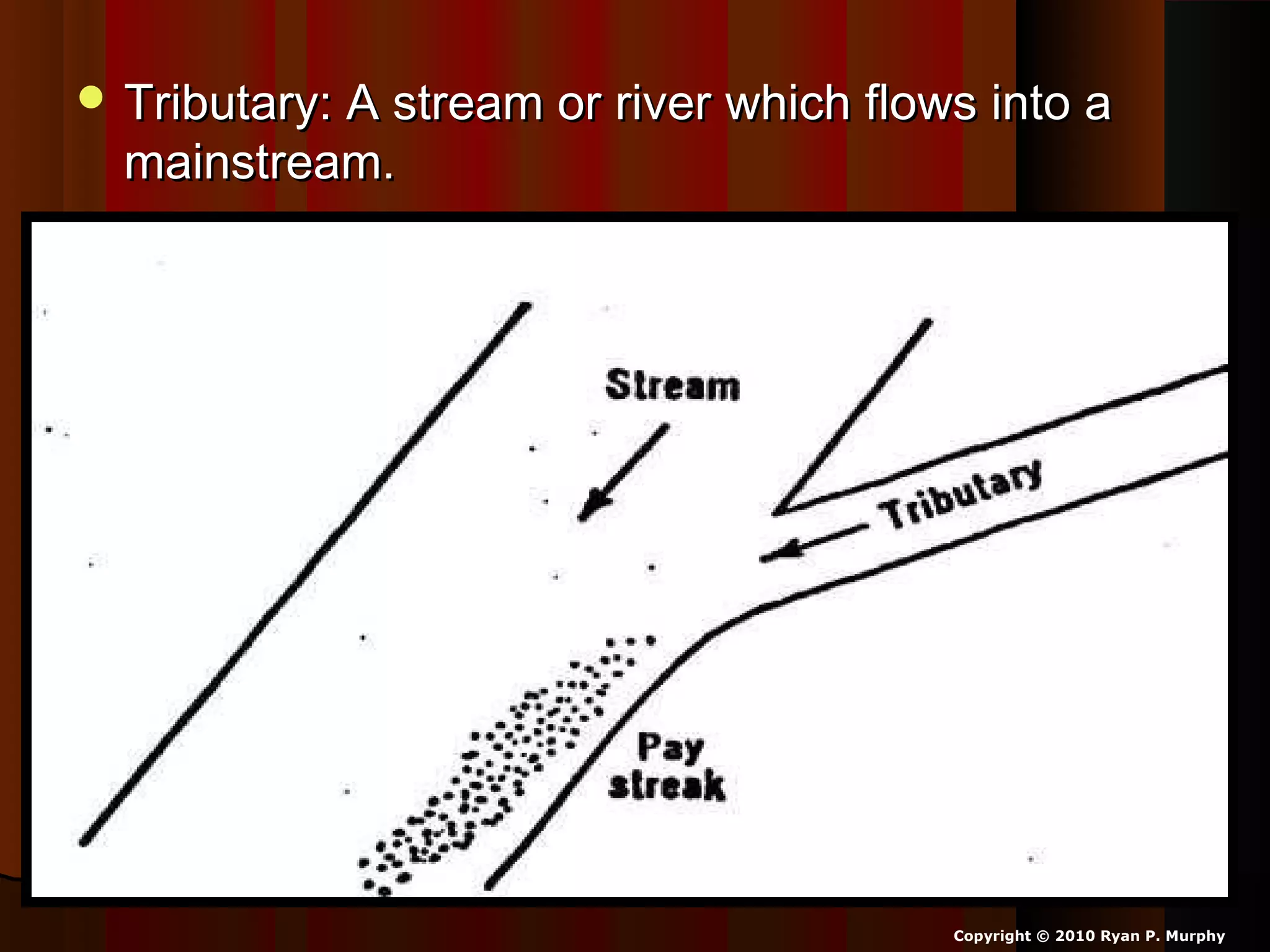
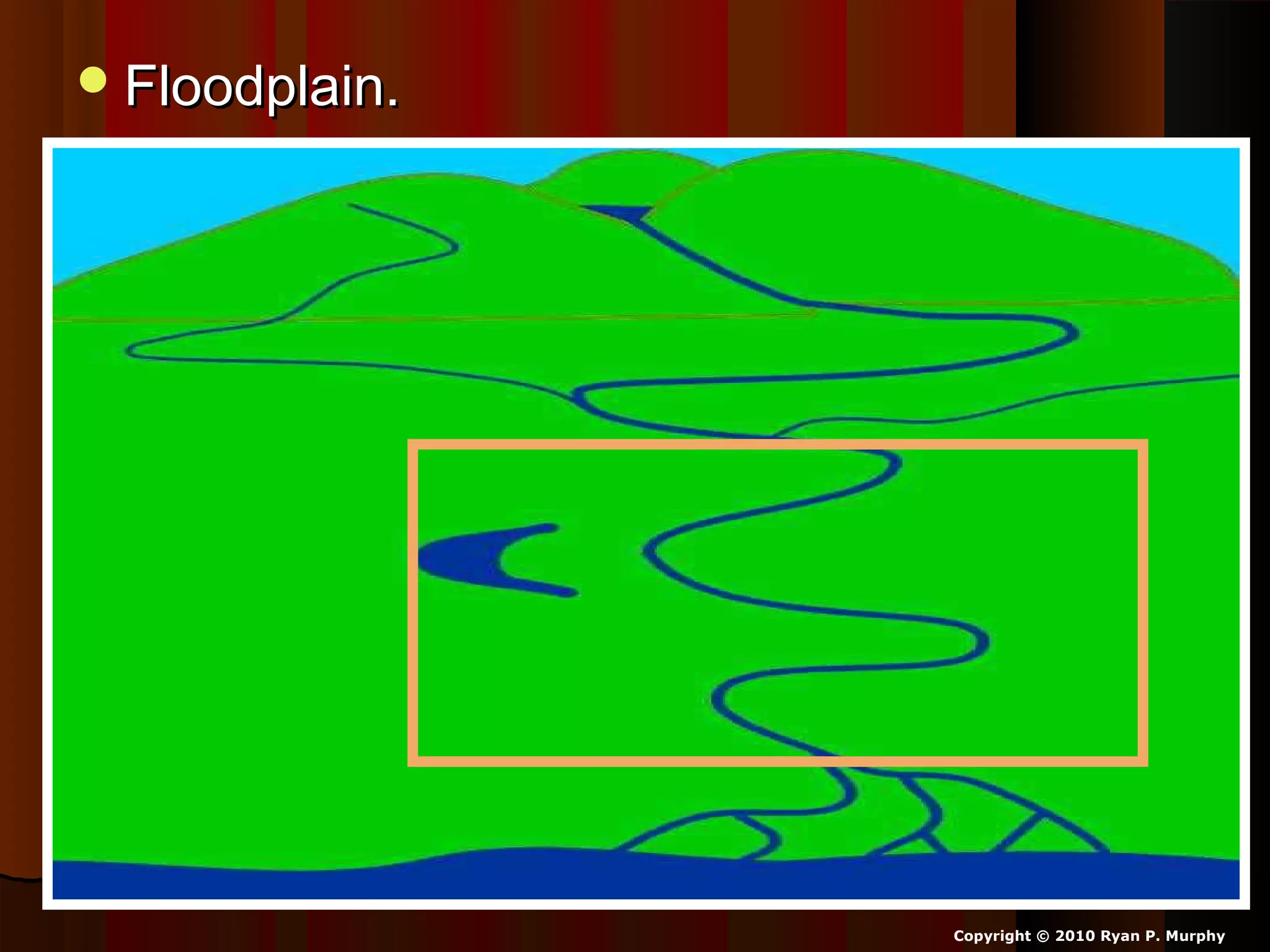
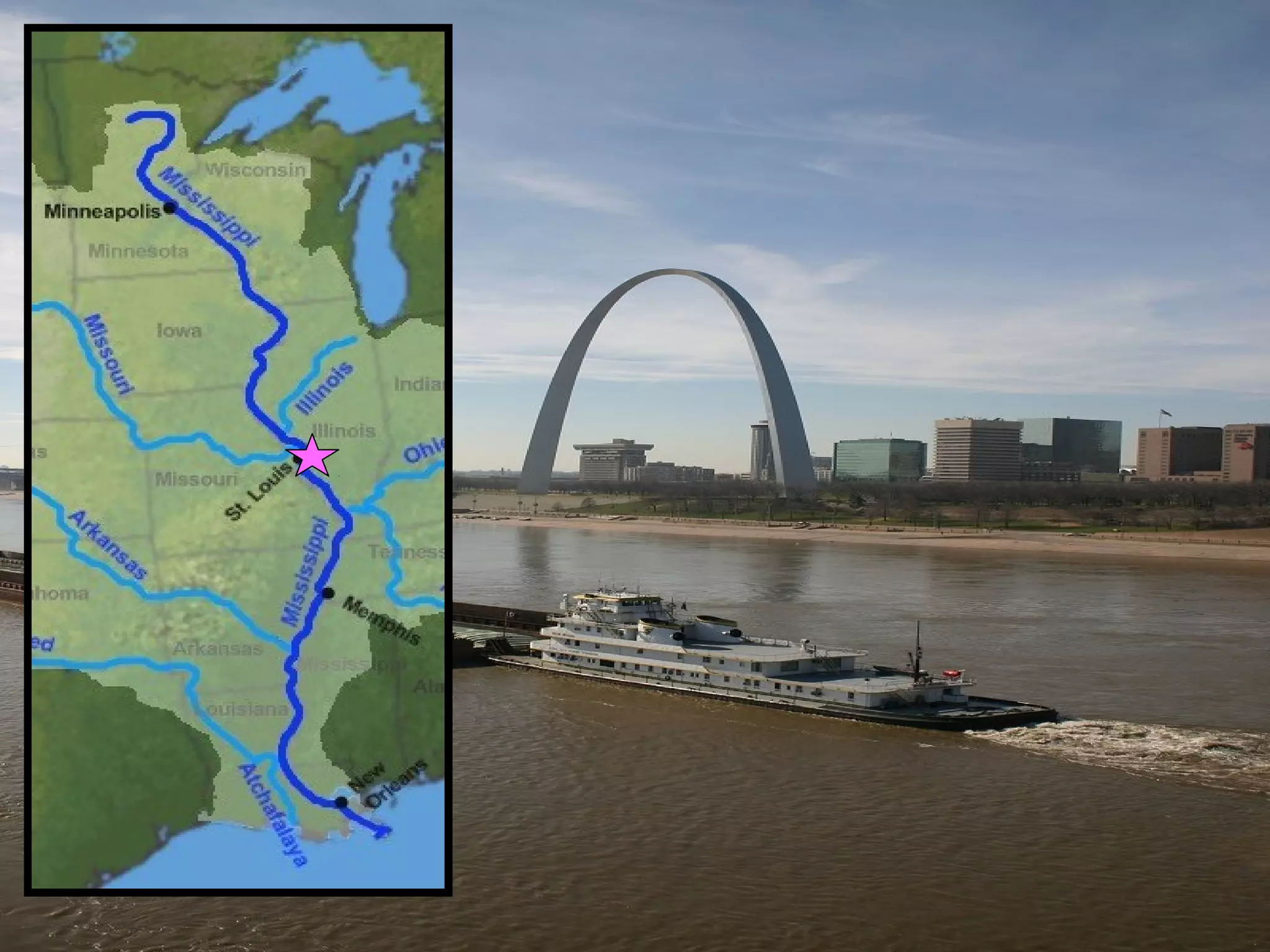
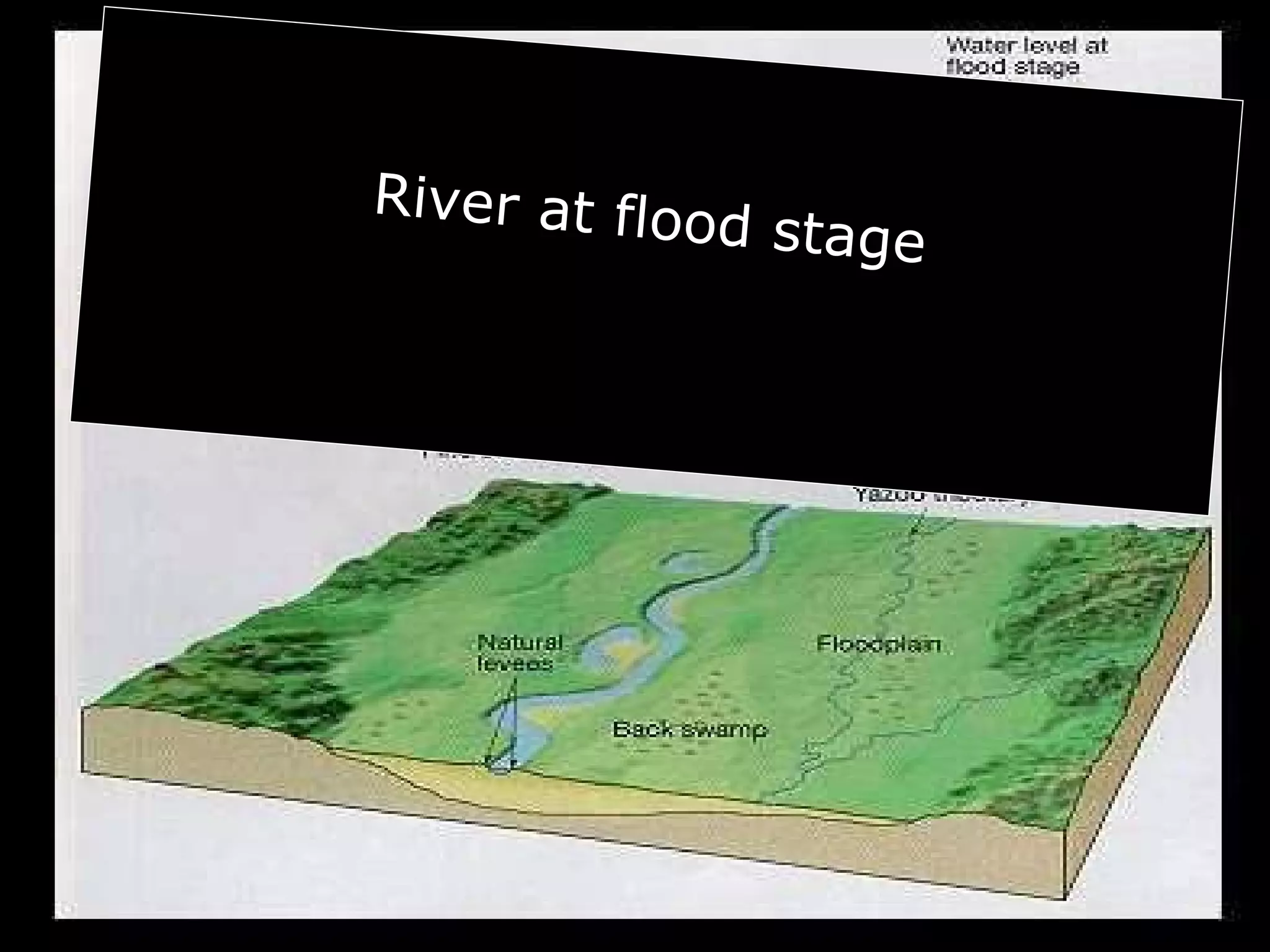
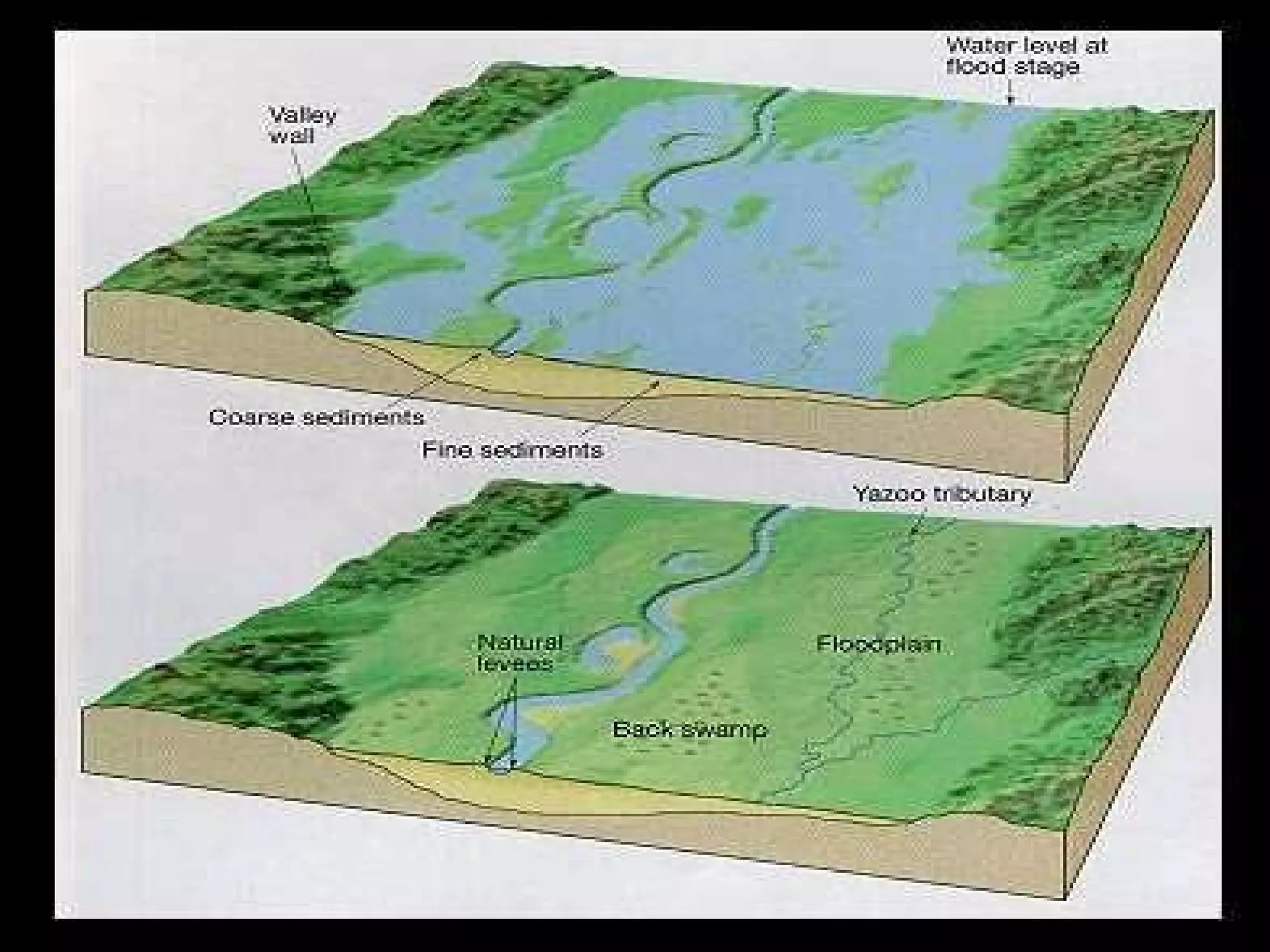
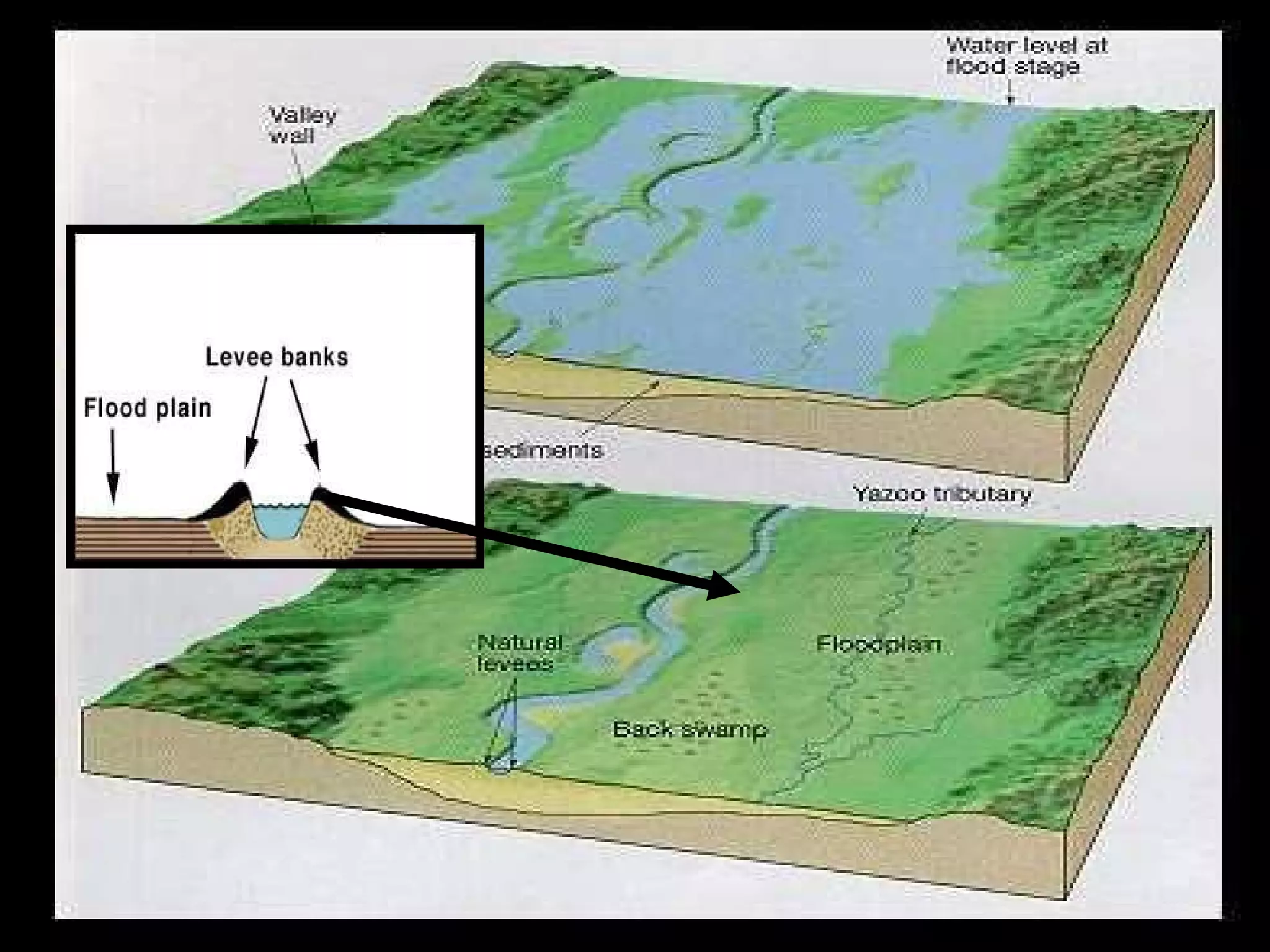
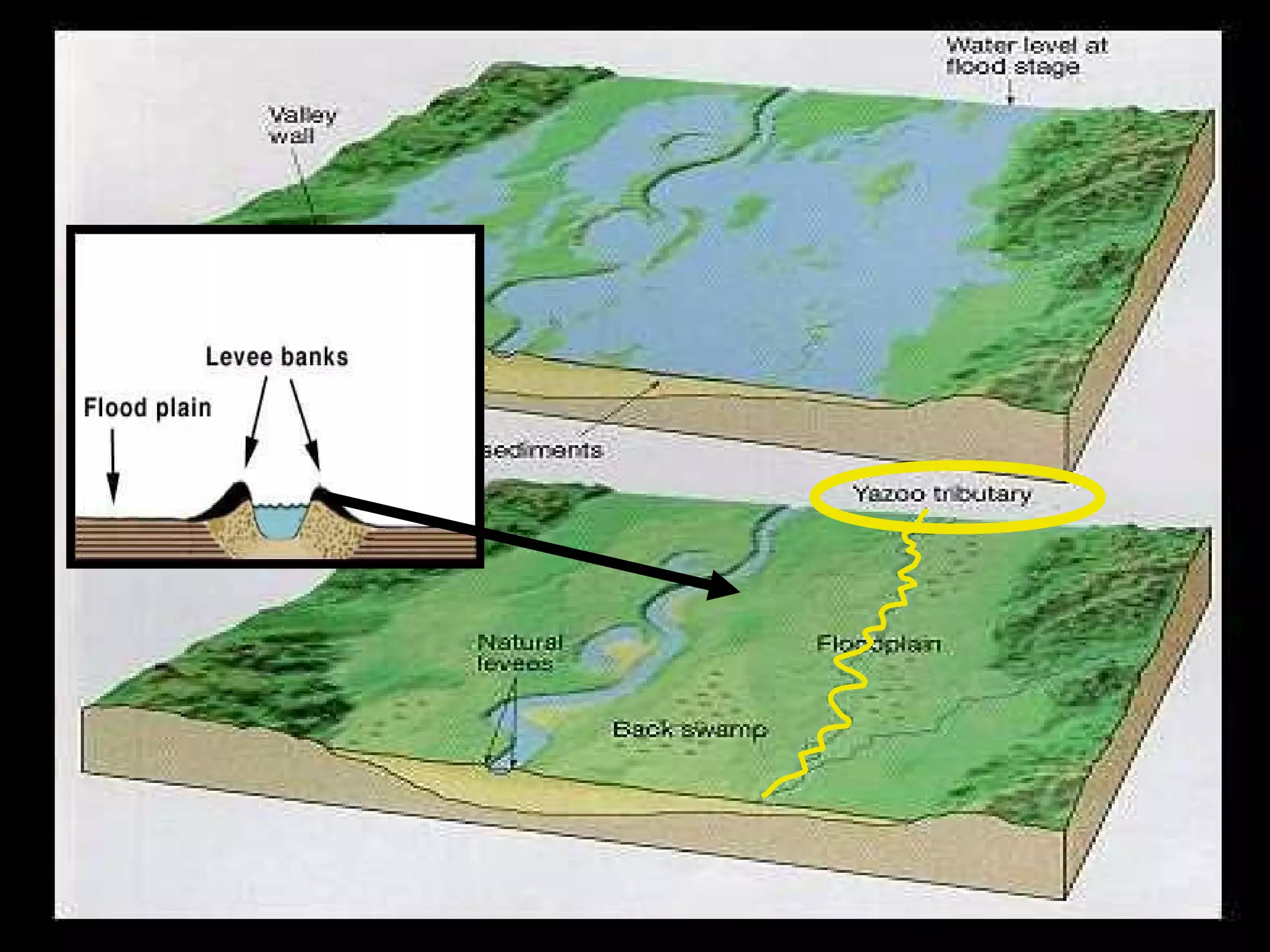
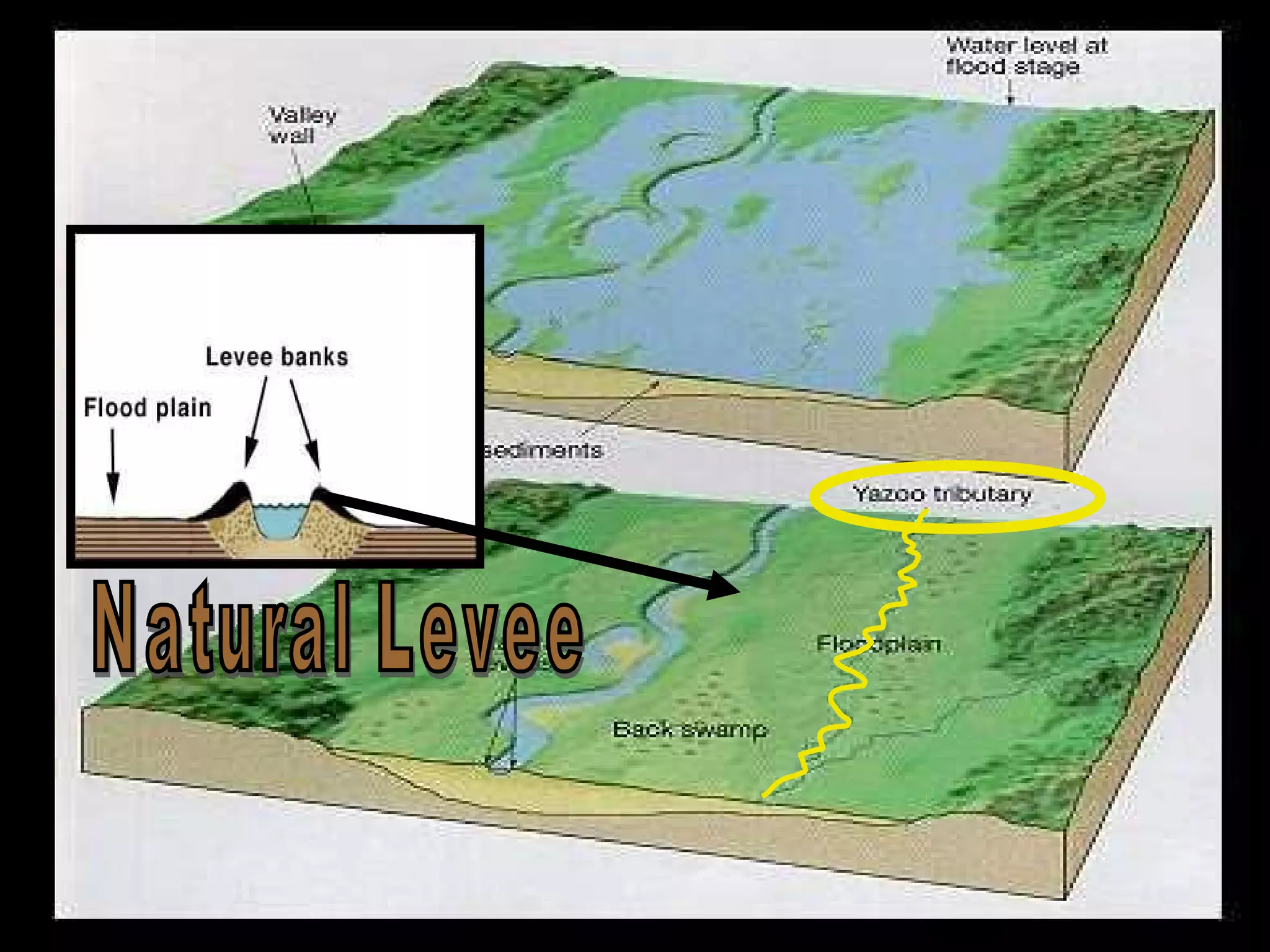
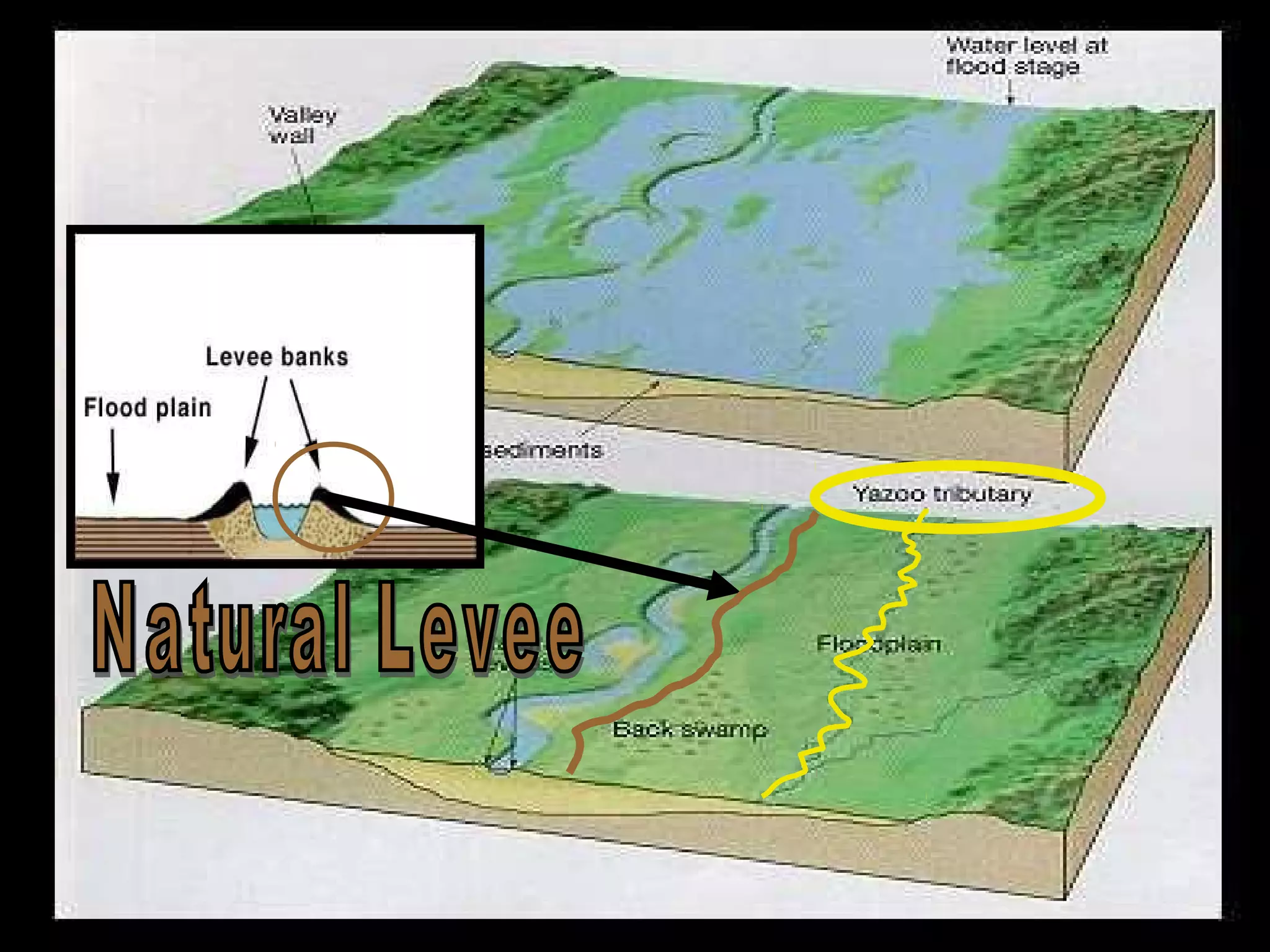
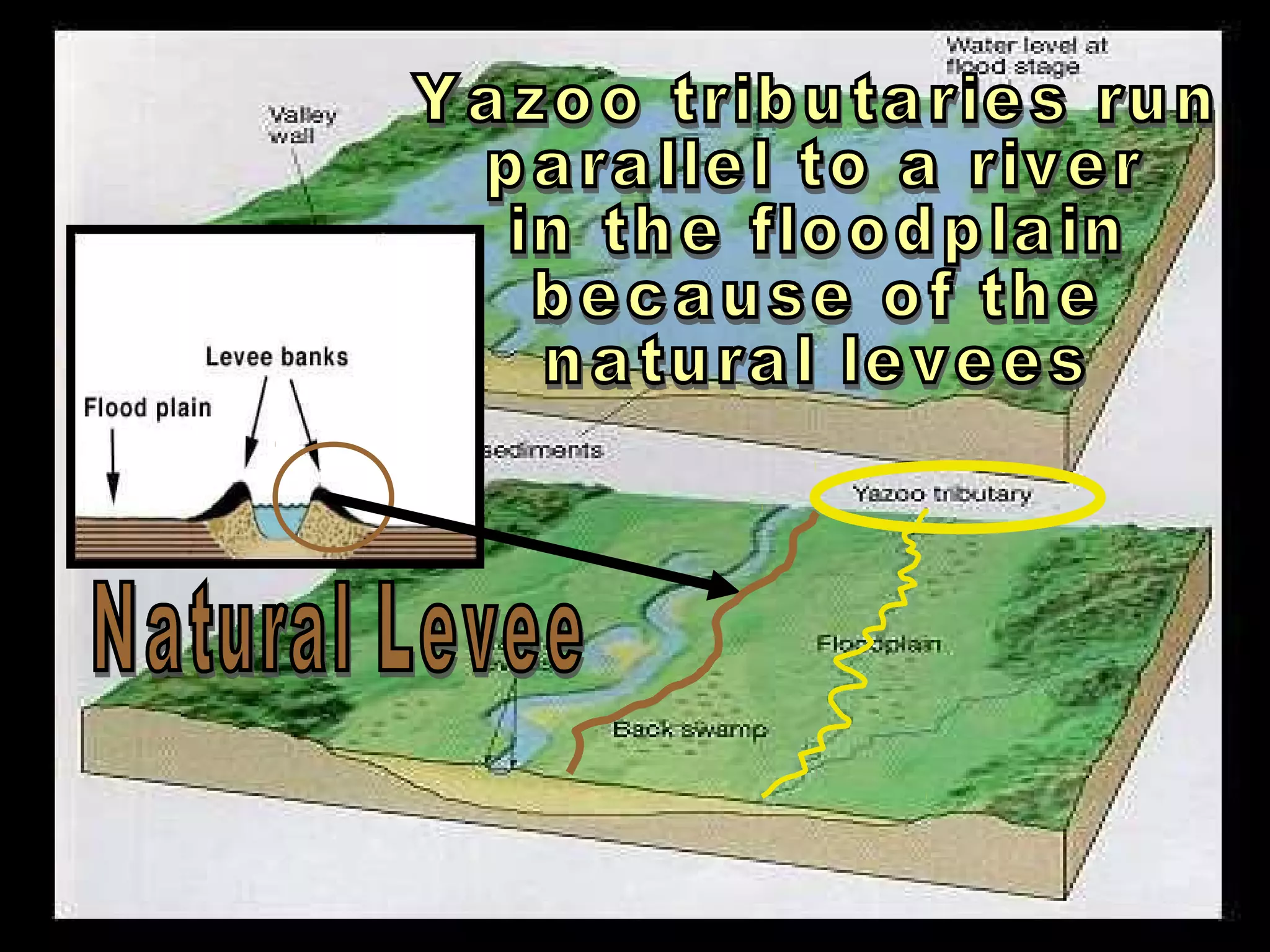
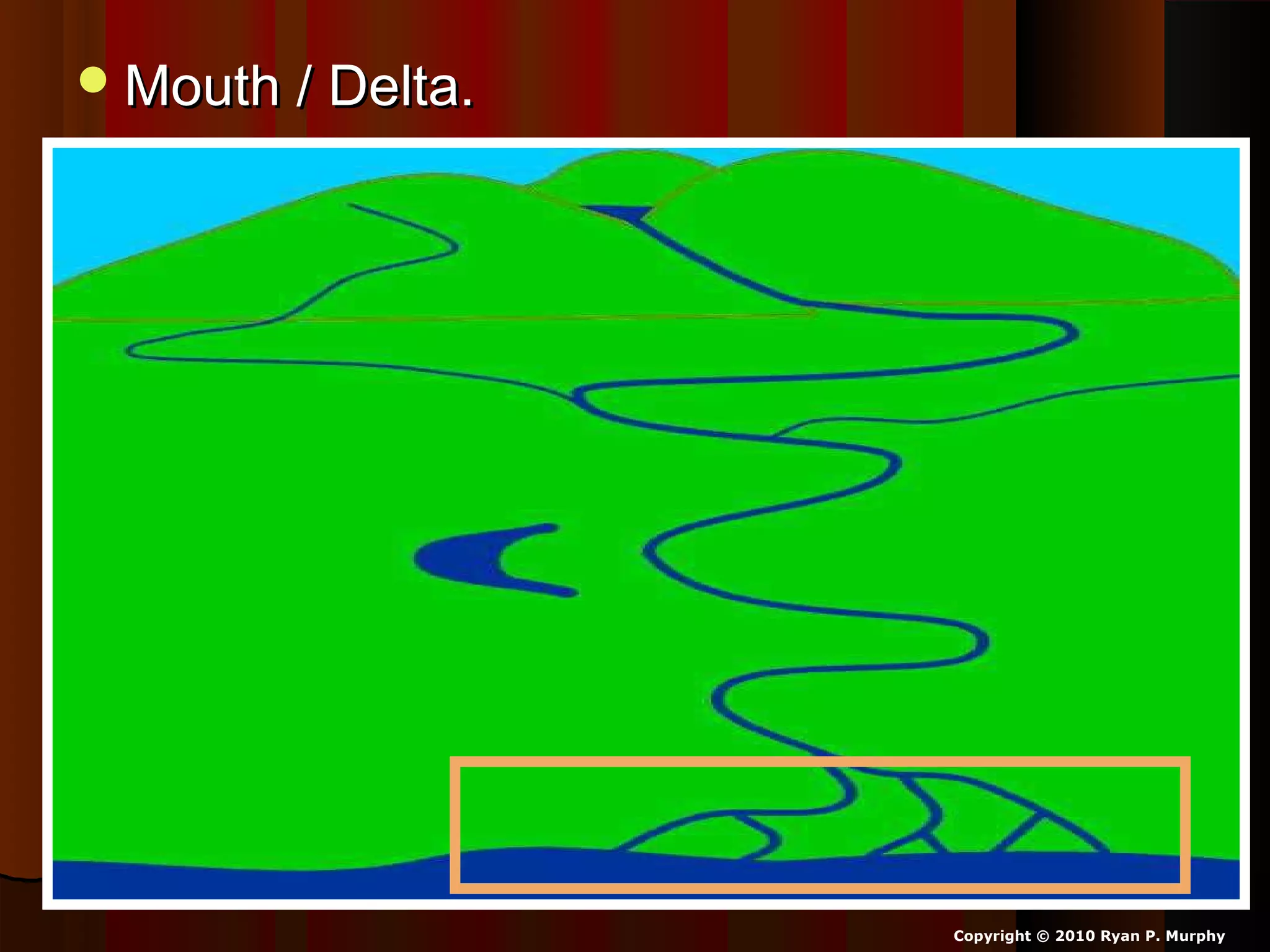
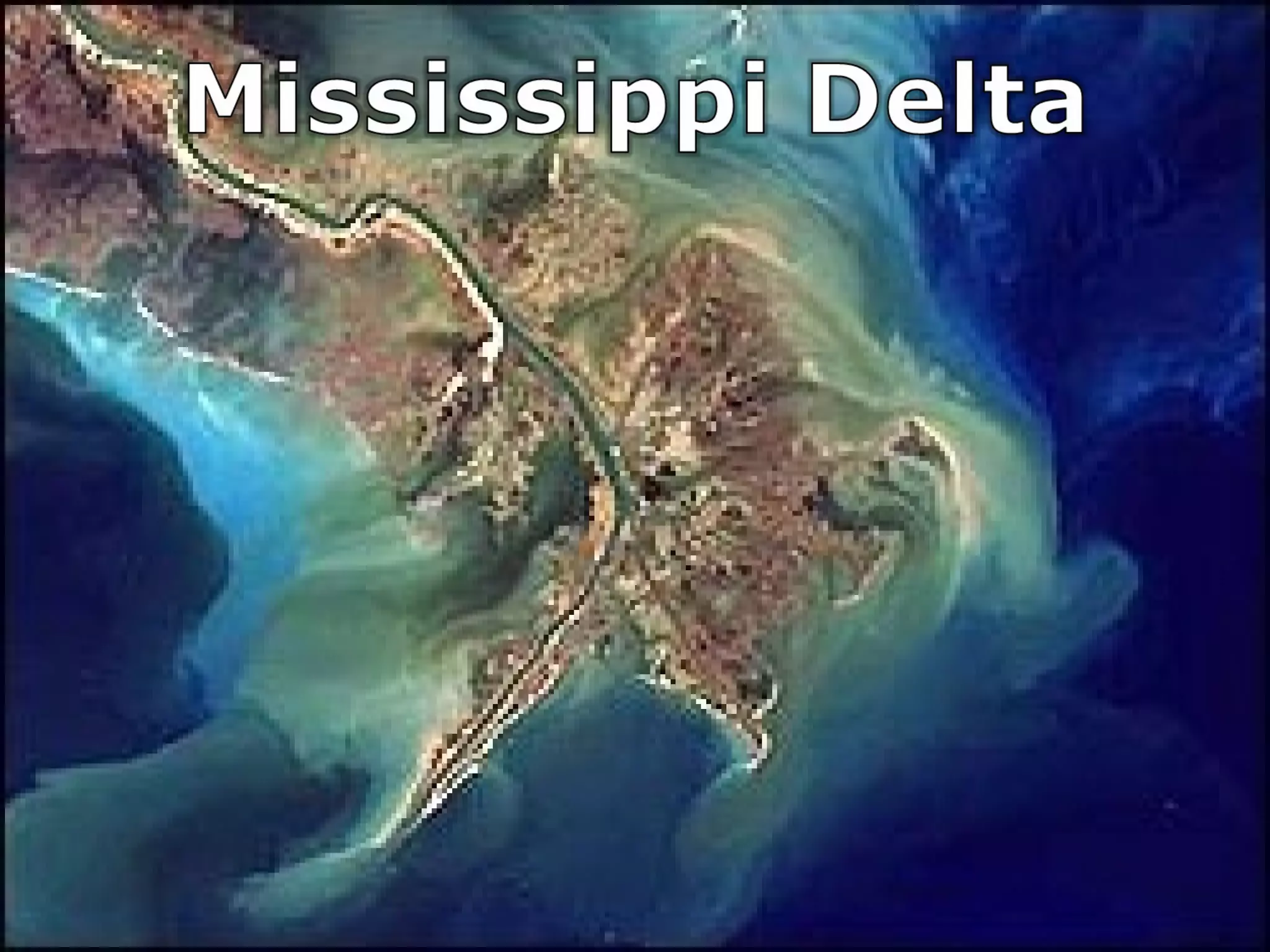
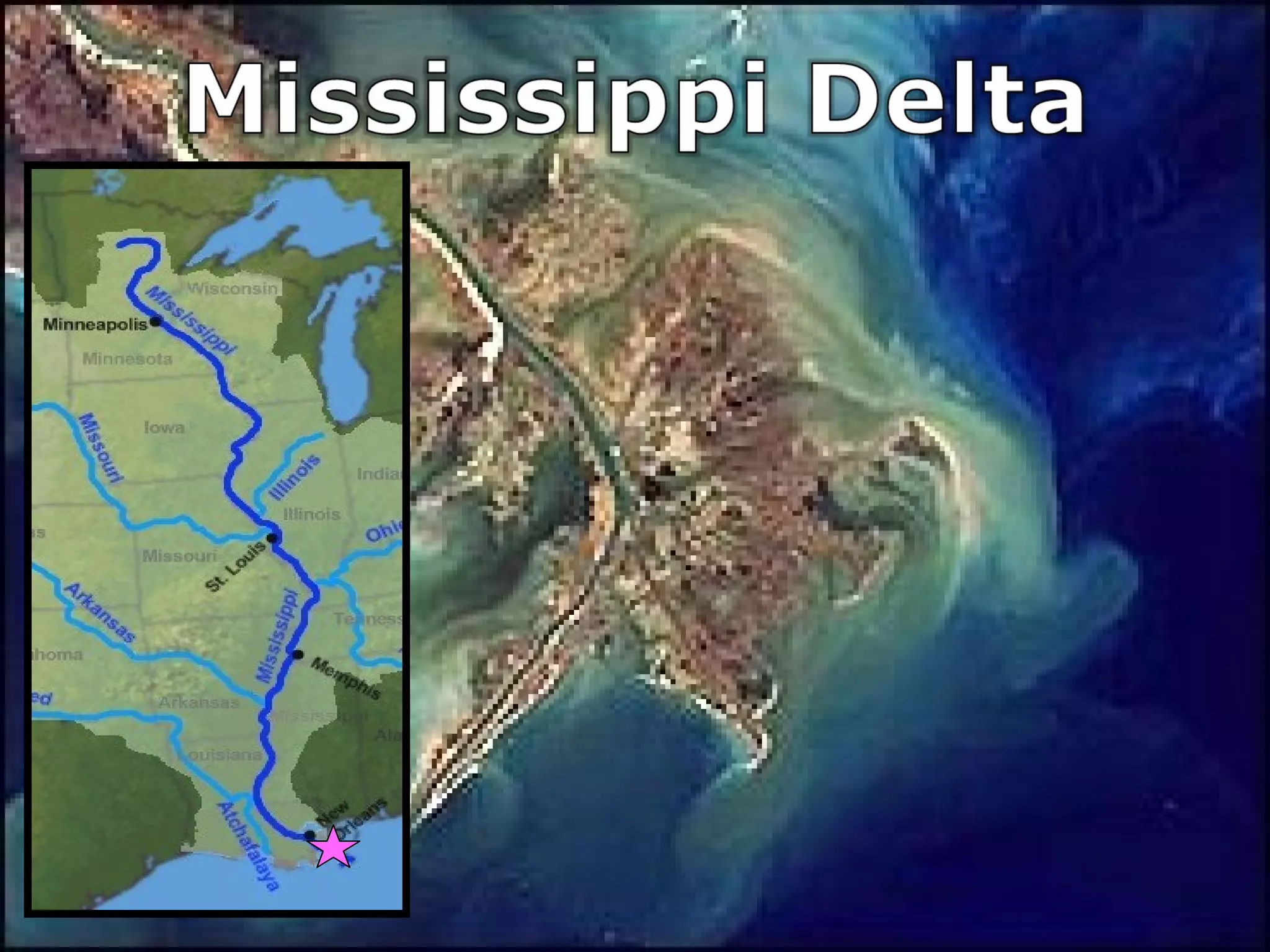
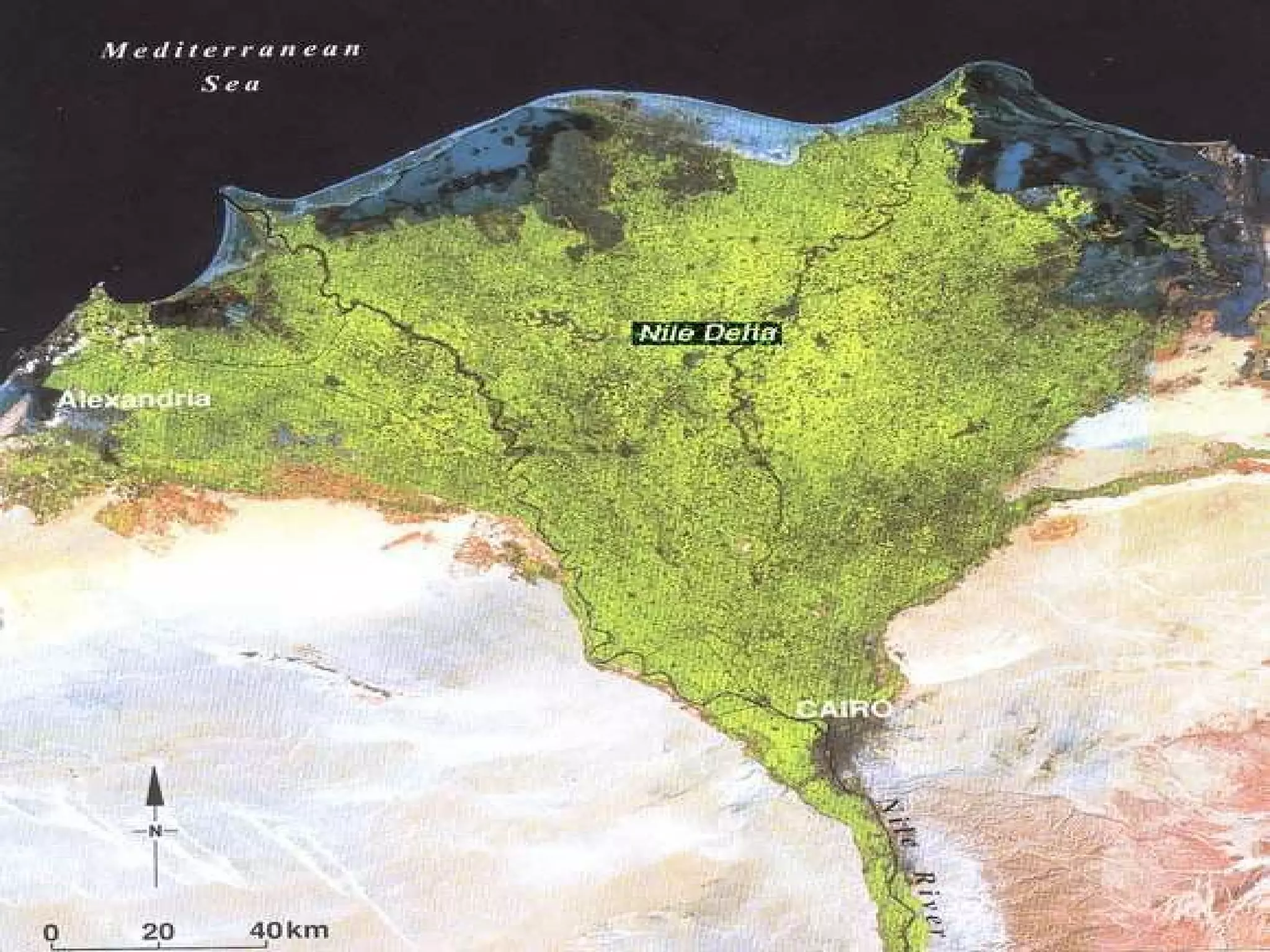
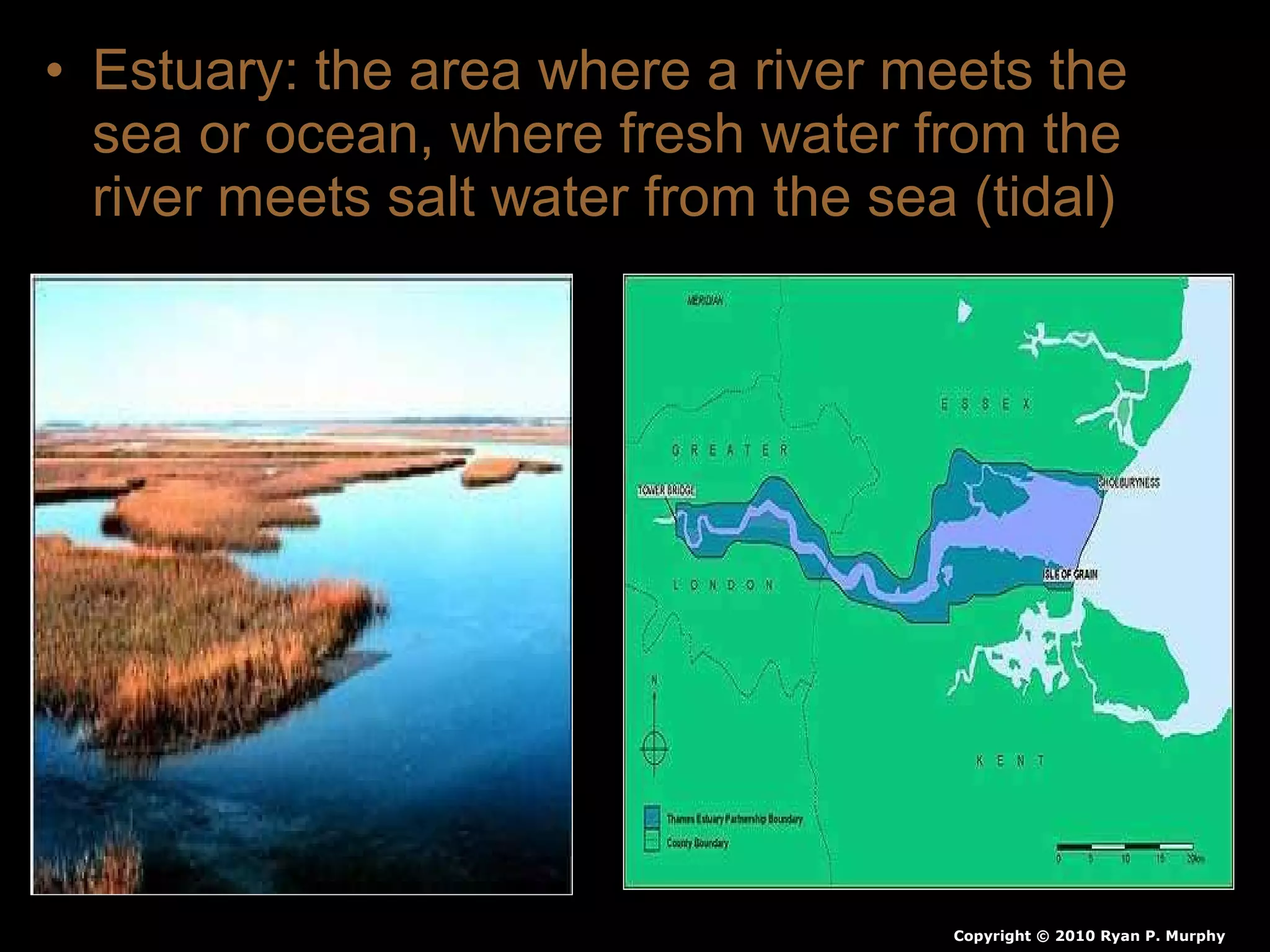
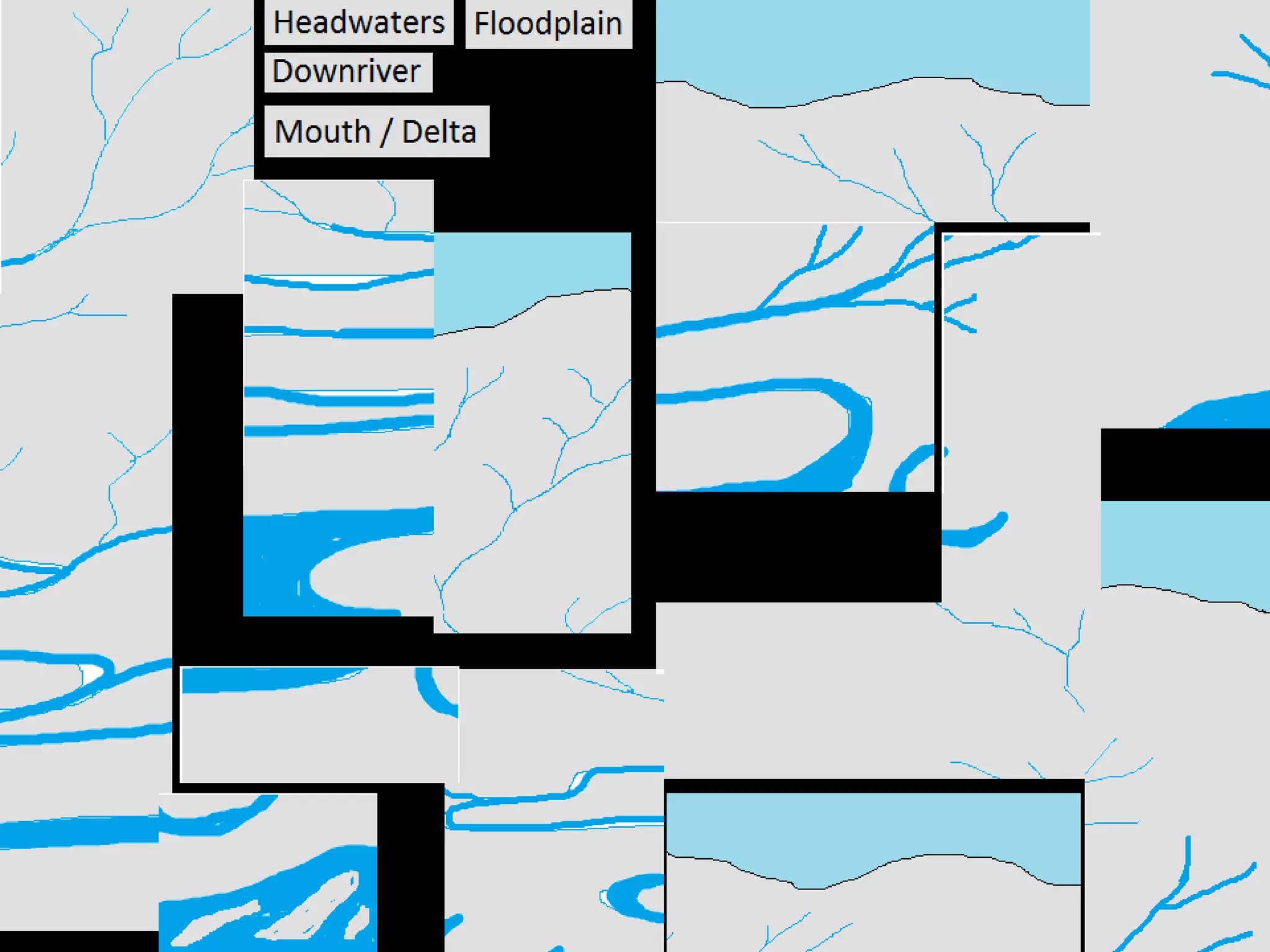
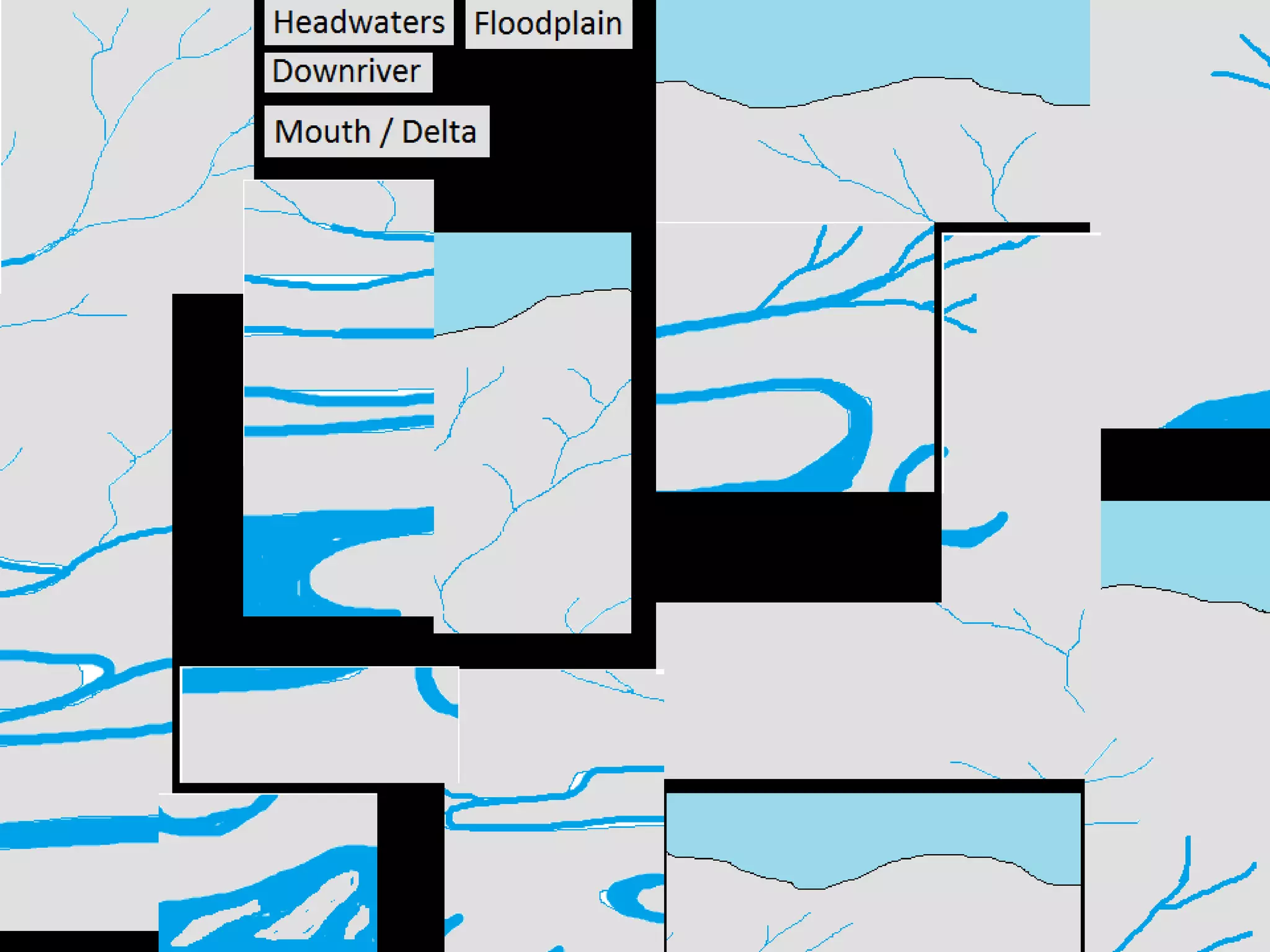
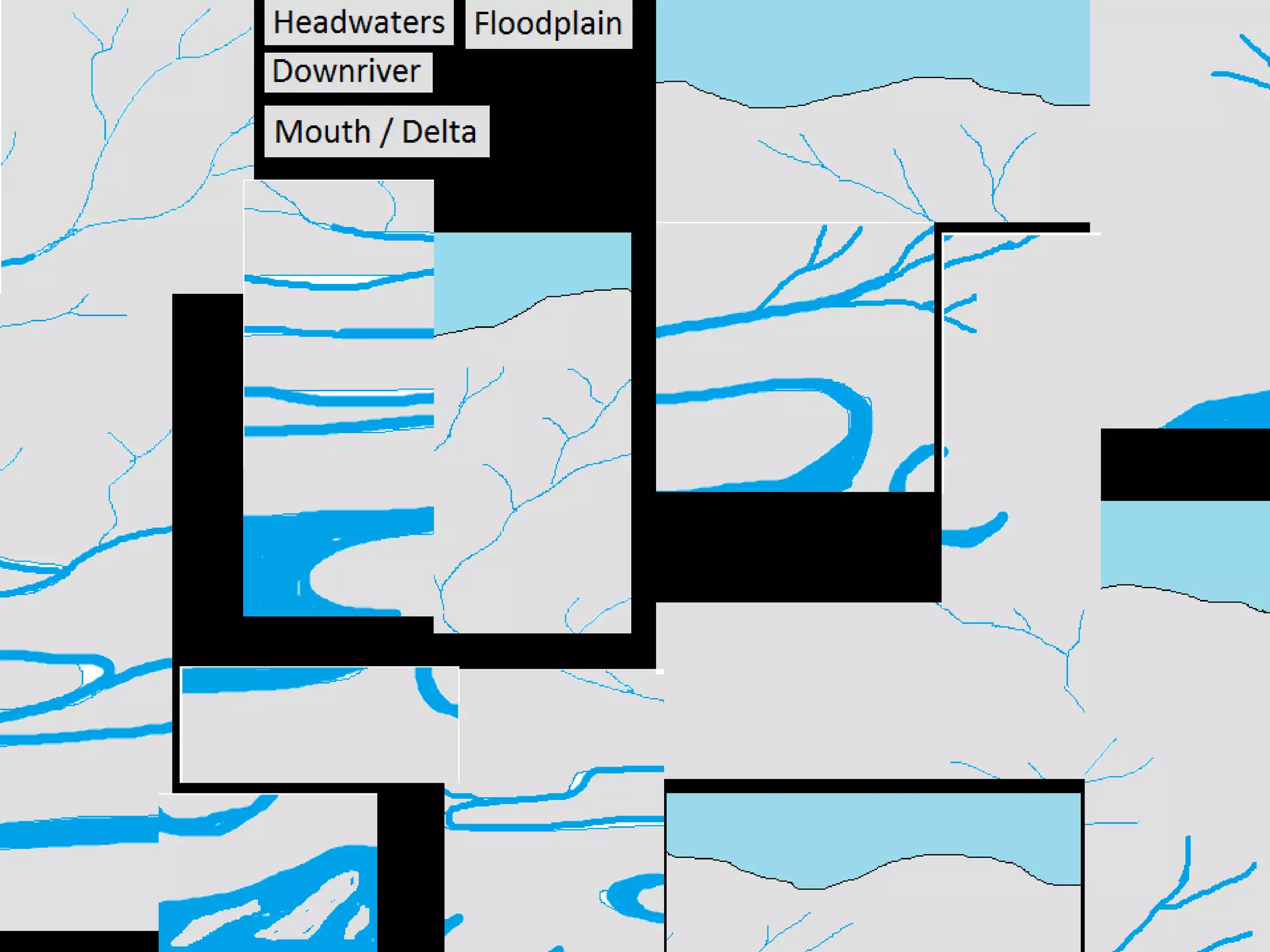
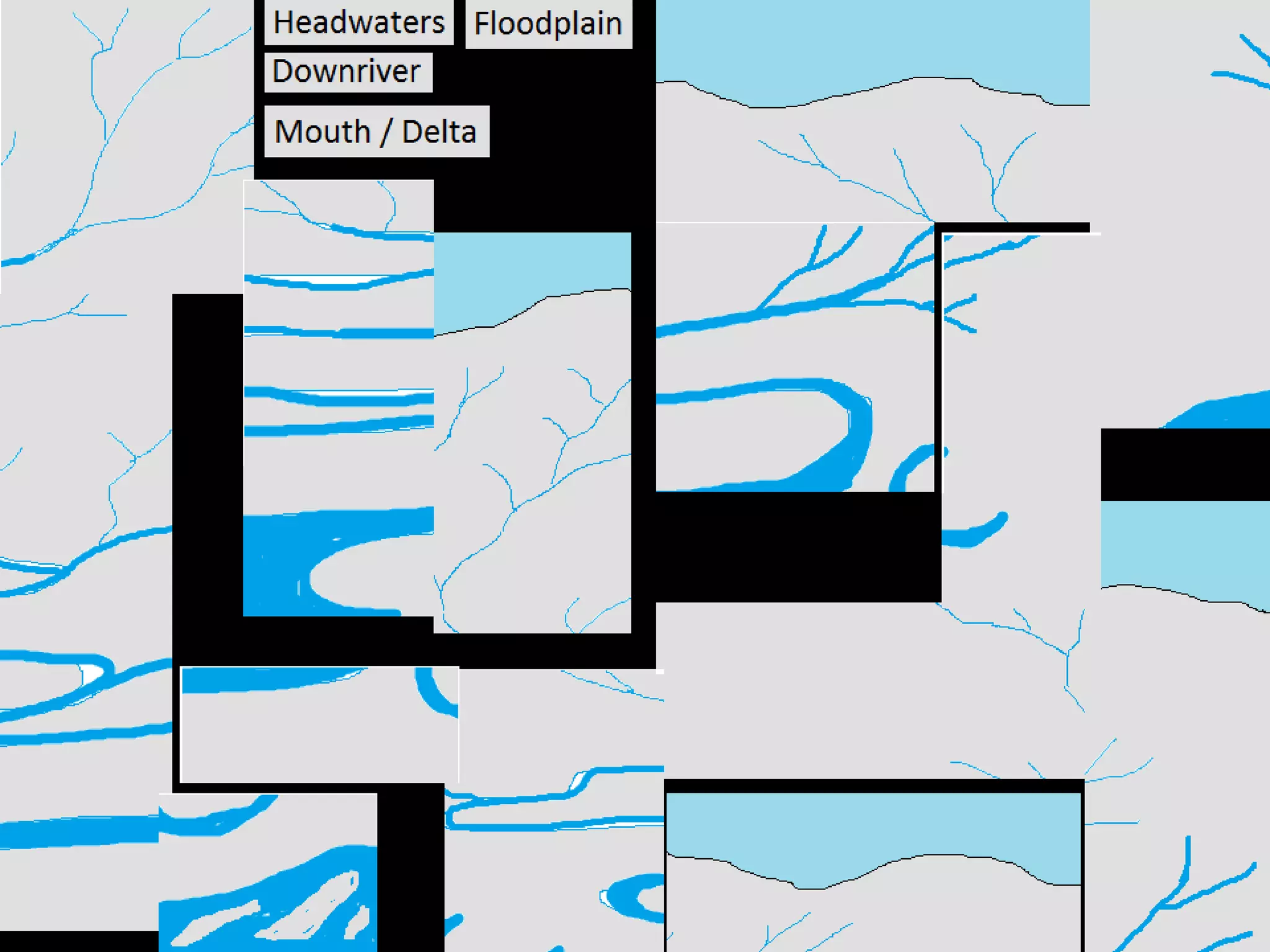
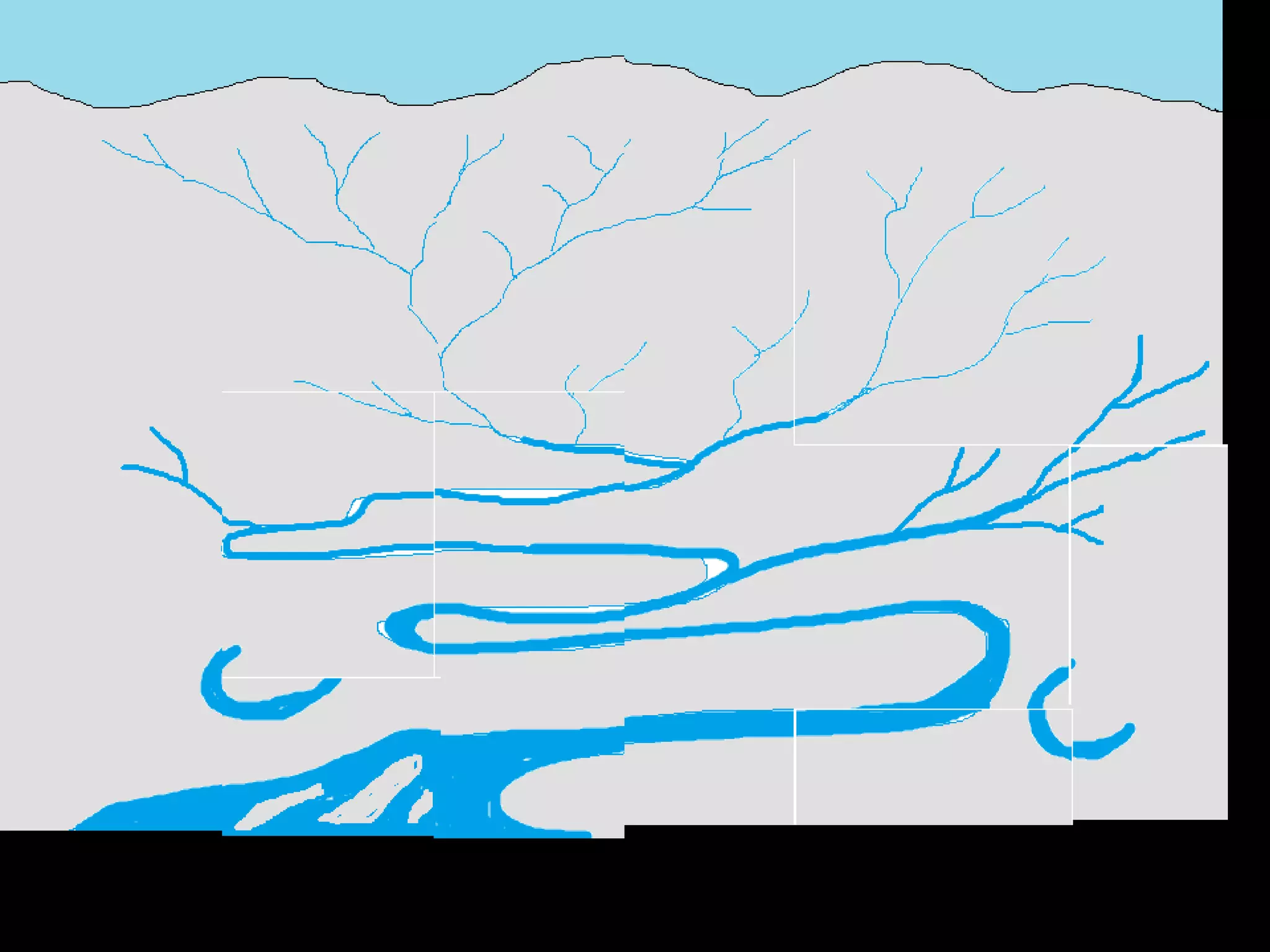
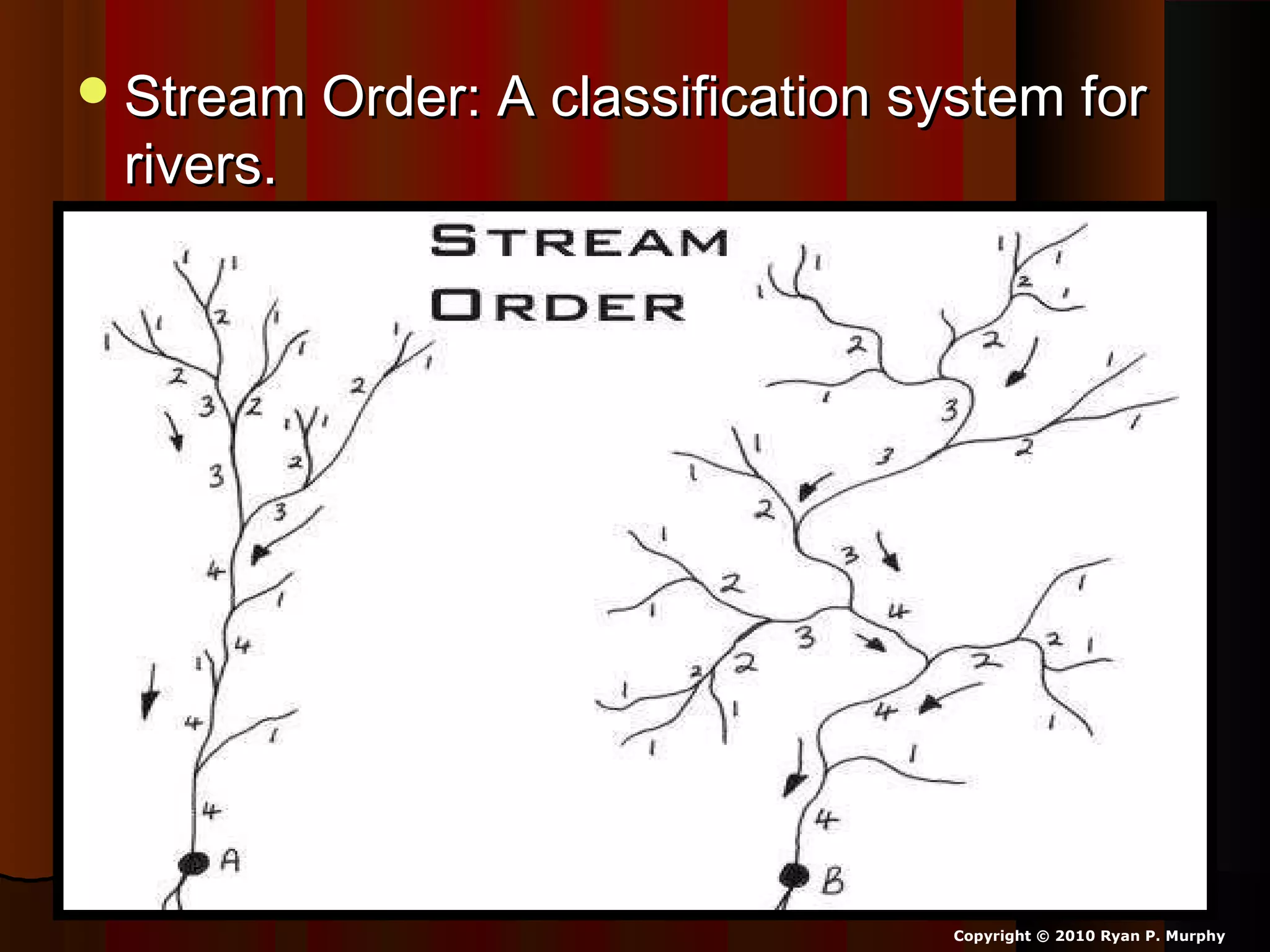
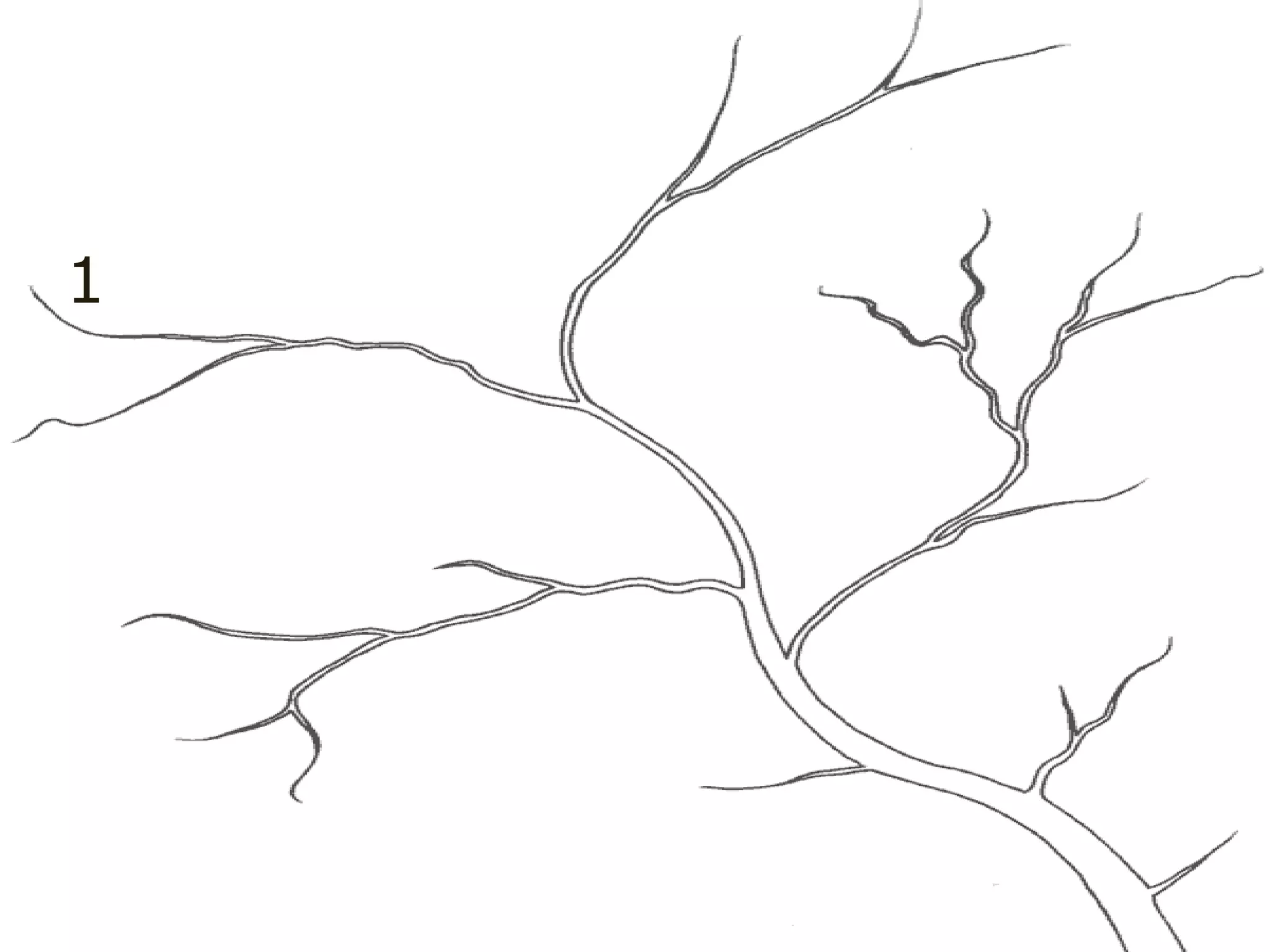
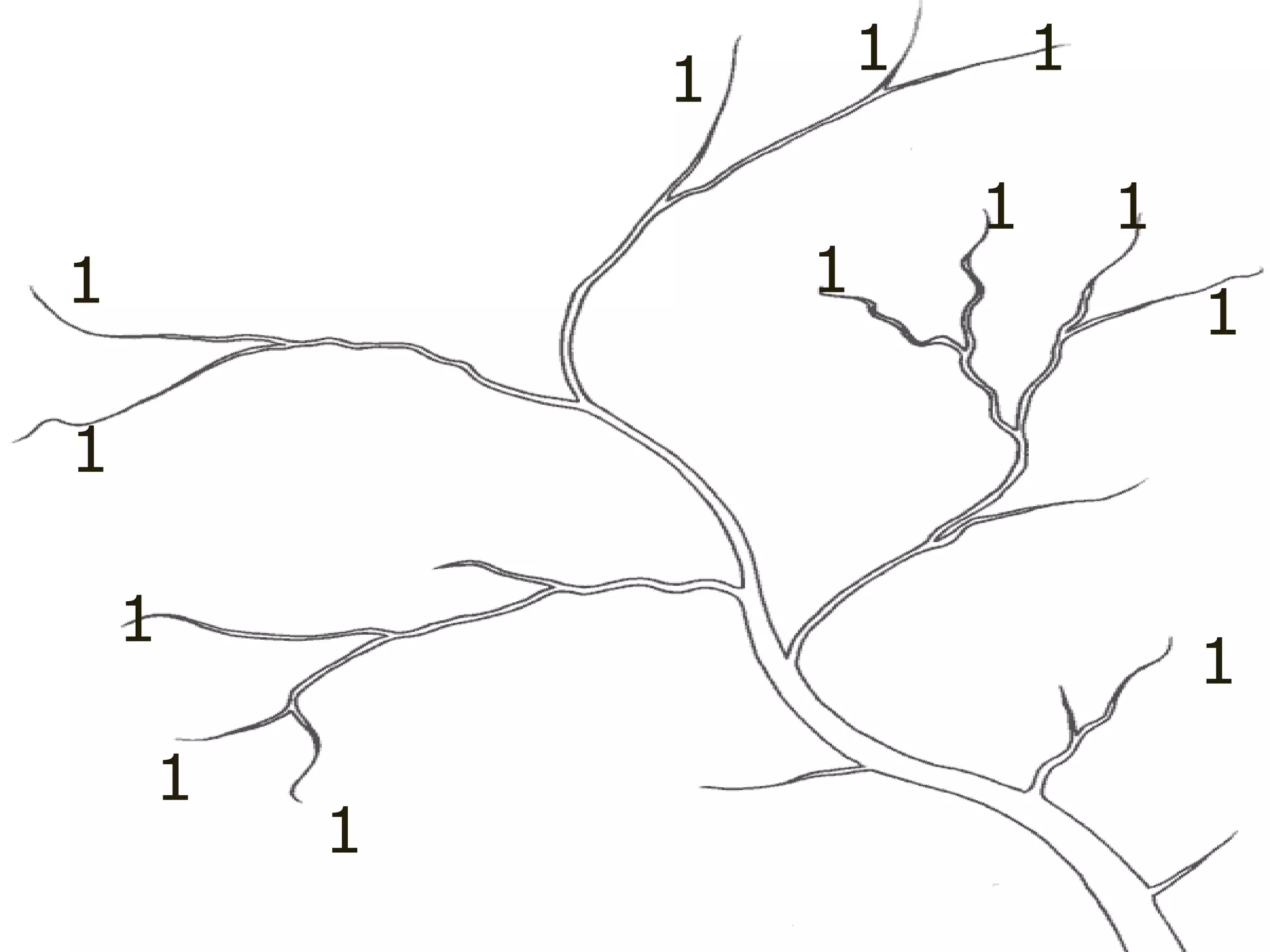
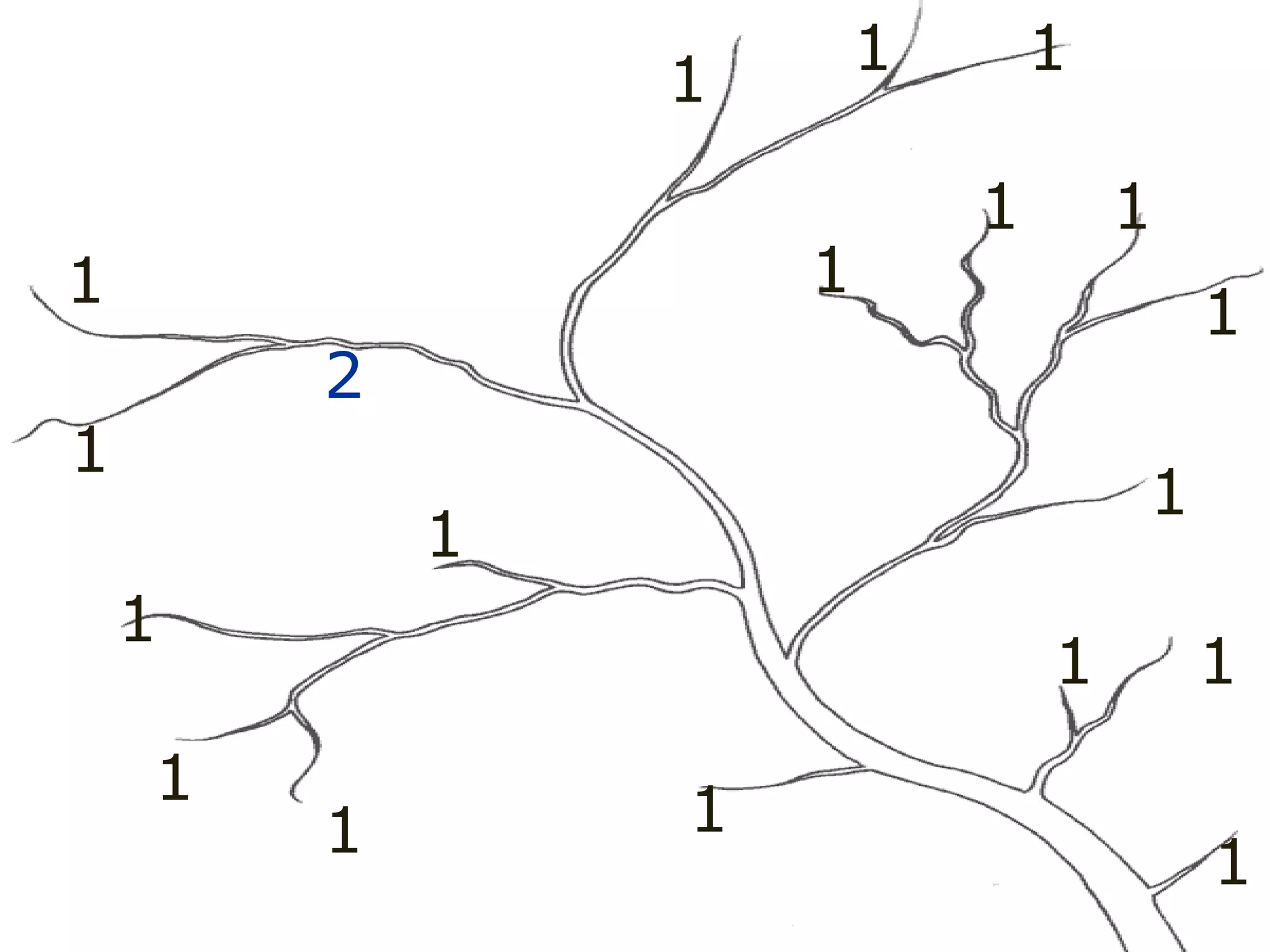
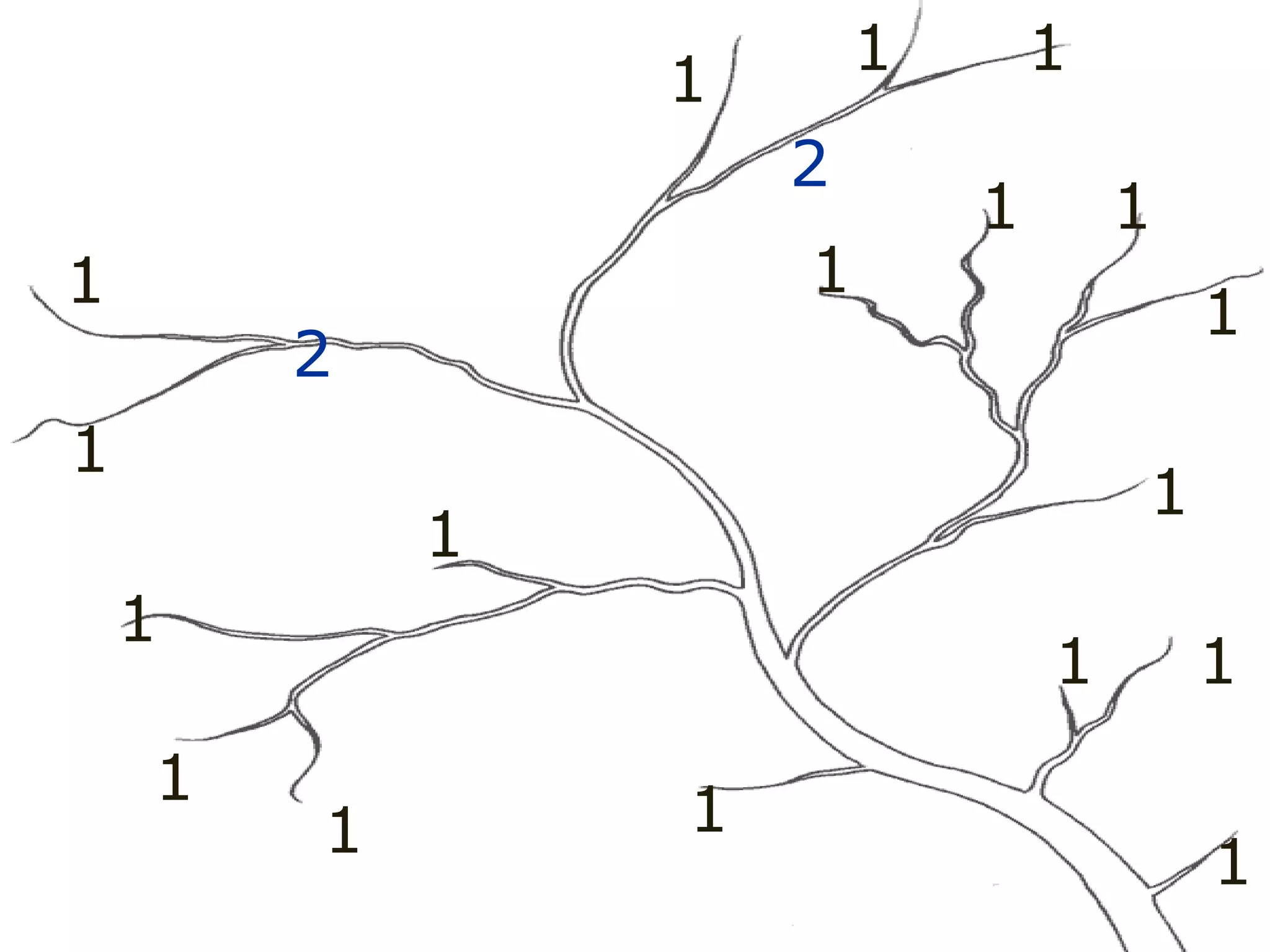
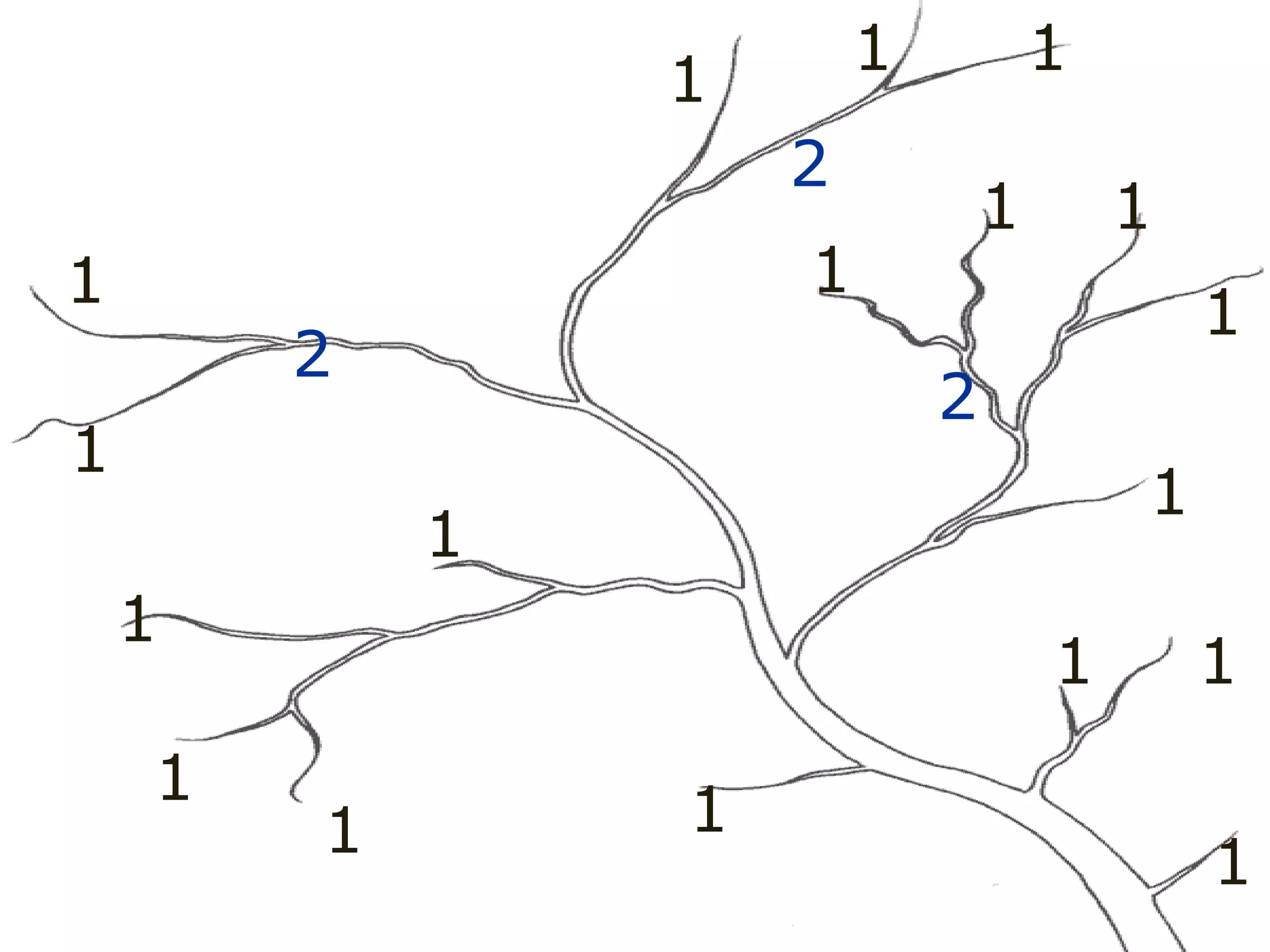
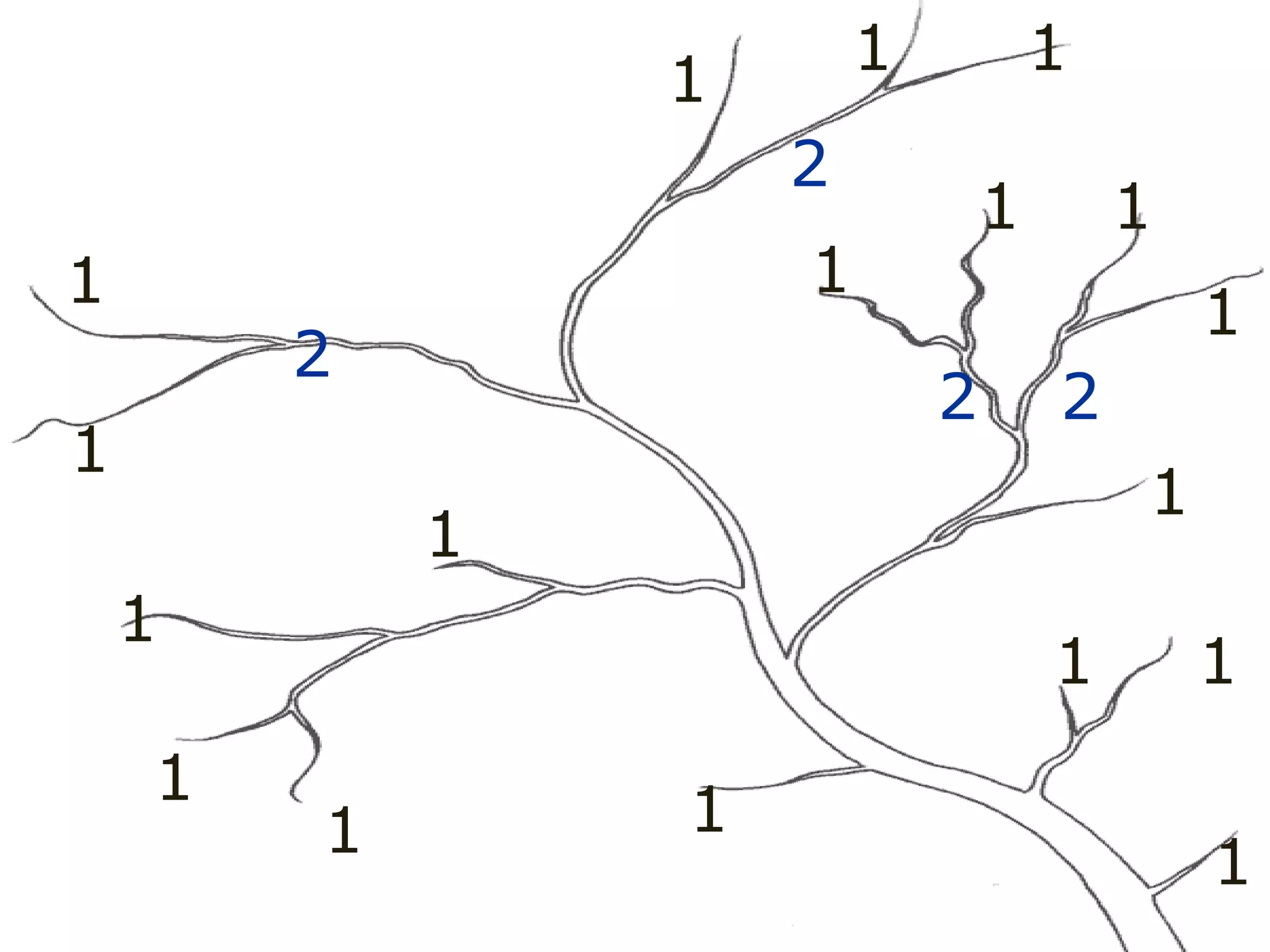
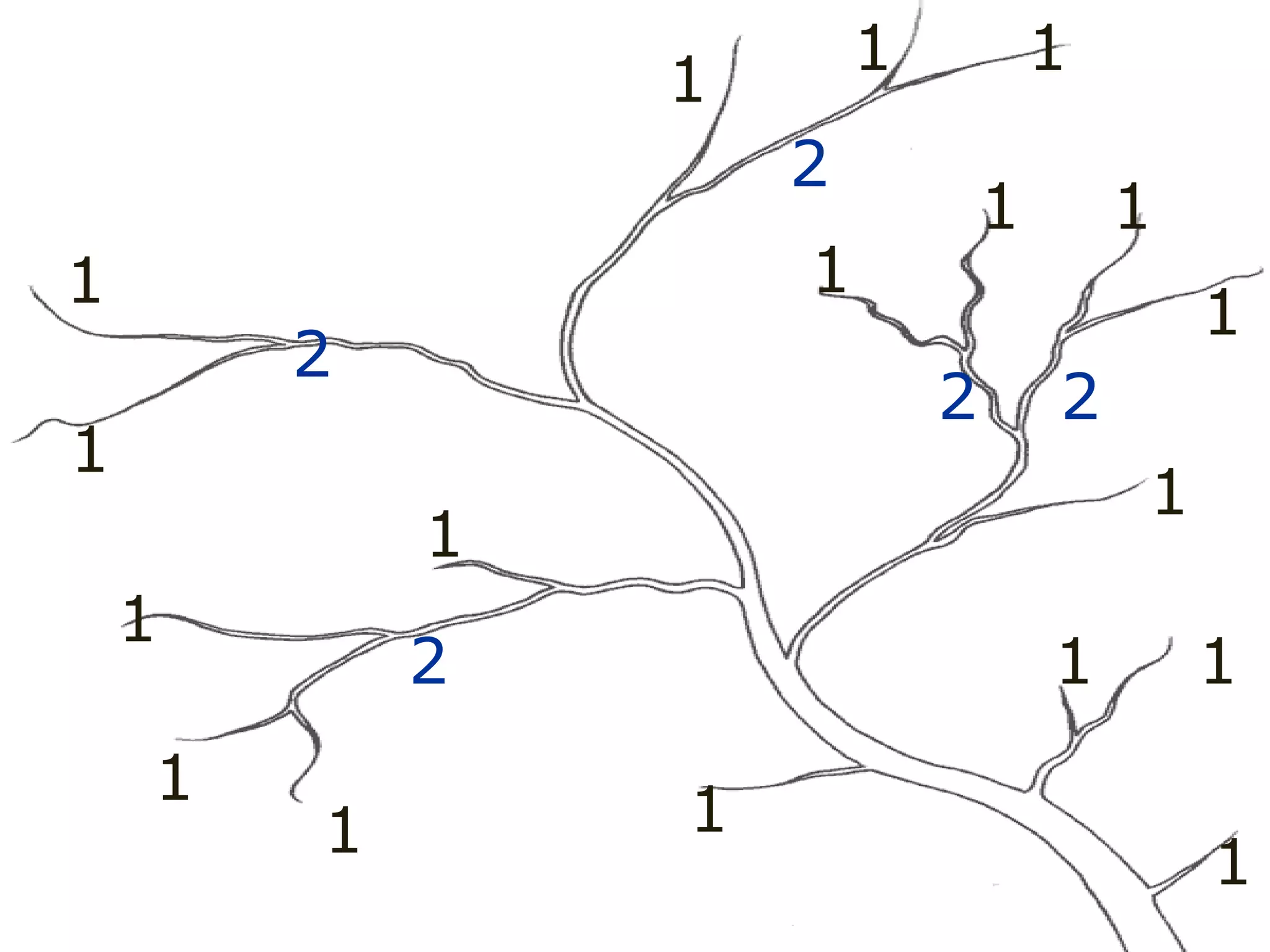
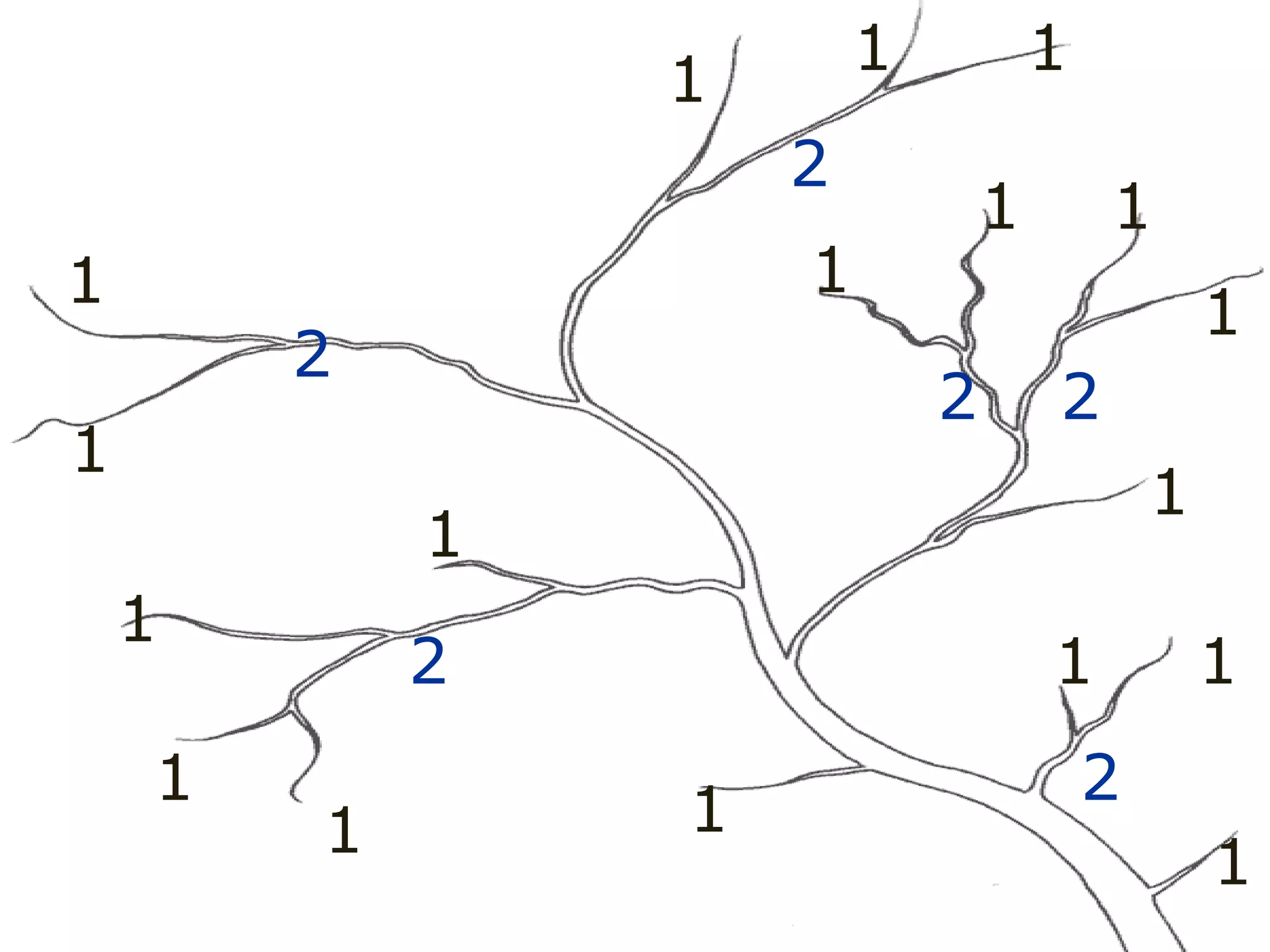
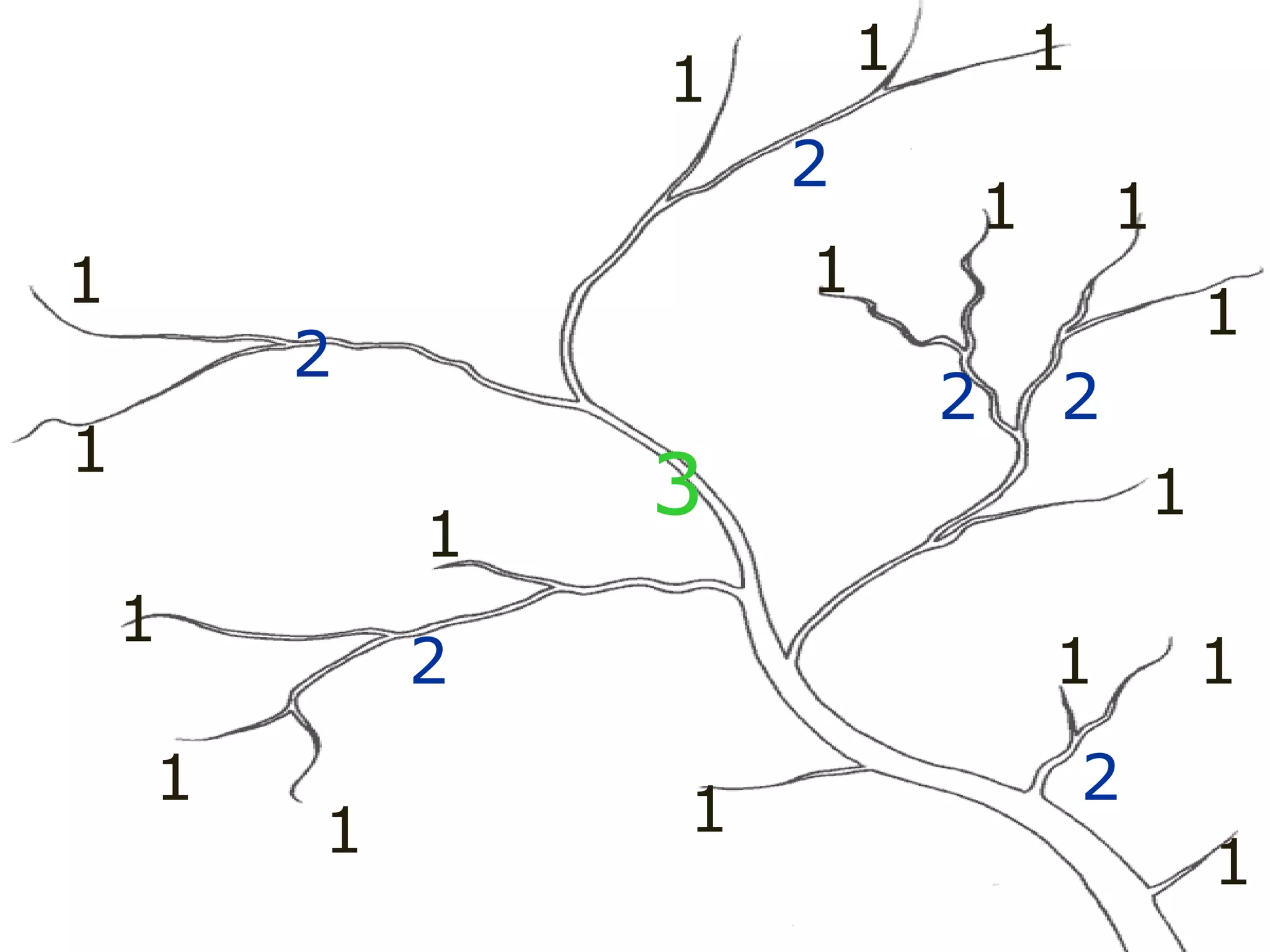
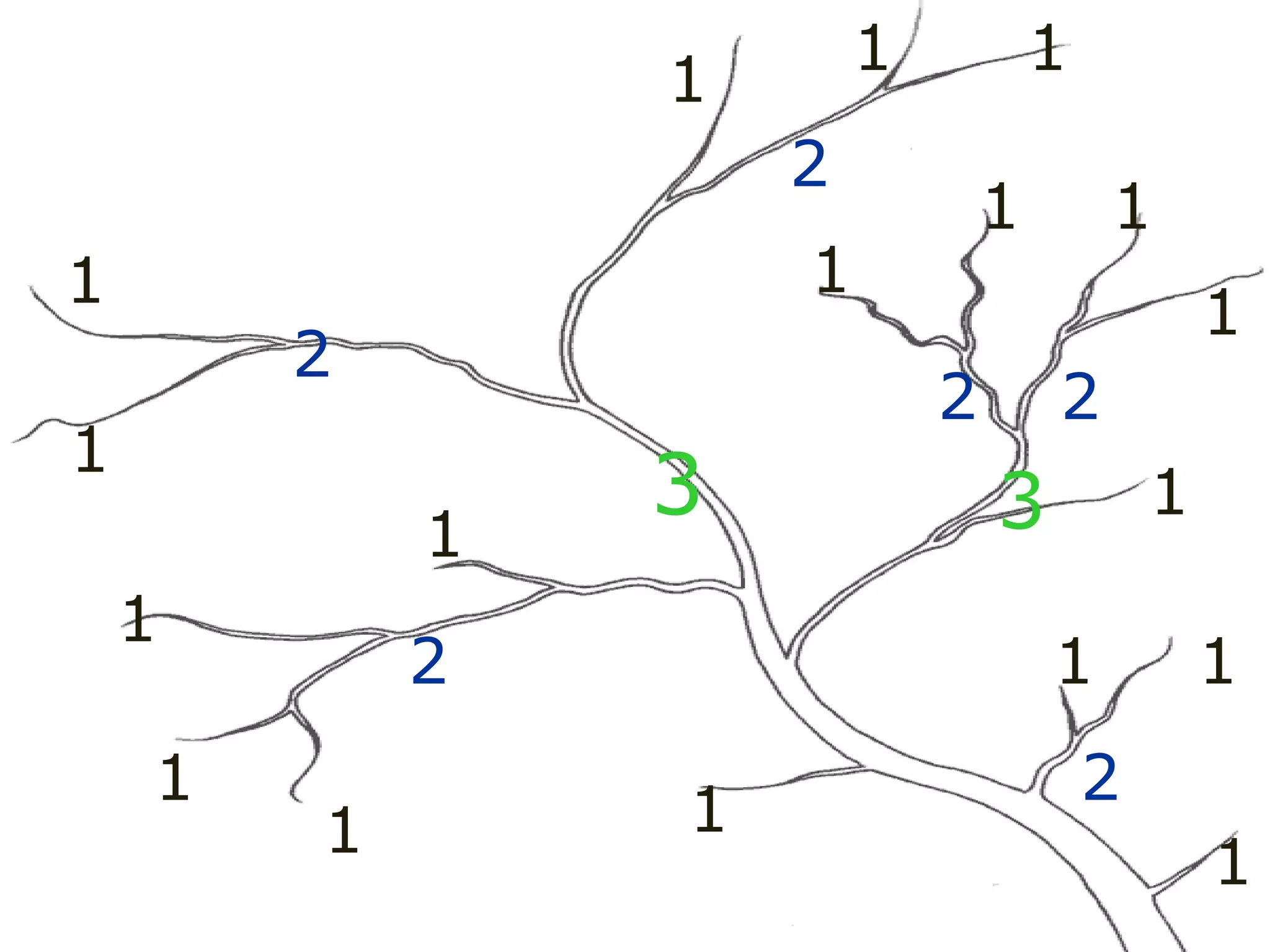
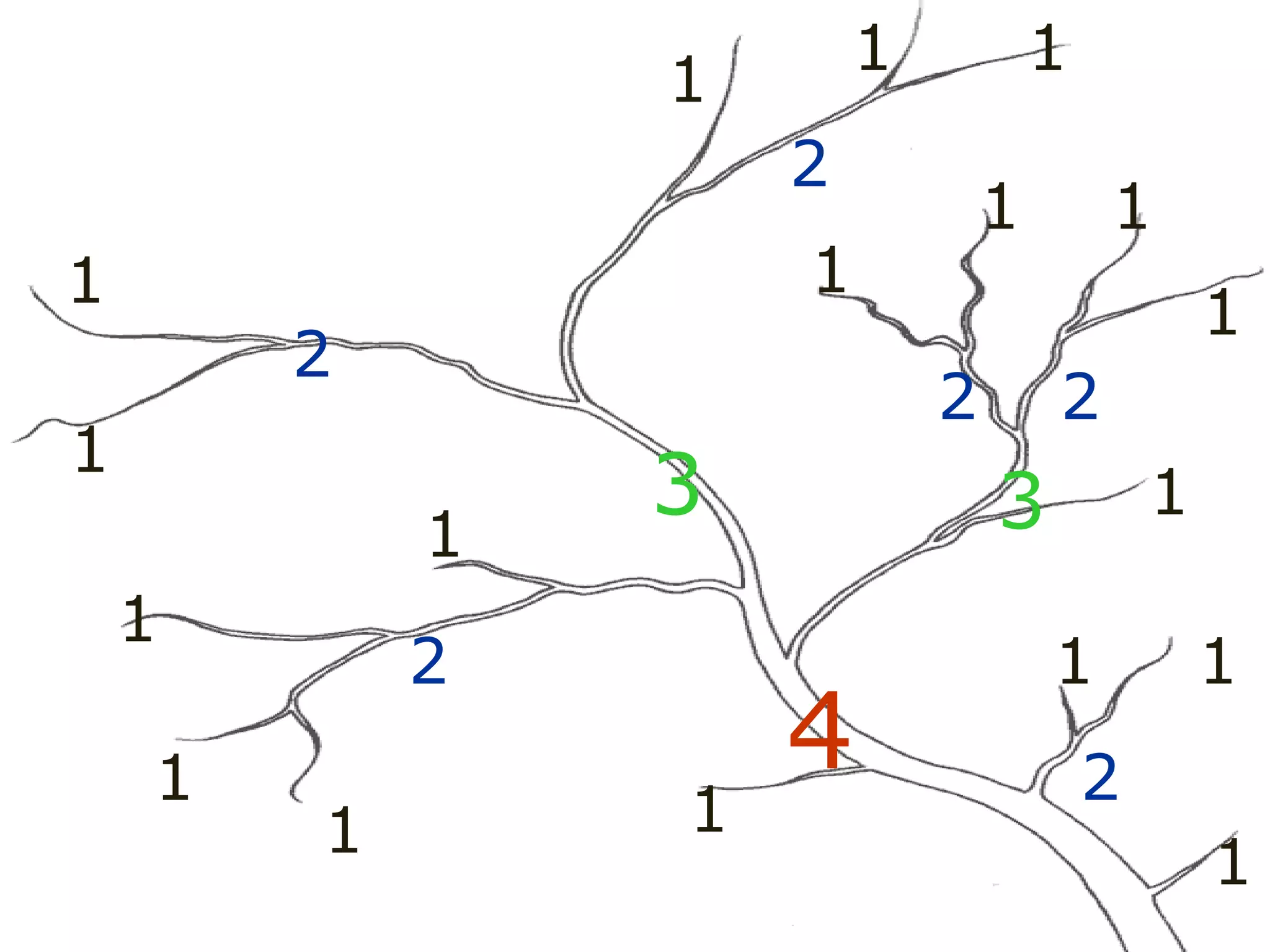
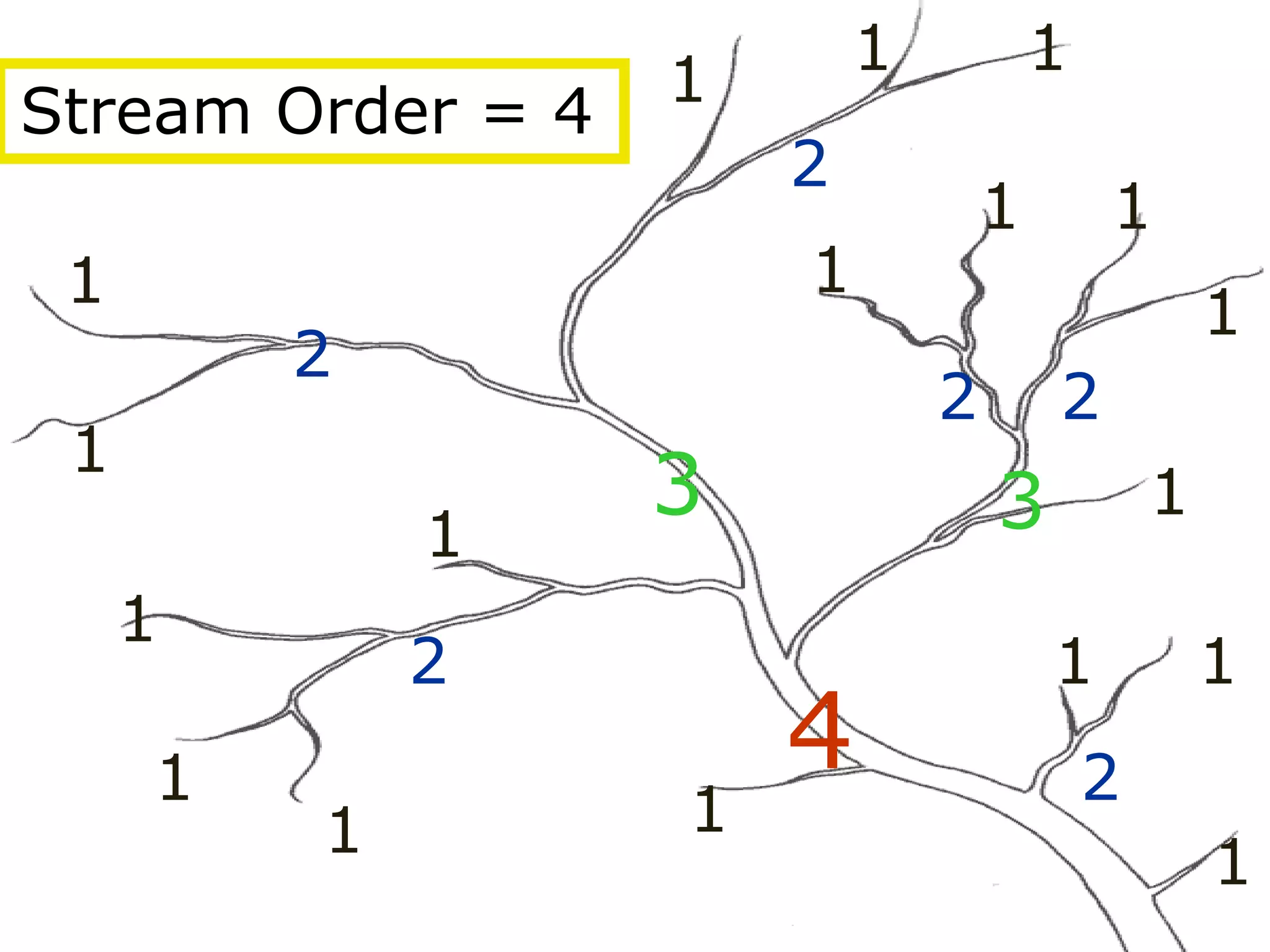
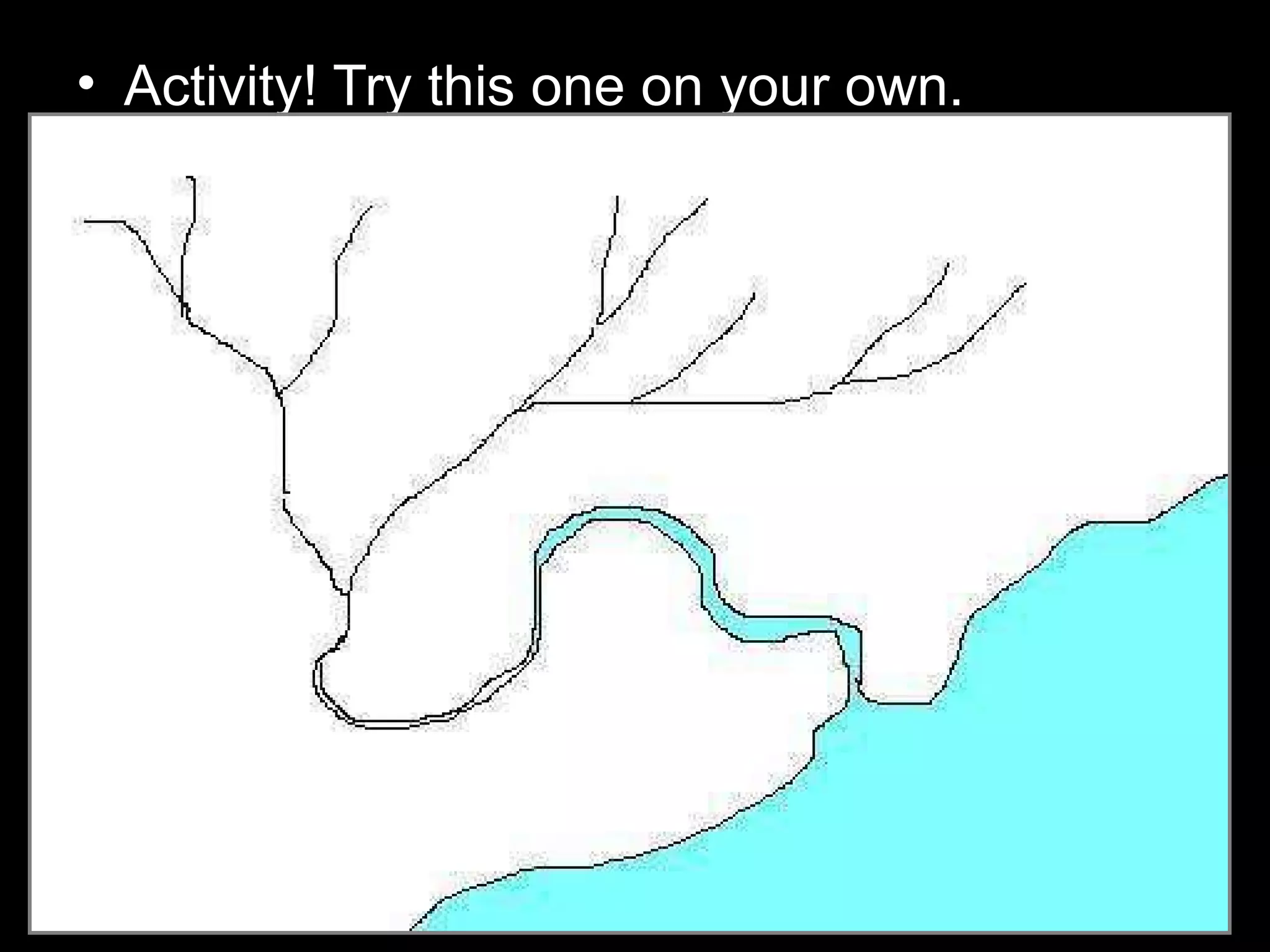
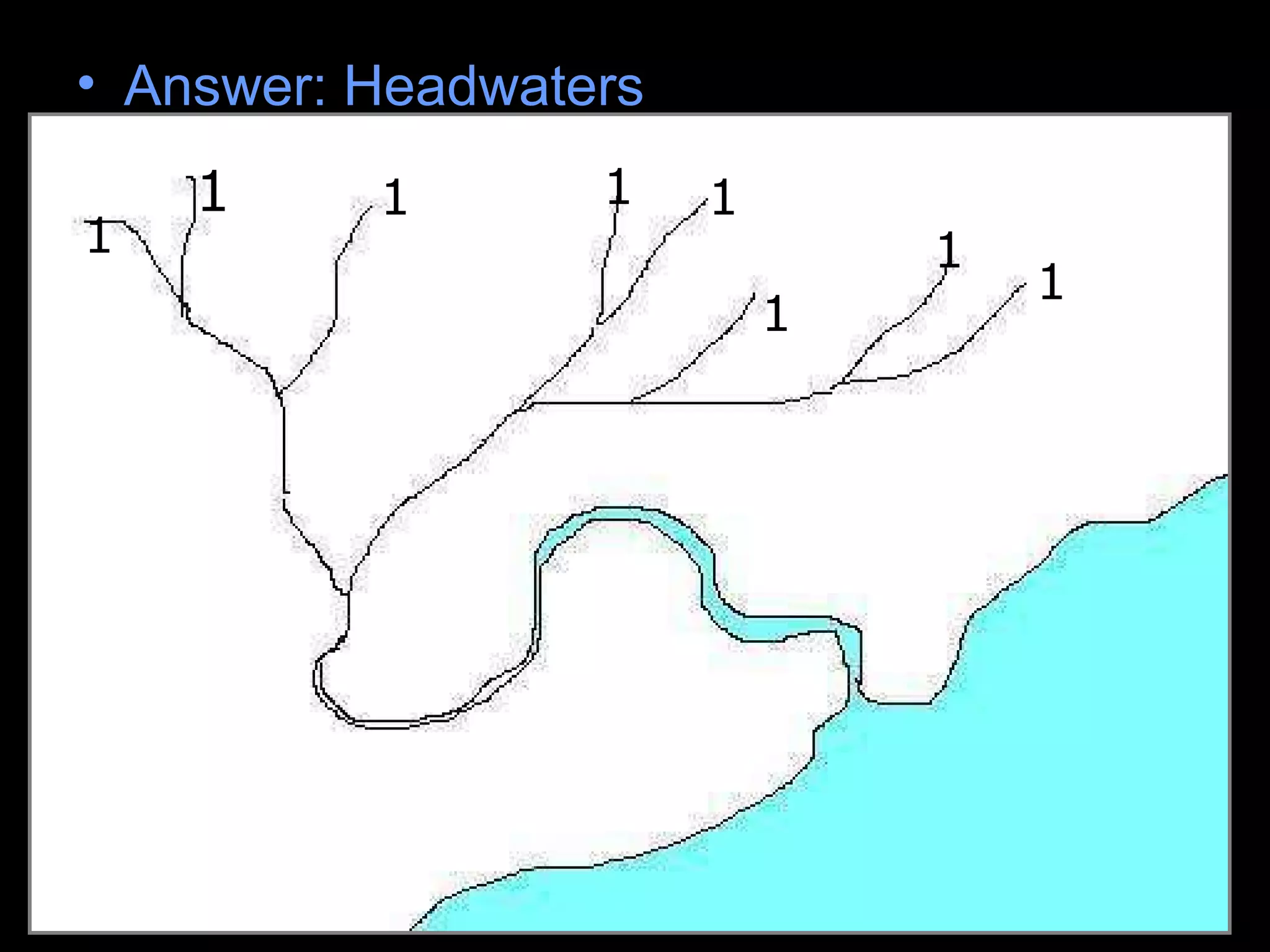
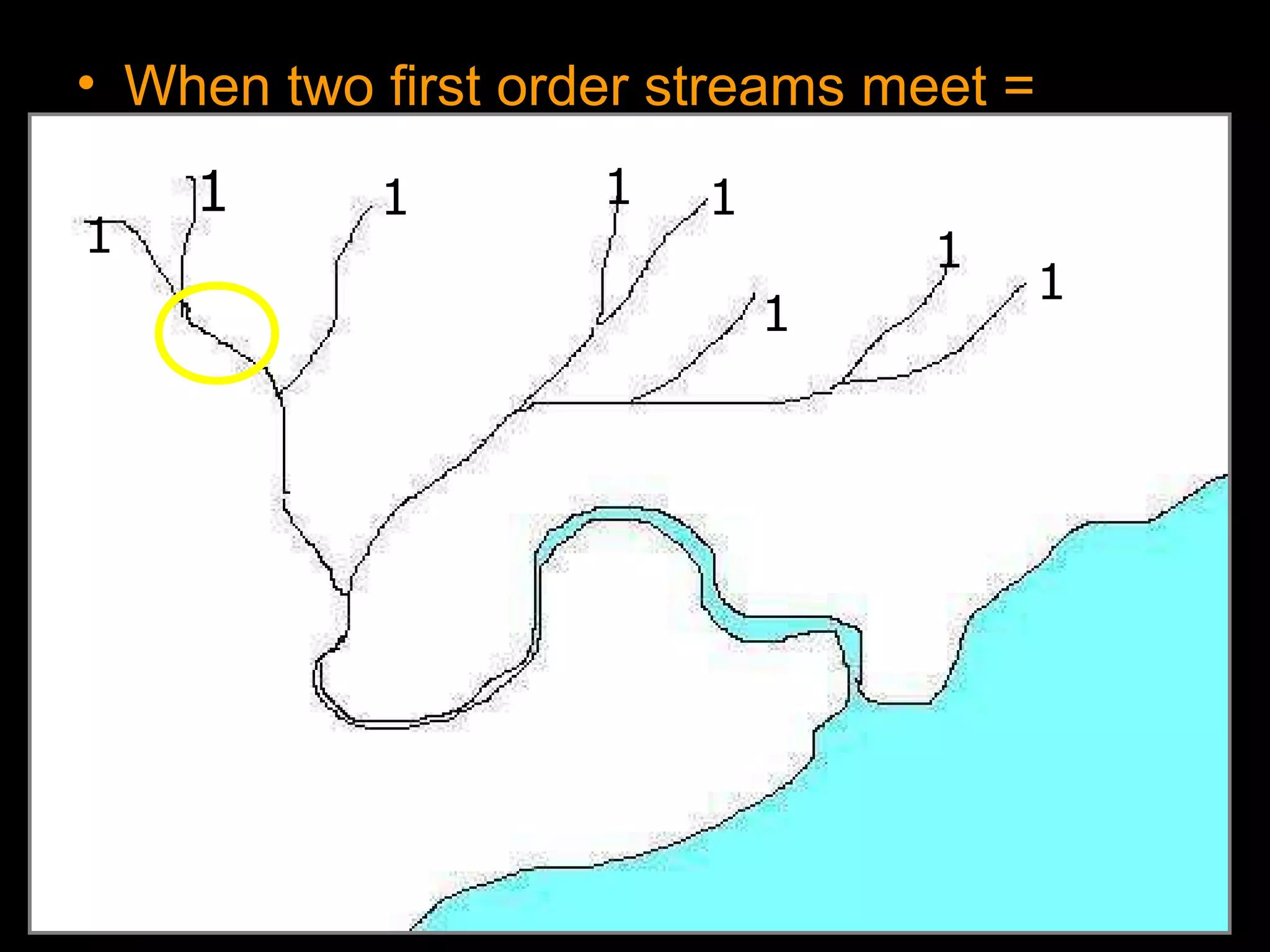
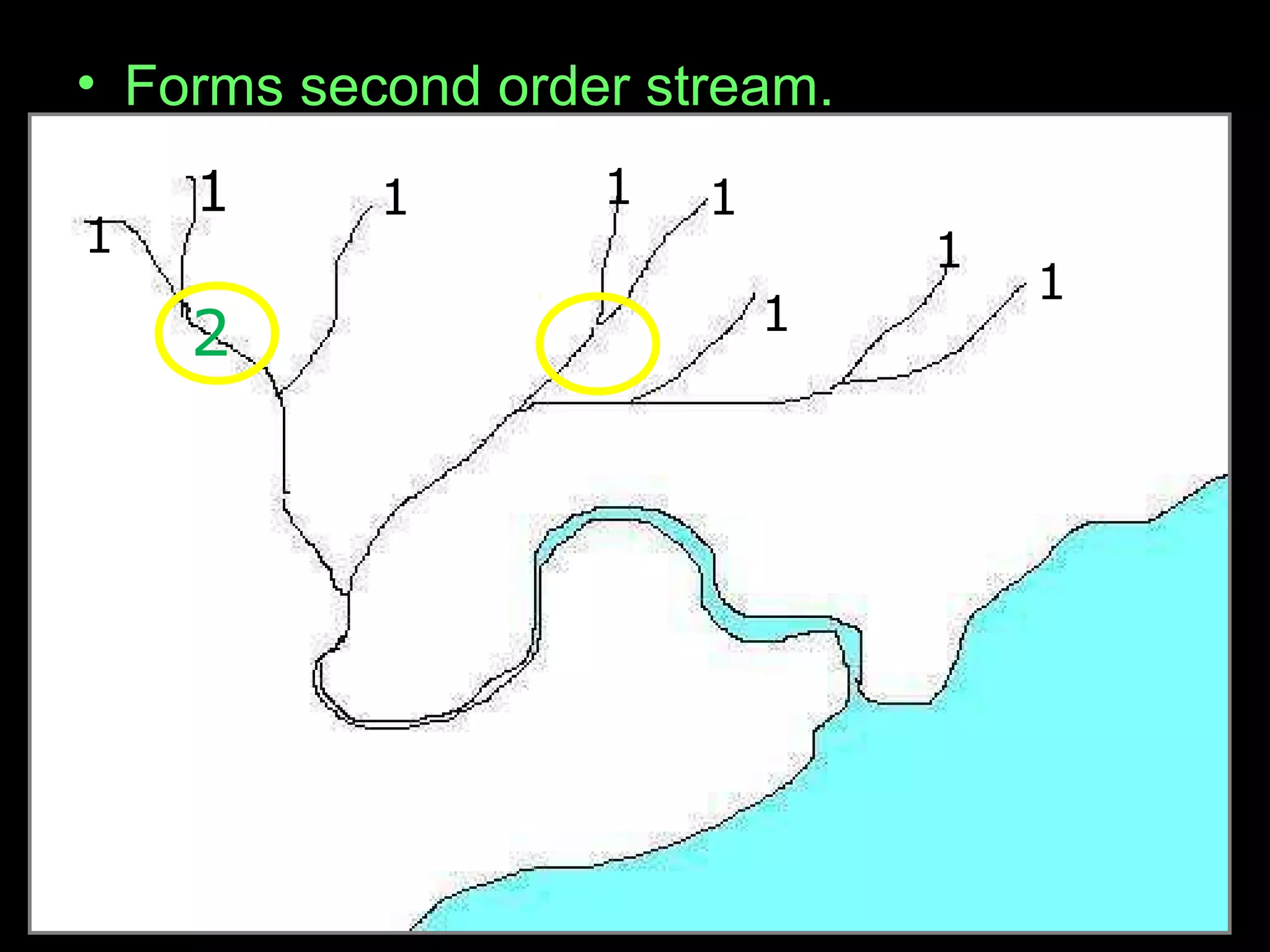
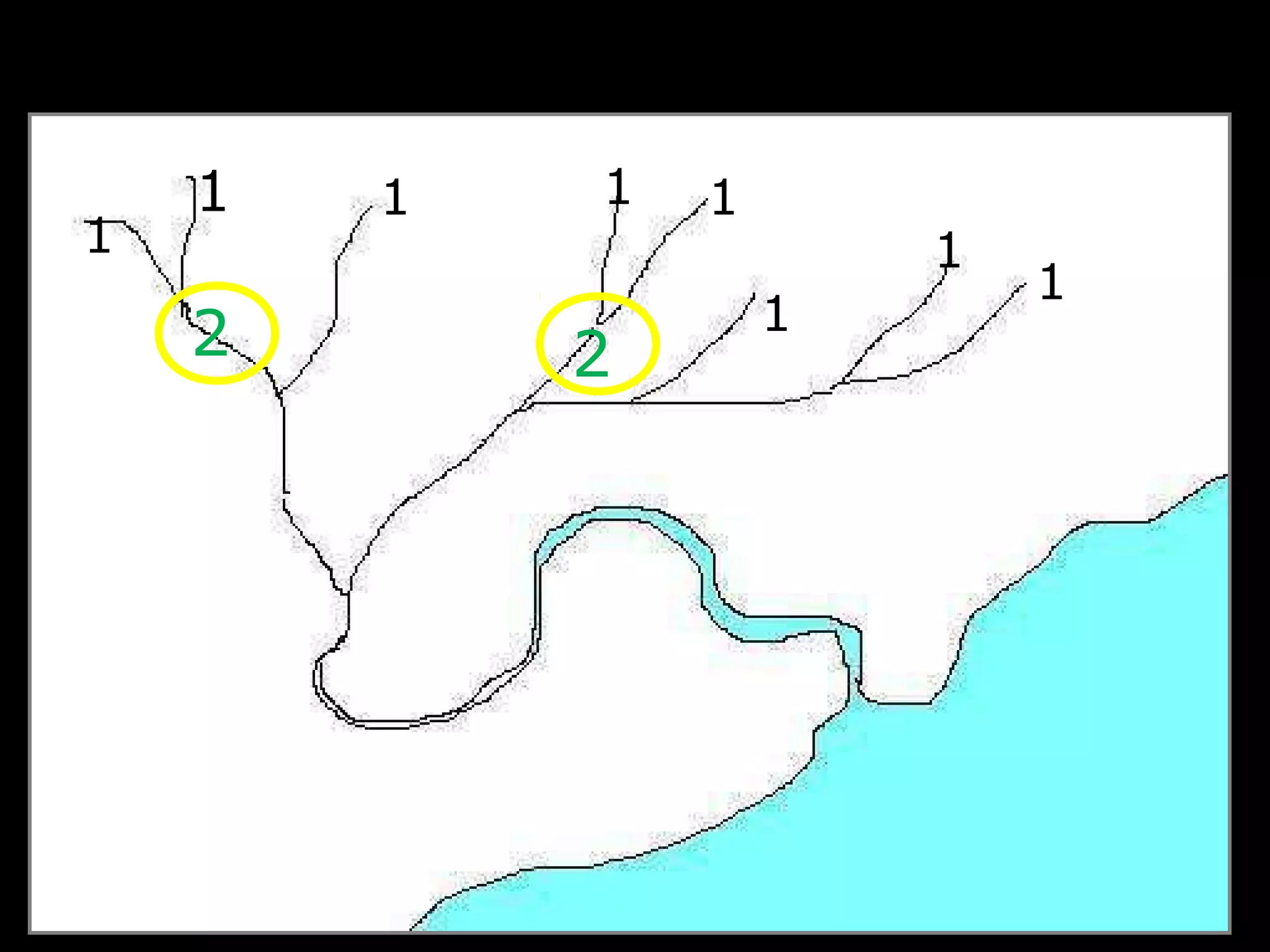
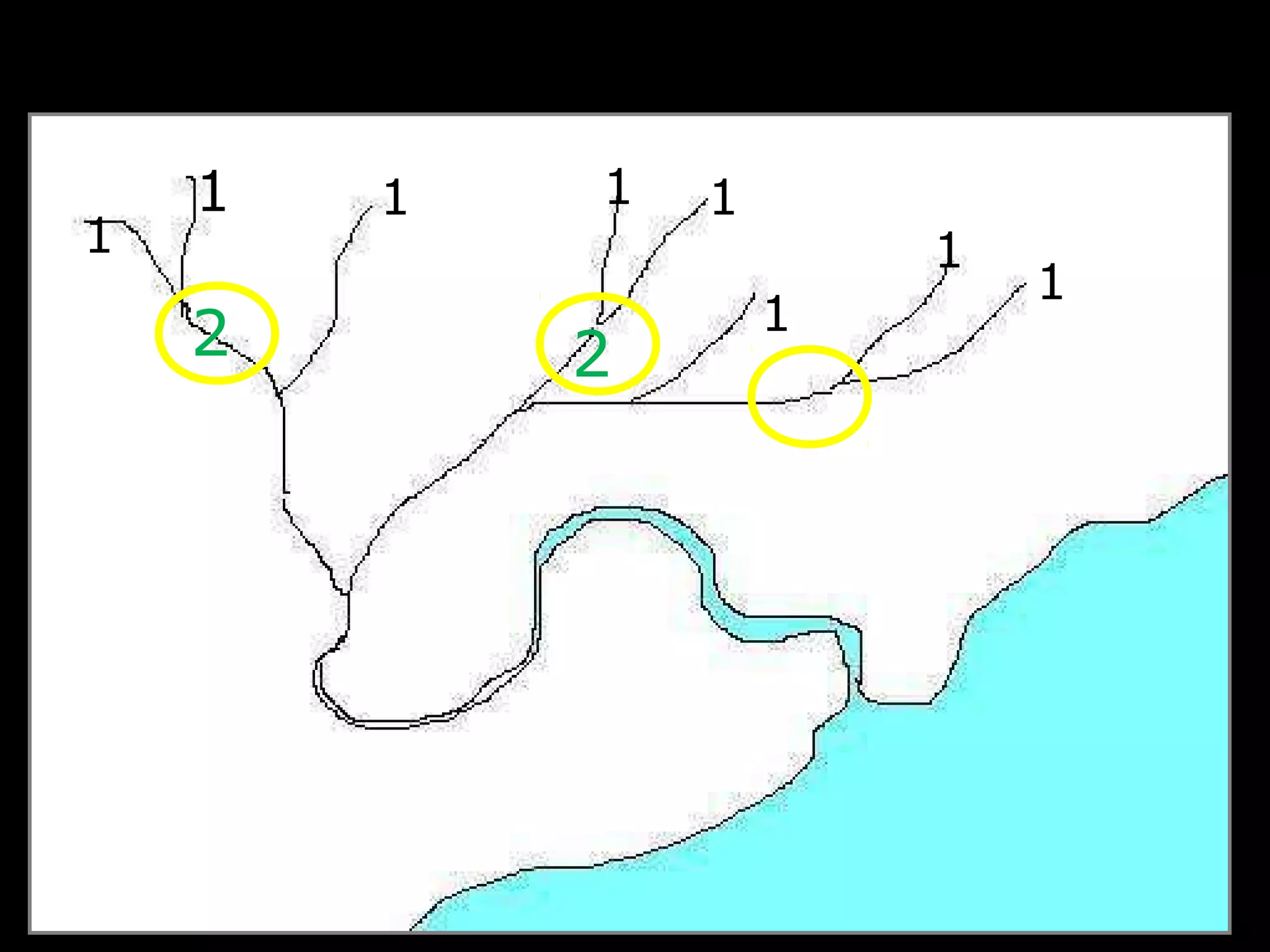
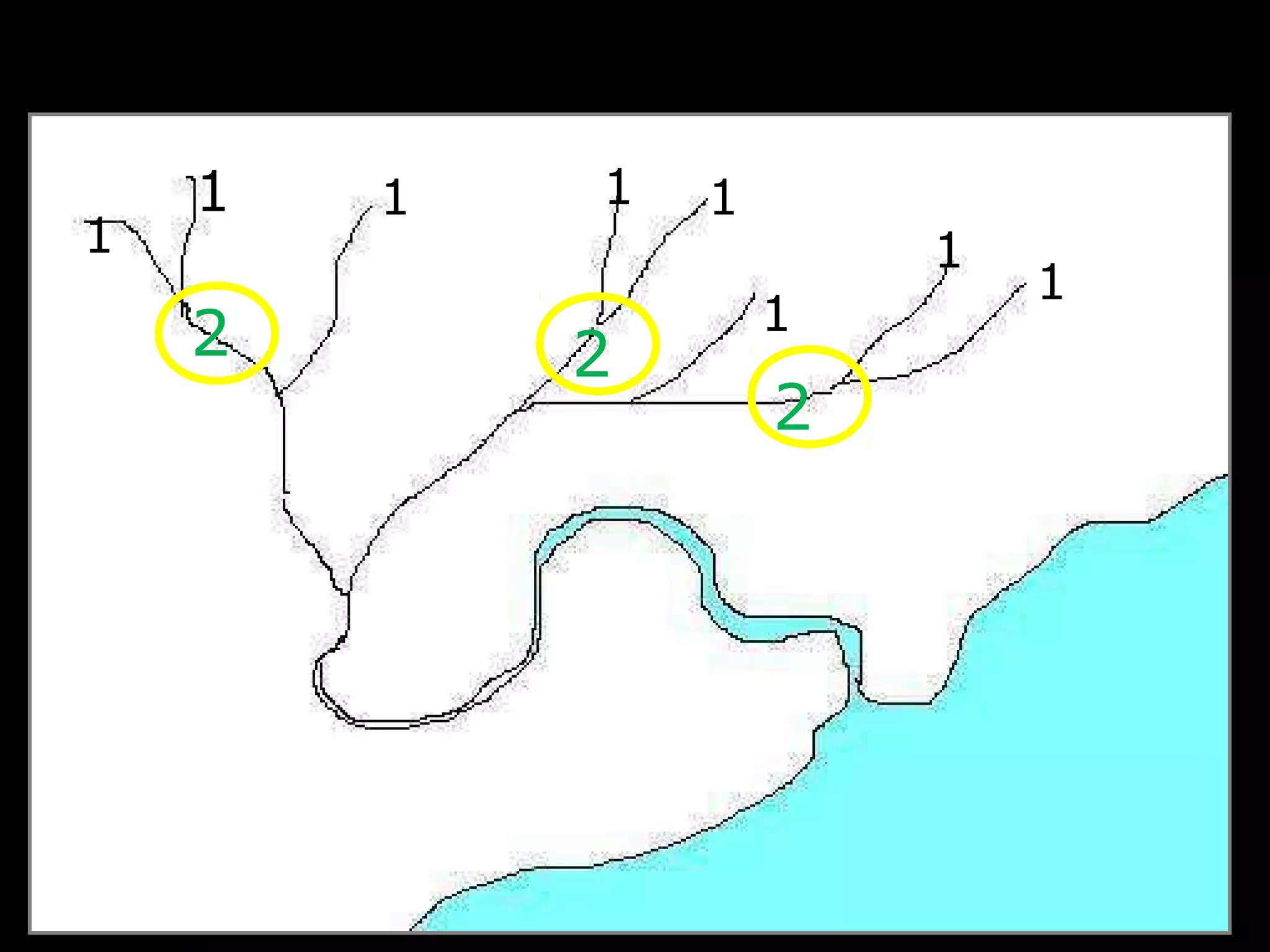
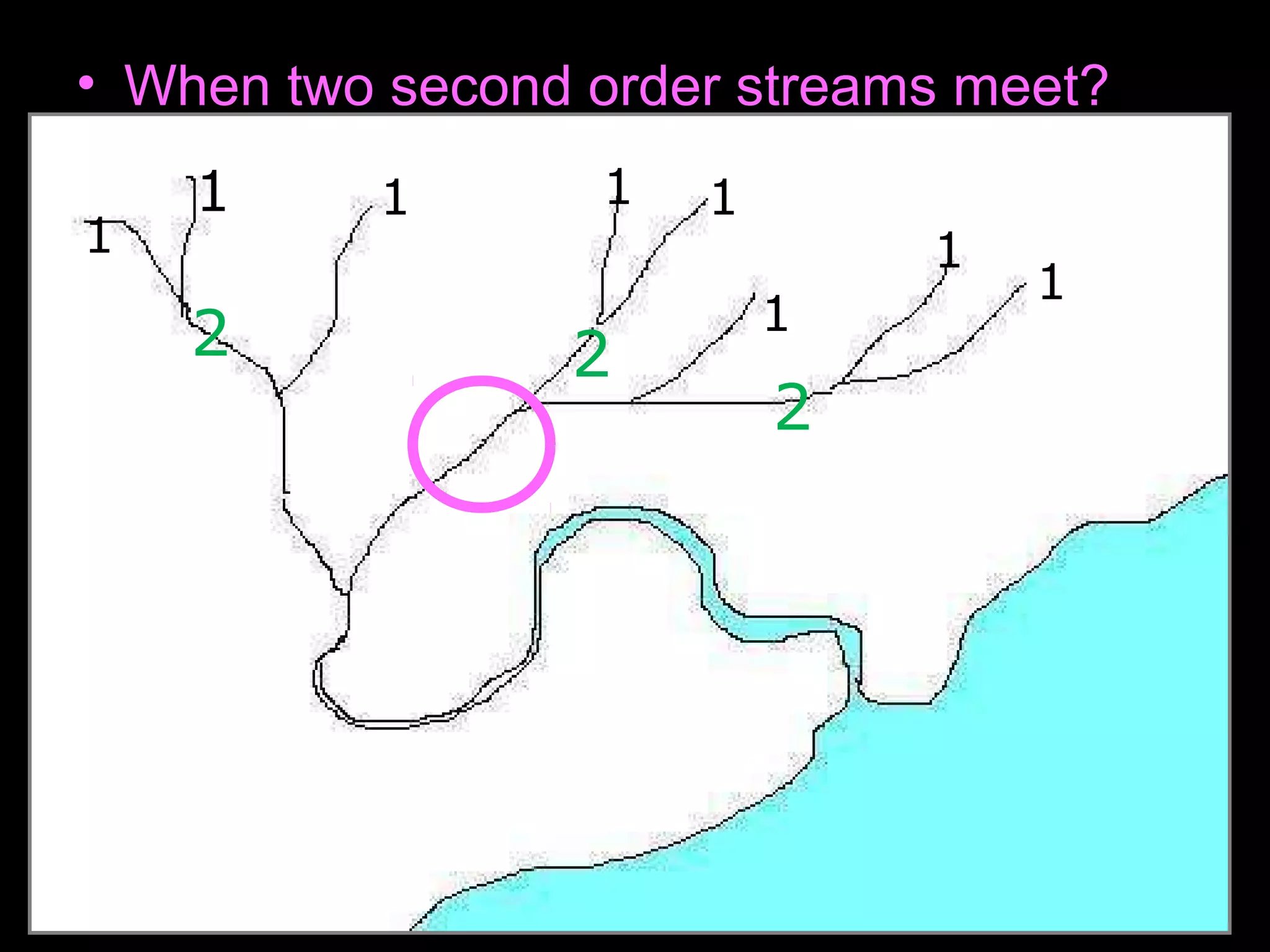
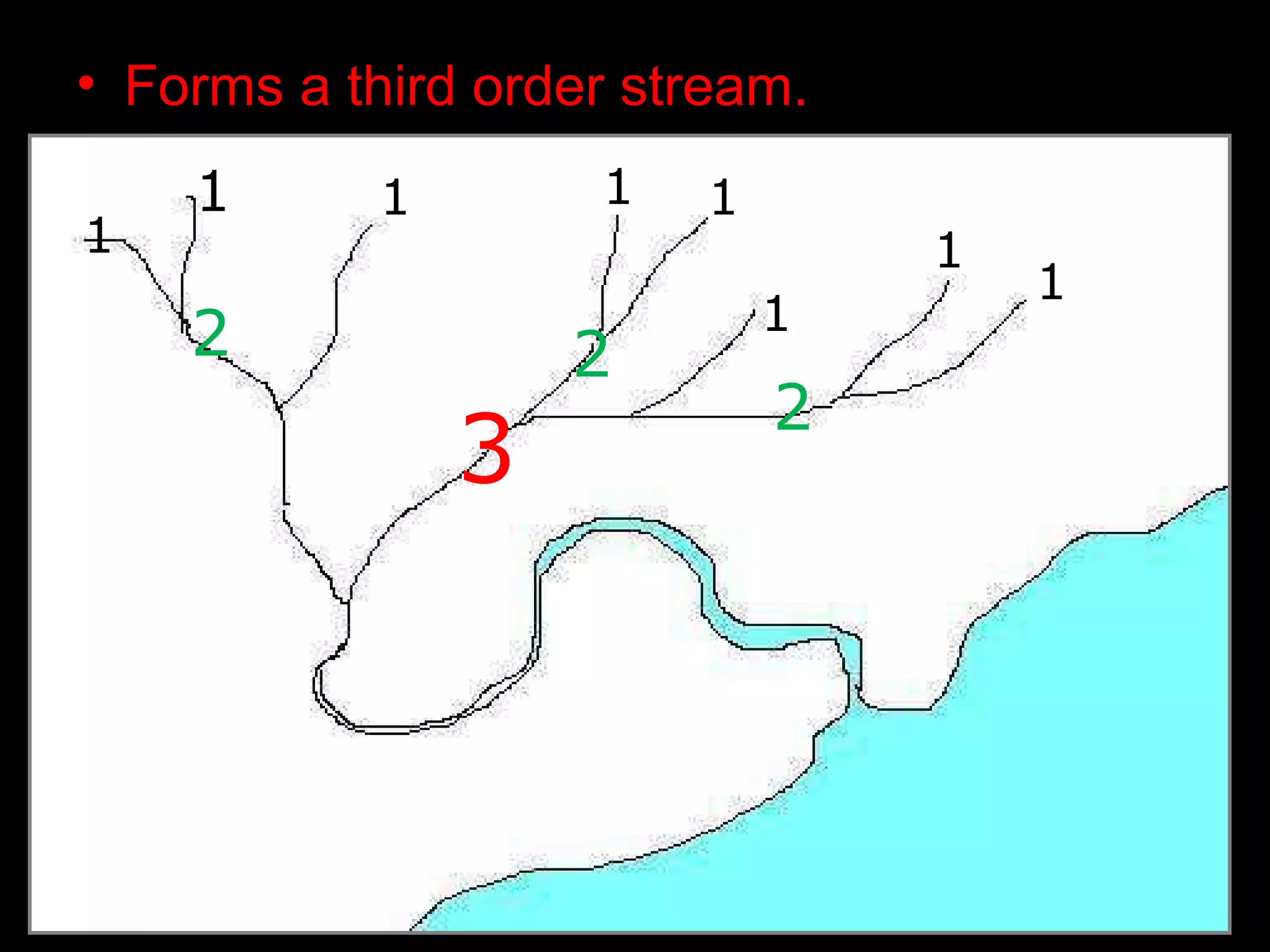
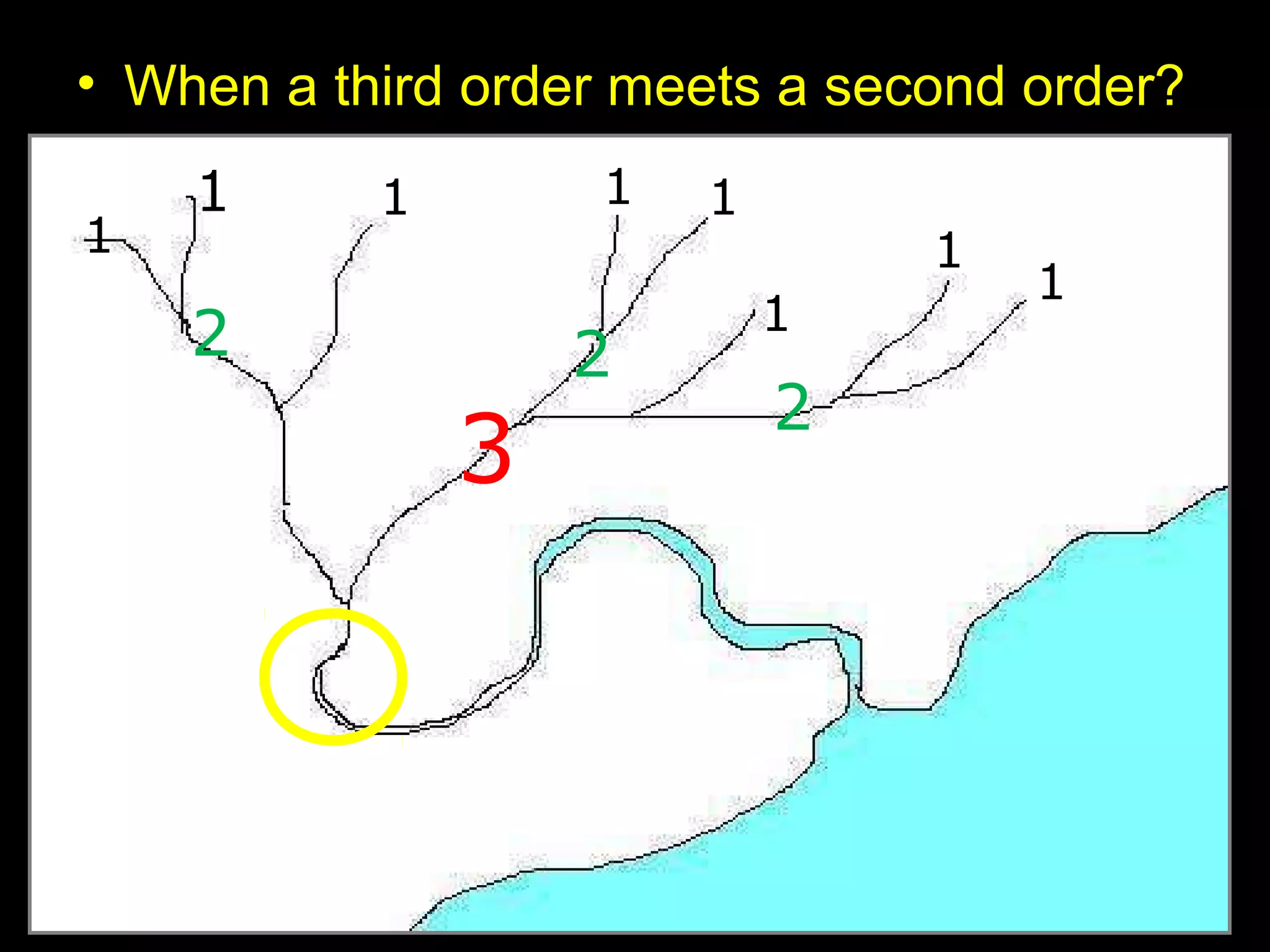
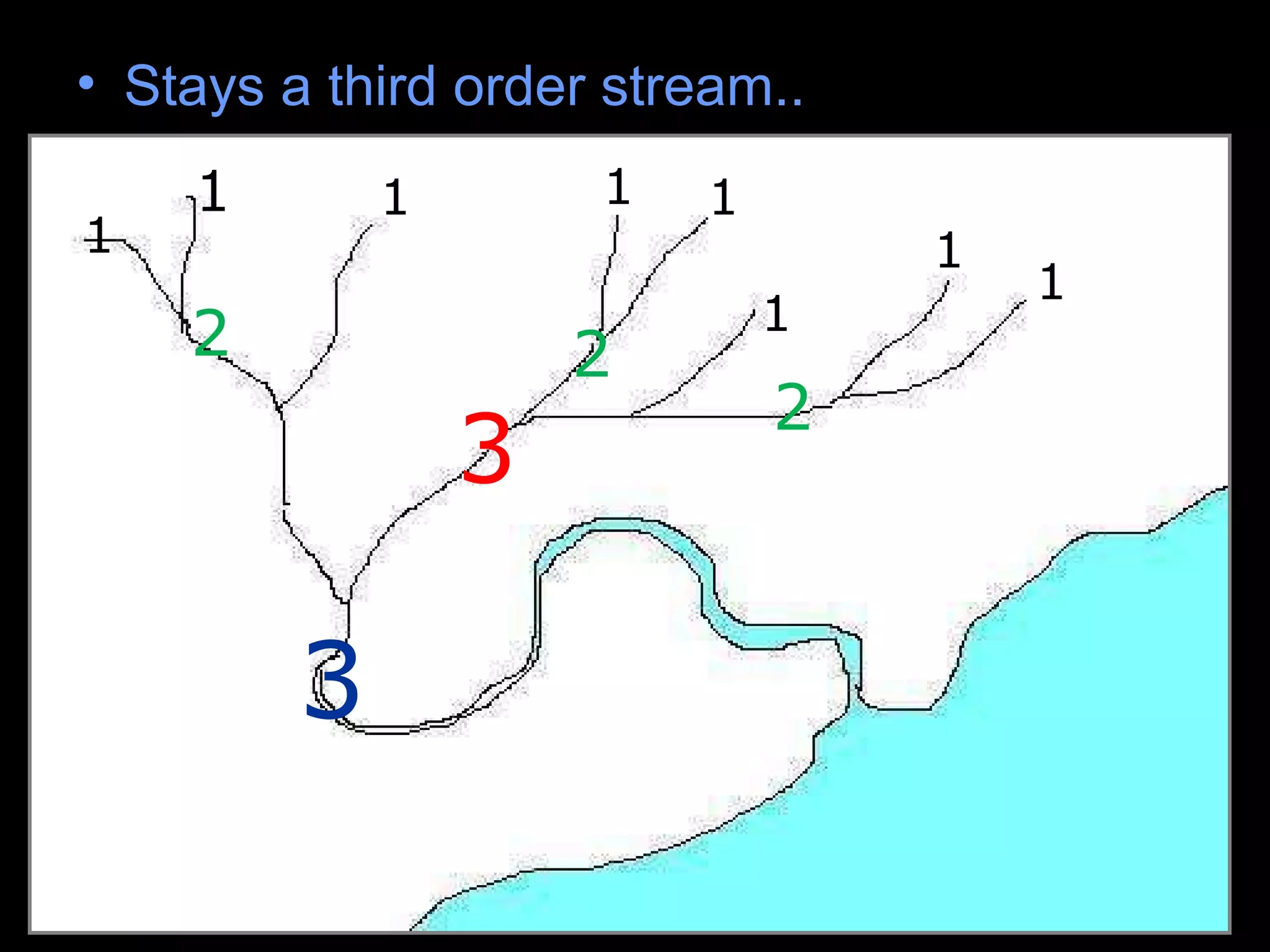
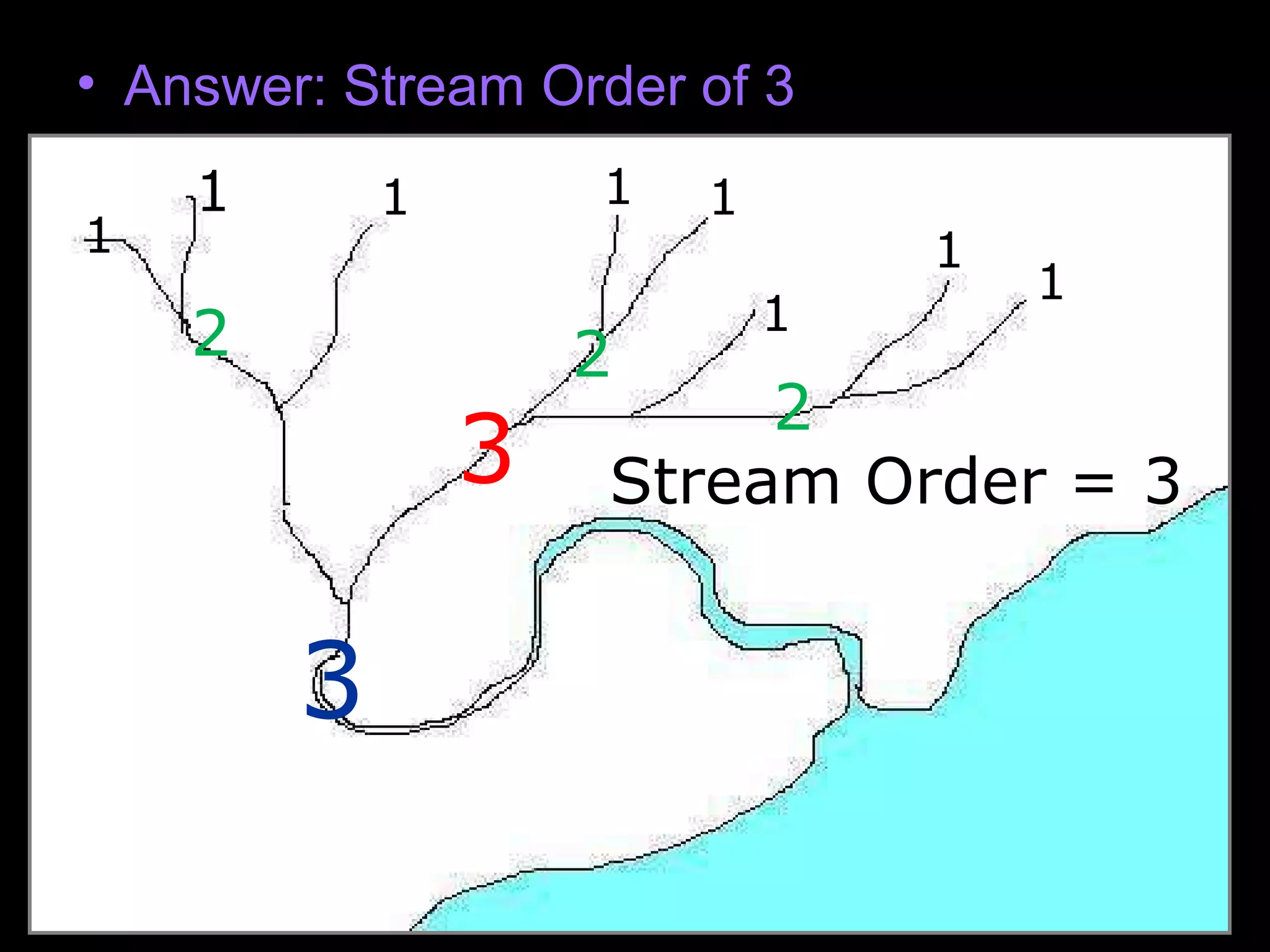
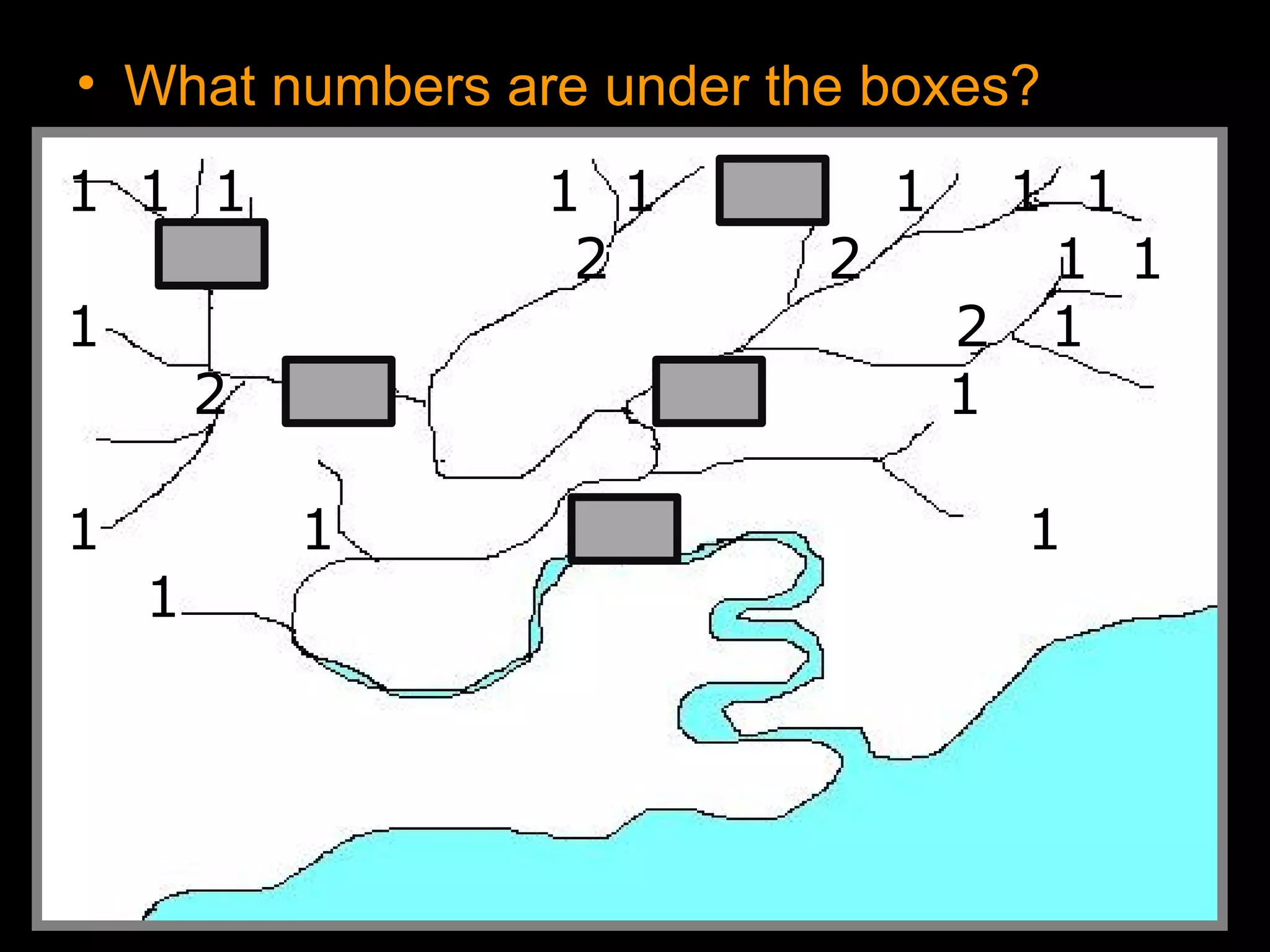
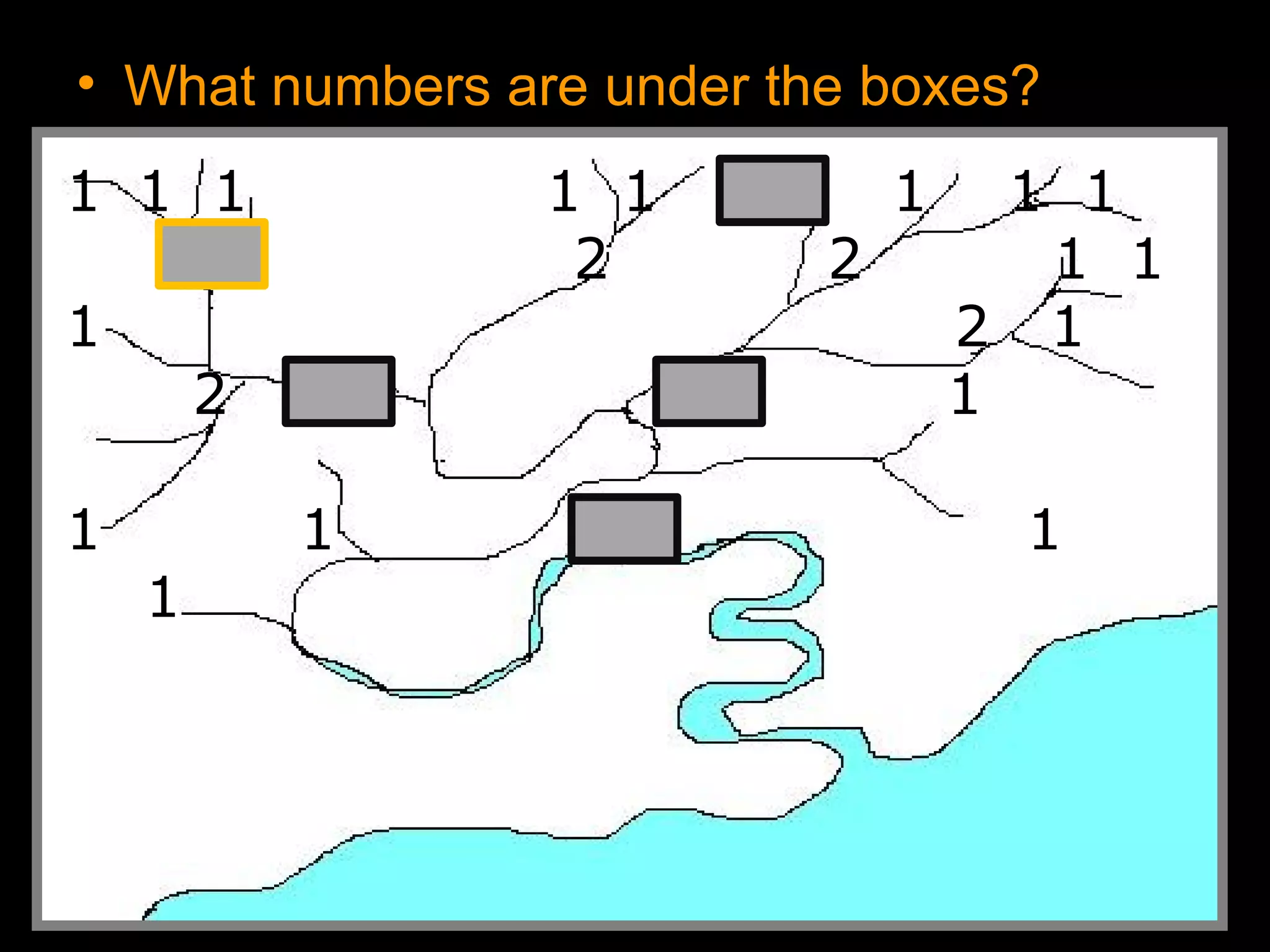
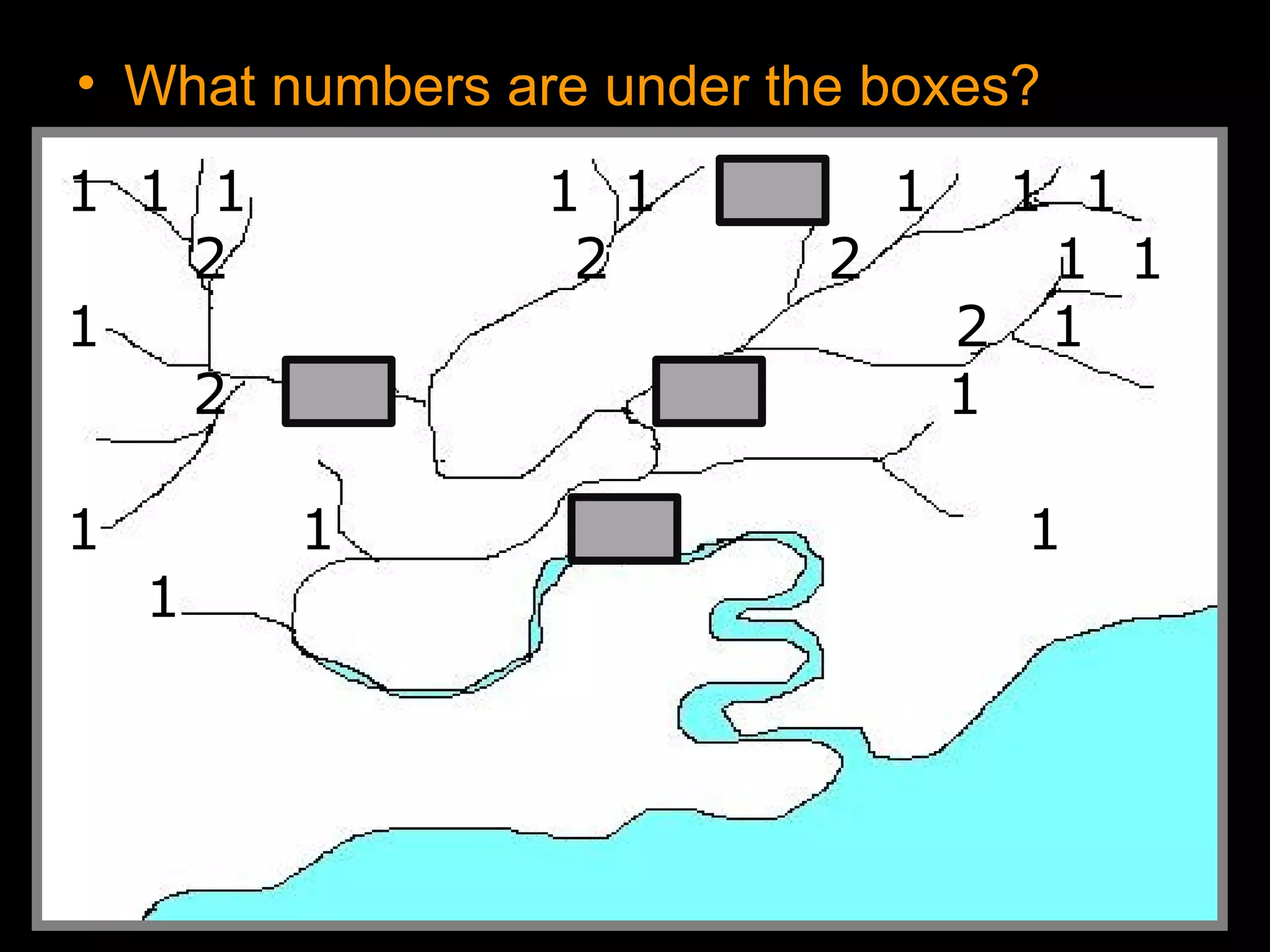
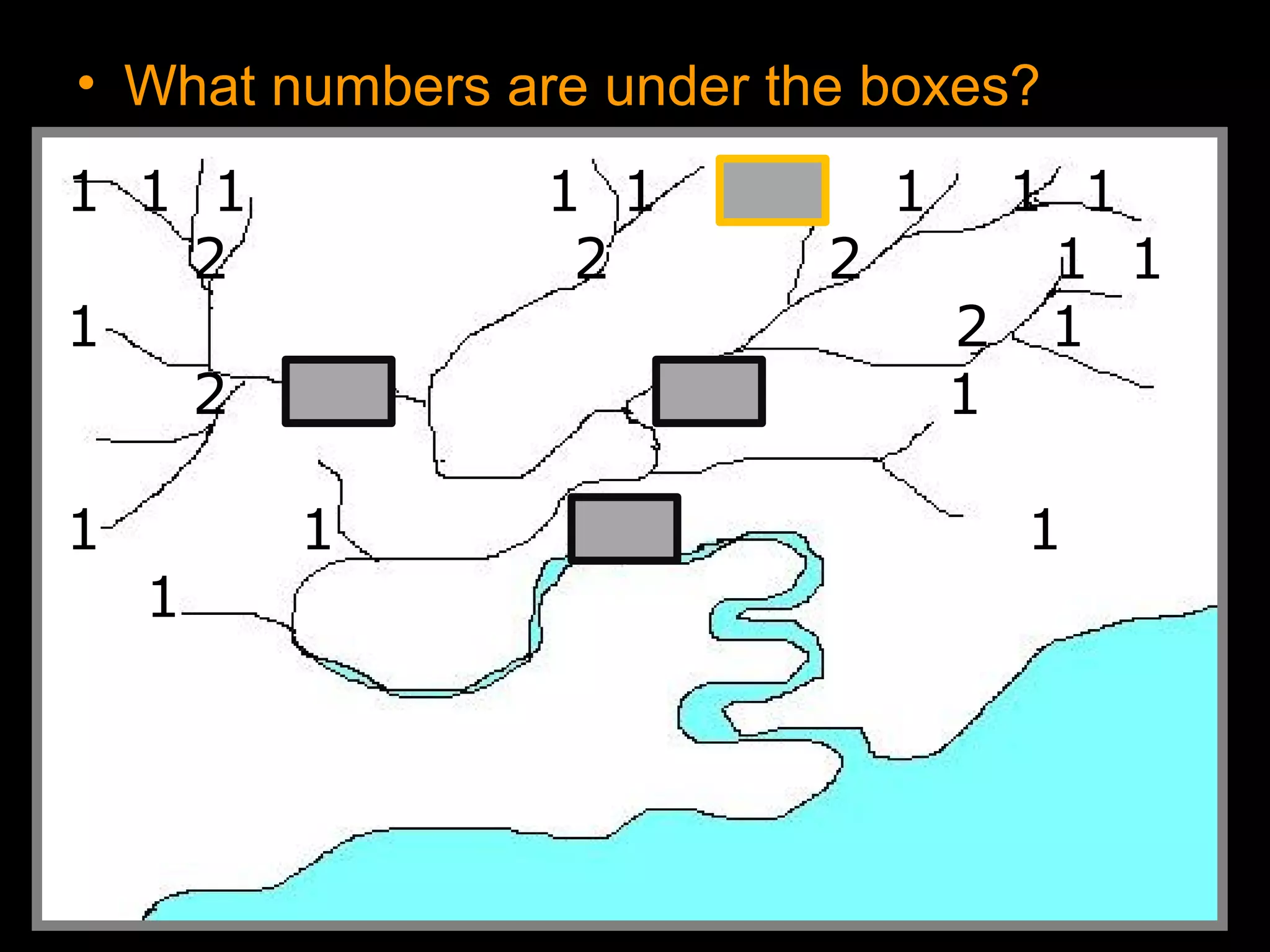
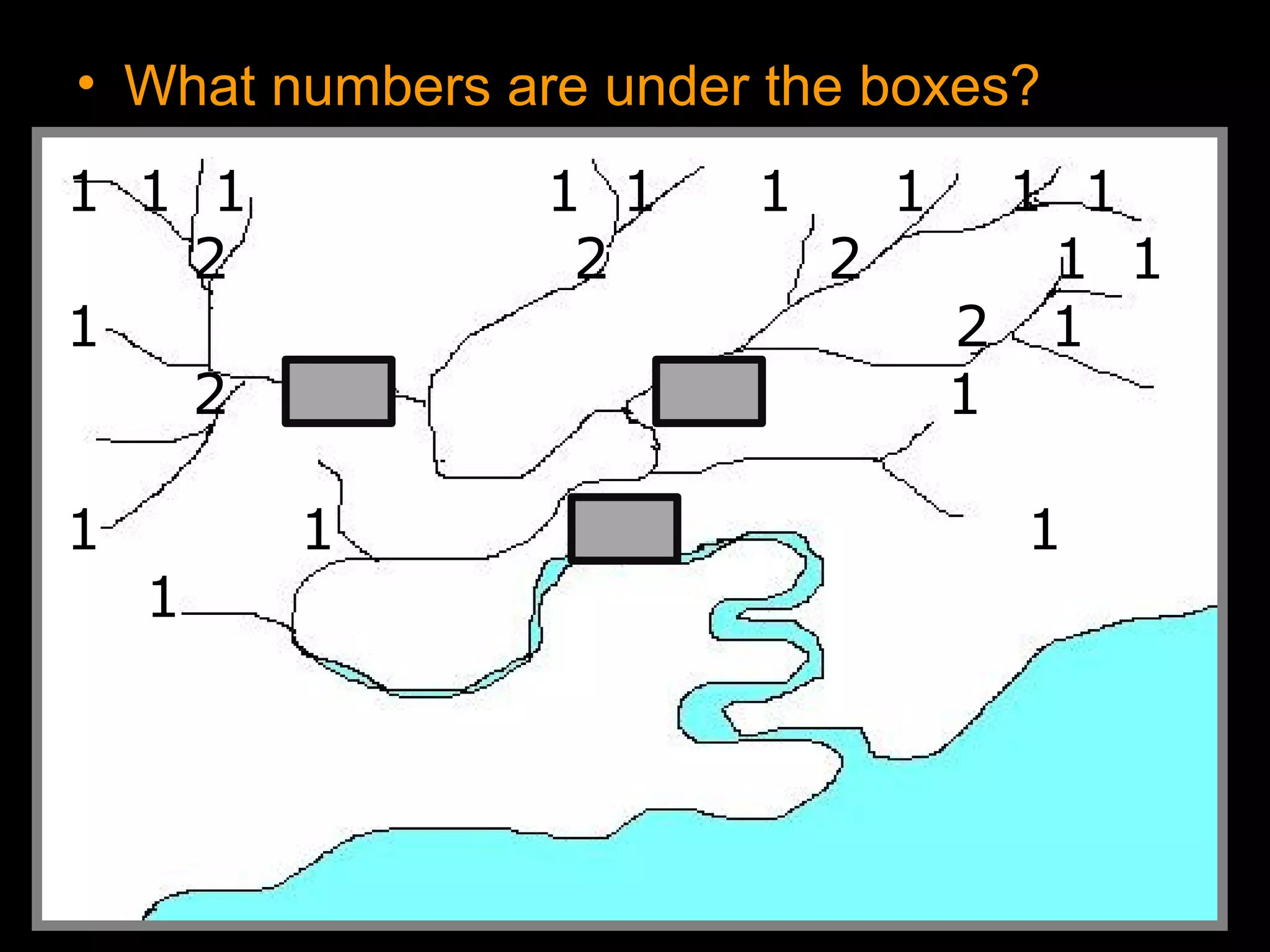
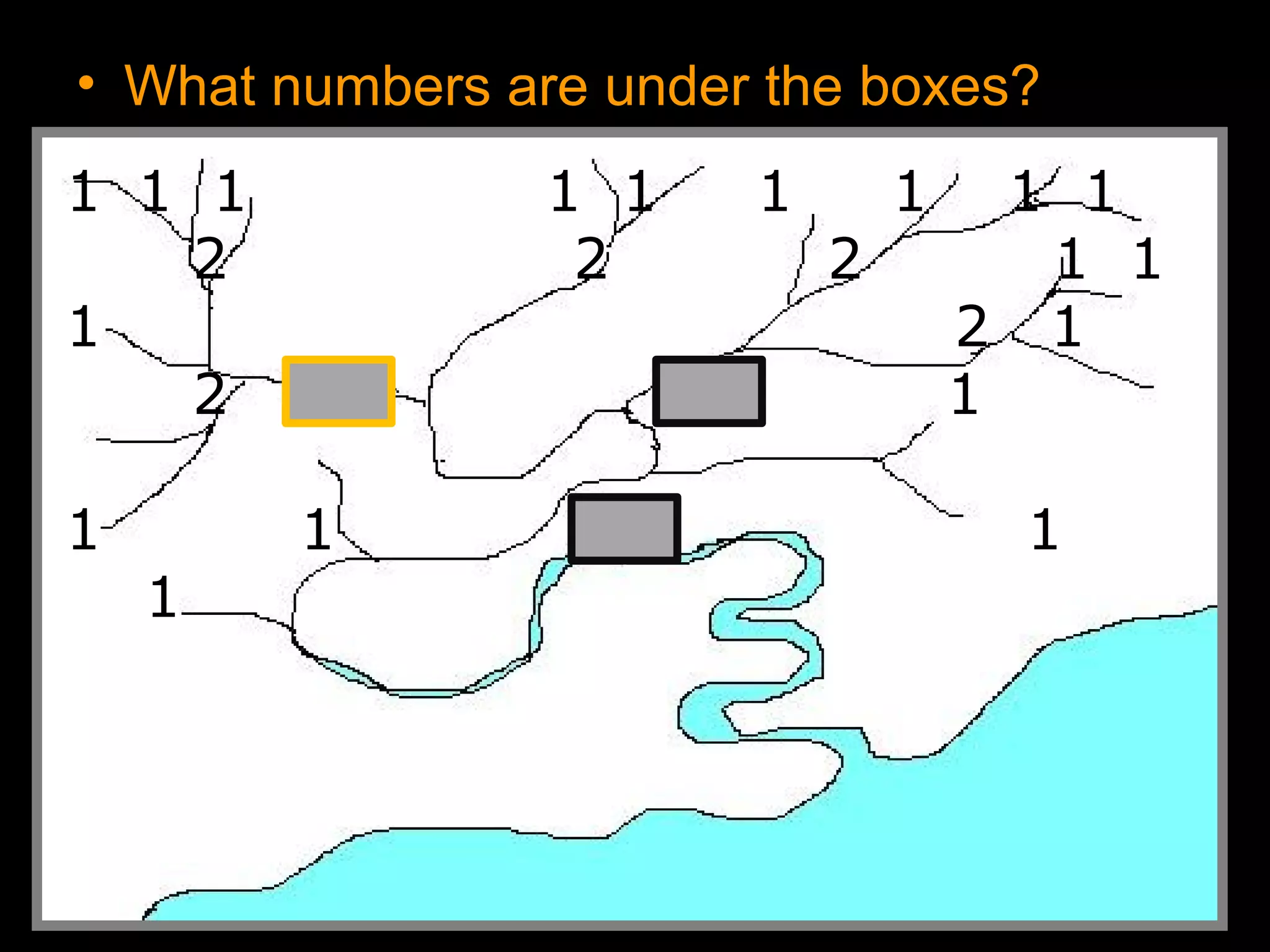
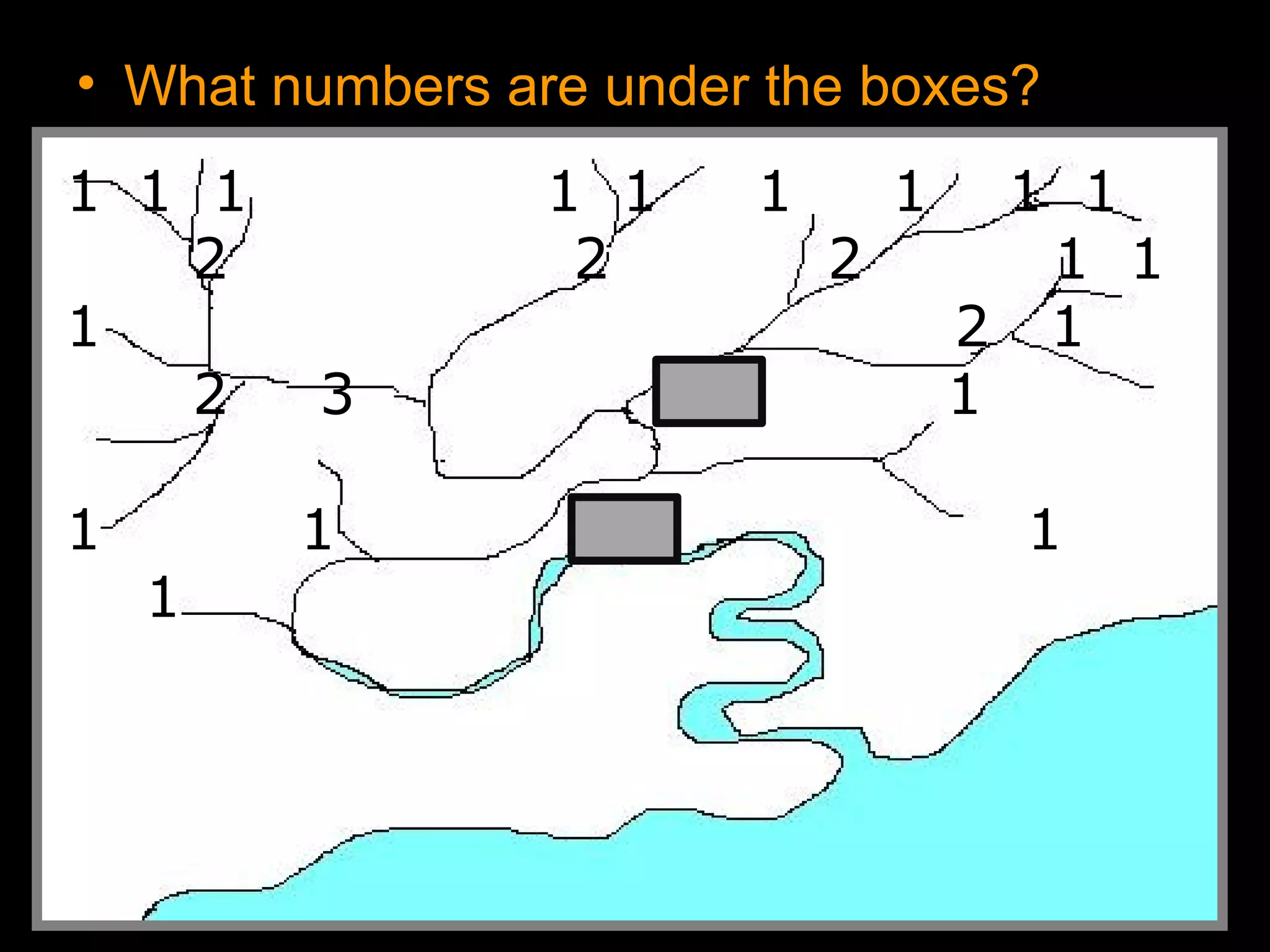
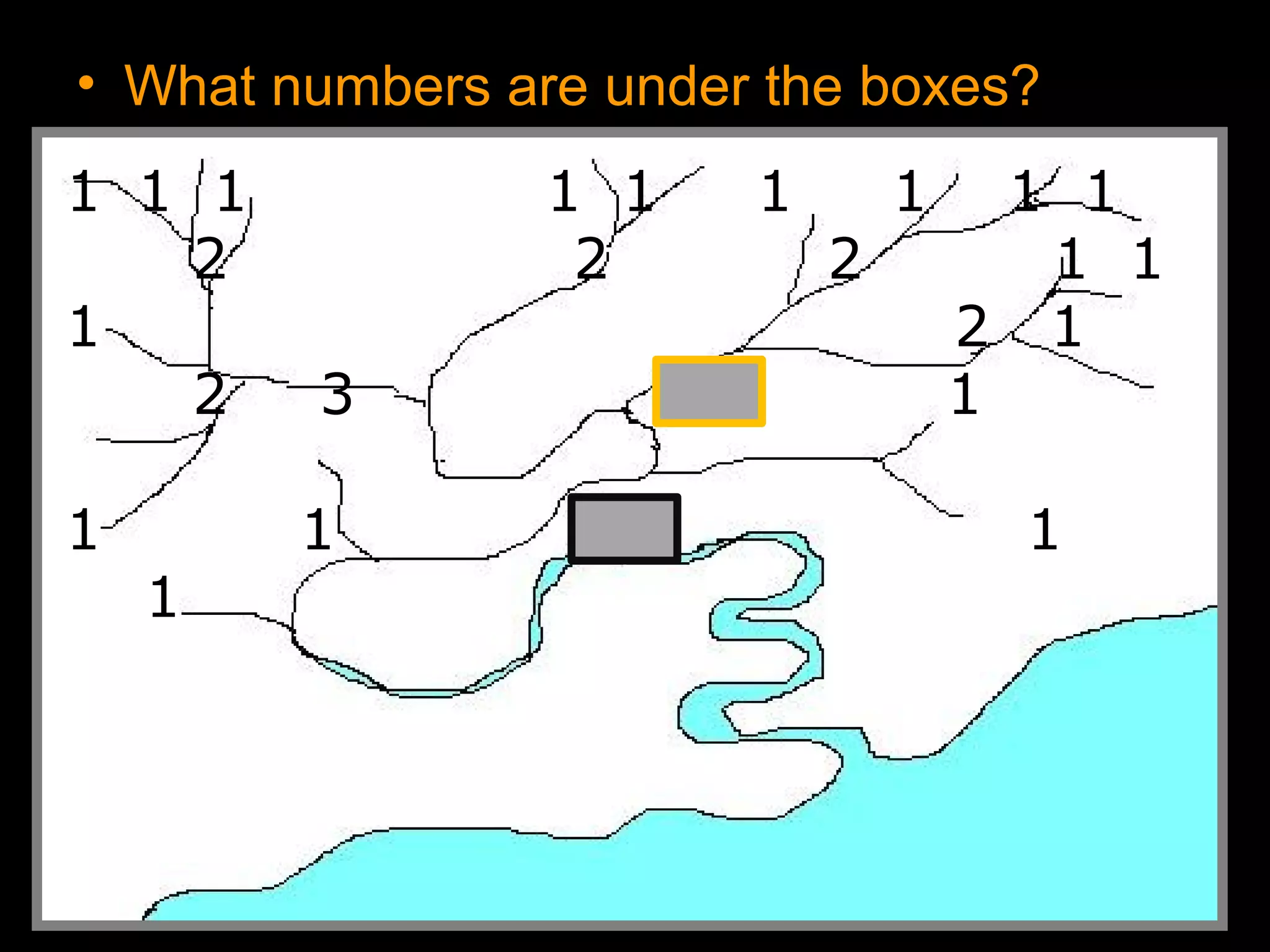
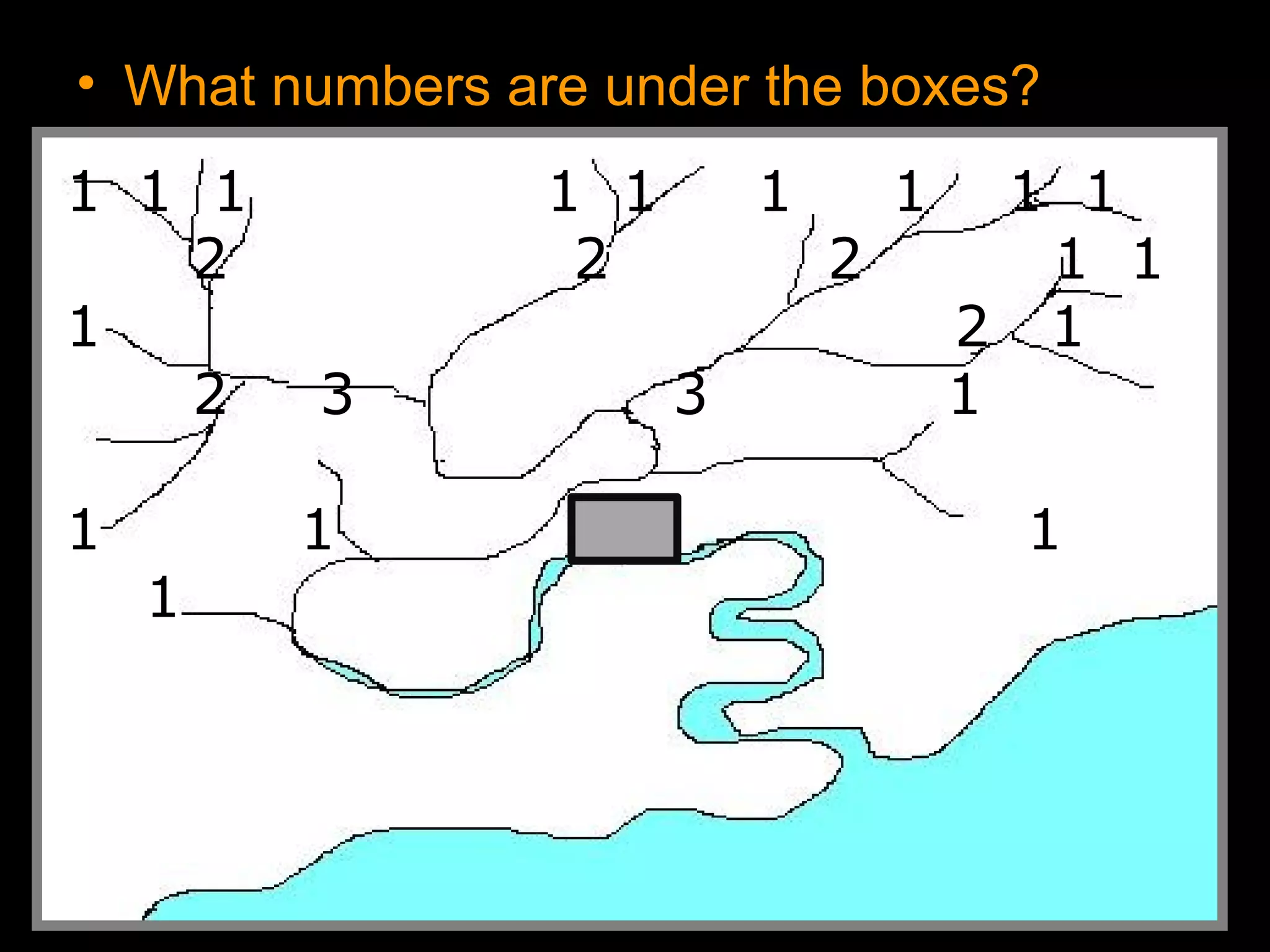
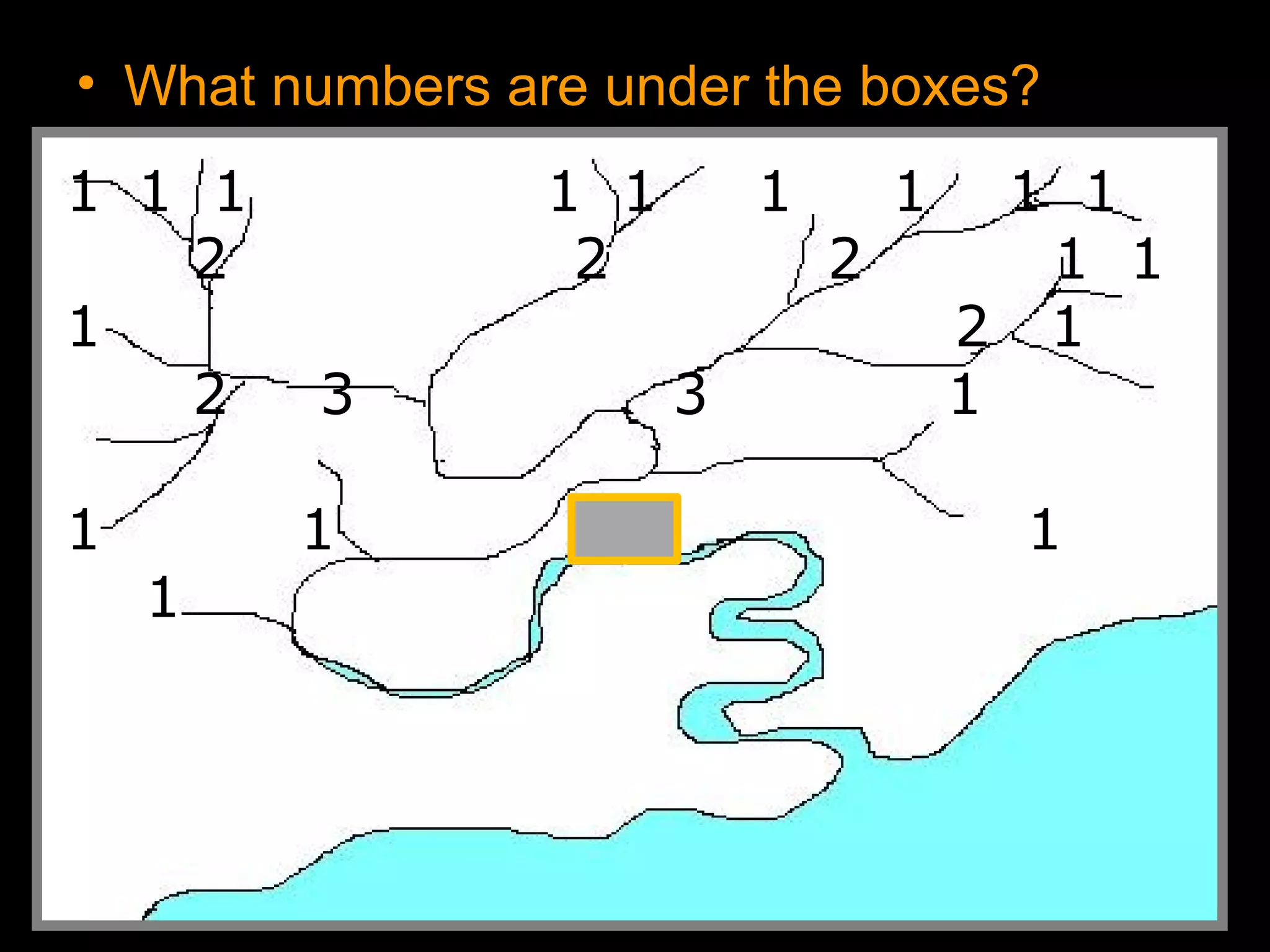
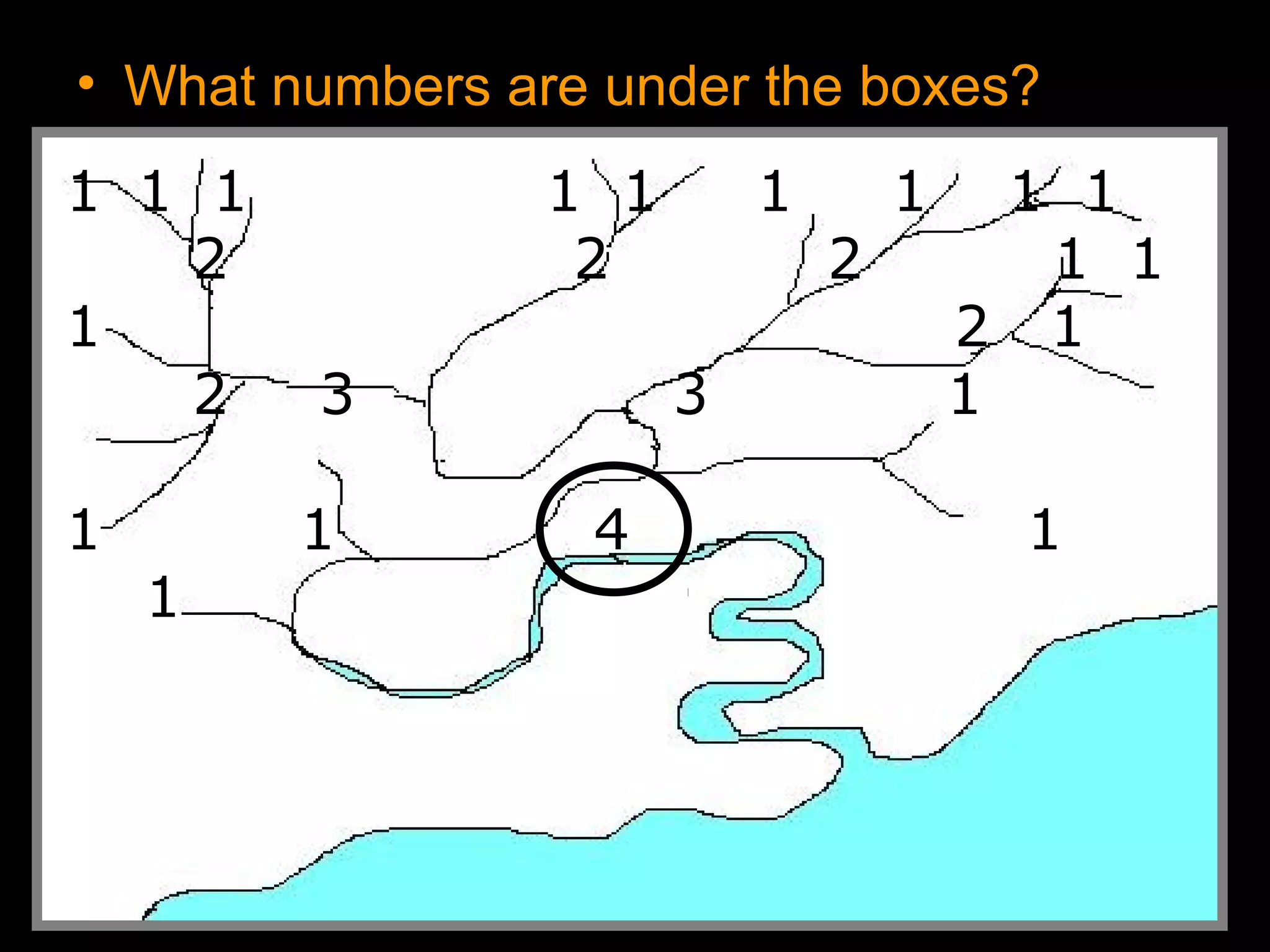
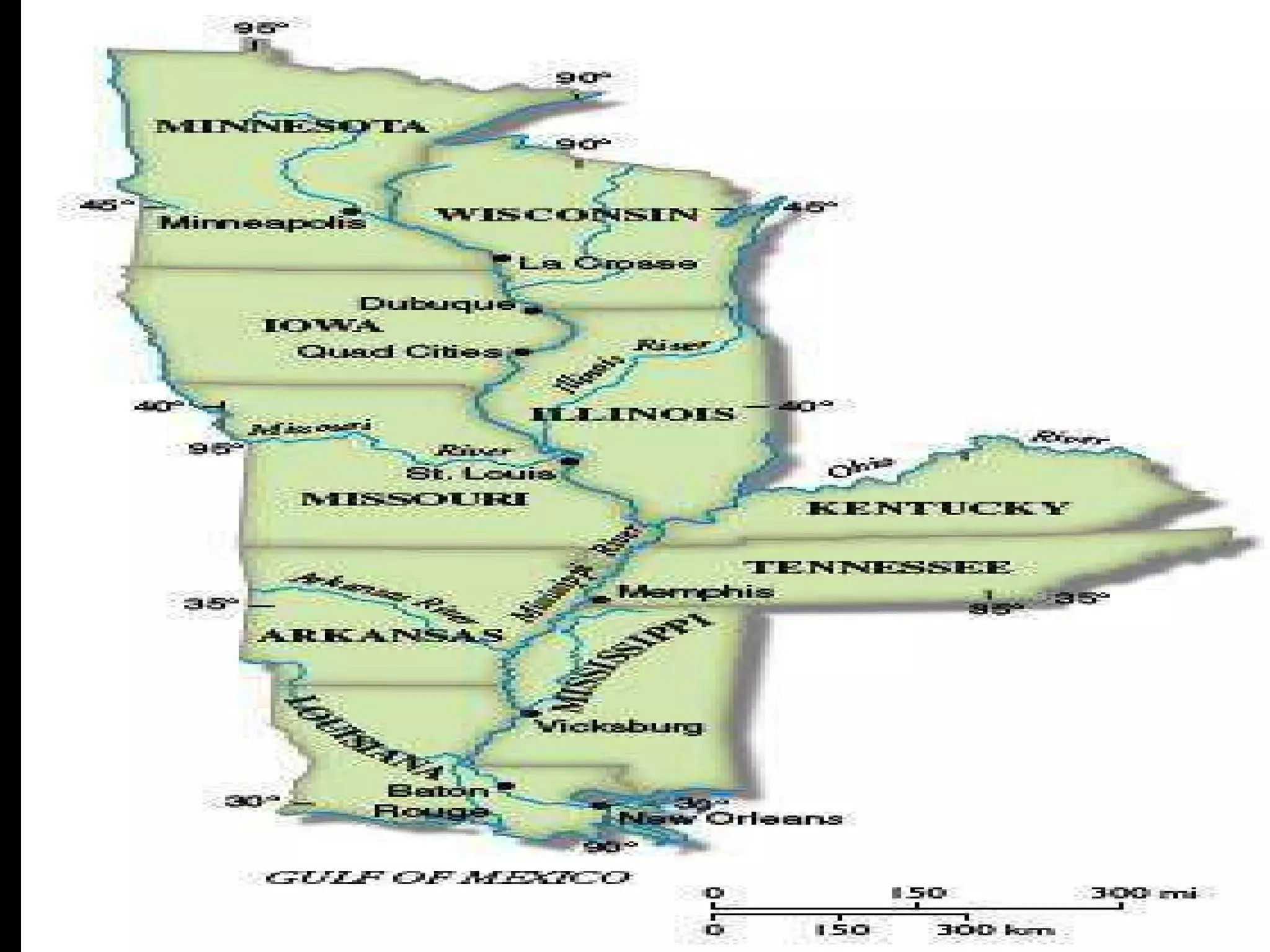
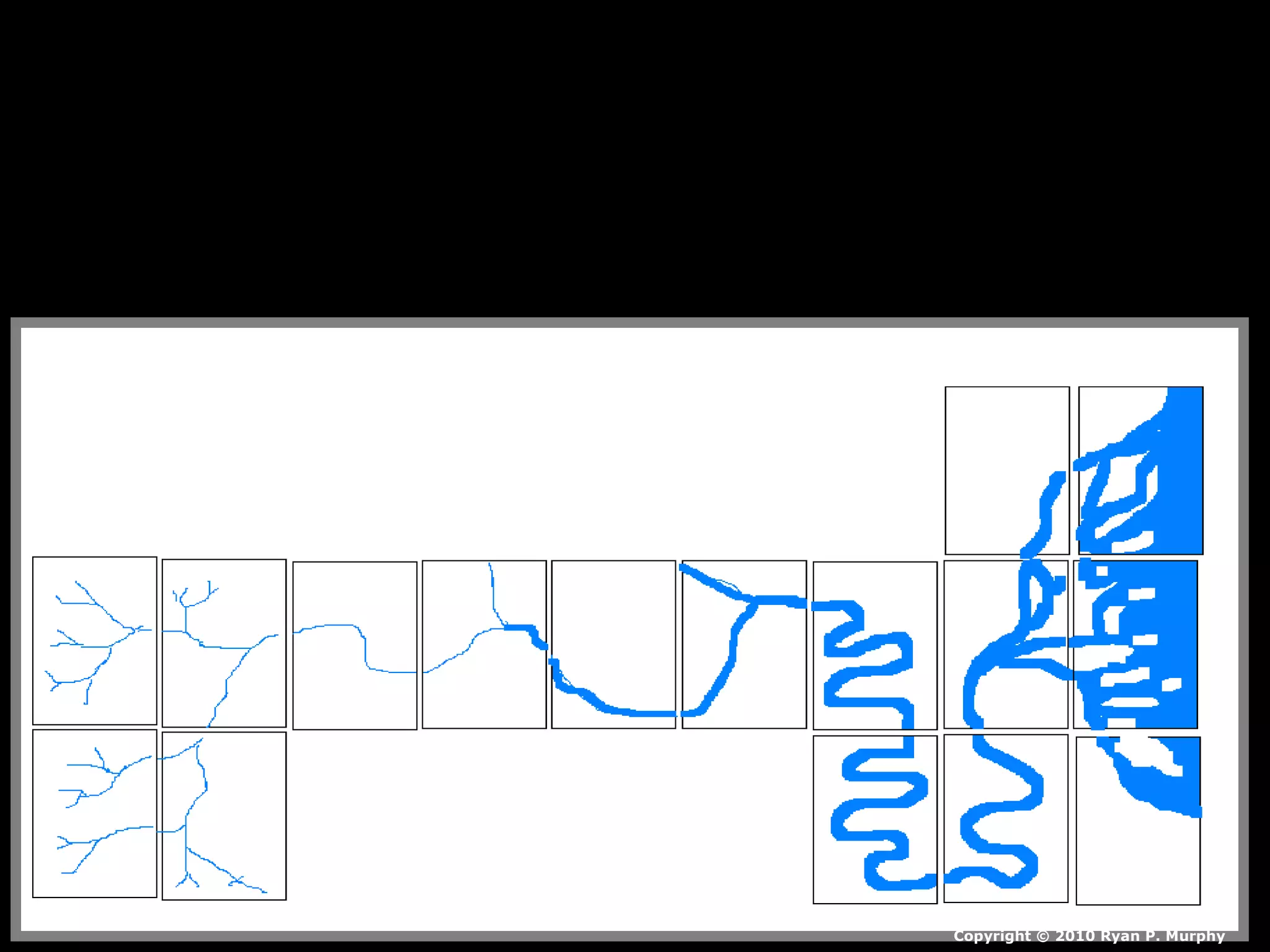
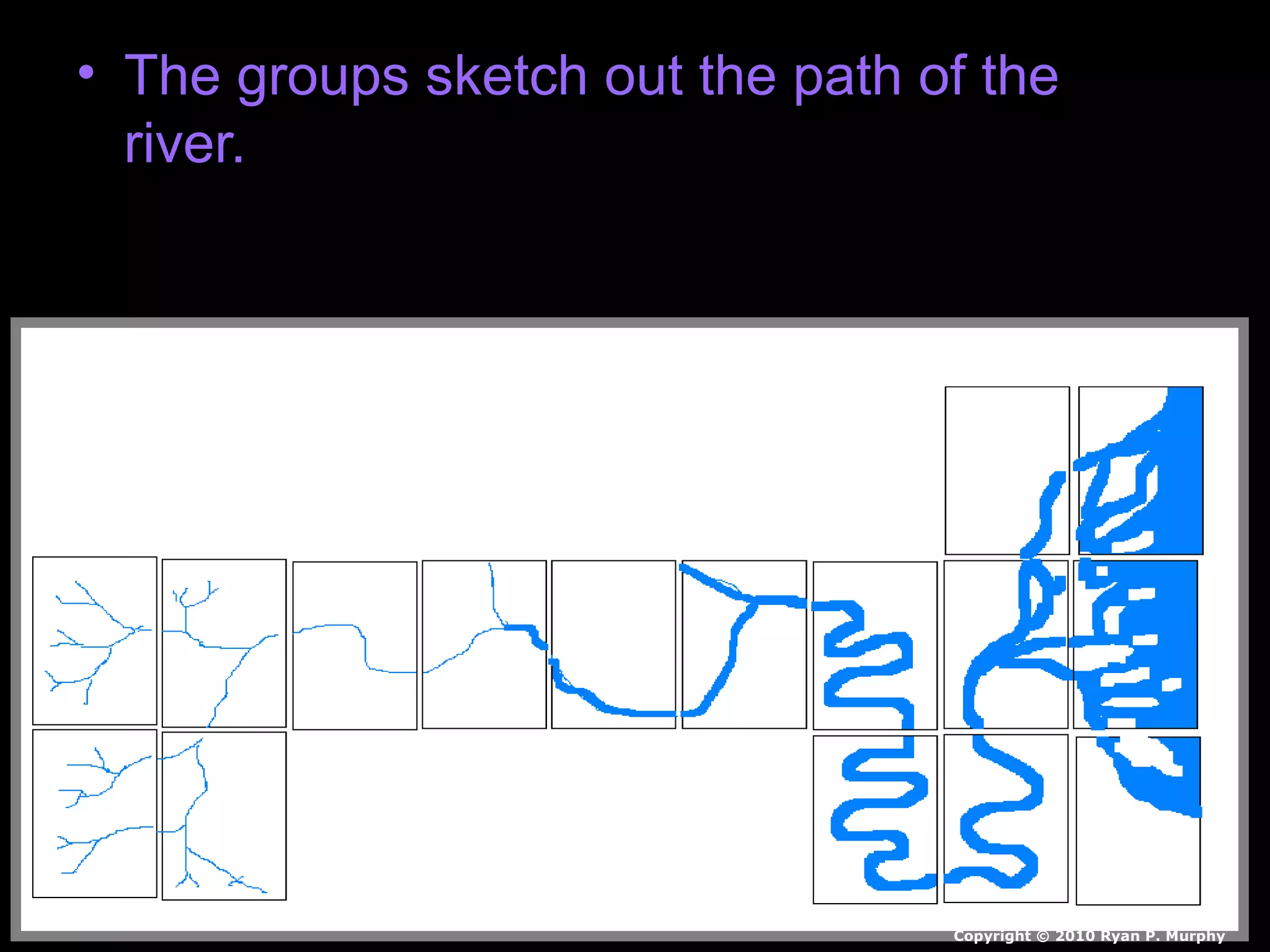
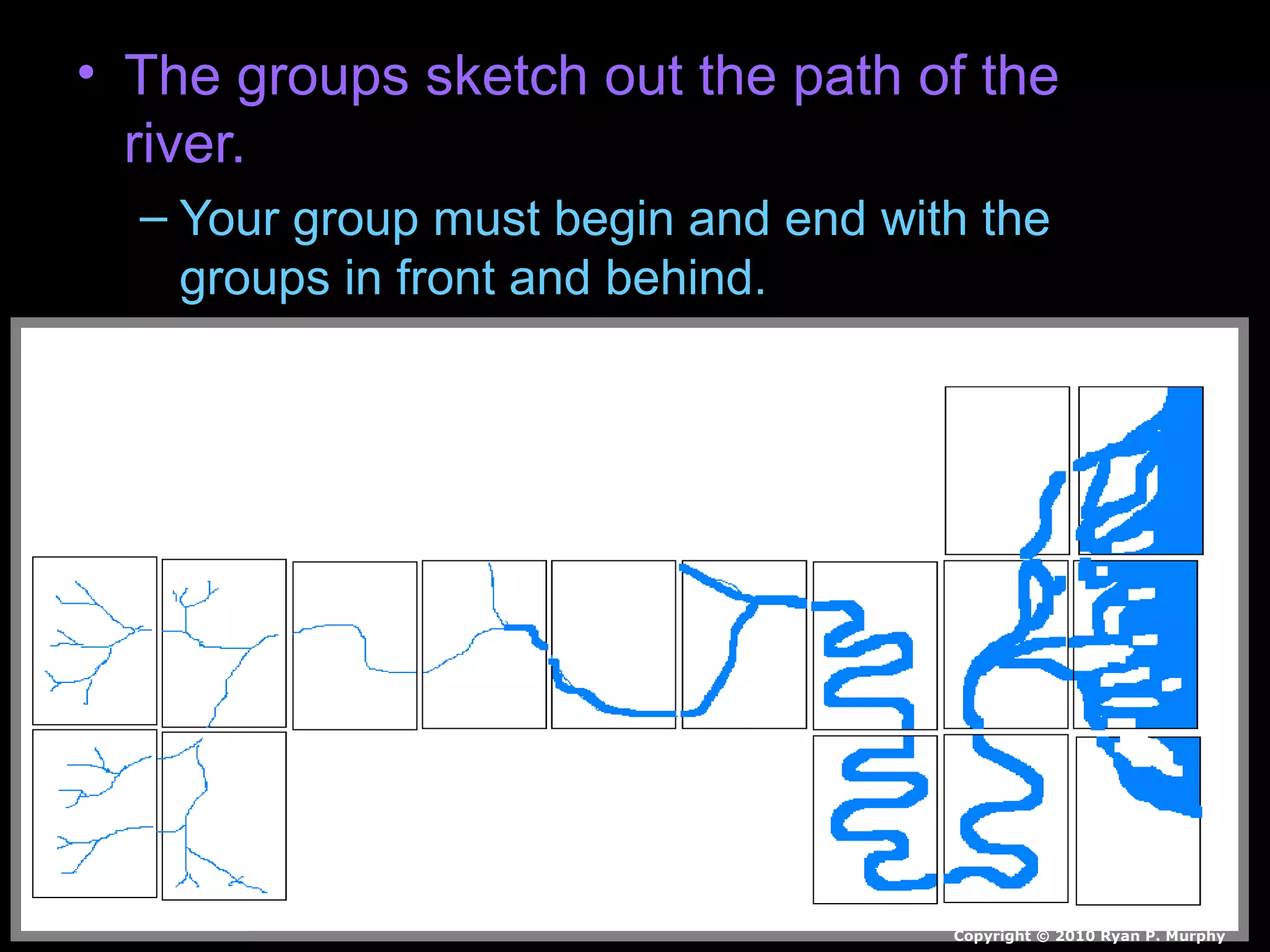
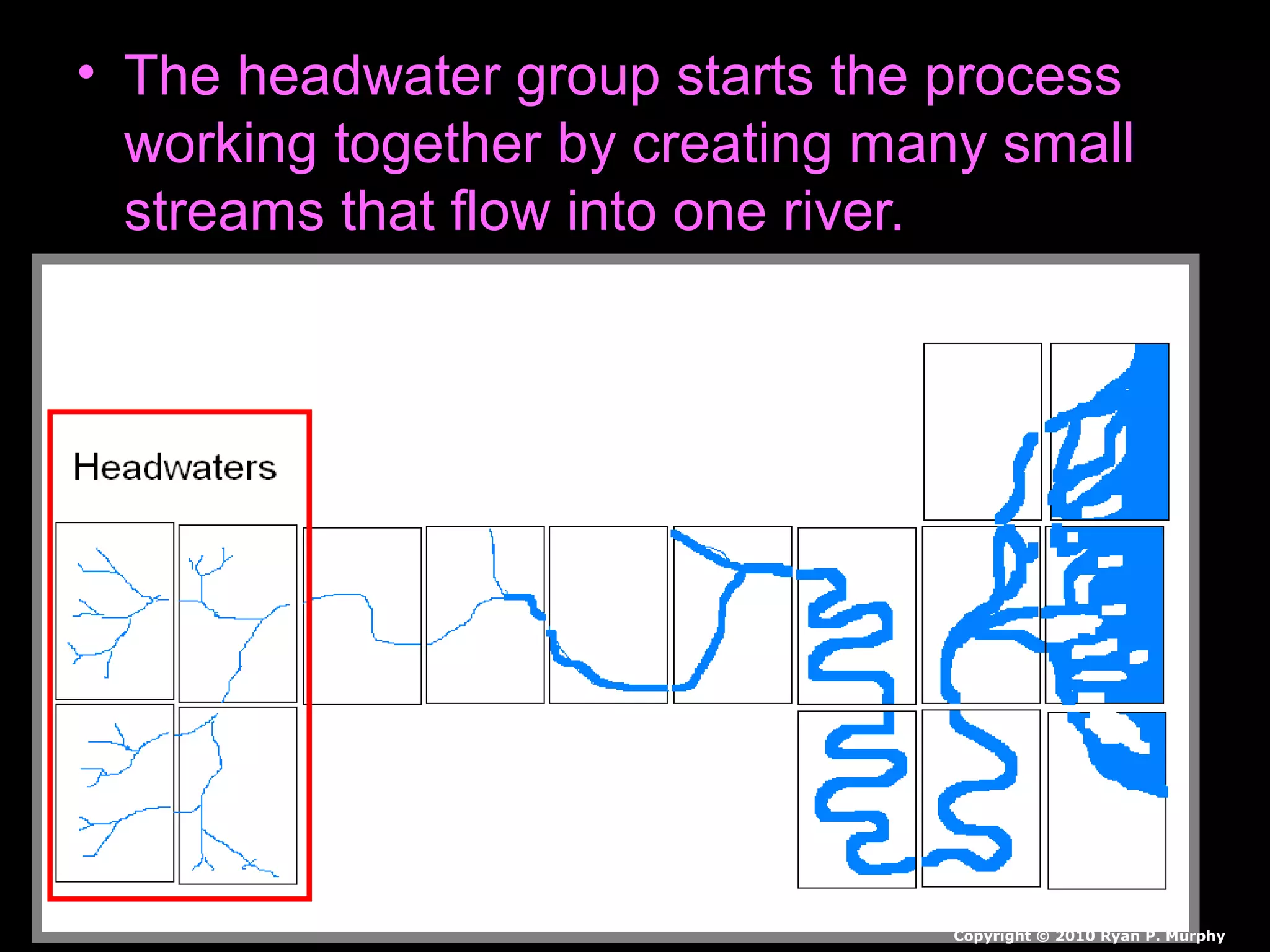
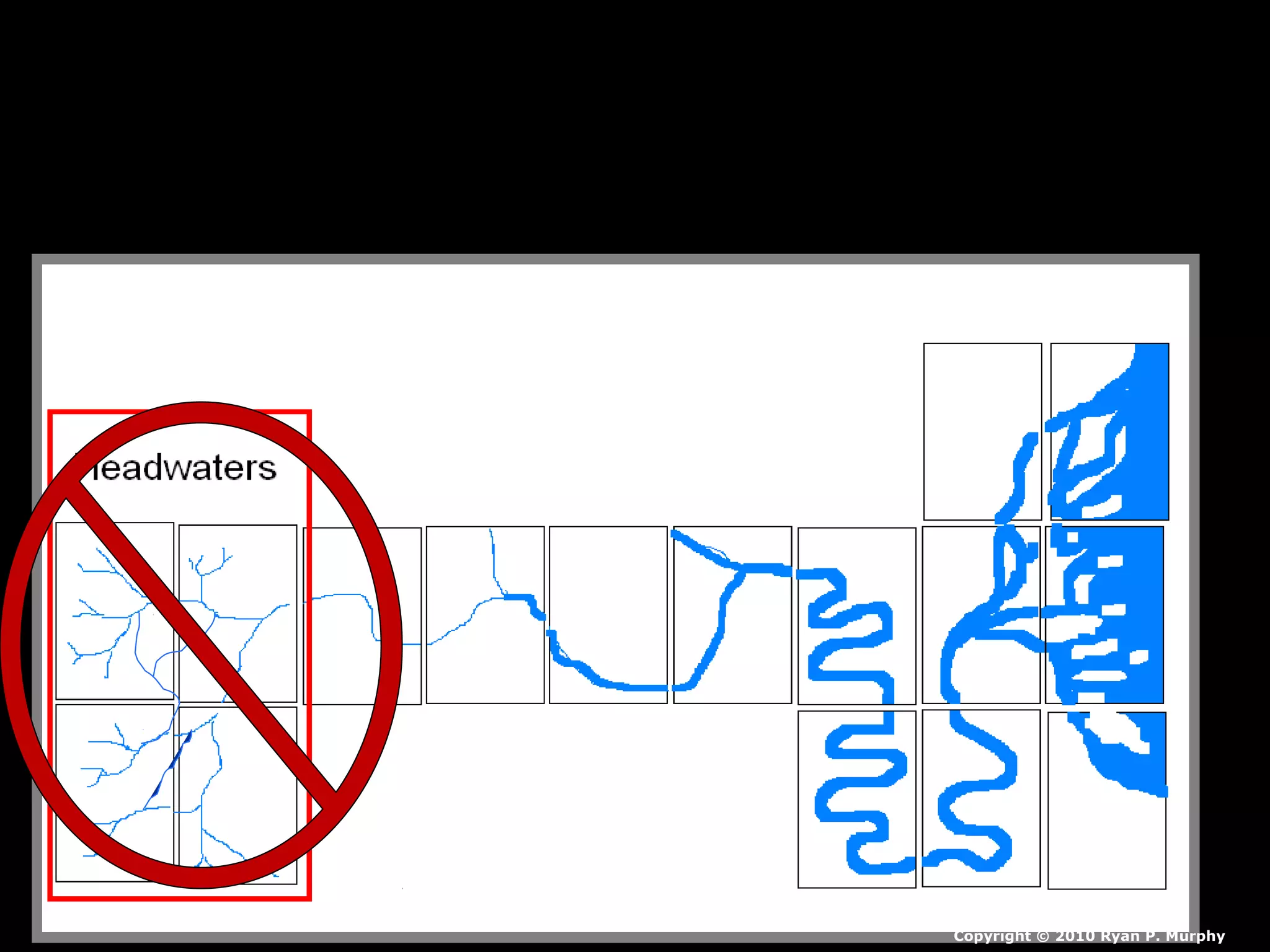
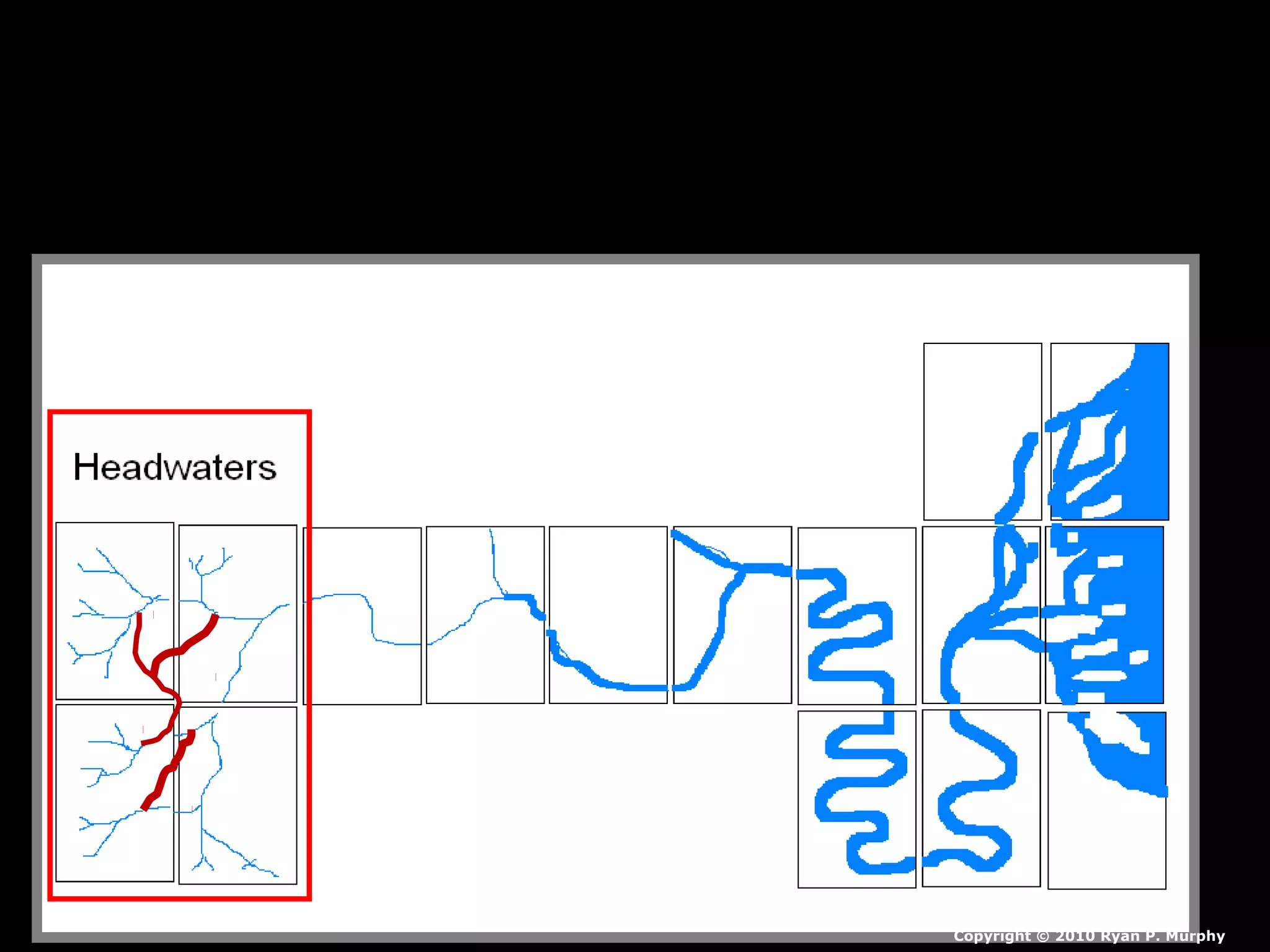
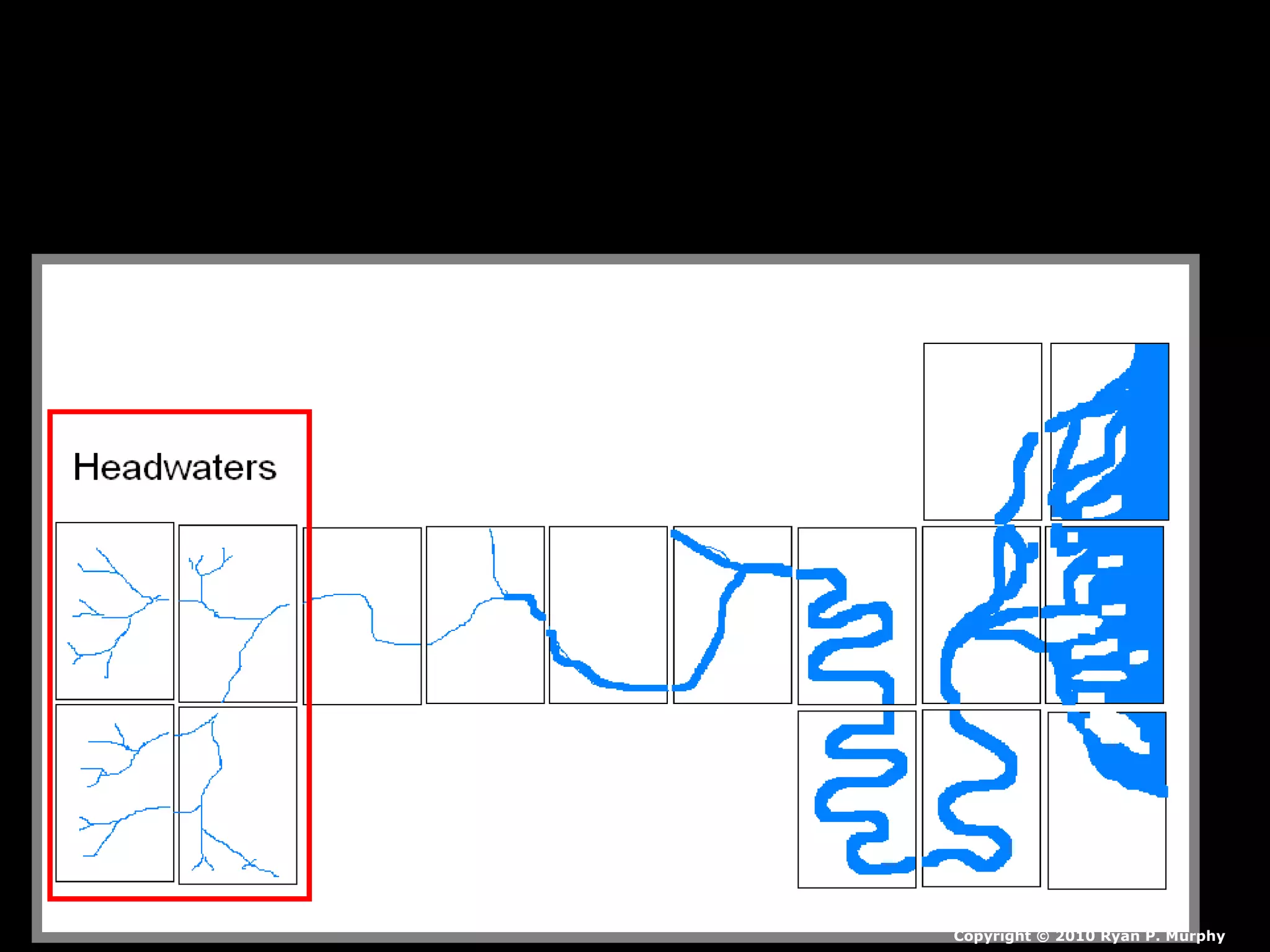
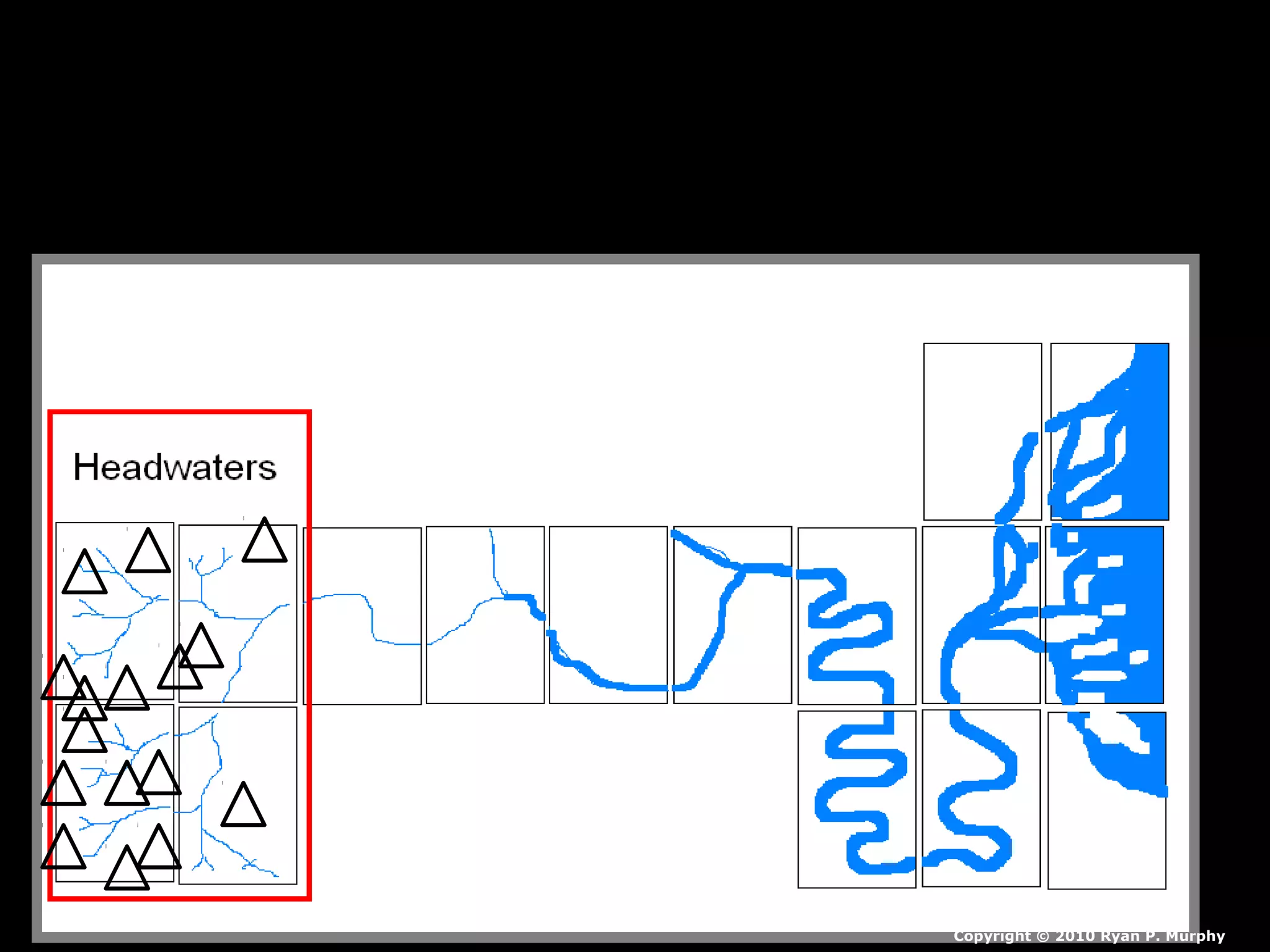
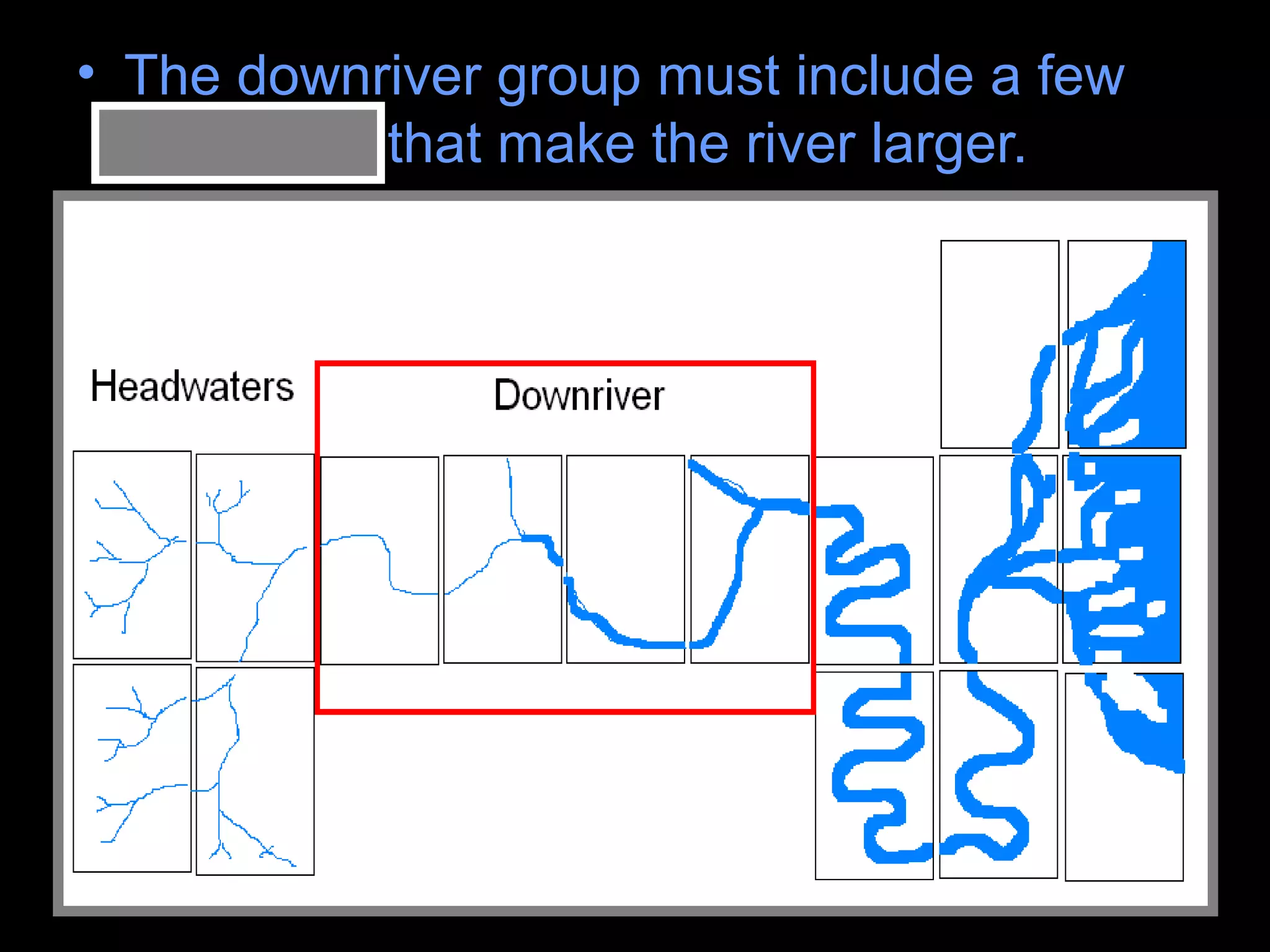
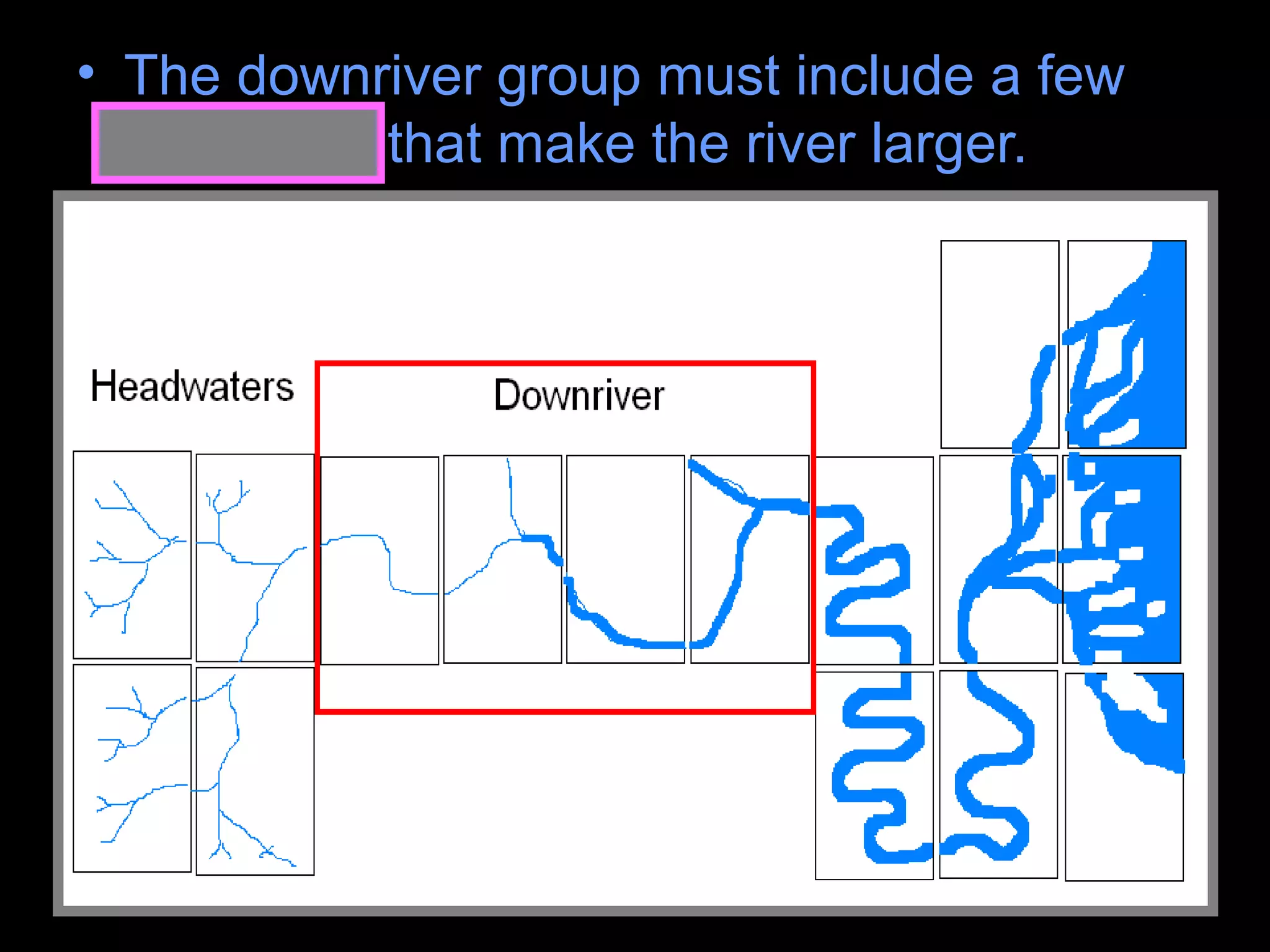
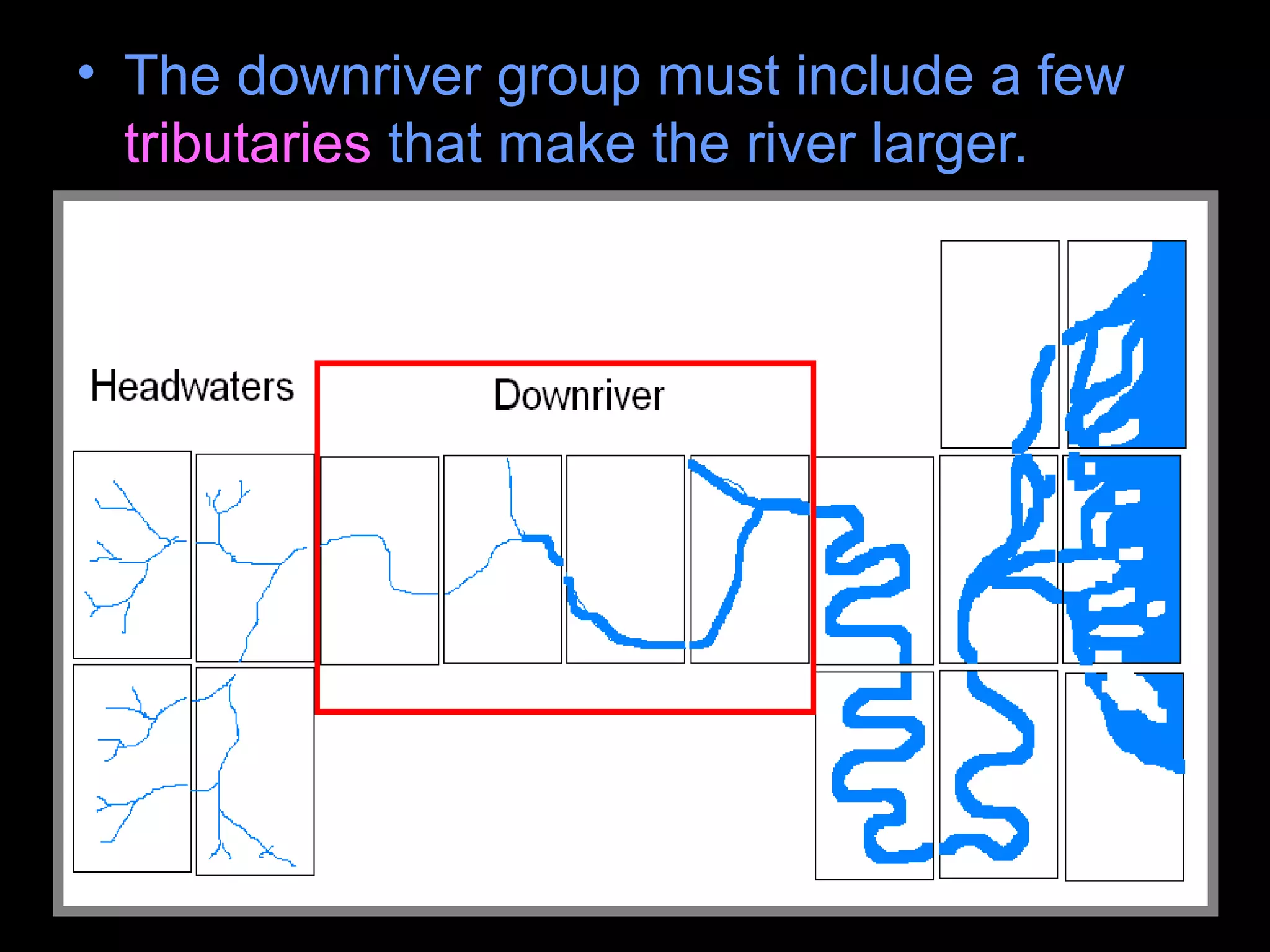
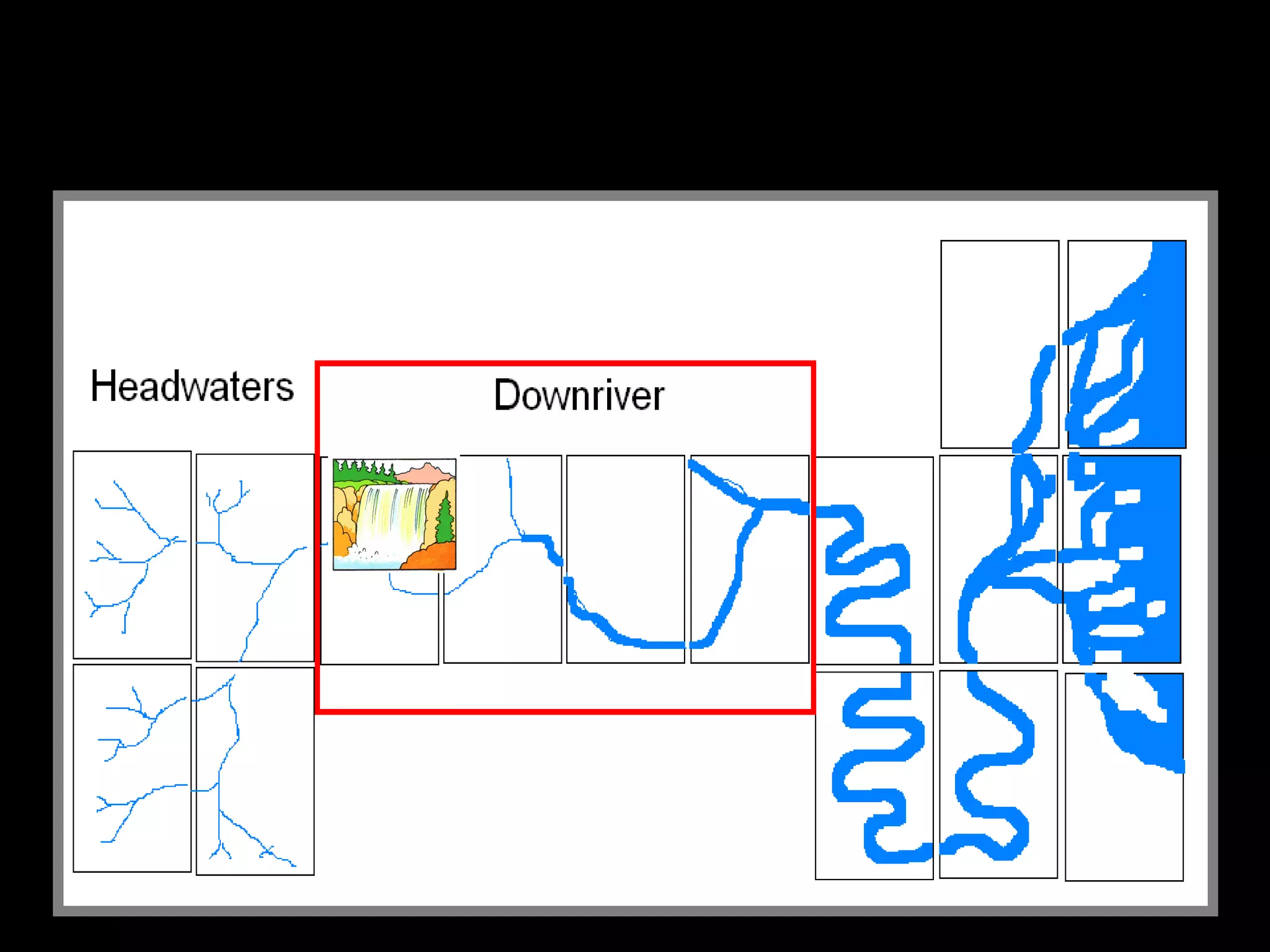
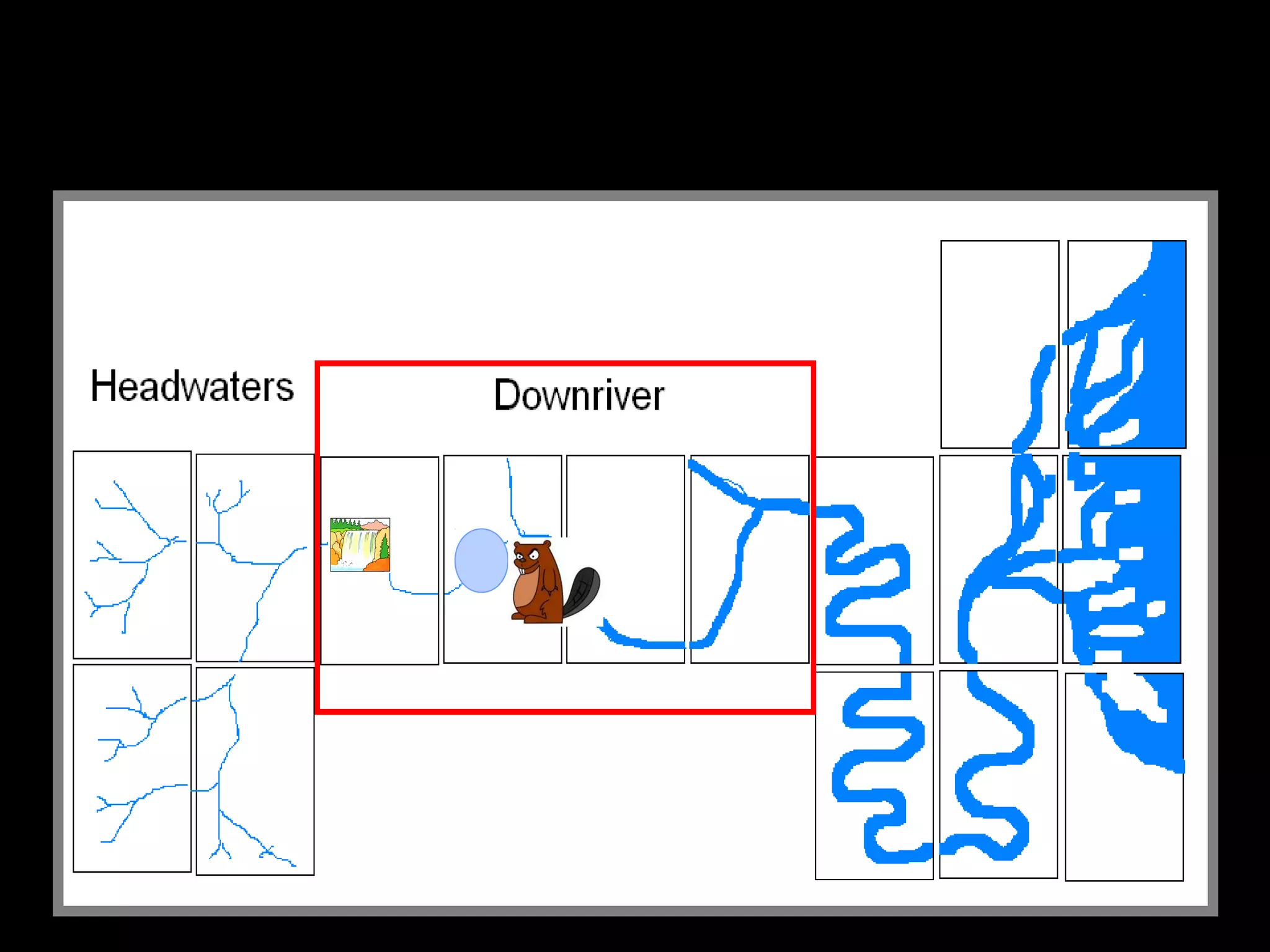
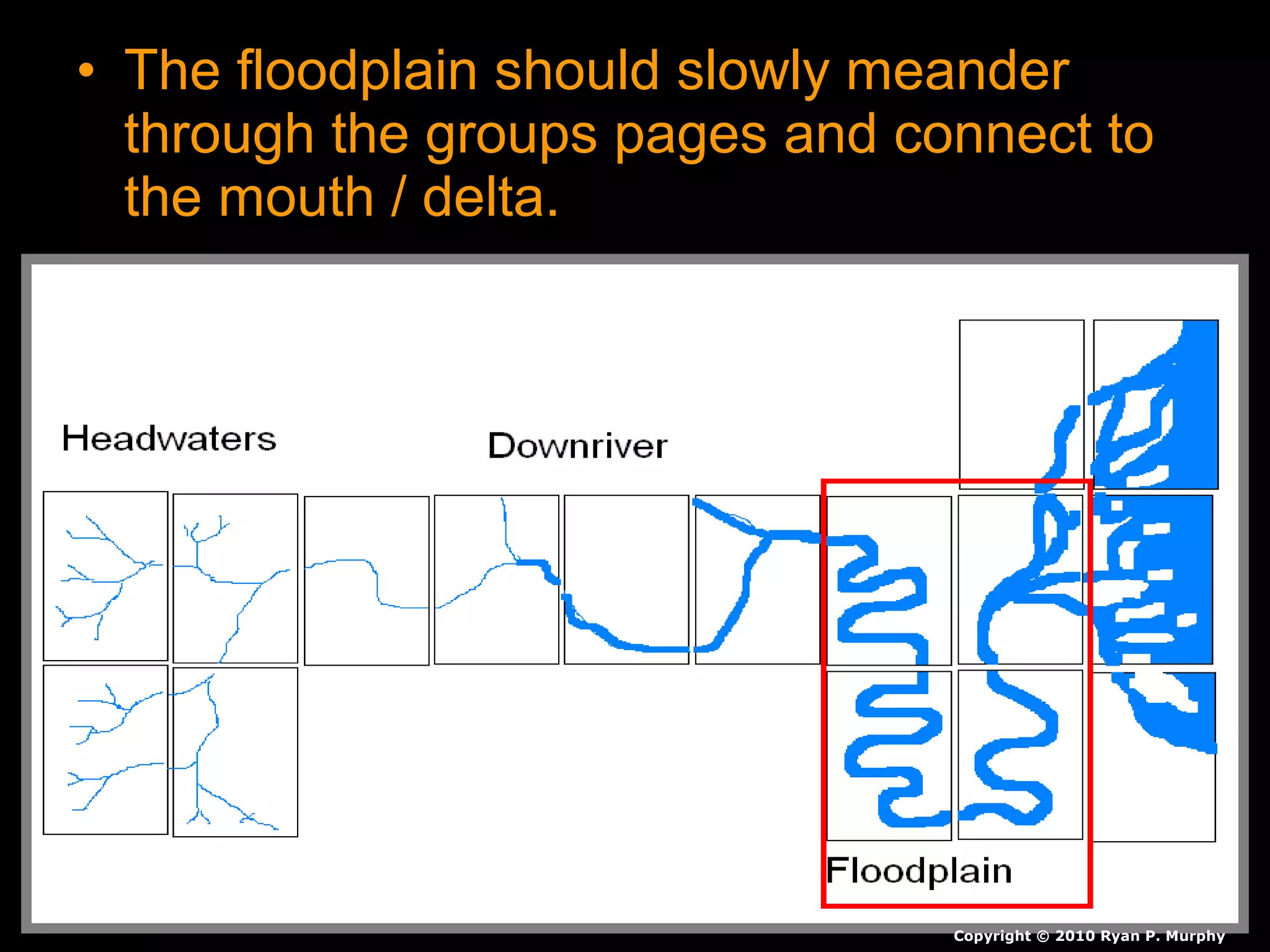
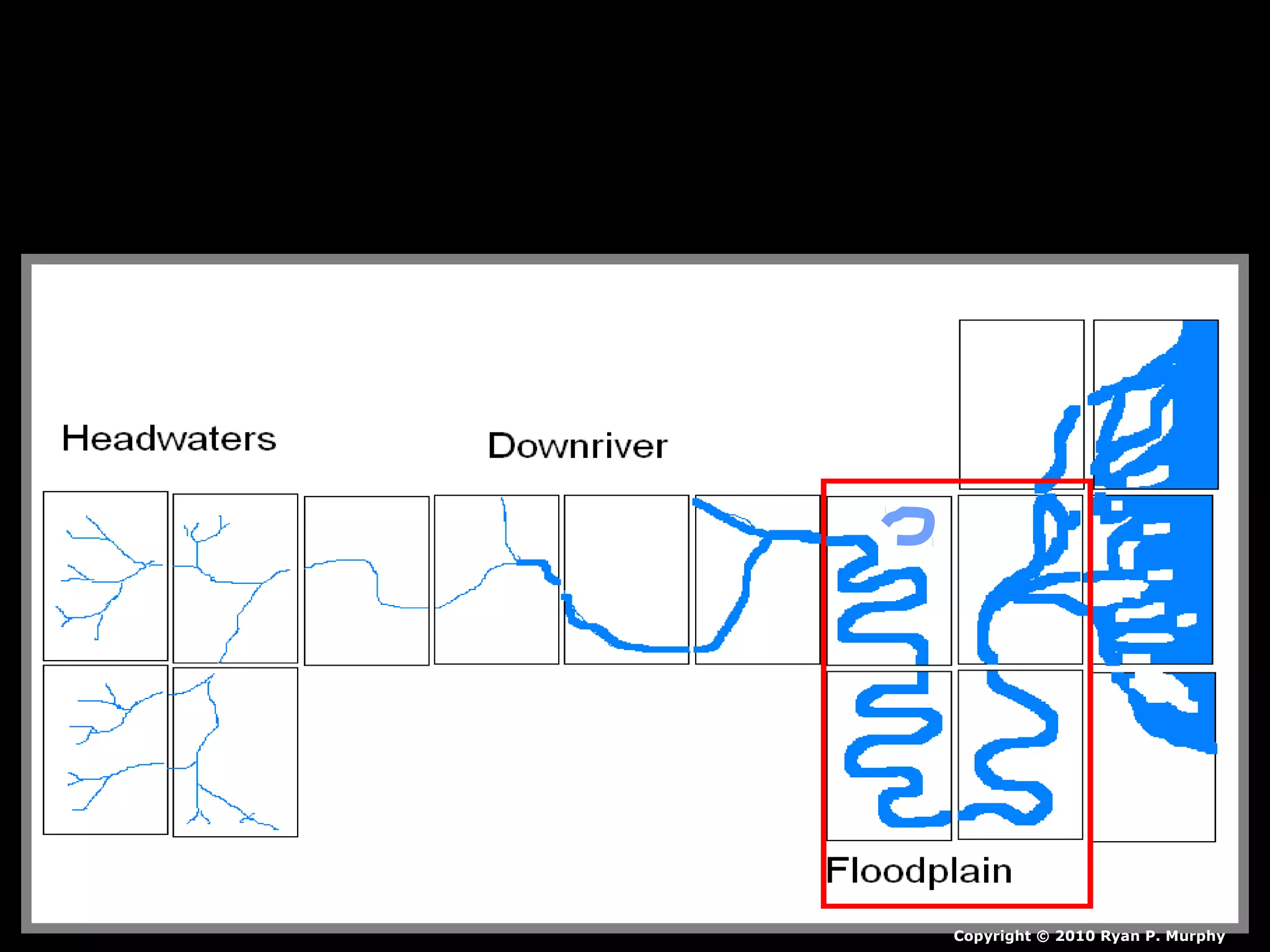
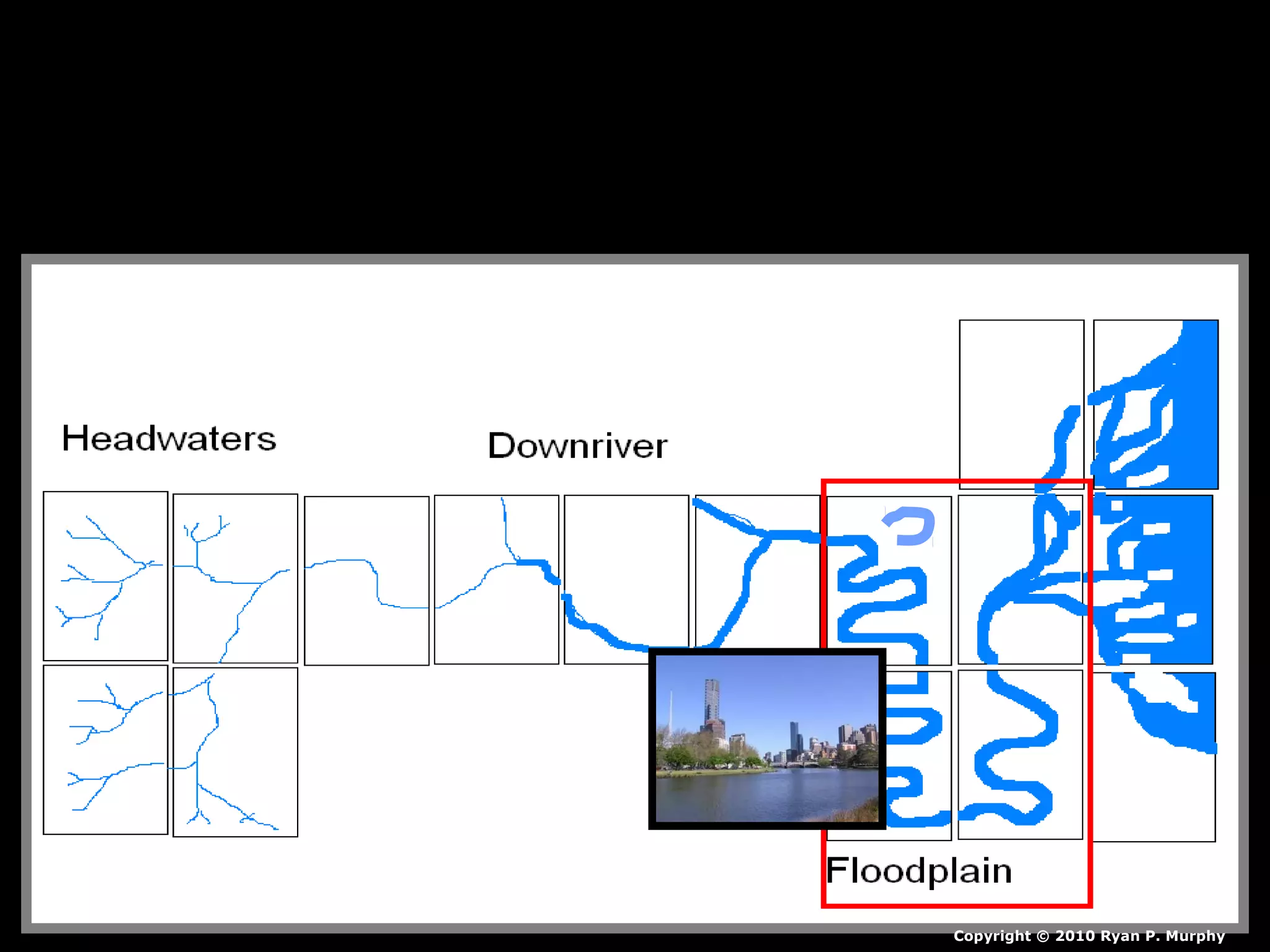
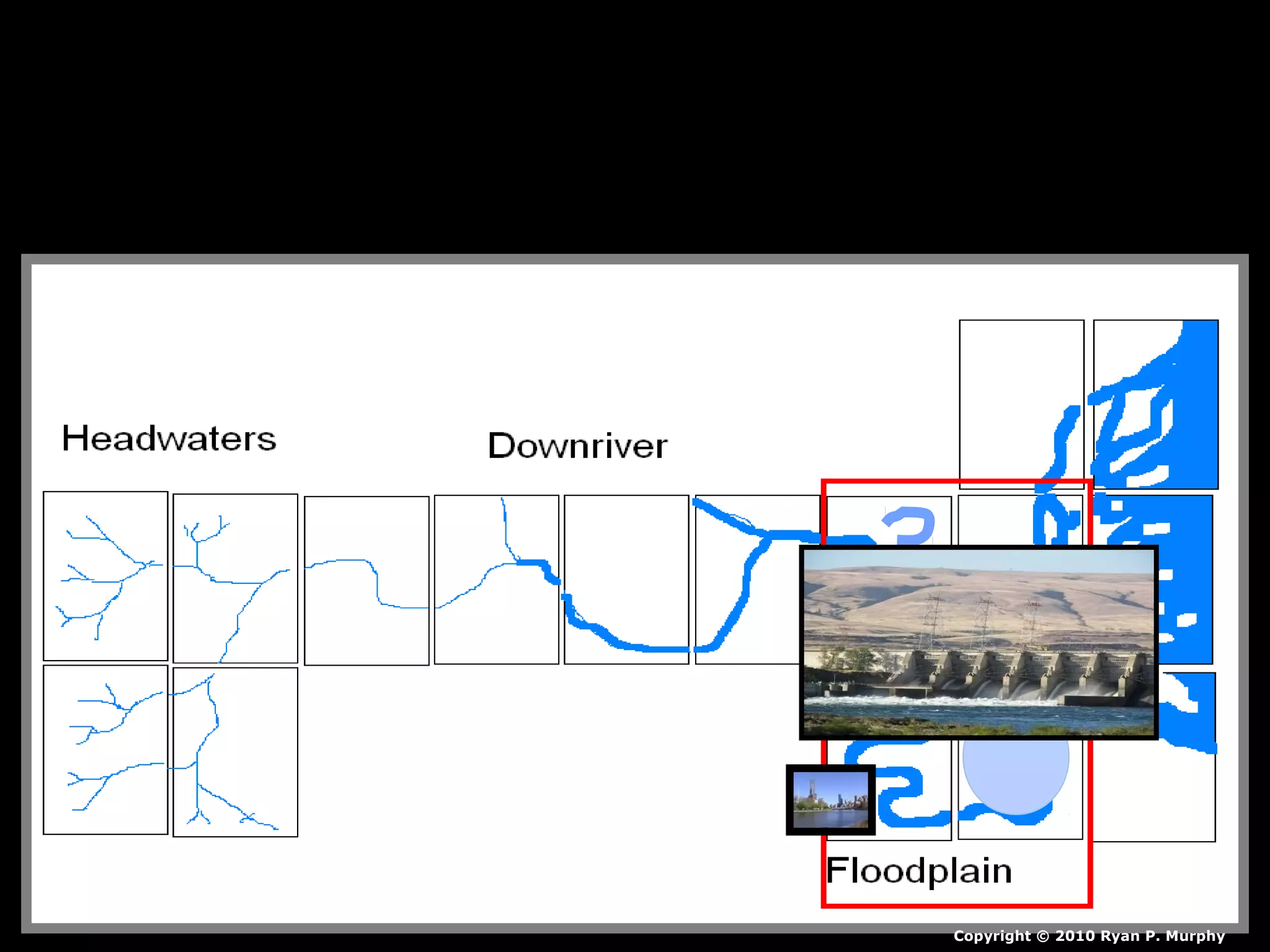
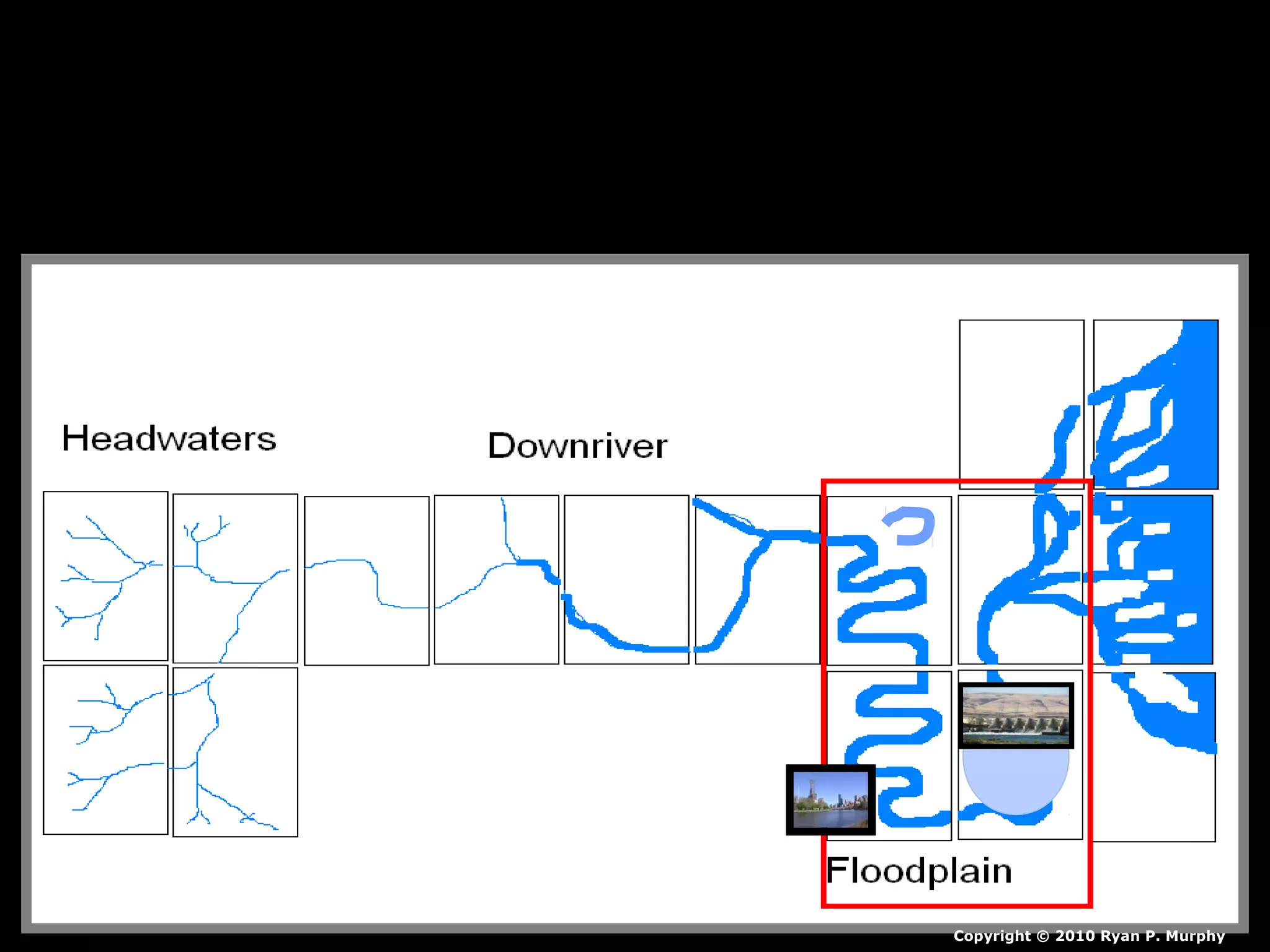
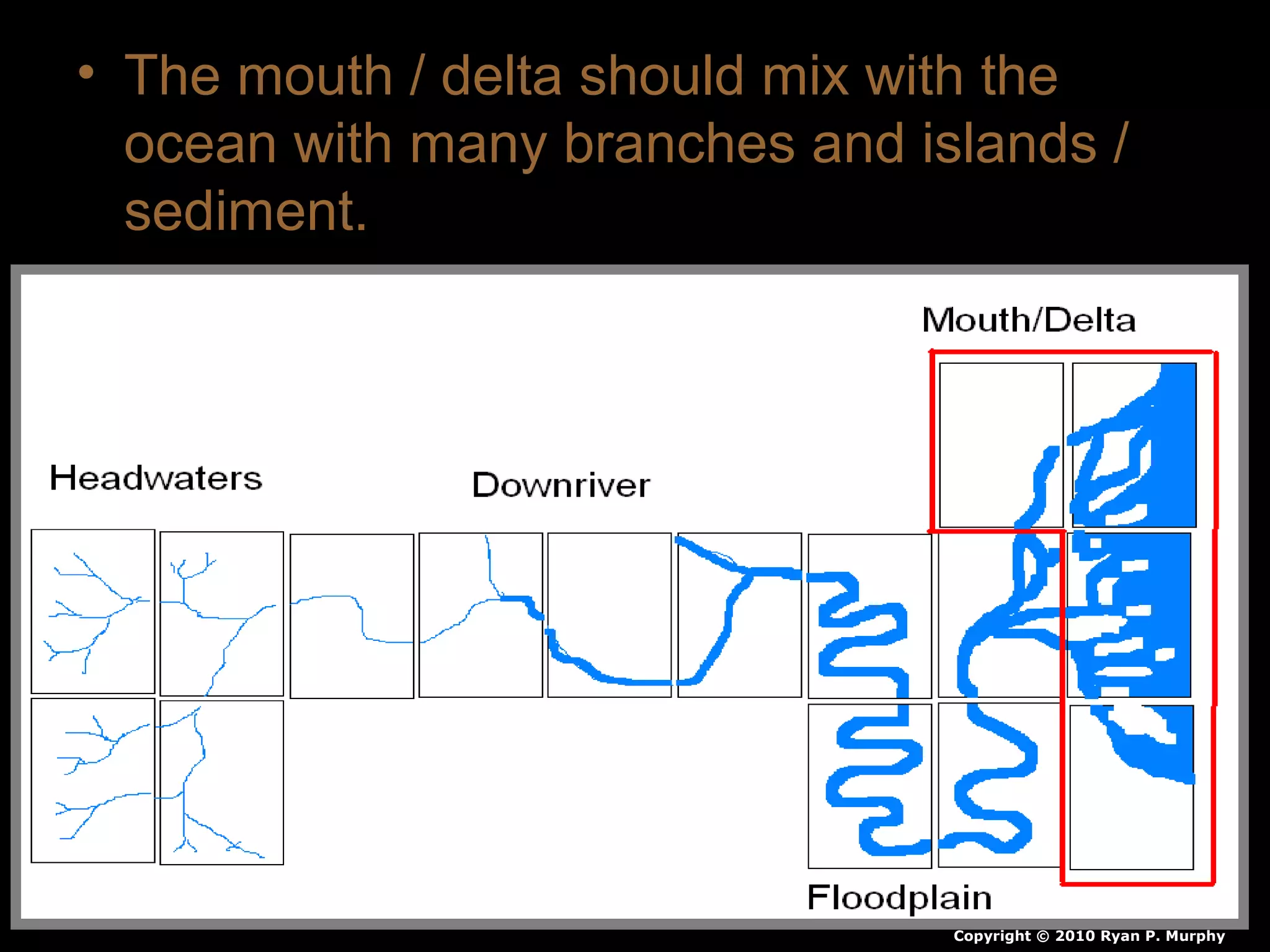
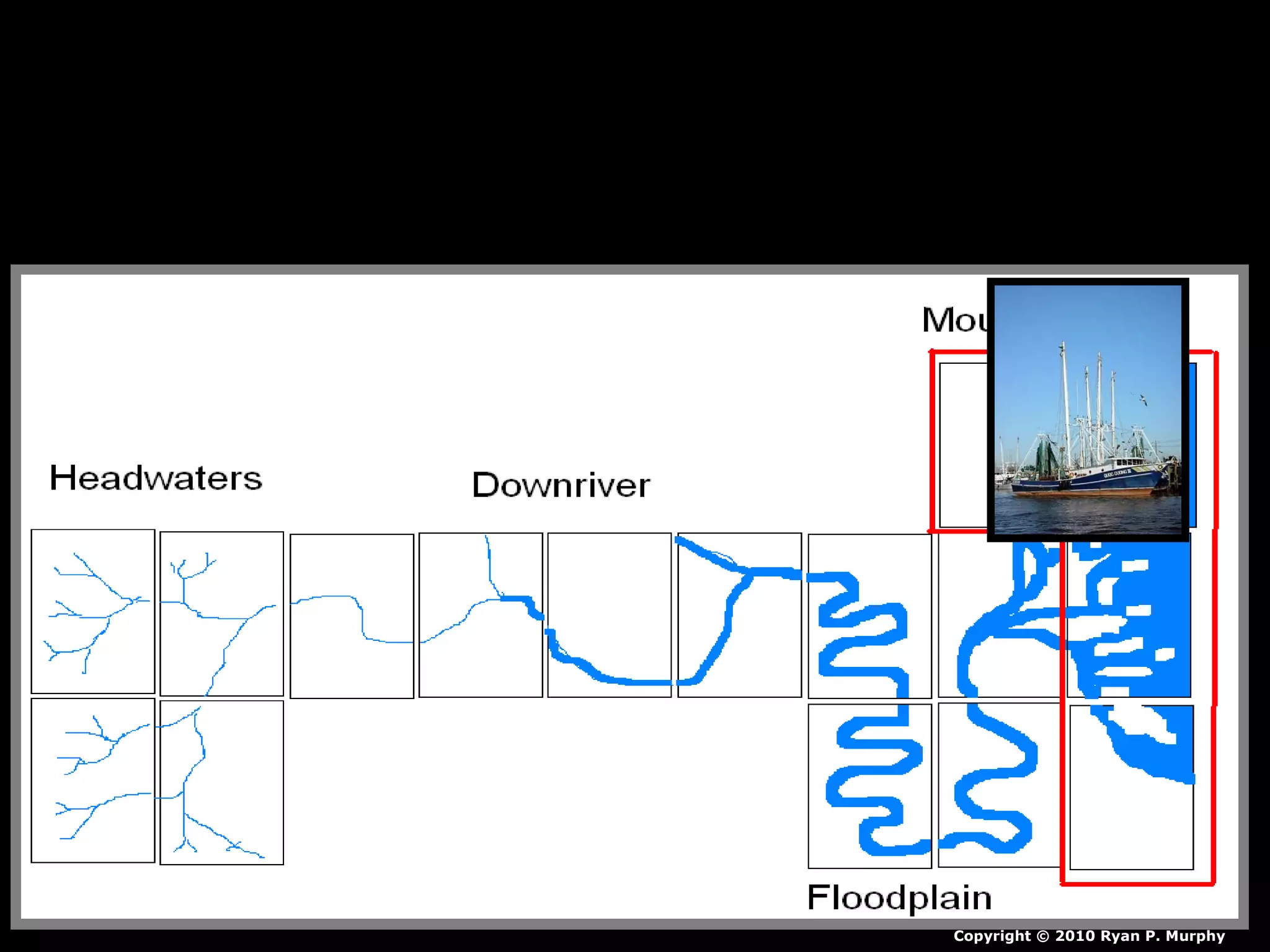
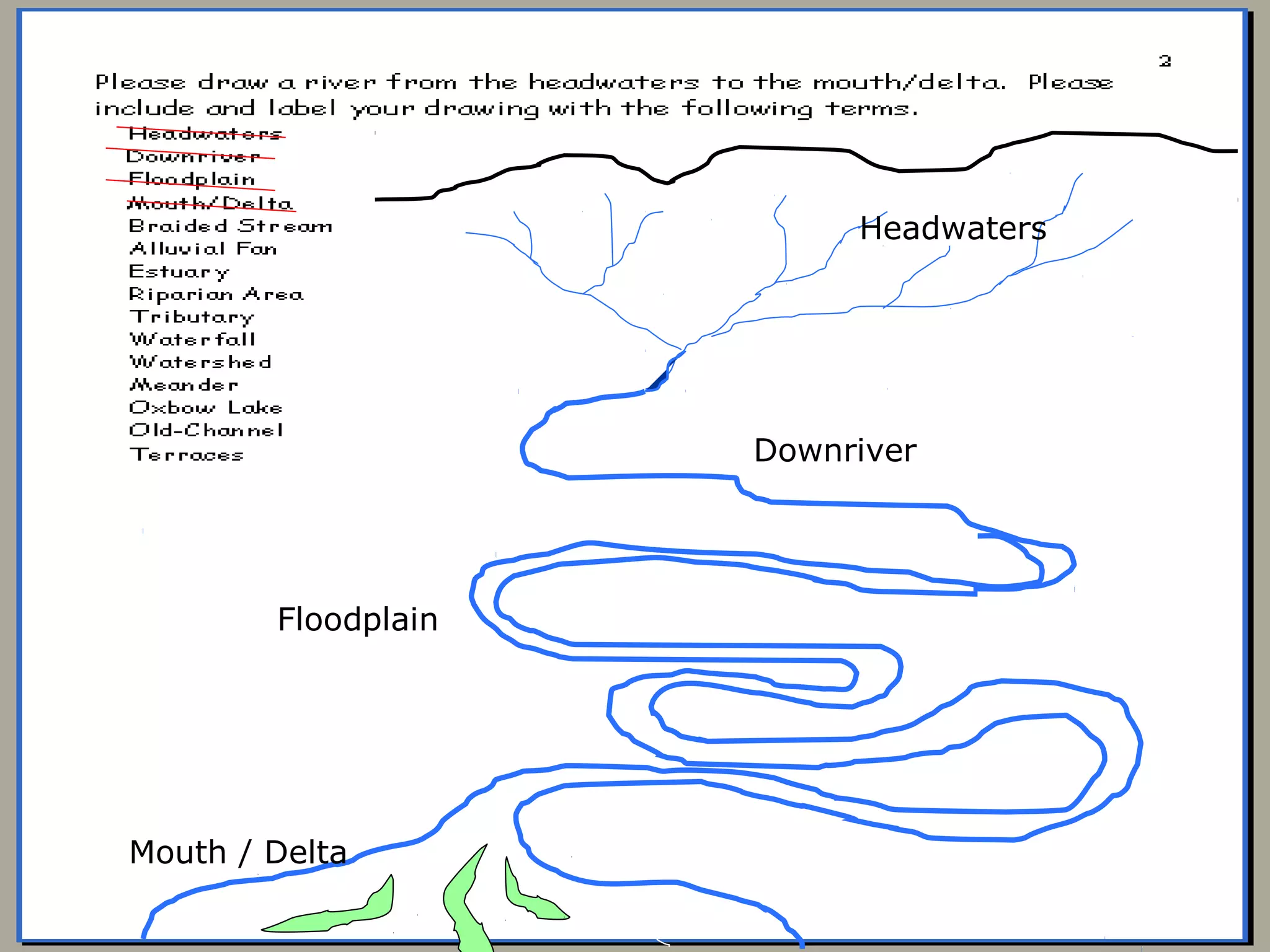
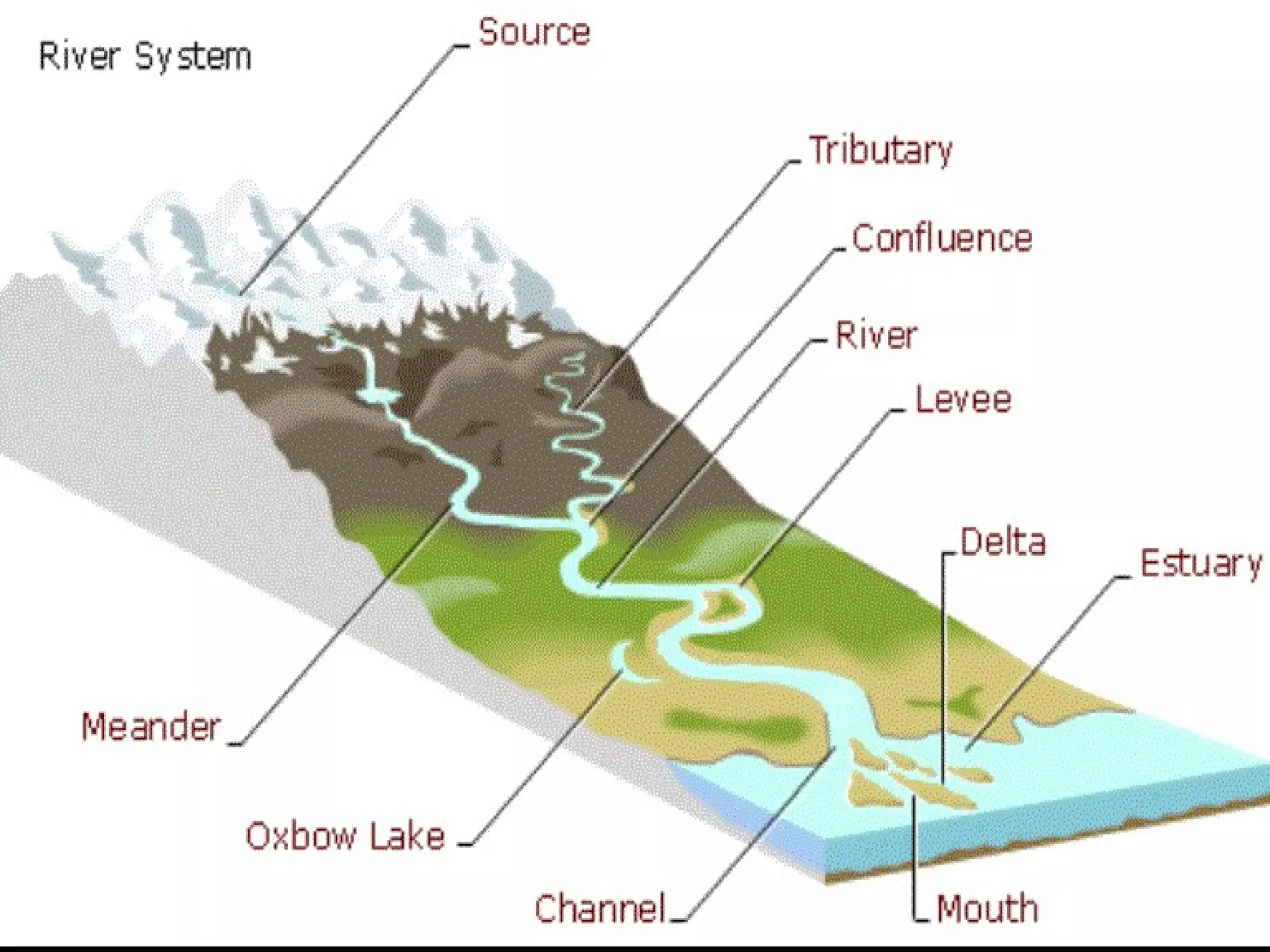
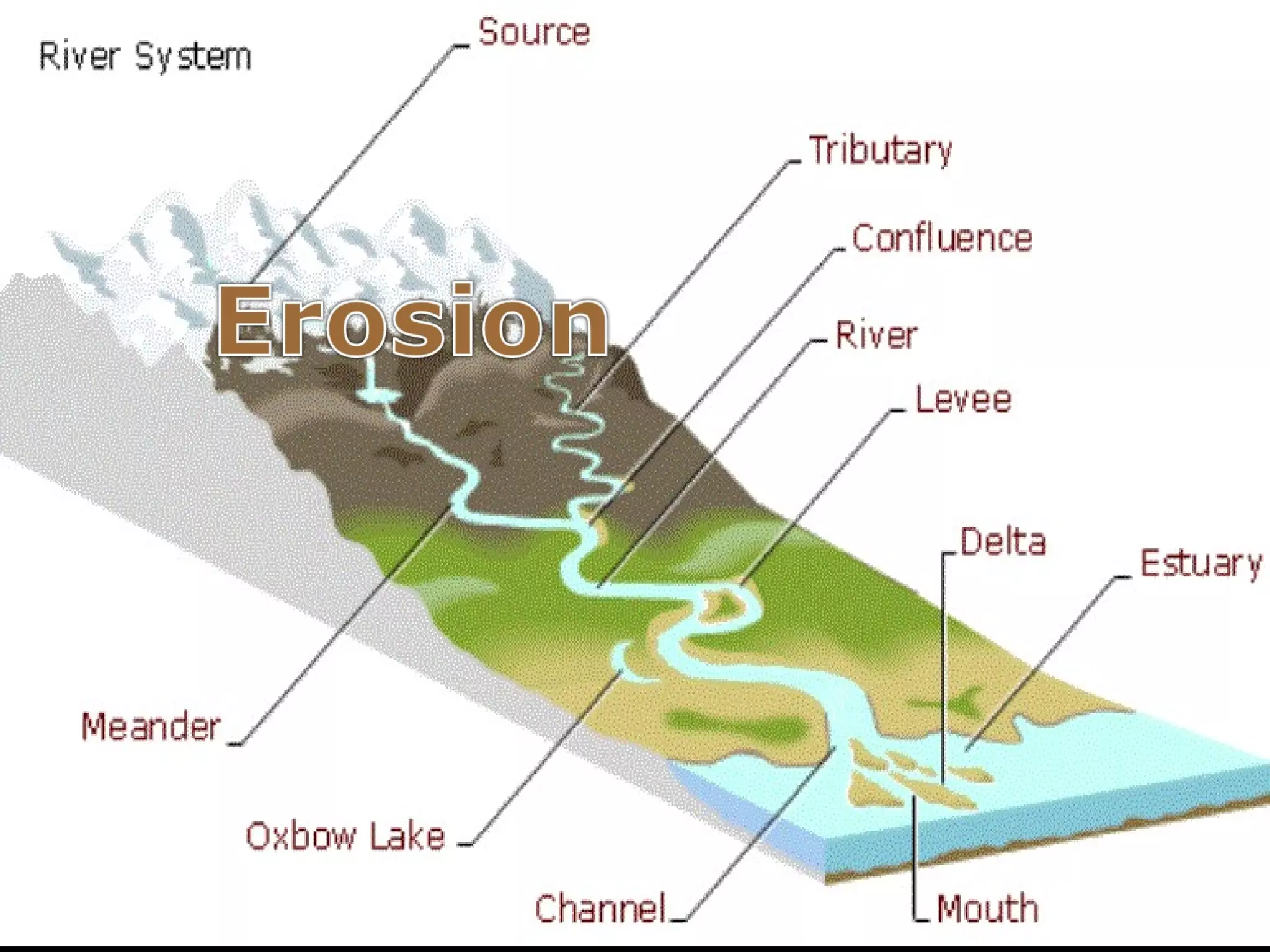
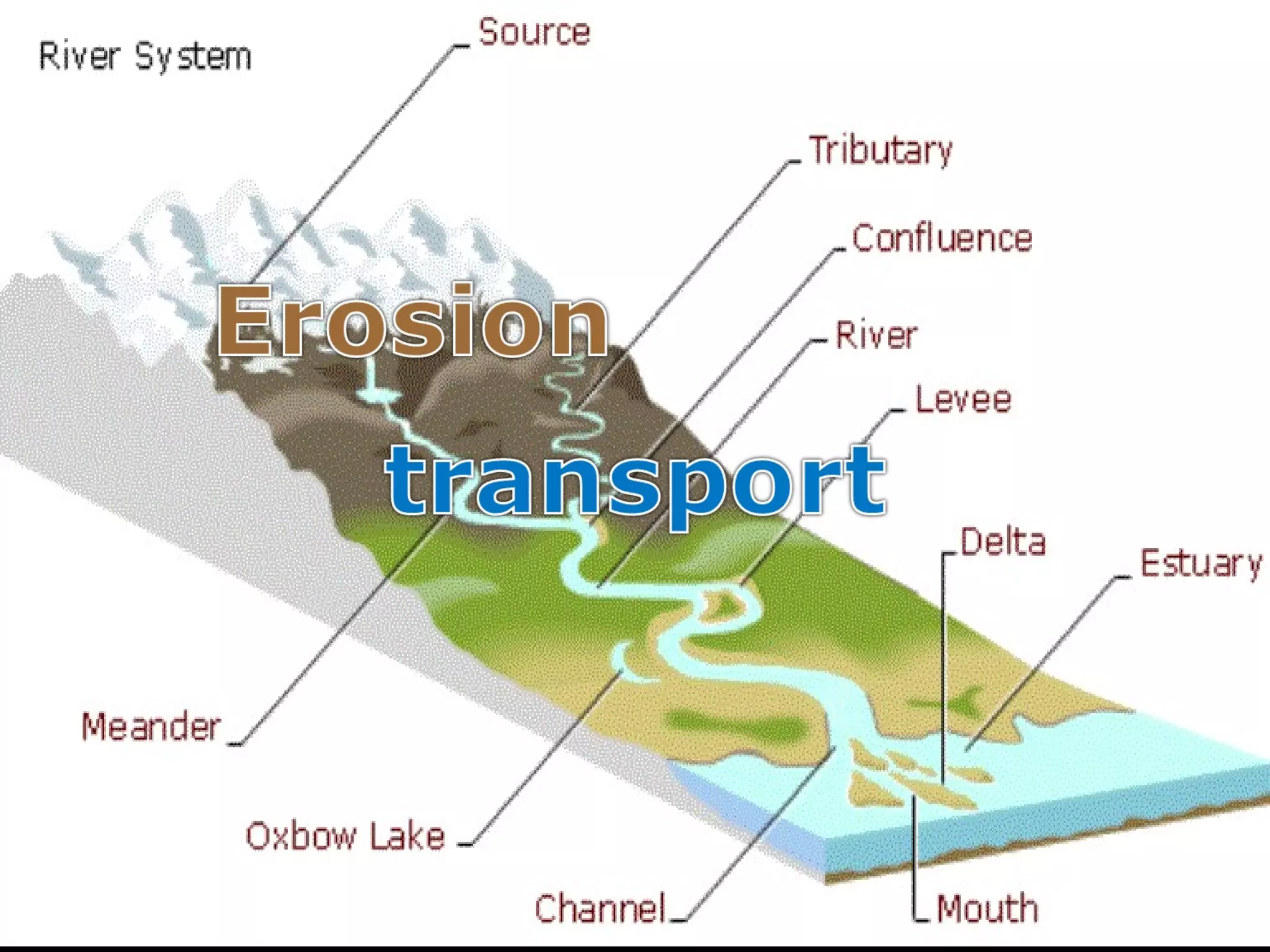
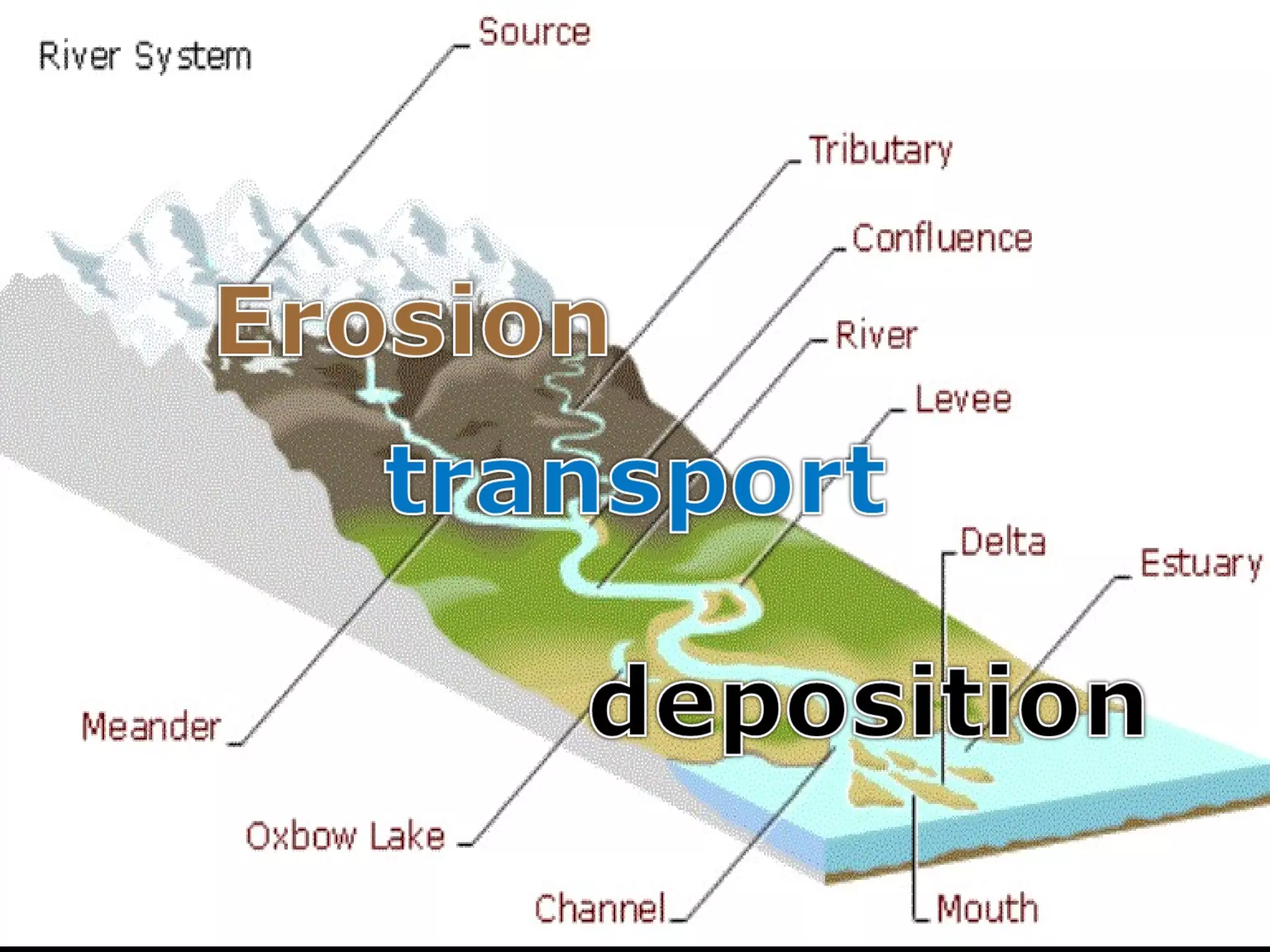
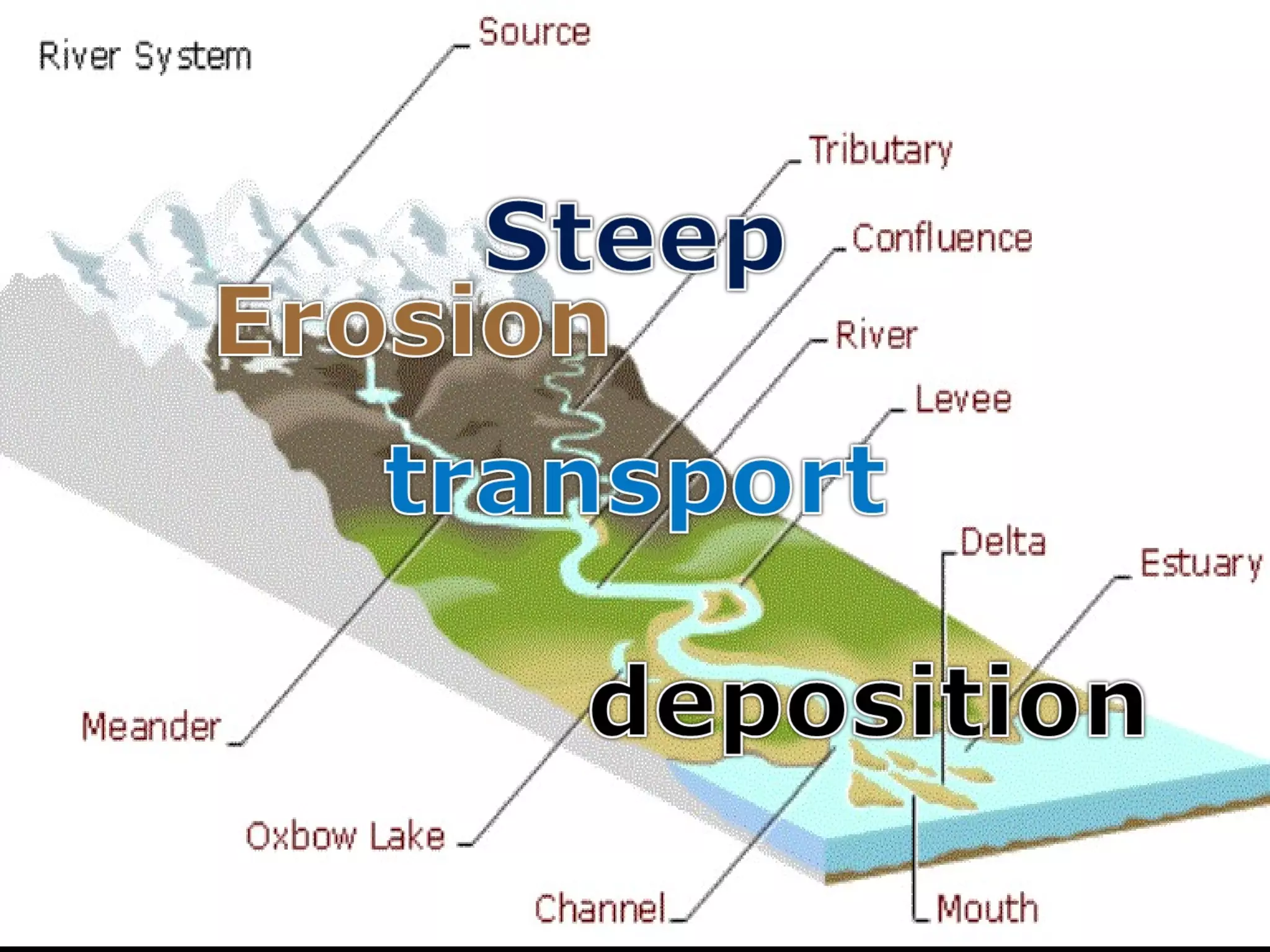
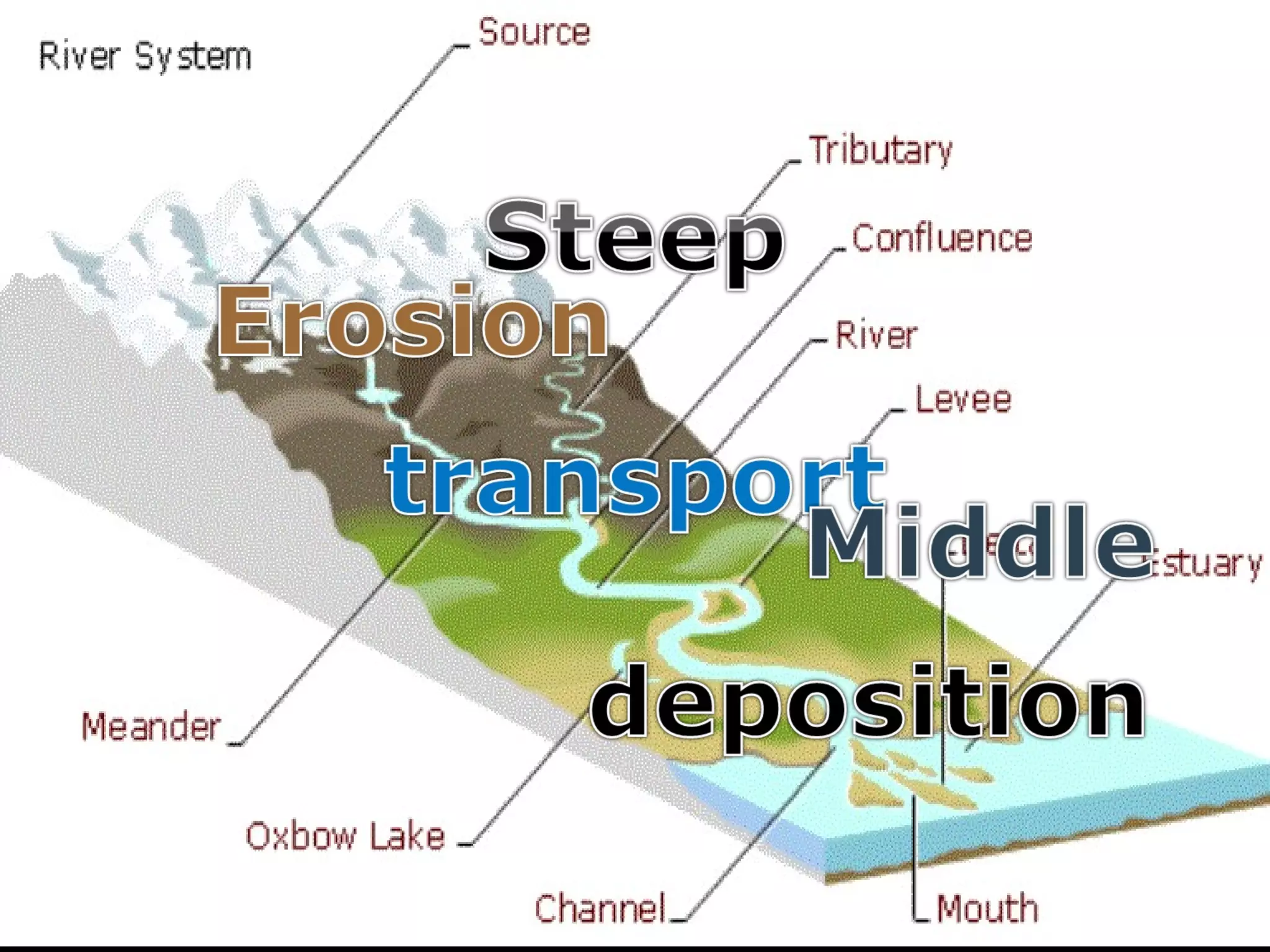
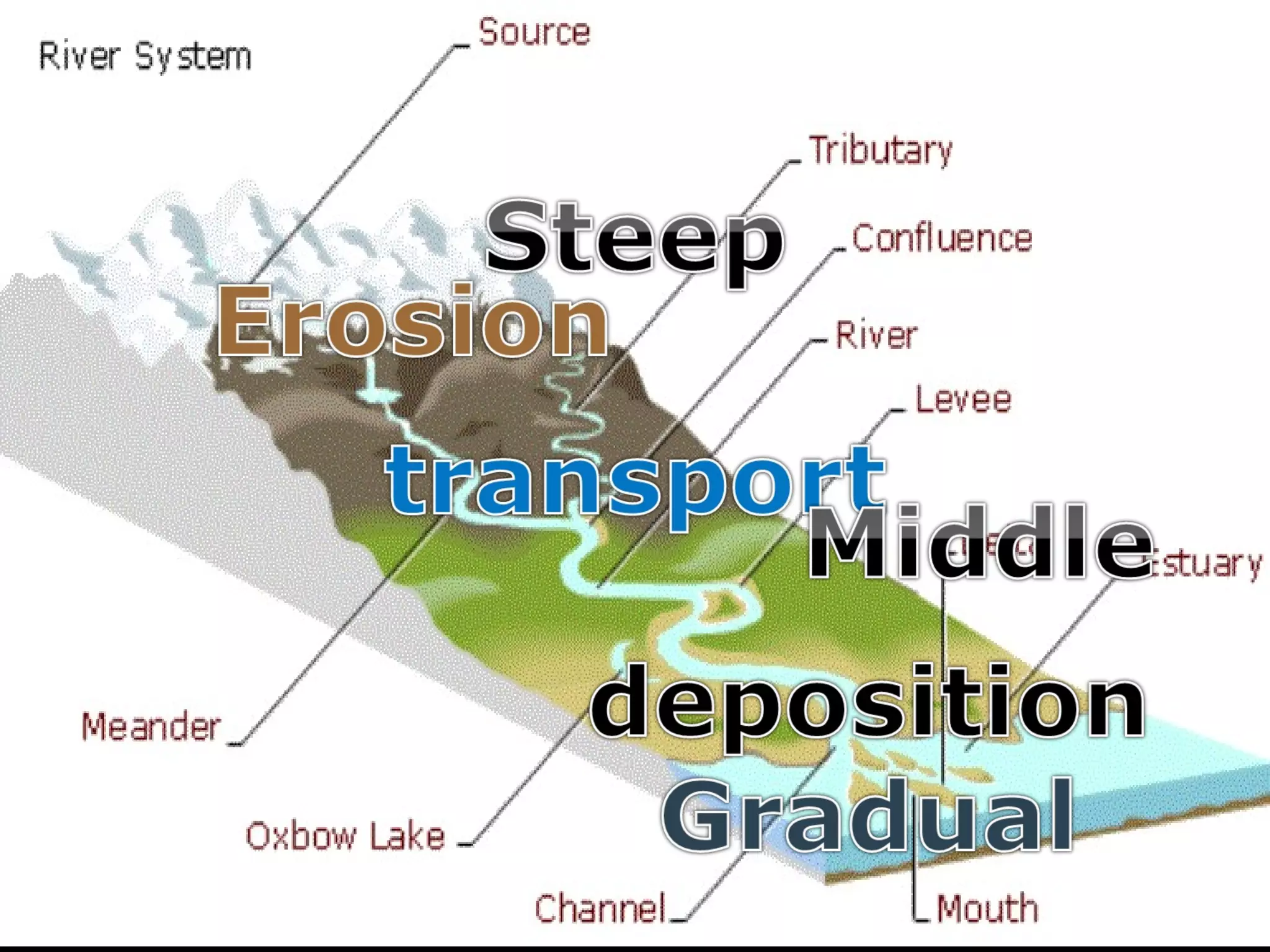
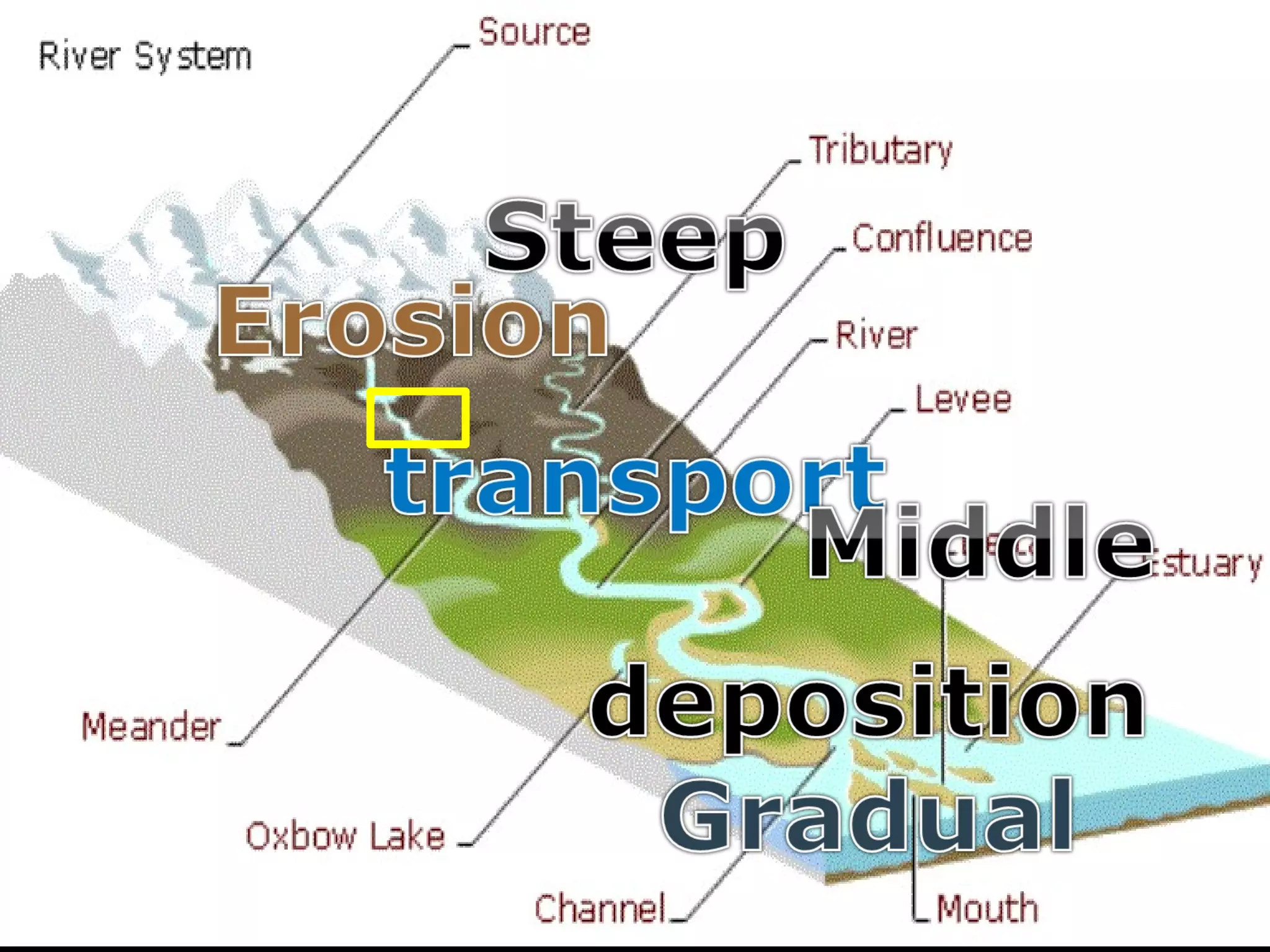
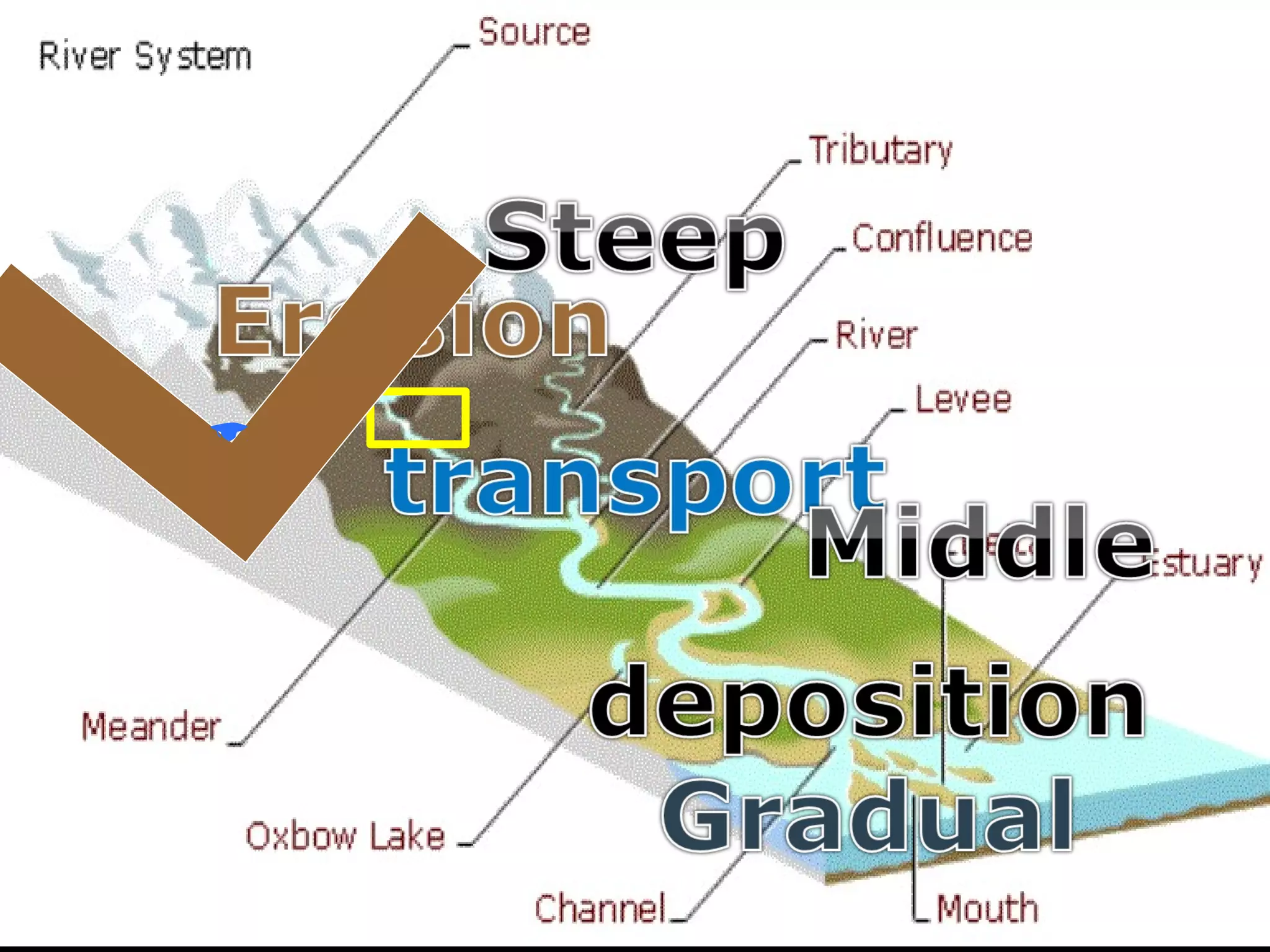
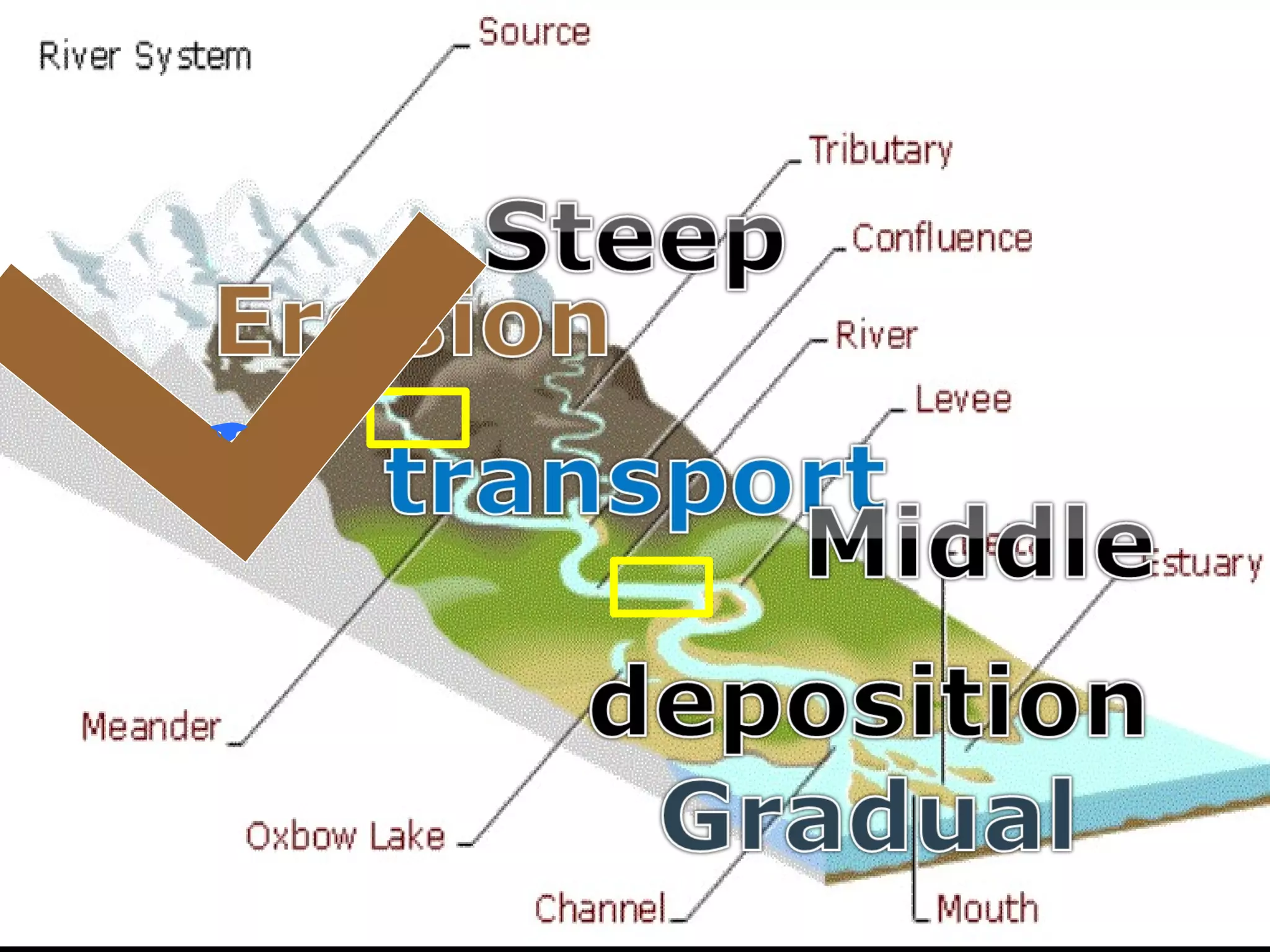
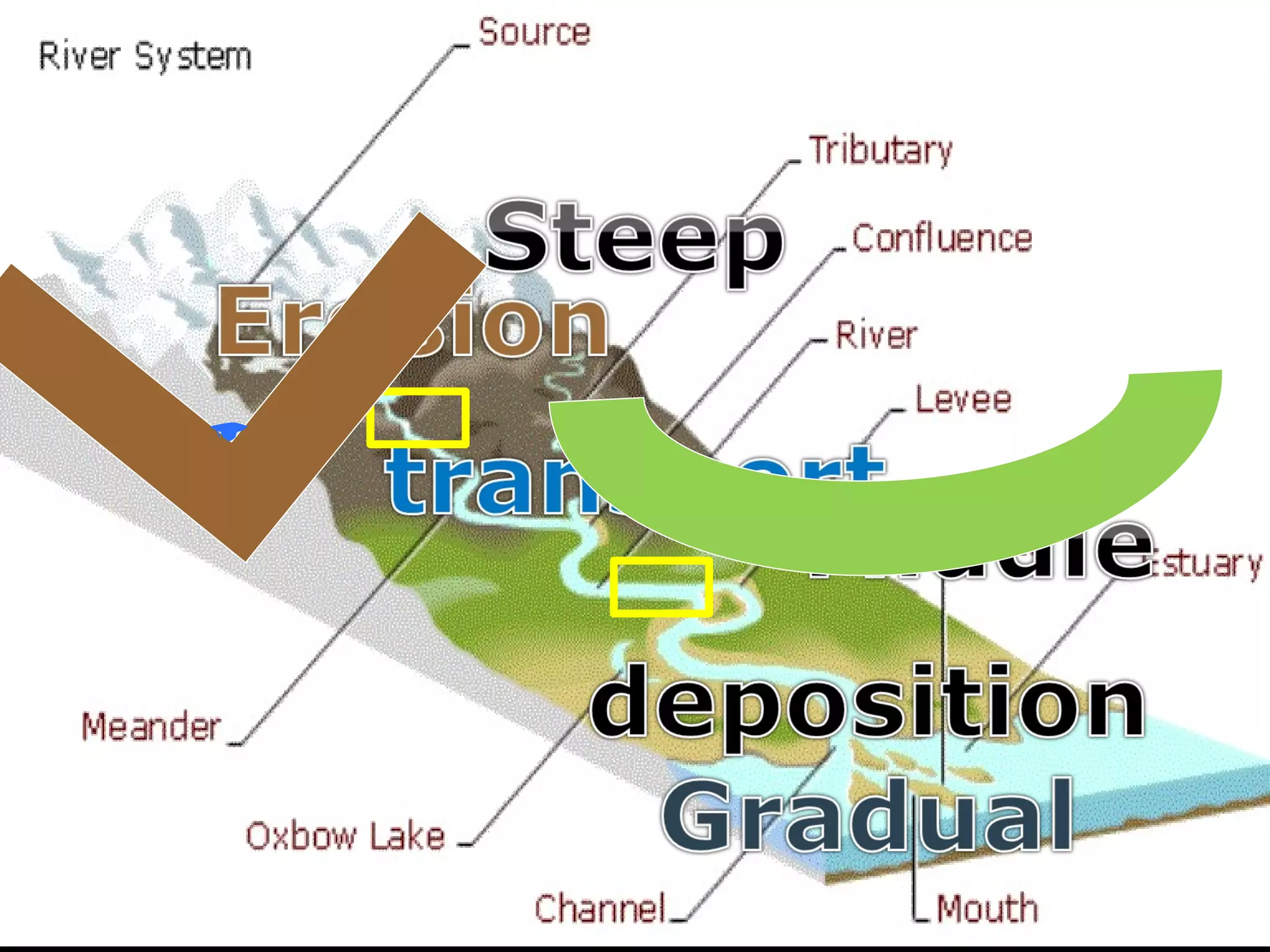
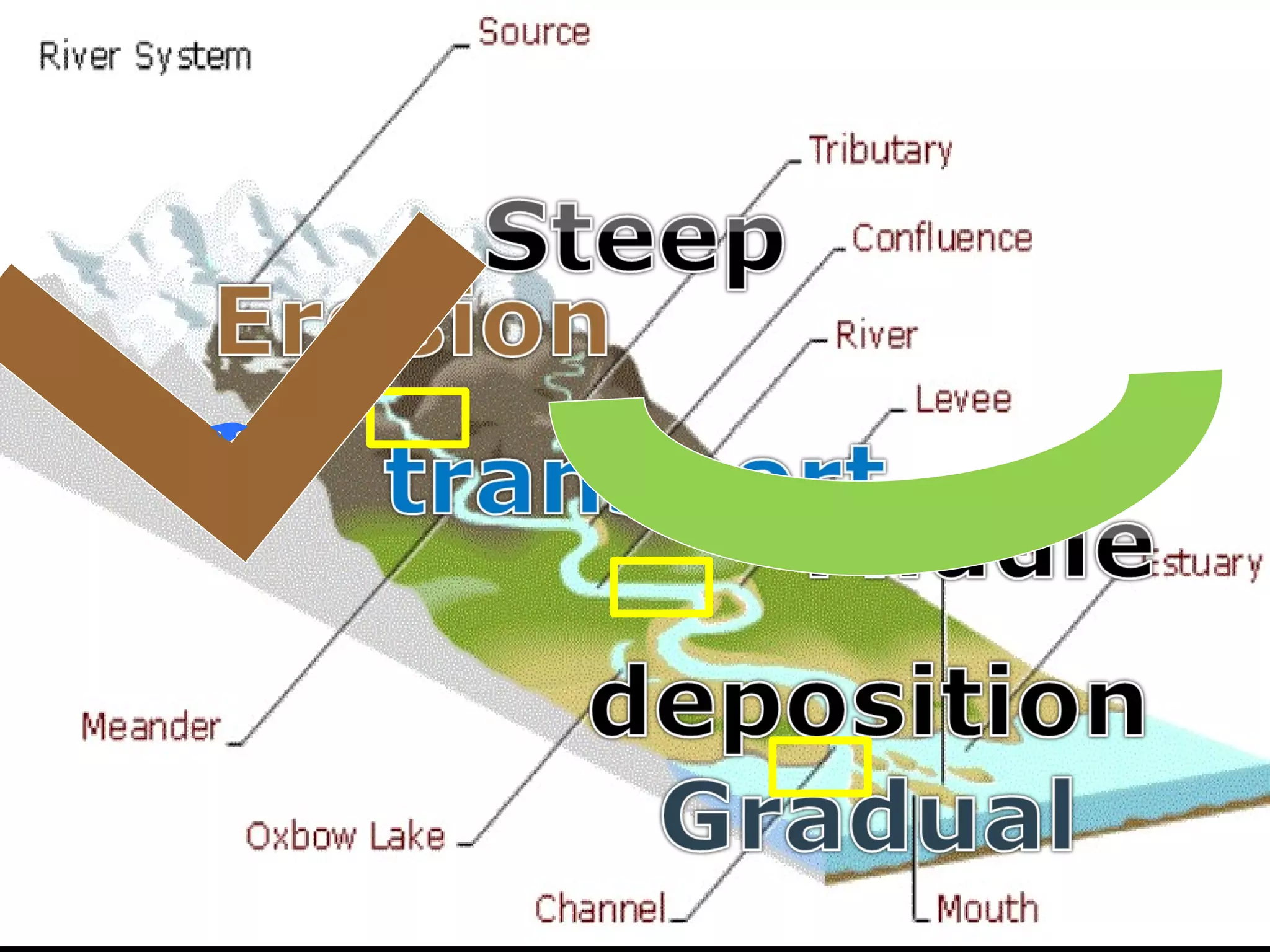
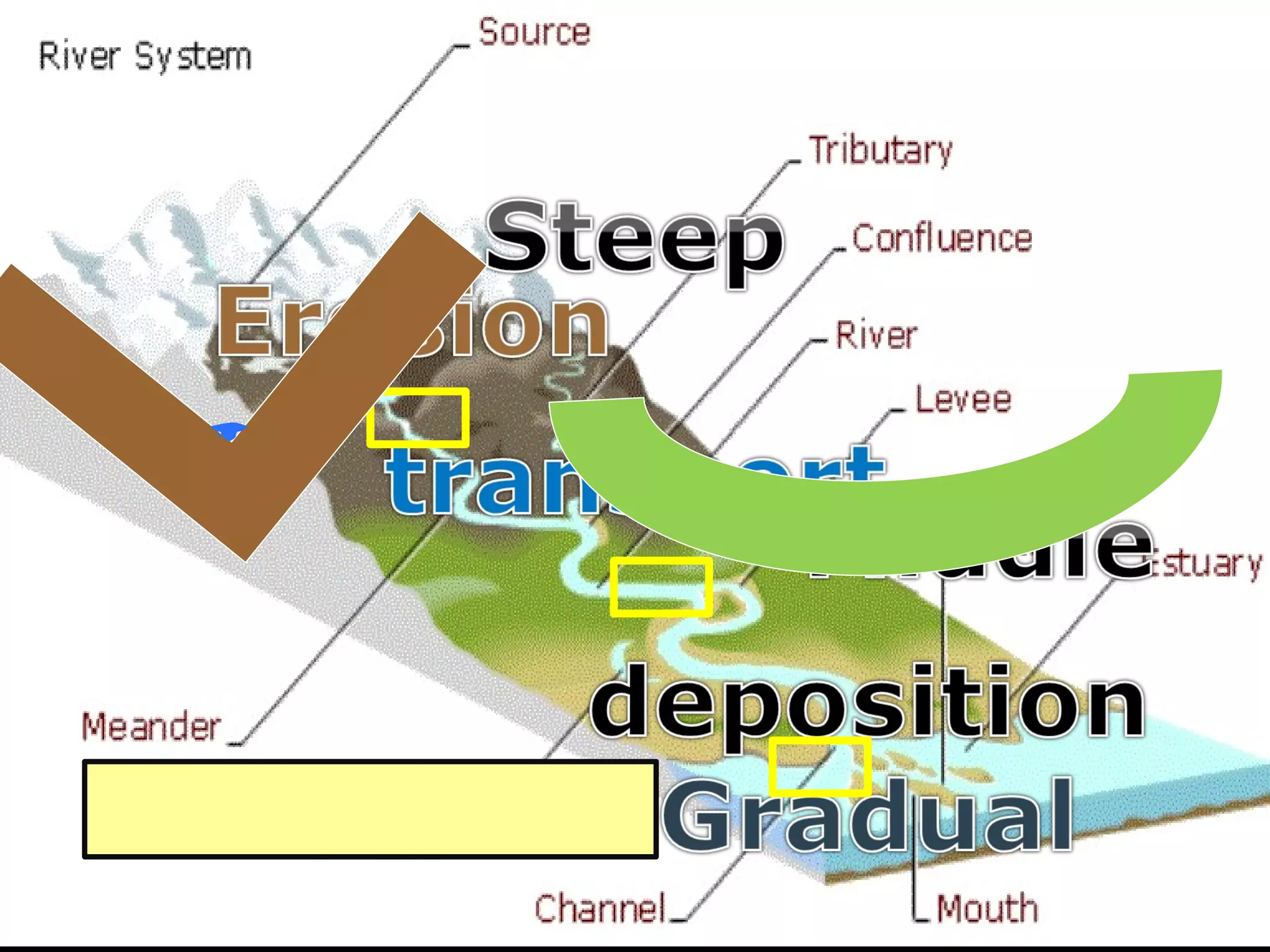
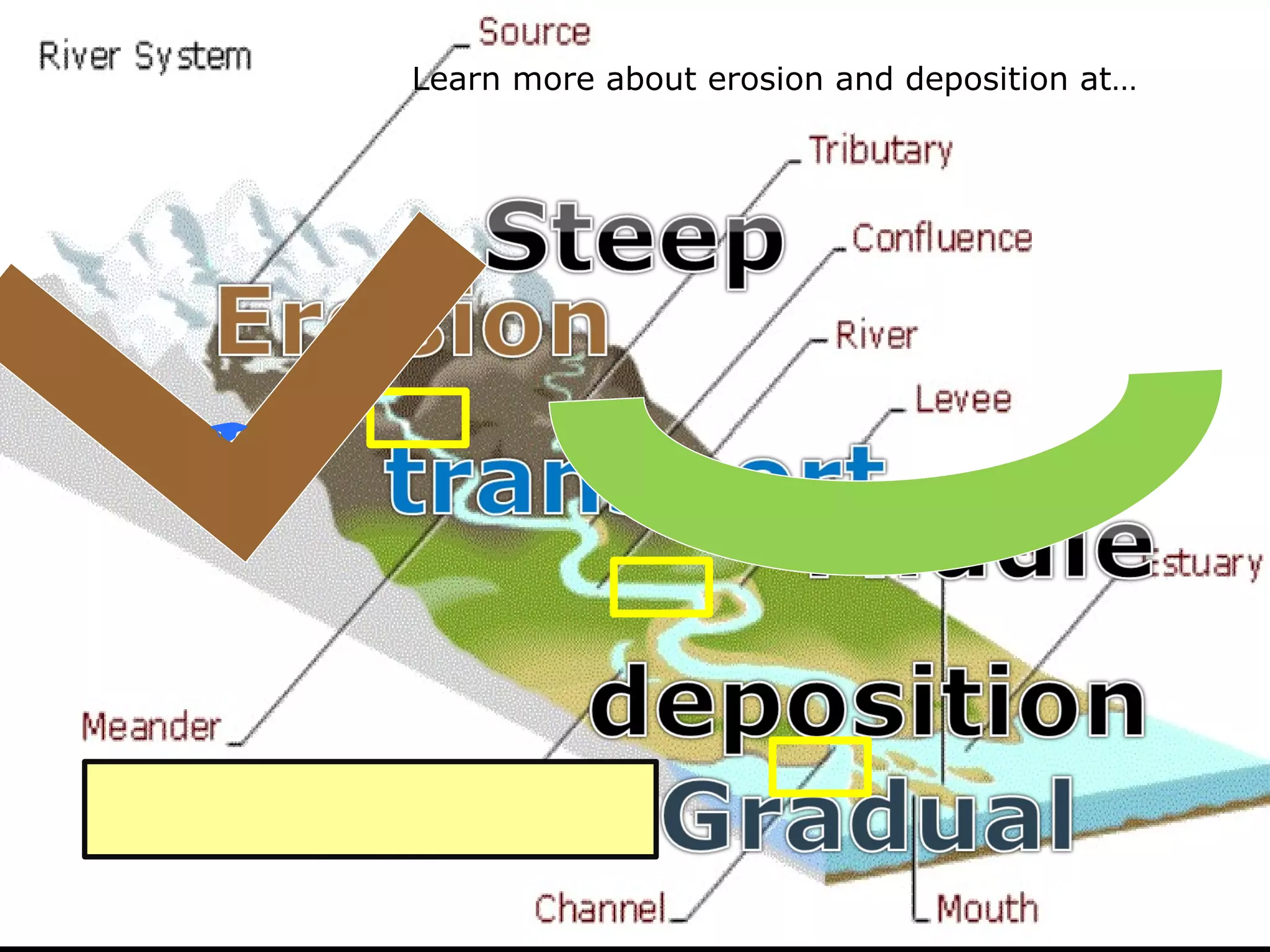
The document provides guidance on taking effective science notes, emphasizing clarity and organization, and covers the topic of watersheds in the United States. It includes important definitions related to rivers, such as 'headwaters,' 'tributary,' and 'floodplain,' and outlines various activities for students to engage with the material. Additionally, it contains links for further learning and interactive assignments designed to enhance understanding of river systems.