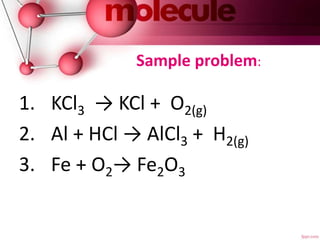
This document discusses balancing chemical equations. It explains that a chemical equation describes a chemical reaction by showing the reactants and products. It also notes that balancing a chemical equation establishes the quantitative relationship between reactants and products by using coefficients. There are three main steps to balancing an equation: 1) writing the unbalanced equation, 2) balancing the equation by applying the law of conservation of mass so each element has the same number of atoms on both sides, and 3) indicating the states of matter of the reactants and products using abbreviations like (g) or (s). An example problem of balancing the equation for the reaction of tin oxide with hydrogen gas to form tin and water vapor is provided.