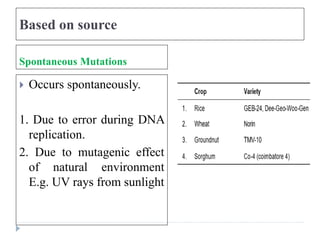
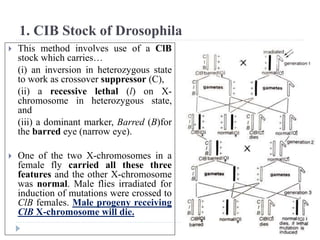
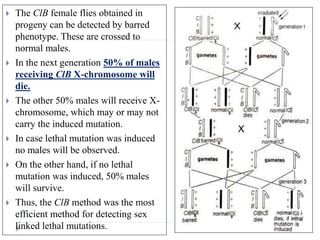
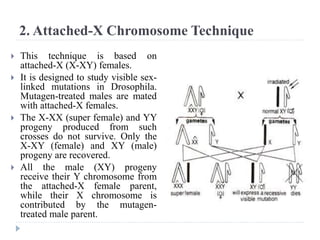
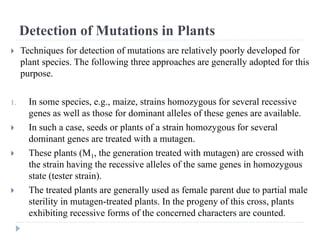
1. The document discusses mutation and its detection. It defines mutation as heritable changes in the genome excluding those from other organisms.
2. It describes different types of mutations such as spontaneous versus induced, forward versus reverse, nuclear versus cytoplasmic, and more.
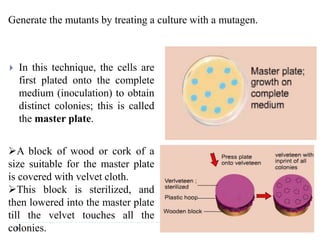
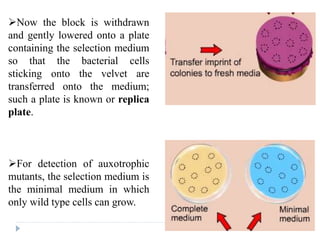
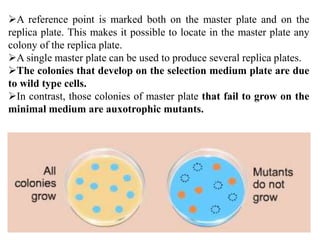
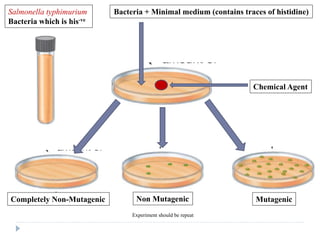
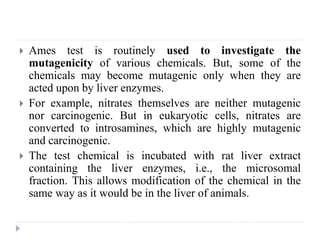
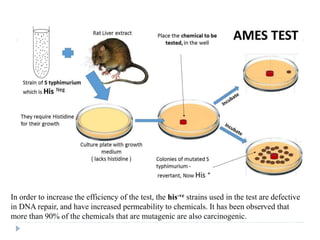
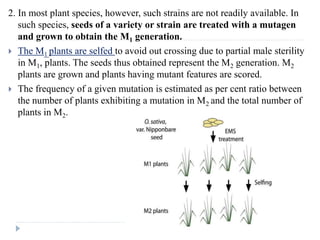
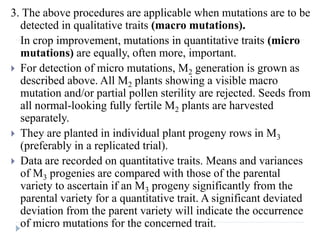
3. Methods of detecting mutations in prokaryotes and eukaryotes are described. For prokaryotes, techniques like replica plating and the Ames test are used. For eukaryotes, each individual must be examined for mutant phenotypes.